-
摘要:
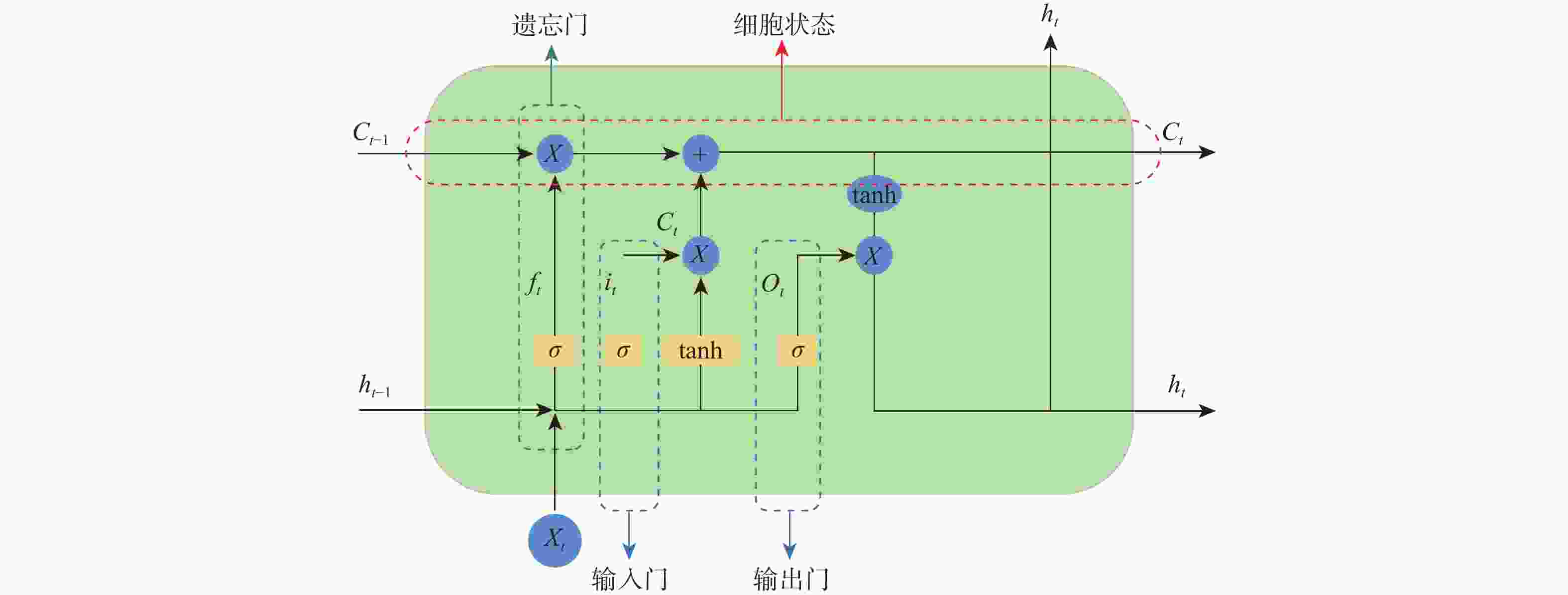
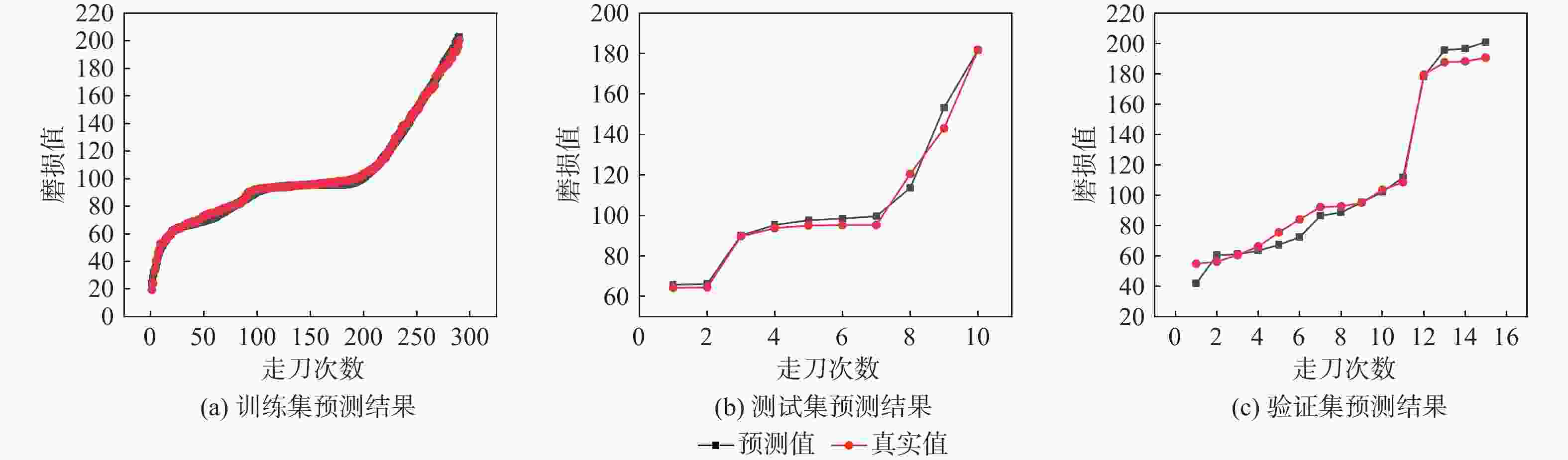
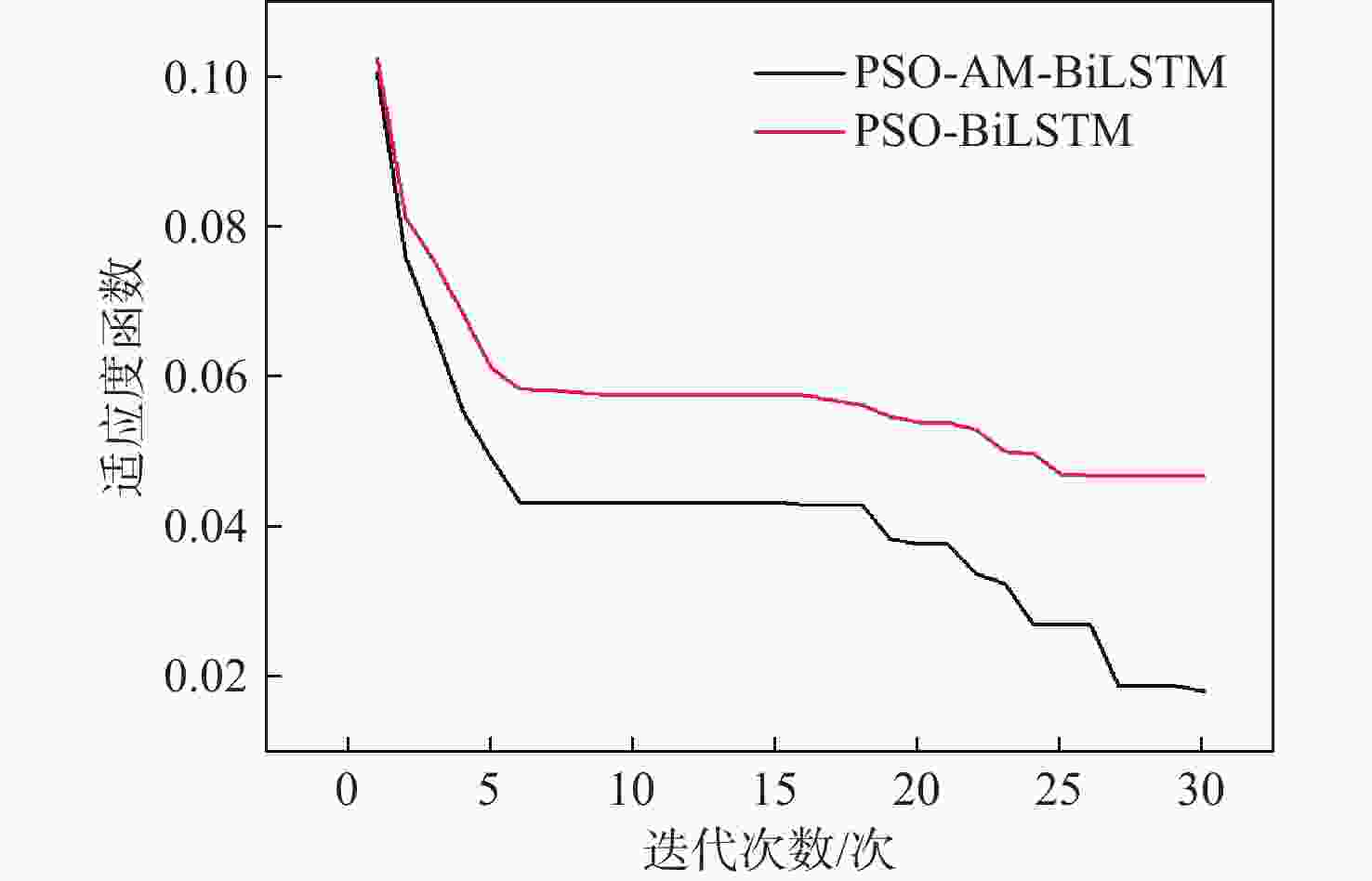
针对刀具磨损故障诊断中存在的监测数据单一和特征信号处理效果差的问题,提出了一种基于注意力机制(AM)改进的粒子群算法(PSO)优化双向长短时记忆(BiLSTM)神经网络来实现端到端的刀具磨损预测方法。根据传感器信号进行多域特征提取,构建优质的信号输入样本;利用卡尔曼滤波对输入样本进行多传感器数据融合,得到鲁棒性更高的融合数据样本,在此基础上,通过PSO对BiLSTM网络进行超参数寻优,根据优化的超参数建立神经网络模型;基于注意力机制赋予输入影响权重,改进PSO-BiLSTM以获得更好的刀具磨损预测效果。对比实验结果验证了所提模型在刀具磨损预测中的可行性,其精度相比传统深度学习方法有较大的提升。
-
关键词:
- 刀具磨损 /
- 卡尔曼滤波 /
- 粒子群算法 /
- 注意力机制 /
- 双向长短时记忆神经网络
Abstract:A bi-directional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) neural network optimization end-to-end tool wear prediction method based on attention mechanism (AM) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is proposed to address the issues of single monitoring data and poor feature signal processing in tool wear fault diagnosis. Firstly, based on the sensor data, to construct high-quality signal input samples, extract the multi-domain feature. With multi-sensor data to obtain the fused data samples with higher robustness, the Kalman filter is used to fuse the input samples. On this basis, the hyperparameters of the BiLSTM are optimized by PSO, and the neural network model is built according to the optimized hyperparameters. Finally, based on the attention mechanism to give weights to the input influences, the PSO-BiLSTM is improved to obtain a better tool wear prediction. The suggested model's validity and feasibility in tool wear prediction are confirmed by comparative experimental findings, and its accuracy is significantly higher than that of classical deep learning. This approach offers a fresh viewpoint on tool wear prediction.
-
表 1 PSO-BiLSTM模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of the PSO-BiLSTM model
网络参数 初始值 初始化权重 [−0.5,0.5] 遗忘门偏置量 1 输入门偏置量 [0,0.8] 输出门偏置量 [0,0.8] 迭代次数 50 种群个数 5 学习因子c1 2 学习因子c2 2 隐藏层单元数m [10,300] 学习率r [0.01,0.15] 表 2 实验加工参数
Table 2. Experimental processing parameters
主轴速度/
(r·min−1)进给速度/
(mm·min−1)径向切深/
mm轴向切深/
mm铣削
方式10 400 1 555 0.125 0.2 顺铣 表 3 特征指标
Table 3. Characteristic index
序号 特征名称 序号 特征名称 1 峰峰值 11 峰值指标 2 方差 12 脉冲指标 3 均值 13 裕度指标 4 歪度 14 峭度指标 5 峭度 15 均值频率 6 均方值 16 频谱二阶矩 7 方根幅值 17 标准偏差频 8 均方根值 18 峭度频率 9 绝对均值 19 均方根频率 10 波形指标 20 中心频率 表 4 预测结果评价指标
Table 4. Evaluations of the prediction results
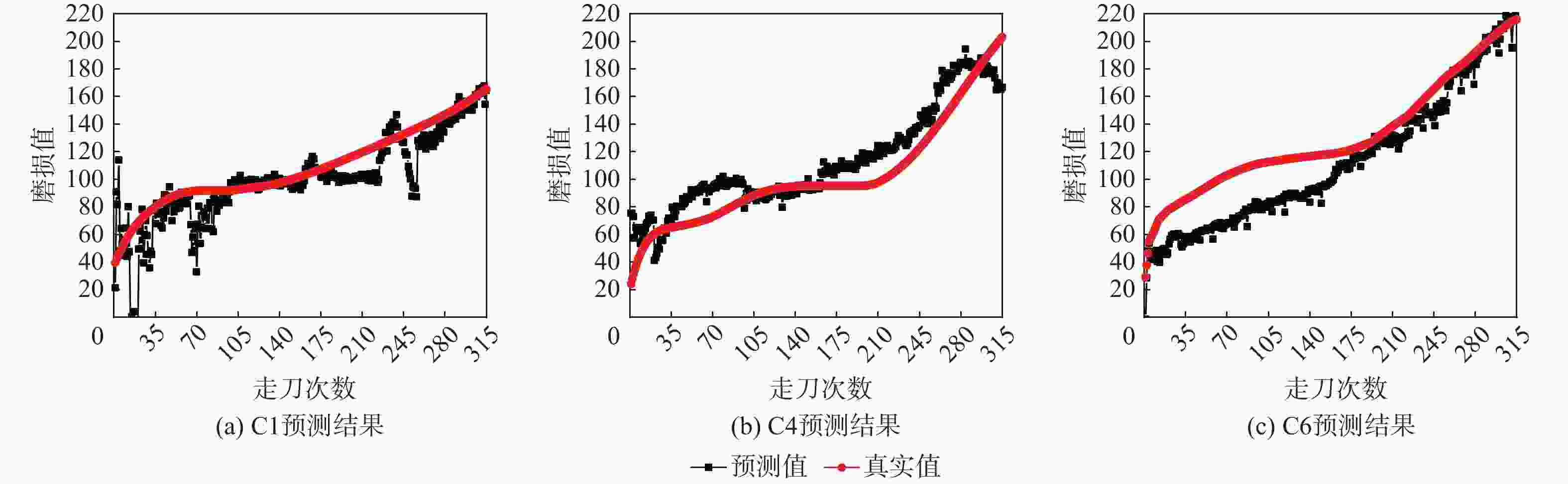
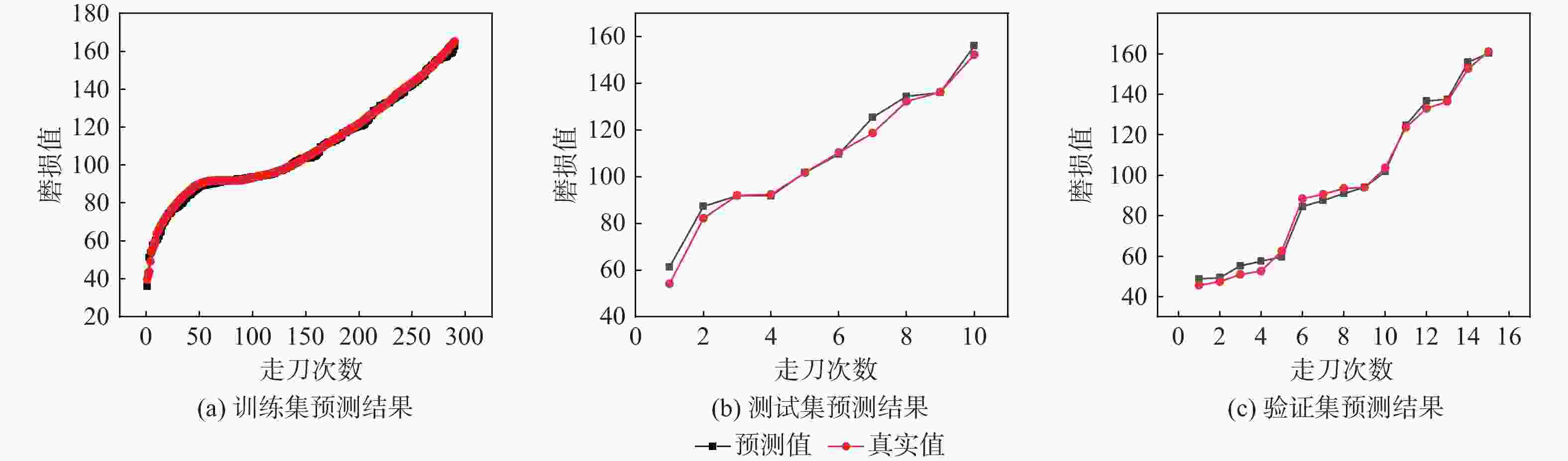
模型 RMSE MAPE R2 C1 C4 C6 C1 C4 C6 C1 C4 C6 PSO-AM-BiLSTM 2.906 6.85 5.22 2.563 5.54 4.32 0.994 0.991 0.992 PSO-CNN 6.72 8.66 8.31 5.02 7.97 6.83 0.91 0.907 0.903 PSO-BPNN 11.384 13.027 17.51 10.34 12.76 11.85 0.87 0.81 0.83 PSO-LSTM 16.34 15.27 17.08 12.17 13.03 14.05 0.75 0.85 0.80 -
[1] CHEN Y X, JIN Y, JIRI G. Predicting tool wear with multi-sensor data using deep belief networks[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 99(5): 1917-1926. [2] 谢振龙, 岳彩旭, 刘献礼, 等. 基于EMD-SVM的钛合金铣削过程刀具磨损监测[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2022, 42(5): 988-996.XIE Z L, YUE C X, LIU X L, et al. Tool wear monitoring based on EMD-SVM in milling process of Ti-alloy[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2022, 42(5): 988-996(in Chinese). [3] ZHOU J J, YU J B. Chisel edge wear measurement of high-speed steel twist drills based on machine vision[J]. Computers in Industry, 2021, 128: 103436. [4] LI L H, AN Q B. An in-depth study of tool wear monitoring technique based on image segmentation and texture analysis[J]. Measurement, 2016, 79(2): 44-52. [5] MORGAN J, O’DONNELL G E. Cyber physical process monitoring systems[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2018, 29(6): 1317-1328. doi: 10.1007/s10845-015-1180-z [6] 戴稳, 张超勇, 孟磊磊, 等. 基于深度学习与特征后处理的支持向量机铣刀磨损预测模型[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2020, 26(9): 2331-2343.DAI W, ZHANG C Y, MENG L L, et al. Support vector machine milling wear prediction model based on deep learning and feature re-processing[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2020, 26(9): 2331-2343(in Chinese). [7] 郑圆, 胡建中, 贾民平, 等. 一种基于参数优化变分模态分解的滚动轴承故障特征提取方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(21): 195-202.ZHENG Y, HU J Z, JIA M P, et al. A method for rolling bearing fault feature extraction based on parametric optimization VMD[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(21): 195-202(in Chinese). [8] 李聪波, 万腾, 陈行政, 等. 基于切削功率的数控车削批量加工刀具磨损在线监测[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2018, 24(8): 1910-1919.LI C B, WAN T, CHEN X Z, et al. On-line monitoring method of tool wear for NC turning in batch processing based on cutting power[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2018, 24(8): 1910-1919(in Chinese). [9] 何彦, 凌俊杰, 王禹林, 等. 基于长短时记忆卷积神经网络的刀具磨损在线监测模型[J]. 中国机械工程, 2020, 31(16): 1959-1967.HE Y, LING J J, WANG Y L, et al. In-process tool wear monitoring model based on LSTM-CNN[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(16): 1959-1967(in Chinese). [10] 曹大理, 孙惠斌, 张纪铎, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的刀具磨损在线监测[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2020, 26(1): 74-80.CAO D L, SUN H B, ZHANG J D, et al. In-process tool condition monitoring based on convolution neural network[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2020, 26(1): 74-80(in Chinese). [11] 王丽华, 杨家巍, 张永宏, 等. 基于堆叠降噪自编码的刀具磨损状态识别[J]. 中国机械工程, 2018, 29(17): 2038-2045. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2018.17.004WANG L H, YANG J W, ZHANG Y H, et al. Tool wear condition recognition based on SDAE[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(17): 2038-2045(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2018.17.004 [12] LUO J H, ZHANG X. Convolutional neural network based on attention mechanism and Bi-LSTM for bearing remaining life prediction[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(1): 1076-1091. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02503-2 [13] ALJAMAL M A, ABDELGHAFFAR H M, RAKHA H A. Developing a neural-Kalman filtering approach for estimating traffic stream density using probe vehicle data[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(19): 4325. doi: 10.3390/s19194325 [14] 沈涛, 李舜酩. 针对滚动轴承故障的批标准化CNN-LSTM诊断方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2022, 28(12): 3946-3955.SHEN T, LI S M. CNN-LSTM method with batch normalization for rolling bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 28(12): 3946-3955(in Chinese). [15] 吴飞, 农皓业, 马晨浩. 基于PSO-LSTM模型的刀具磨损预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 984-997.WU F, NONG H Y, MA C H. Tool wear predictionmethod based on PSO-LSTM model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 984-997(in Chinese). [16] ZHANG J S, JIANG Y C, WU S M, et al. Prediction of remaining useful life based on bidirectional gated recurrent unit with temporal self-attention mechanism[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 221: 108297. [17] PHM Society. PHM data challenge 2010[DB/OL]. (2023-07-25)[2010-05-18]. http://www.phmsociety. org/competition/phm/10. -







 下载:
下载: