-
摘要:
临近空间长航时飞行器能源系统主要包括太阳电池、储能电池、能源控制器和配电器,其中,能源控制器实现太阳电池最大功率跟踪和对储能电池充电功能。传统的临近空间飞行器能源控制器一般采用单升压或单降压拓扑结构,存在不足,对此,采用一种四开关升降压变换器拓扑及对应的控制方法,该控制方法针对四开关升降压变换器在实际电源设计中由于控制死区造成的模式频繁切换的问题,提出一种模型预测控制(MPC)与多步离散法相结合的四模式控制策略。该策略在传统的Buck和Boost两模式基础上,通过预测模型推导出占空比控制率,利用多步离散法,并将极限占空比考虑其中,进而在控制死区内划分出2种扩展模式:扩展Buck (E-Buck)模式和扩展Boost (E-Boost)模式。同时,利用输入电压检测单元,实现了变换器在四模式下的平滑切换。仿真实验验证了所提控制策略的有效性。
Abstract:The energy system of a near-space long-endurance aircraft mainly includes solar cells, energy storage batteries, energy controllers, and power distributors. The solar cells’ maximum power point tracking and energy storage battery charging are handled by the energy controller. The single boost or single buck topologies used by conventional energy controllers for near-space vehicles have multiple disadvantages. To address these issues, a four-switch Buck-Boost converter topology and a corresponding control method are proposed. Through practical power supply designs of the four-switch Buck-Boost converter, this control approach seeks to address the issue of frequent mode switching brought on by the control dead zone. A combined control strategy of model predictive control (MPC) and the multi-step discretization method is proposed. Based on the traditional Buck and Boost two-mode operation, this strategy derives the duty cycle control from the predictive model and incorporates the limit duty cycle using the multi-step discretization method. As a result, two extended modes—extended Buck (E-Buck) and extended Boost (E-Boost) are defined within the dead zone. Additionally, an input voltage detection unit is employed to achieve smooth transitions between the four modes. Through simulation trials, the suggested control strategy’s efficacy was confirmed.
-
Key words:
- near-space /
- Buck-Boost /
- model predictive control /
- mode switching /
- limit duty cycle
-
表 1 4种工作模式的占空比
Table 1. Duty cycle of four work modes
模式 占空比表达式 Buck $ \begin{gathered} {d_1}(k) = \frac{{L({i_{{L,\text{ref}}}} - {i_{{L}}}(k)) + {R_{{L}}}{i_{{L}}}(k){T_{\text{s}}} + {T_{\text{s}}}{V_{\text{o}}}(k)}}{{{V_{\text{i}}}(k){T_{\text{s}}}}} \\ {d_2}(k) = 0 \\ \end{gathered} $ E-Buck $ \begin{gathered} {d_1}(k) = - \{[C{(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )^3} + L{\tau ^2}(2{R_{{L}}}\tau - 3L)]{i_{{L}}}(k) + \\ \quad\quad [L{\tau ^3} - C\tau {(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )^2} + CL\tau ({R_{{L}}}\tau - 2L)]{V_{\text{o}}}(k){d_{{\text{2,max}}}} + \\ \quad\quad[C{(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )^2} - L{\tau ^2} + CL(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau ) - 2C{L^3}]{V_{\text{i}}}(k)\tau + \\ \quad\quad{i_{\text{o}}}(k)L{\tau ^2}(3L - {R_{{L}}}\tau ) - C{L^3}{i_{{L,\text{ref}}}}\}/(3C{L^2}{V_{\text{i}}}(k)\tau ) \\ {d_2}(k) = {d_{2,\min }} \\ \end{gathered} $ E-Boost $ \begin{gathered} {d_1}(k) = {d_{{\text{1,max}}}} \\ {d_2}(k) = - \{[C{(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )^3} + 2{R_{{L}}}L{\tau ^3} - 3{L^2}{\tau ^2}]{i_{{L}}}(k) + \\ \quad\quad[L{\tau ^3} + CL({R_{{L}}}{\tau ^2} - 2L\tau ) - C\tau {(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )^2}]{V_{\text{o}}}(k) + \\ \quad\quad{d_{{\text{1,max}}}}{V_{\text{i}}}(k)\tau [C{(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )^2} - L{\tau ^2} + C{L^2} + \\ \quad\quad CL(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )] + {i_{\text{o}}}(k)L{\tau ^2}(3L - {R_{{L}}}\tau ) - C{L^3}{i_{{L,\text{ref}}}}\}/ \\ \quad\quad\{3L{\tau ^2}(2L - {R_{{L}}}\tau ){i_{{L}}}(k) + 3[C\tau {(L - {R_{{L}}}\tau )^2} - L{\tau ^3}]{V_{\text{o}}}(k)\} \\ \end{gathered} $ Boost $ \begin{gathered} {d_1}(k) = 1 \\ {d_2}(k) = 1 - \frac{{{\text{ }}(L - {R_{{L}}}{T_{\text{s}}}){i_{{L}}}(k) + {V_{\text{i}}}(k){T_{\text{s}}} - L{i_{{L,\text{ref}}}}}}{{{V_{\text{o}}}(k){T_{\text{s}}}}} \\ \end{gathered} $ 表 2 电压范围与工作模式
Table 2. Voltage range and operating modes
工作模式 输入电压范围/V Buck $ [{V_{{\text{o,ref}}}}/{d_{{\text{1,max}}}},400] $ E-Buck $ ({V_{{\text{o,ref}}}},{V_{{\text{o,ref}}}}/{d_{{\text{1,max}}}}) $ E-Boost $ ({V_{{\text{o,ref}}}}(1 - {d_{{\text{2,min}}}}),{V_{{\text{o,ref}}}}) $ Boost $ [200,{V_{{\text{o,ref}}}}(1 - {d_{{\text{2,min}}}})] $ 表 3 仿真实验参数
Table 3. Simulation experiment parameters
主要参数 数值 电感$ L/{\text{mH}} $ 300 电感电阻$ {R_{{L}}}/\Omega $ 0.022 输出电容$ C/{\text{μF}} $ 35 开关周期$ {T_{\text{s}}}/{\text{μs}} $ 5 输出电压参考值$ {V_{{\text{o,ref}}}}/{\text{V}} $ 310 最大占空比$ {d_{{\text{1,max}}}},{d_{{\text{2,max}}}} $ 0.96 最小占空比$ {d_{{\text{1,min}}}},{d_{{\text{2,min}}}} $ 0.04 表 4 不同控制策略实验对比结果
Table 4. Comparison of experimental results for different control strategies
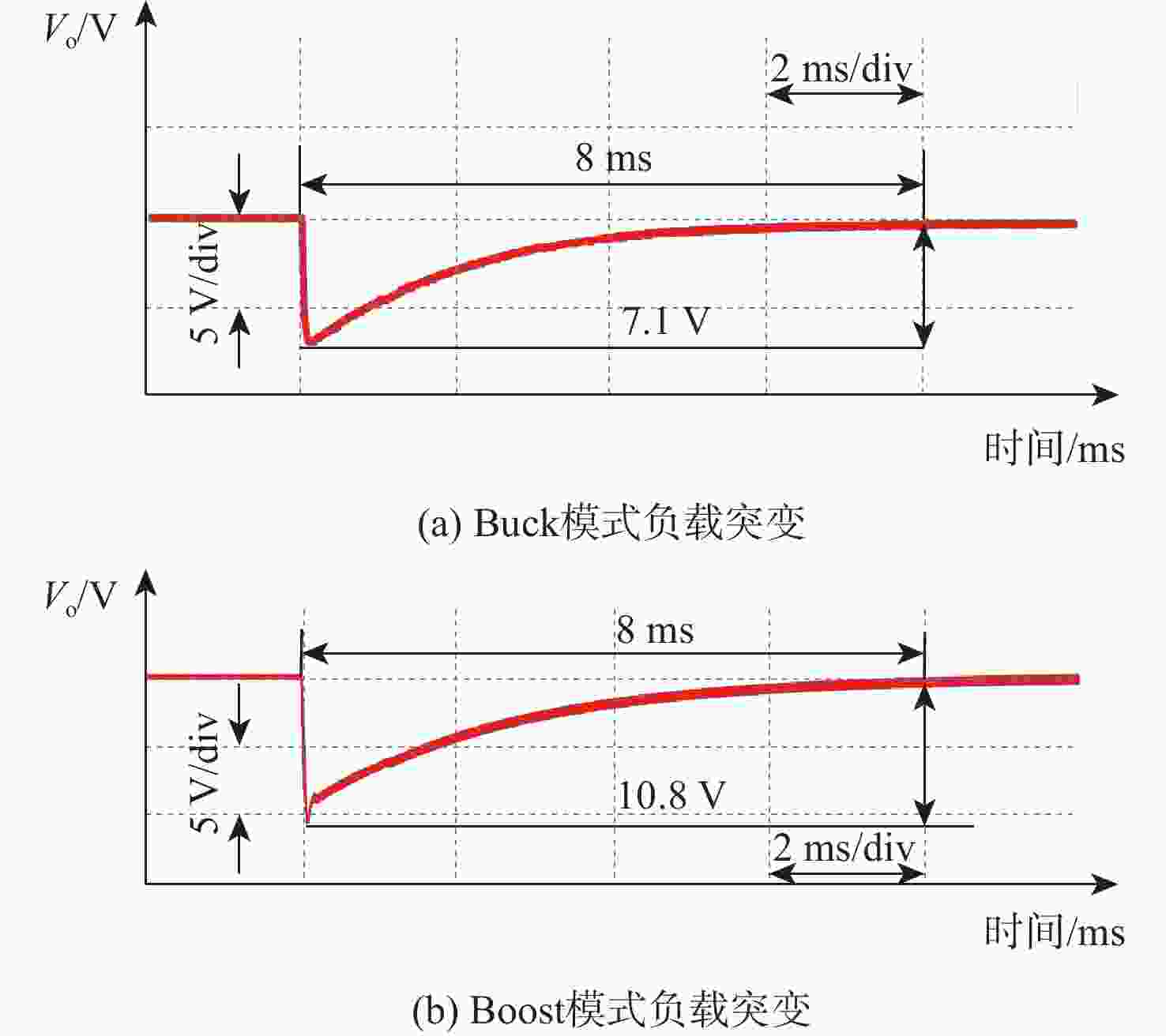
变换器工况 $ {V_{\text{o}}} $跌落/V $ {V_{\text{o}}} $跌落相对
提高/%调节时间/ms 调节时间
相对提高/%本文提出的
控制策略双环PI
控制策略三模式MPC
策略本文提出的
控制策略双环PI
控制策略三模式MPC
策略$ {V_{\text{i}}} $从400 V阶跃至350 V 0.4 2.2 81.8 2 4 50.0 $ {V_{\text{i}}} $从200 V阶跃至250 V 4.4 7.6 42.1 3 7 57.1 Buck模式负载突变 6.0 7.1 15.5 4 8 50.0 Boost模式负载突变 9.8 10.8 9.3 4 8 50.0 $ {V_{\text{i}}} $从350 V阶跃至320 V 5.6 11.6 51.7 3 5 40.0 $ {V_{\text{i}}} $从320 V阶跃至300 V 4.4 5.0 12.0 4 5 20.0 $ {V_{\text{i}}} $从300 V阶跃至250 V 3.0 9.3 67.7 3 5 40.0 -
[1] 杨君琳, 蒋崇文, 祝明, 等. 临近空间发展现状、问题及对策研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2024, 26(5): 128-136. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2024.05.013YANG J L, JIANG C W, ZHU M, et al. Research on the current status, issues, and counter measures of near-space development[J]. China Engineering Science, 2024, 26(5): 128-136(in Chinese). doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2024.05.013 [2] 黄宛宁, 张晓军, 李智斌, 等. 临近空间科学技术的发展现状及应用前景[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(21): 46-62.HUANG W N, ZHANG X J, LI Z B, et al. Development status and application prospect of near space science and technology[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2019, 37(21): 46-62(in Chinese). [3] 裴行政, 许志尧, 宋伟, 等. 空间电源低气压放电的相关问题研究[J]. 电源技术, 2024, 48(3): 464-470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2024.03.018PEI X Z, XU Z Y, SONG W, et al. Research on issues related to low-pressure discharge of space power systems[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2024, 48(3): 464-470(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2024.03.018 [4] CHEN Y X. Electrical breakdown of gases in subatomospheric pressure[D]. Auburn: Auburn University, 2016. [5] BROWN J E C, DOBKIN D, GALBIS P M, et al. DC-DC converter enabling rapid output voltage changes: US9069365[P]. 2015-06-30. [6] 马钊. 应用于便携式电池供电系统的DC-DC降压变换器的研究与设计[D]. 北京: 首都师范大学, 2008.MA Z. Research and design of DC-DC Buck converter applied to portable battery power supply system[D]. Beijing: Capital Normal University, 2008(in Chinese). [7] REN X Y, RUAN X B, QIAN H, et al. Three-mode dual-frequency two-edge modulation scheme for four-switch Buck-Boost converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2009, 24(2): 499-509. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2008.2005578 [8] 黄剑峰, 马皓. Buck与推挽级联式DC/DC变换器的研究[J]. 电力电子技术, 2008, 42(6): 30-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-100X.2008.06.012HUANG J F, MA H. Investigation on Buck and push-pull cascade DC-DC converter[J]. Power Electronics, 2008, 42(6): 30-32(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-100X.2008.06.012 [9] XU G N, LI Z J, WANG S, et al. Study on high efficiency power supply with wide input voltage for stratospheric airships[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-7. [10] ZELJKOVIC S, REITER T, GERLING D. Single-stage reconfigurable DC/DC converter for wide input voltage range operation in HEVs[C]//Proceedings of the International Power Electronics Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 774-781. [11] 李山, 宋立风, 章治国. 四开关Buck-Boost变换器的三模式控制方法研究[J]. 电源学报, 2019, 17(3): 111-119.LI S, SONG L F, ZHANG Z G. Study on three-mode control method for four-switch Buck-Boost converter[J]. Journal of Power Supply, 2019, 17(3): 111-119(in Chinese). [12] ZHOU Z J, LI H Y, WU X K. A constant frequency ZVS control system for the four-switch Buck-Boost DC-DC converter with reduced inductor current[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(7): 5996-6003. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2884950 [13] GUO Z Q, MAO T H. Efficiency optimization and control strategy of four-switch Buck-Boost converter for wide conversion ratio[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2023, 38(9): 10702-10715. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2023.3282203 [14] YU Z, KAPELS H, HOFFMANN K F. A novel control concept for high-efficiency power conversion with the bidirectional non-inverting Buck-Boost converter[C]//Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-10. [15] 方天治, 王愿, 张惠丽, 等. 四管Buck-Boost变换器的改进型三模式变频软开关控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(21): 4544-4557.FANG T Z, WANG Y, ZHANG H L, et al. Improved three-mode variable-frequency soft-switching control strategy for a four-transistor Buck-Boost converter[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(21): 4544-4557(in Chinese). [16] VAZQUEZ S, RODRIGUEZ J, RIVERA M, et al. Model predictive control for power converters and drives: advances and trends[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(2): 935-947. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2625238 [17] WANG Y, LAN J Y, HUANG X, et al. An improved single-mode control strategy based on four-switch Buck-Boost converter[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 320-325. [18] TSAI C H, TSAI Y S, LIU H C. A stable mode-transition technique for a digitally controlled non-inverting Buck-Boost DC-DC converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(1): 475-483. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2327565 [19] LI Y, ZHANG Z B, LI K J, et al. Predictive current control for voltage source inverters considering dead-time effect[J]. CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2020, 4(1): 35-42. doi: 10.30941/CESTEMS.2020.00006 [20] 耿强, 王亮, 周湛清, 等. 五桥臂逆变器双永磁电机三矢量预测控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(1): 87-95.GENG Q, WANG L, ZHOU Z Q, et al. Three-vector-based predictive control for dual permanent magnet synchronous motors fed by the five-leg inverter[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(1): 87-95(in Chinese). [21] 杨惠, 晁凯悦, 孙向东, 等. 基于矢量作用时间的双向DC-DC变换器预测电流控制方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(S1): 70-80.YANG H, CHAO K Y, SUN X D, et al. Predictive current control method of bidirectional DC-DC converter based on vector action time[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(S1): 70-80(in Chinese). [22] 王祯, 尹项根, 陈玉, 等. 基于连续控制集模型预测控制的MMC桥臂电流控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(10): 85-91. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20190811002WANG Z, YIN X G, CHEN Y, et al. Arm current control strategy of modular multilevel converter based on continuous control set model predictive control[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(10): 85-91(in Chinese). doi: 10.7500/AEPS20190811002 [23] 吴岩, 王玮, 曾国宏, 等. 四开关Buck-Boost变换器的多模式模型预测控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(10): 2572-2583.WU Y, WANG W, ZENG G H, et al. Multi-mode model predictive control strategy for the four-switch Buck-Boost converter[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(10): 2572-2583(in Chinese). -






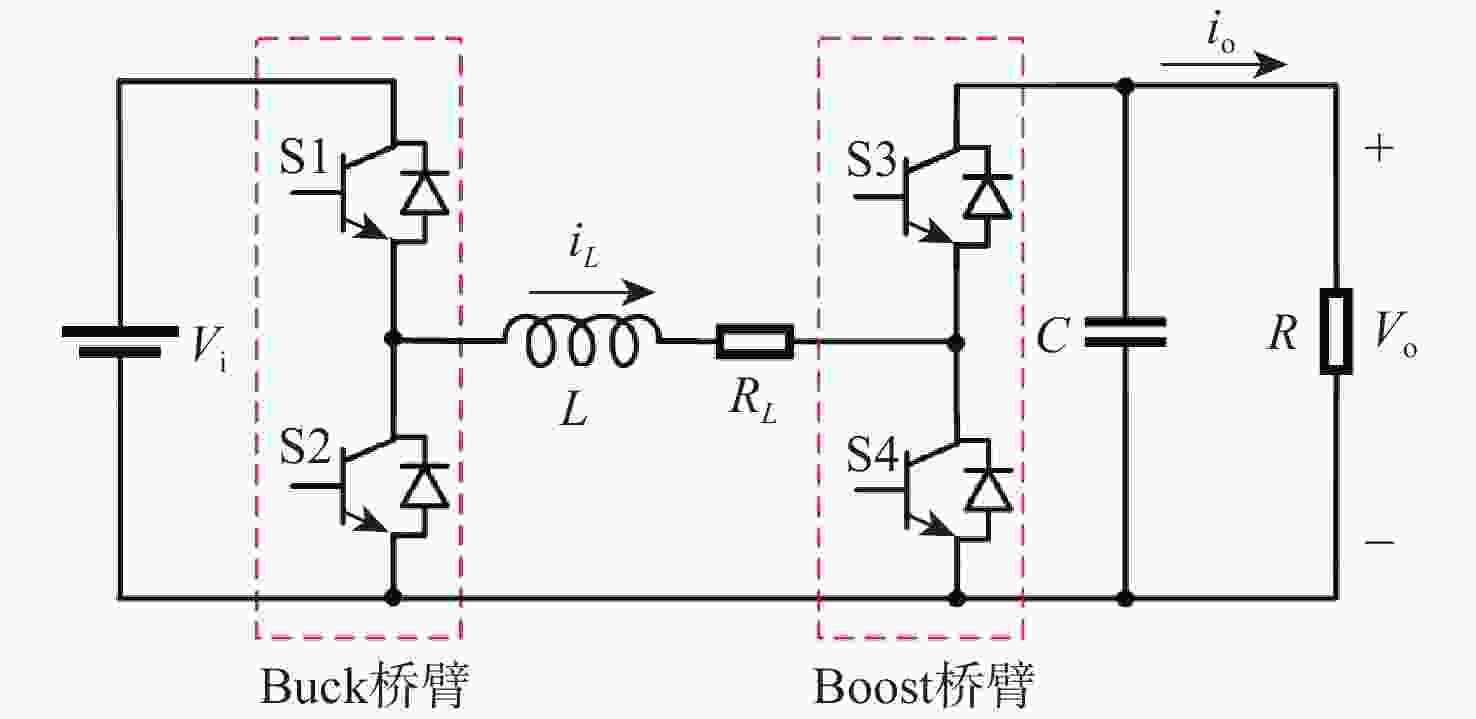
 下载:
下载: