Adaptive model predictive control of virtual coupled based on artificial potential field
-
摘要:
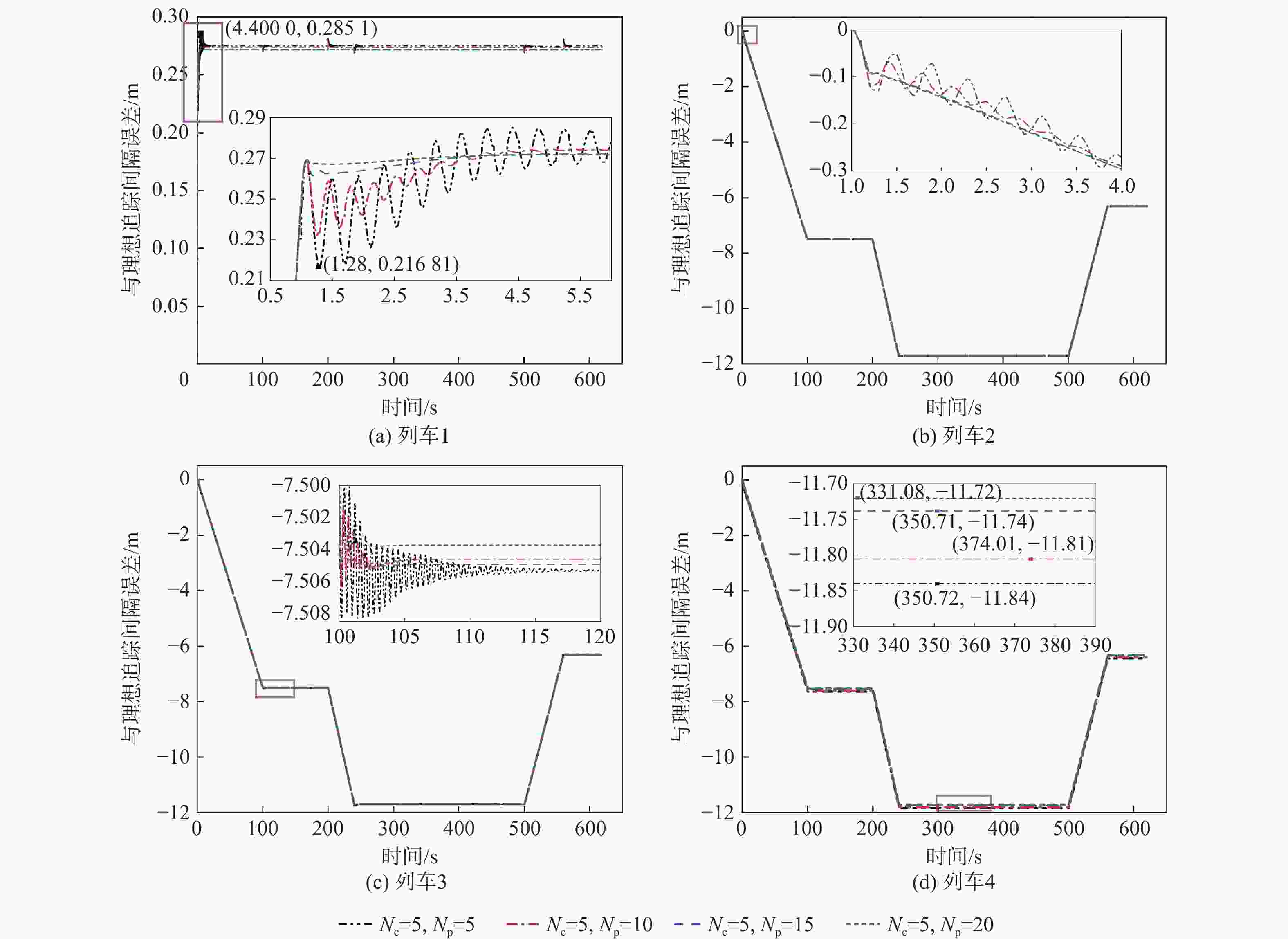
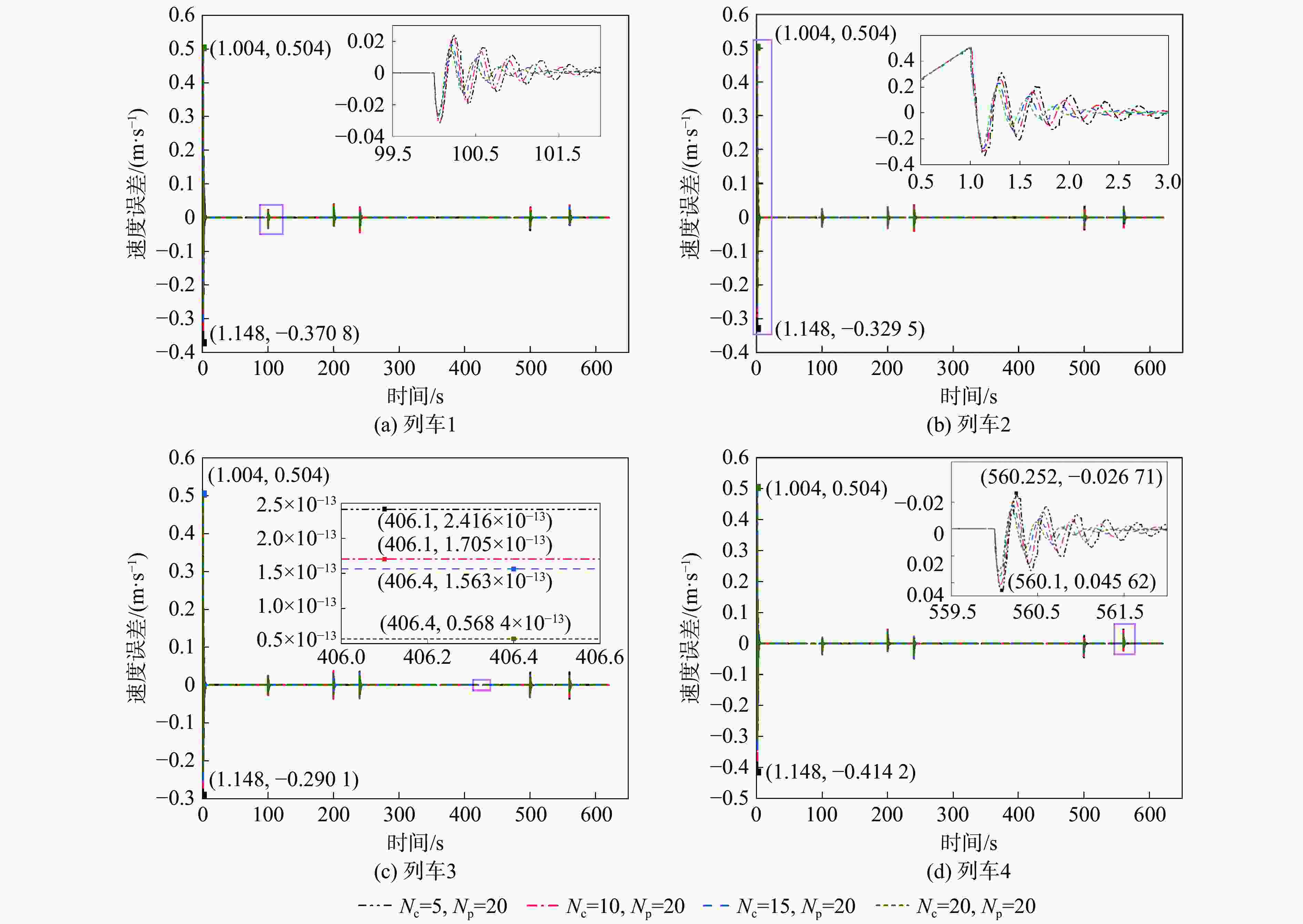
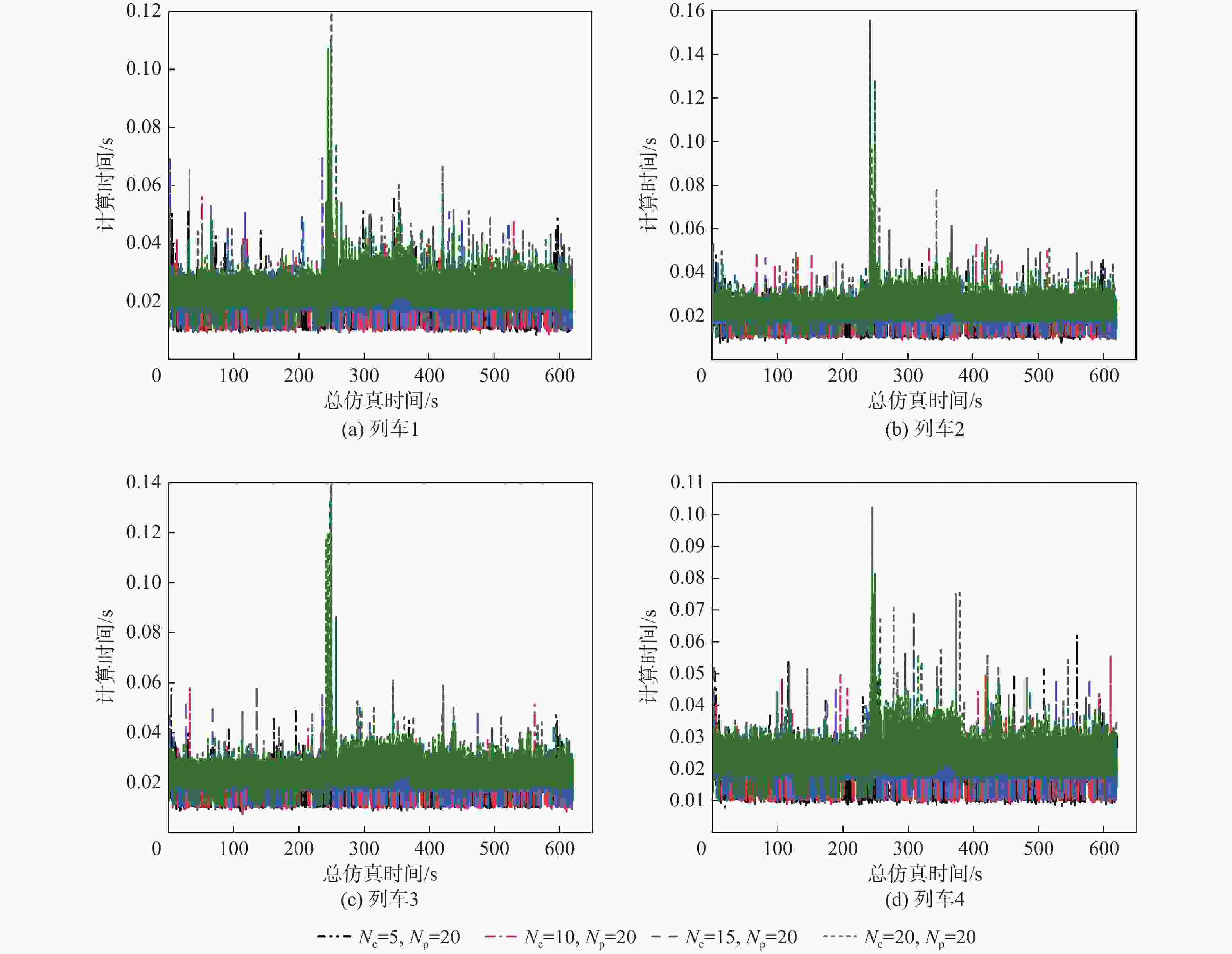
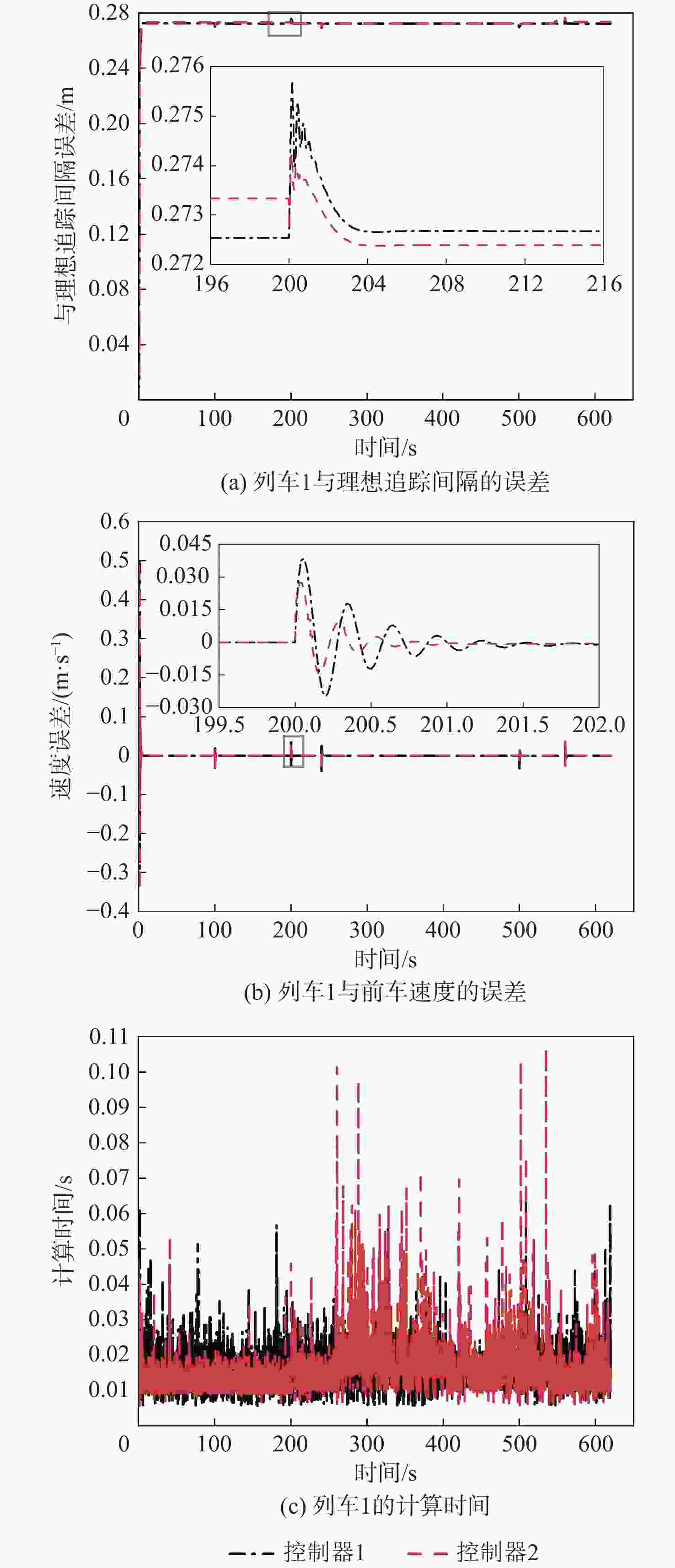
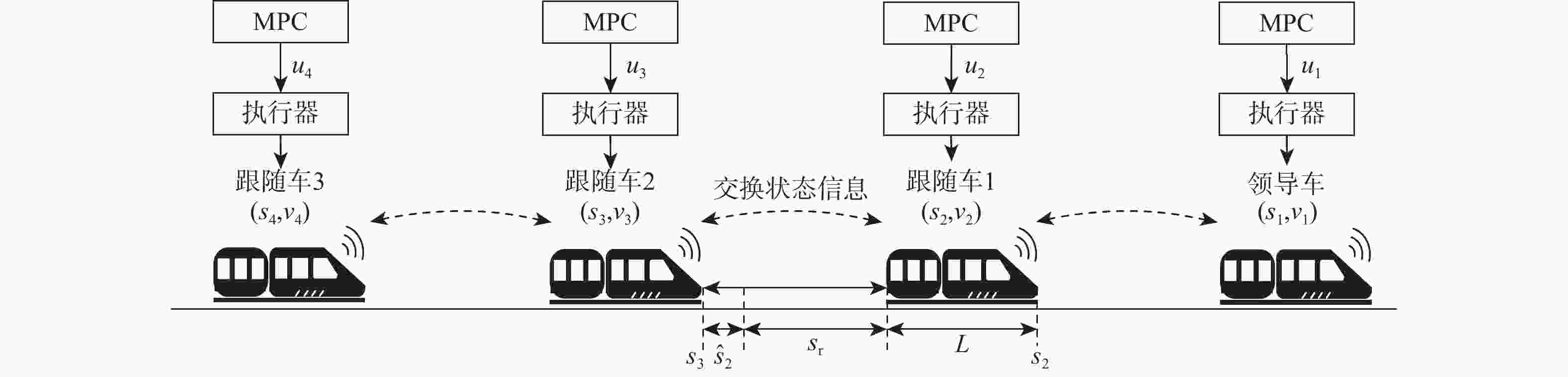
现今,列车高速度、高密度追踪控制对编队列车运行的安全性提出更高的要求。为满足人们对列车运行过程中自适应性和准确性的需求,提出一种基于人工势场的虚拟编组(VC)自适应模型预测控制(MPC)方法。将VC列车作为研究对象,采用MPC方法建立基于列车平衡态的动力学模型,以控制精度和平稳性、安全性为优化目标,并将基于人工势场设置的防撞函数加入目标函数,从而实现编队的防撞控制;分析不同时域参数对系统控制精度和计算效率的影响作用,设计对应的适应度函数,基于遗传算法(GA)求得不同工况下的最优时域参数组合,并制定时域参数更新策略,在确保列车编组准确控制的同时提高系统的实时性;在MATLAB平台上搭建4列车追踪运行场景,仿真验证所提方法的有效性。结果表明:相较于传统的模型预测控制器,基于人工势场的模型预测控制器在间隔控制上准确度提高了94.8%,可有效避免列车间发生碰撞,保证了列车运行的安全性;另外,采用自适应控制律的控制器可根据列车运行状态对系统进行实时调整,在确保高控制精度的前提下,计算效率提高10%。研究结果验证了所提方法的可行性,提高了控制器的综合控制性能,并为进一步优化编队控制和保障列车安全运行提供参考。
Abstract:The safety of operating formation trains is now subject to stricter standards due to the high speed and high density tracking control of trains. To meet the need for precision and adaptability during train operation, an adaptive model predictive control (MPC) technique based on an artificial potential field is created for virtual coupled (VC) systems. First, a VC train is used as the research object, and the MPC method is used to create a dynamic model based on the equilibrium state of the train, with control accuracy and smoothness as the optimization objectives. Next, a collision avoidance function based on an artificial potential field setting is added to the objective function, allowing for the realization of the formation’s collision avoidance control. In order to improve the real-time performance of the system and ensure accurate control of the train formation, it is also necessary to analyze the impact of various time domain parameters on the control accuracy and computational efficiency of the system, design the corresponding adaptation function, and base this on a genetic algorithm (GA) that can find the best combinations of time domain parameters under various working conditions. On the MATLAB platform, a 4-train tracking operation scenario is developed as a last step to test the effectiveness of the suggested approach. The study’s findings demonstrate that the artificial potential field-based model predictive controller has interval control accuracy that is 94.8% greater than that of the conventional model predictive controller, successfully preventing train collisions and ensuring the safety of train operation. Furthermore, the adaptive control law controller may adjust the system in real-time based on the train’s operational status, resulting in a 10% increase in computing efficiency and excellent control accuracy. The study’s findings support the viability of the suggested control approach, enhance the controller’s overall control performance, and serve as a guide for future improvements in formation control and ensuring safe train operation.
-
-
[1] 张友兵, 刘岭. 基于虚拟编组的列车控制系统研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2022, 39(3): 94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2022.03.016ZHANG Y B, LIU L. Research on the train control system based on virtual coupling[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2022, 39(3): 94-100(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2022.03.016 [2] PAN D, ZHENG Y P. Dynamic control of high-speed train following operation[J]. PROMET-Traffic & Transportation, 2014, 26(4): 291-297. [3] 刘俊囡. 高速列车编队多智能体运行控制优化方法[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020.LIU J N. Optimization method of multi-agent operation control for high-speed train formation[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020(in Chinese). [4] BAI W Q, LIN Z L, DONG H R, et al. Distributed cooperative cruise control of multiple high-speed trains under a state-dependent information transmission topology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(7): 2750-2763. [5] 汤旻安, 王攀琦. 基于混合系统建模预测控制的列车自动驾驶优化运行[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2019, 16(6): 1527-1534.TANG M A, WANG P Q. Automatic train optimization operation based on hybrid system modeling predictive control[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(6): 1527-1534(in Chinese). [6] 杨辉, 童英赫, 付雅婷, 等. 基于模型补偿的高速列车状态反馈预测控制[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020, 17(10): 2460-2468.YANG H, TONG Y H, FU Y T, et al. State feedback predictive control of high-speed train based on model compensation[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(10): 2460-2468(in Chinese). [7] 林俊亭, 倪铭君. 基于扩张状态观测器的虚拟编组触发模型预测控制[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2023, 23(4): 134-146.LIN J T, NI M J. Trigger model predictive control based on extended state observers for virtual coupling[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2023, 23(4): 134-146(in Chinese). [8] 周红梅. 微型无人机集群编队控制与协作算法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020: 50-59.ZHOU H M. Research on formation control and cooperation algorithm of micro UAV cluster[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020: 50-59(in Chinese). [9] 朱梁鹏. 基于路径跟踪的多智能车辆编队控制研究[D]. 常州: 江苏理工学院, 2021: 56-66.ZHU L P. Research on multi-intelligent vehicle formation control based on path tracking[D]. Changzhou: Jiangsu University of Technology, 2021: 56-66(in Chinese). [10] 吴宝库. 考虑避障的多AGV编队协同控制与路径规划设计[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳大学, 2021: 47-58.WU B K. Cooperative control and path planning design of multi-AGV formation considering obstacle avoidance[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University, 2021: 47-58(in Chinese). [11] 钟嘉灏. 面向多目标多无人机任务分配与航迹规划算法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022: 59-74.ZHONG J H. Research on task assignment and path planning algorithm for multi-target and multi-UAV[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022: 59-74(in Chinese). [12] 熊俊涛, 李中行, 陈淑绵, 等. 基于深度强化学习的虚拟机器人采摘路径避障规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(增刊2): 1-10.XIONG J T, LI Z X, CHEN S M, et al. Obstacle avoidance planning of virtual robot picking path based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(Sup 2): 1-10(in Chinese). [13] 丁伟兵. 园艺电动拖拉机局部路径规划与跟踪控制研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2022: 28-45.DING W B. Research on local path planning and tracking control of horticultural electric tractor[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2022: 28-45(in Chinese). [14] 张志伟. 基于模型预测控制的四轮转向AGV路径跟踪横向控制研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2020: 68-83.ZHANG Z W. Study on lateral control of path tracking for four-wheel-steeling AGV based on model predictive control[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2020: 68-83(in Chinese). [15] 白国星, 孟宇, 刘立, 等. 基于可变预测时域及速度的车辆路径跟踪控制[J]. 中国机械工程, 2020, 31(11): 1277-1284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.11.003BAI G X, MENG Y, LIU L, et al. Path tracking control of vehicles based on variable prediction horizon and velocity[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(11): 1277-1284(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.11.003 [16] 杨阳阳. 基于模型预测控制的路径跟踪控制方法研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2018: 31-49.YANG Y Y. Research on path tracking control method based on model predictive control[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2018: 31-49(in Chinese). [17] YANG Y M, YAN F. Research on train dynamic coupling strategy based on distributed model predictive control[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2183(1): 012029. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2183/1/012029 [18] LIU Y F, ZHOU Y, SU S, et al. An analytical optimal control approach for virtually coupled high-speed trains with local and string stability[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 125: 102886. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2020.102886 [19] ZHANG T R, XU J N, WU B K. Hybrid path planning model for multiple robots considering obstacle avoidance[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 71914-71935. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3188784 [20] HUANG Z W, WANG P P, ZHOU F, et al. Cooperative tracking control of the multiple-high-speed trains system using a tunable artificial potential function[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2022, 2022: 3639586. [21] 吴施鹏. 基于遗传算法的无人驾驶车辆路径跟随控制及研究[D]. 常州: 江苏理工学院, 2021: 40-63.WU S P. Genetic algorithm-based path-following control and research of driverless vehicles[D]. Changzhou: Jiangsu University of Technology, 2021: 40-63(in Chinese). [22] YU D J, DENG F, WANG H Y, et al. Real-time weight optimization of a nonlinear model predictive controller using a genetic algorithm for ship trajectory tracking[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(8): 1110. doi: 10.3390/jmse10081110 [23] WANG M, CHEN J X, YANG H W, et al. Path tracking method based on model predictive control and genetic algorithm for autonomous vehicle[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2022, 2022: 4661401. -






 下载:
下载: