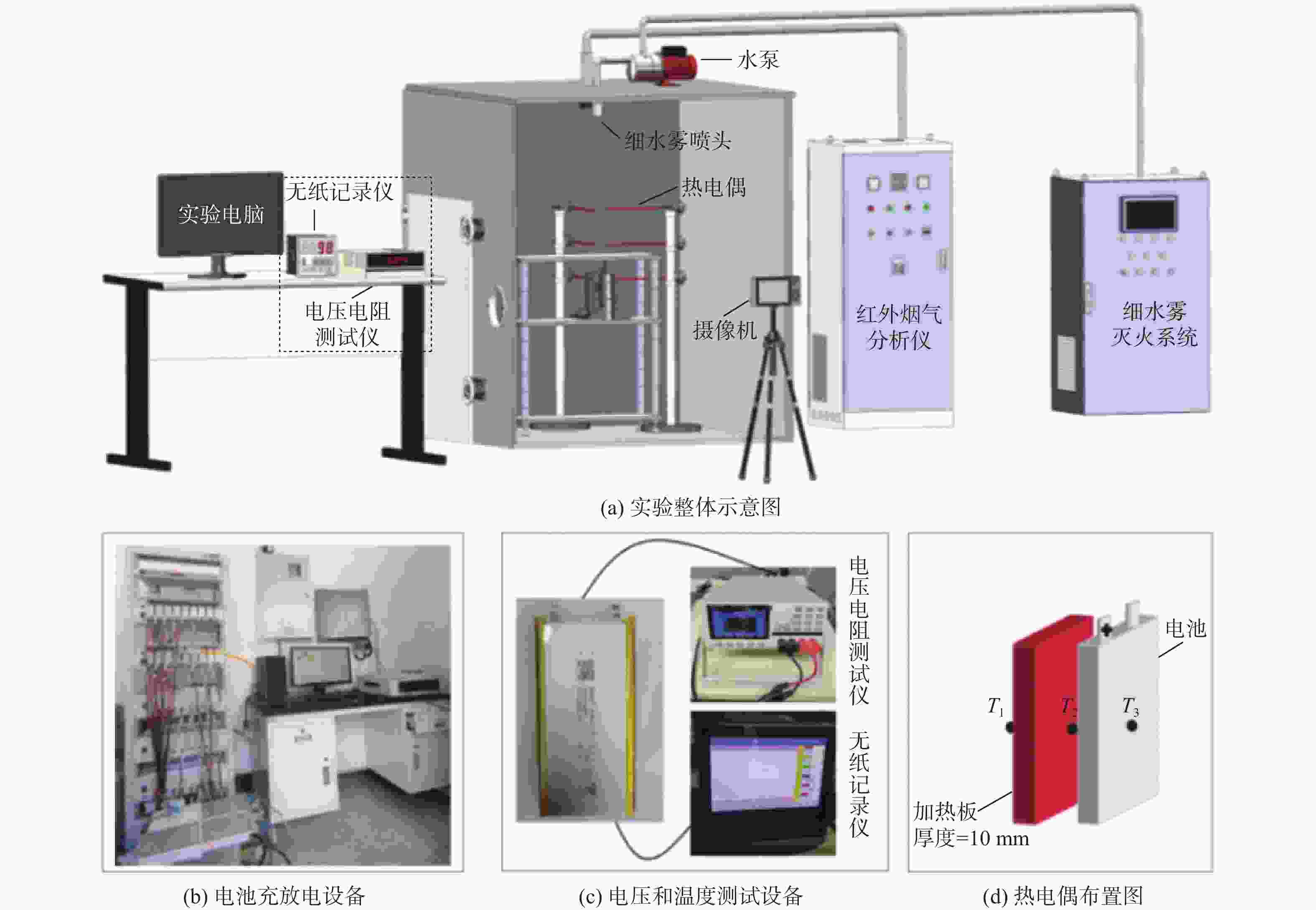
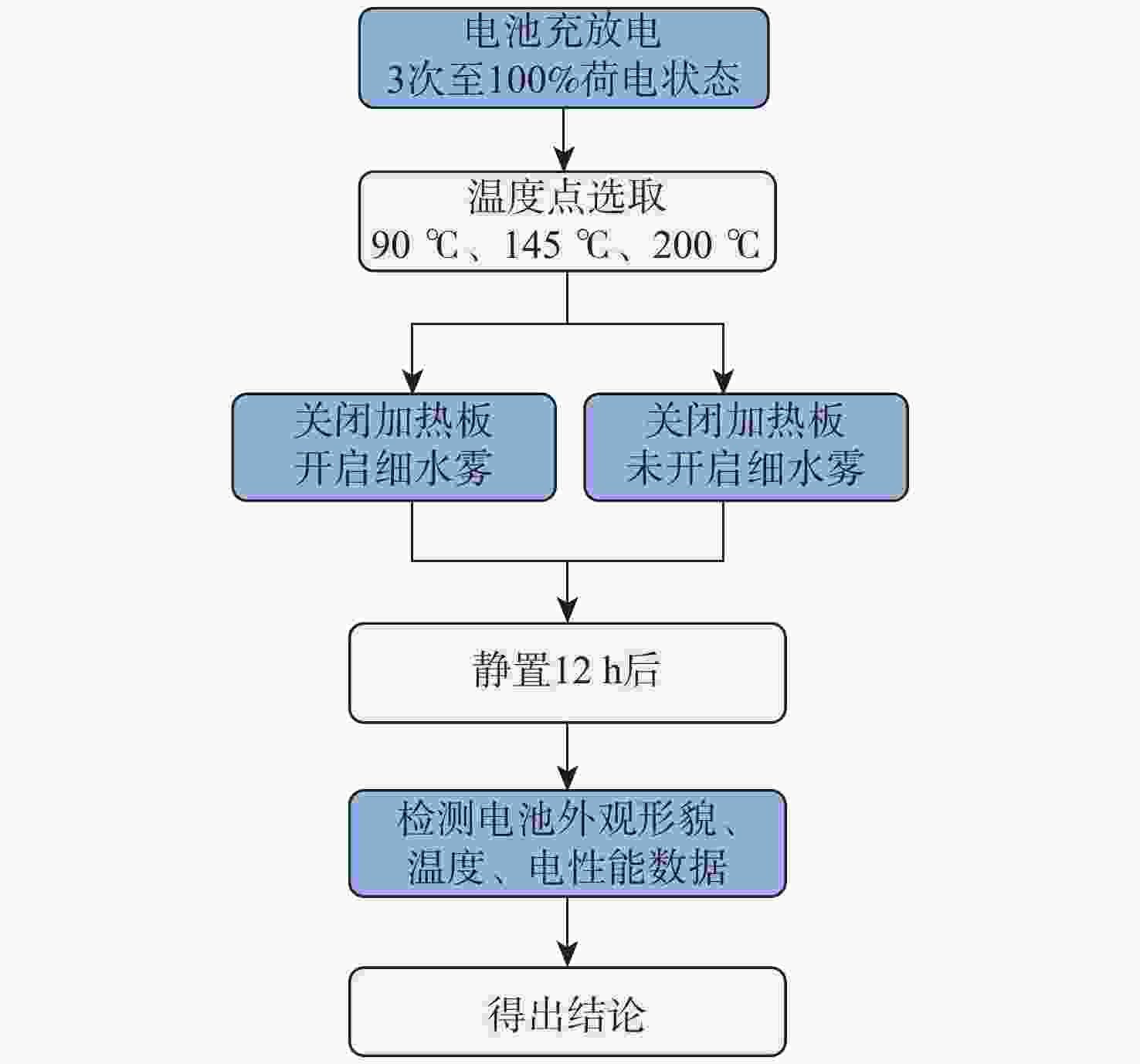
Performance of low-pressure dual-fluid water mist to reduce thermal runaway risk of ternary lithium-ion battery
-
摘要:
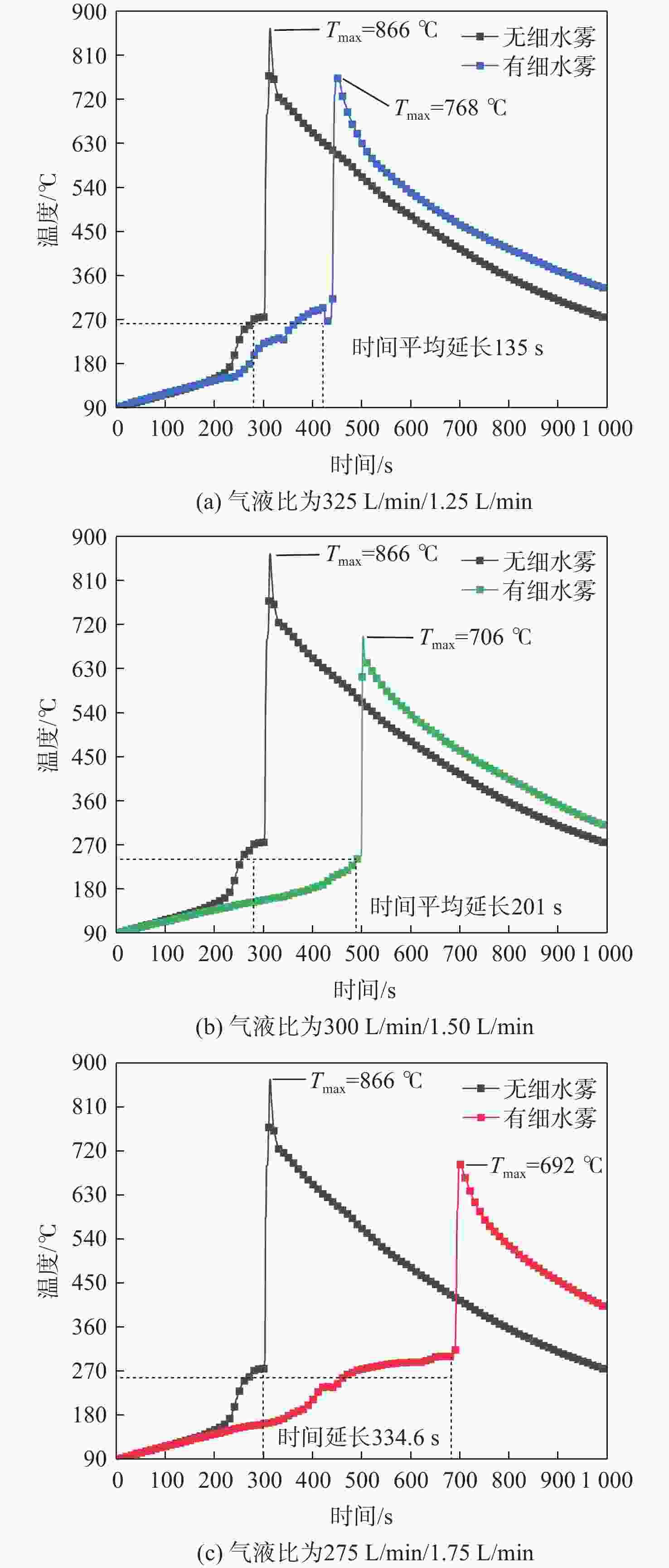
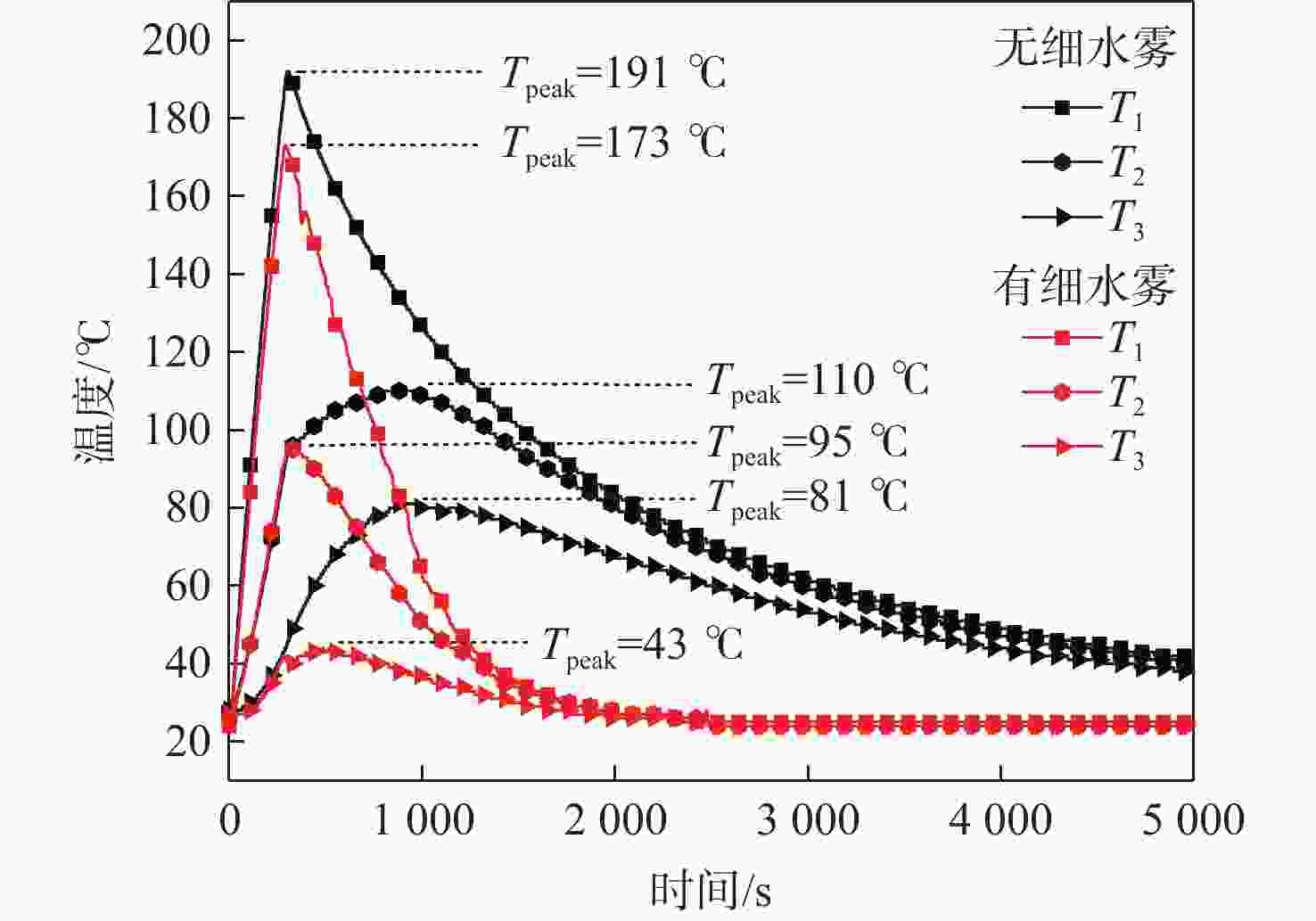
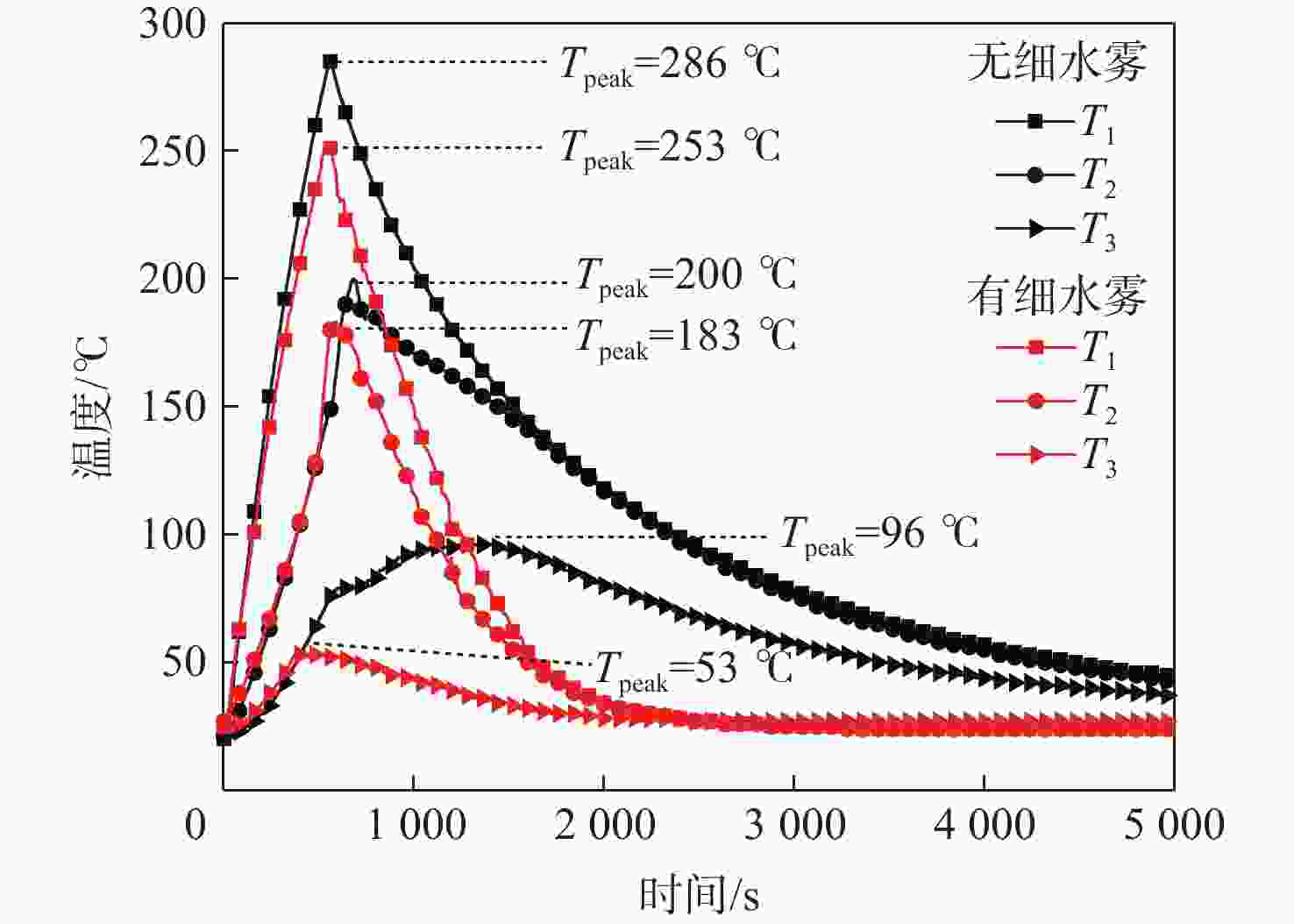
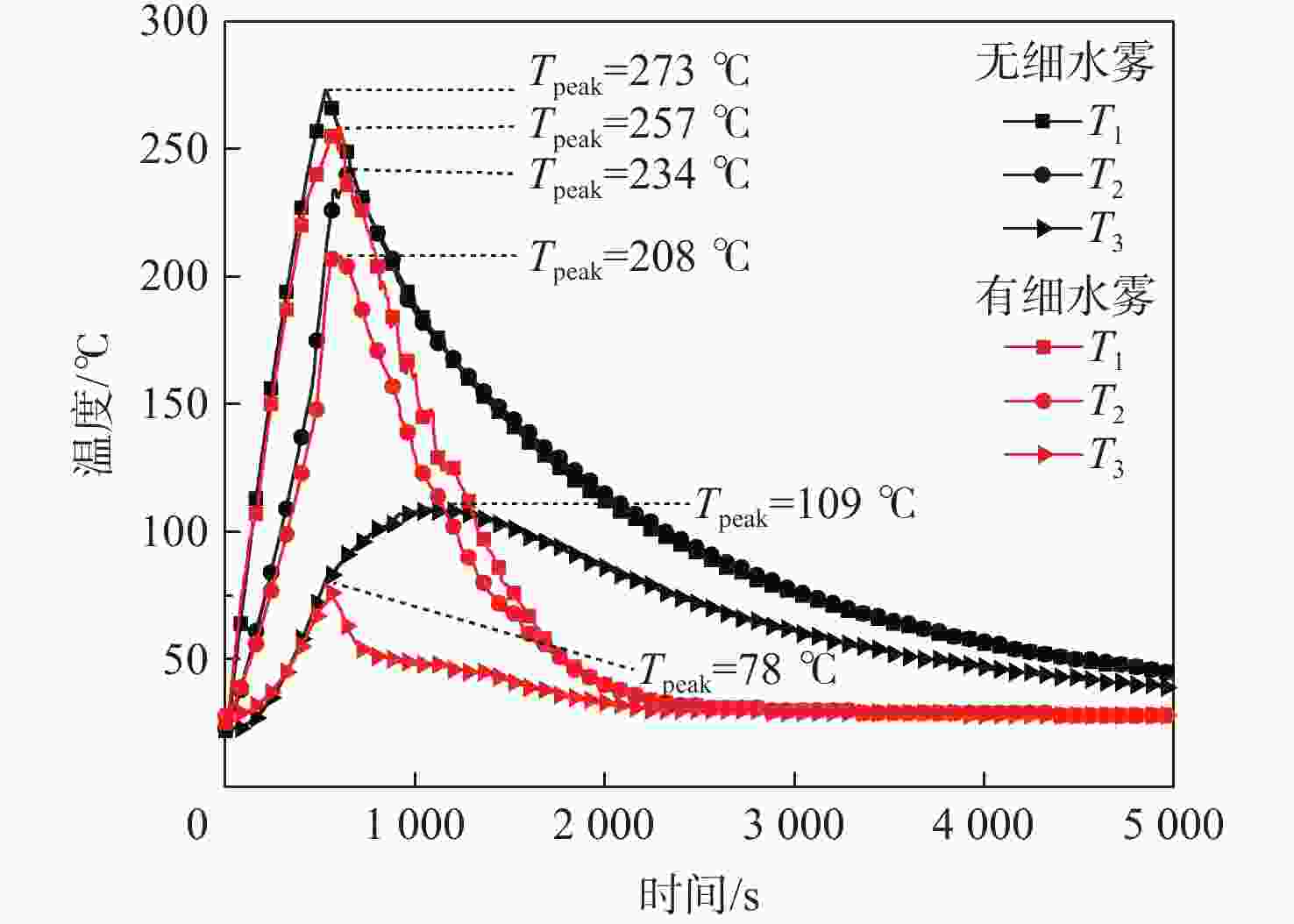
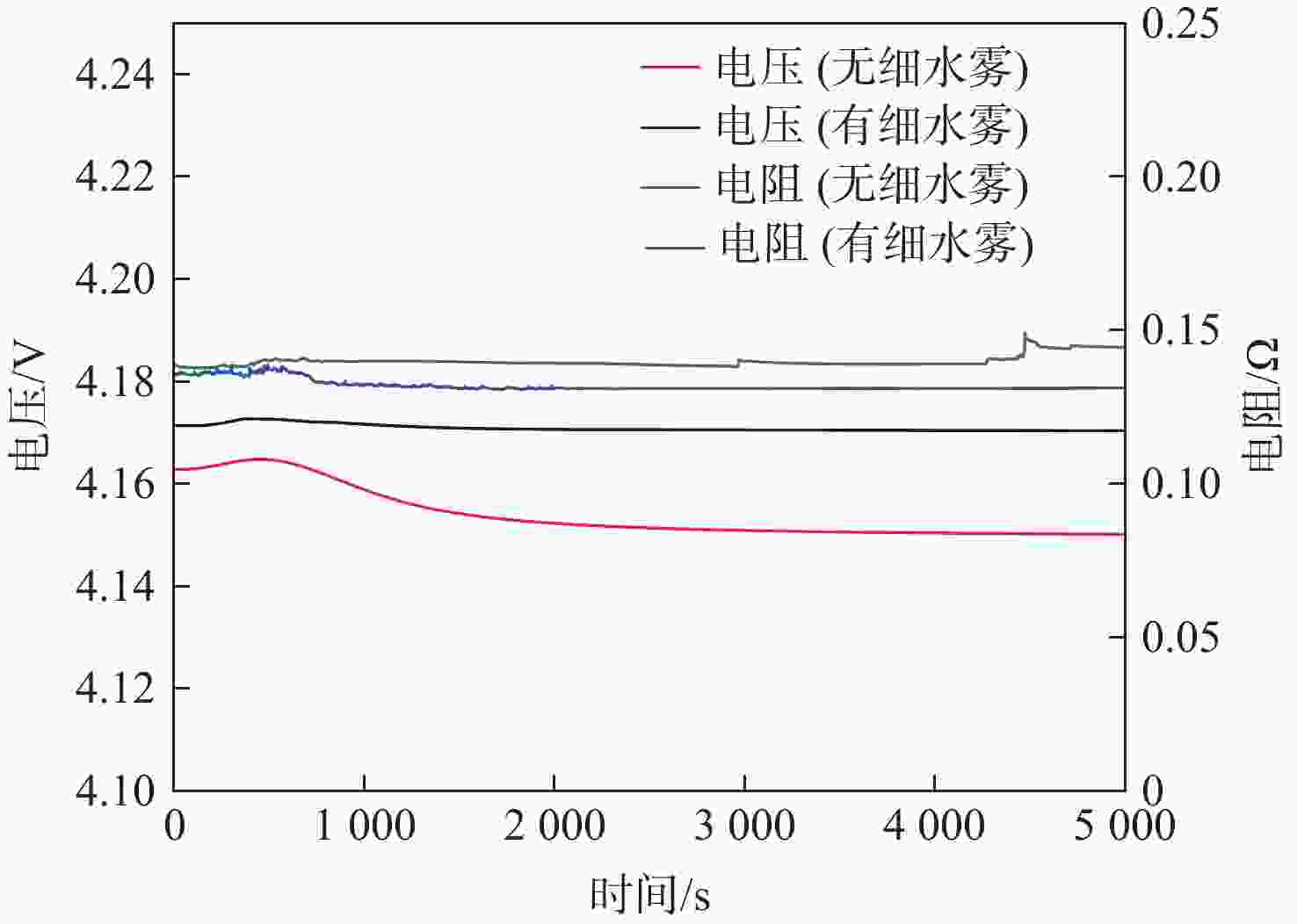
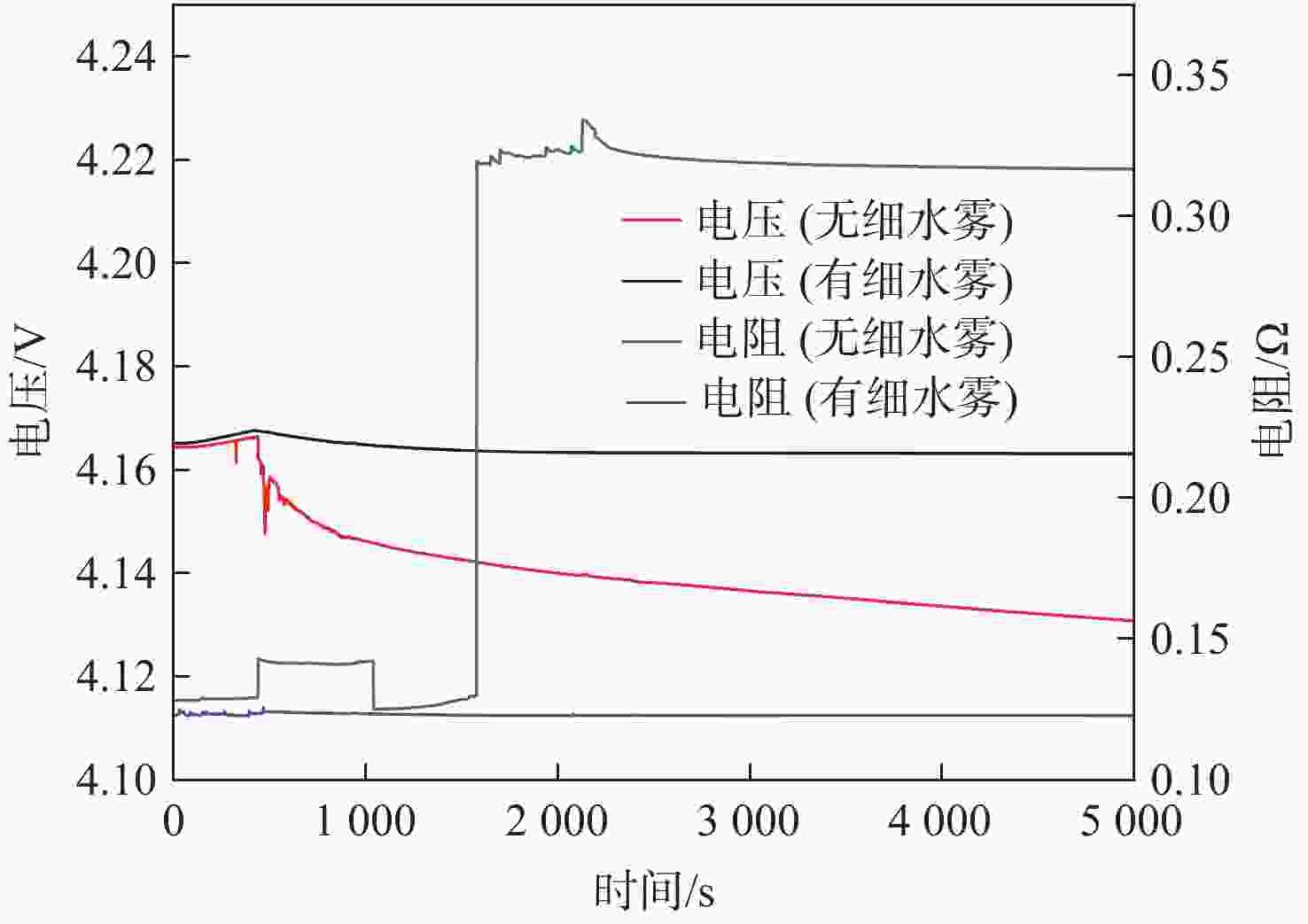
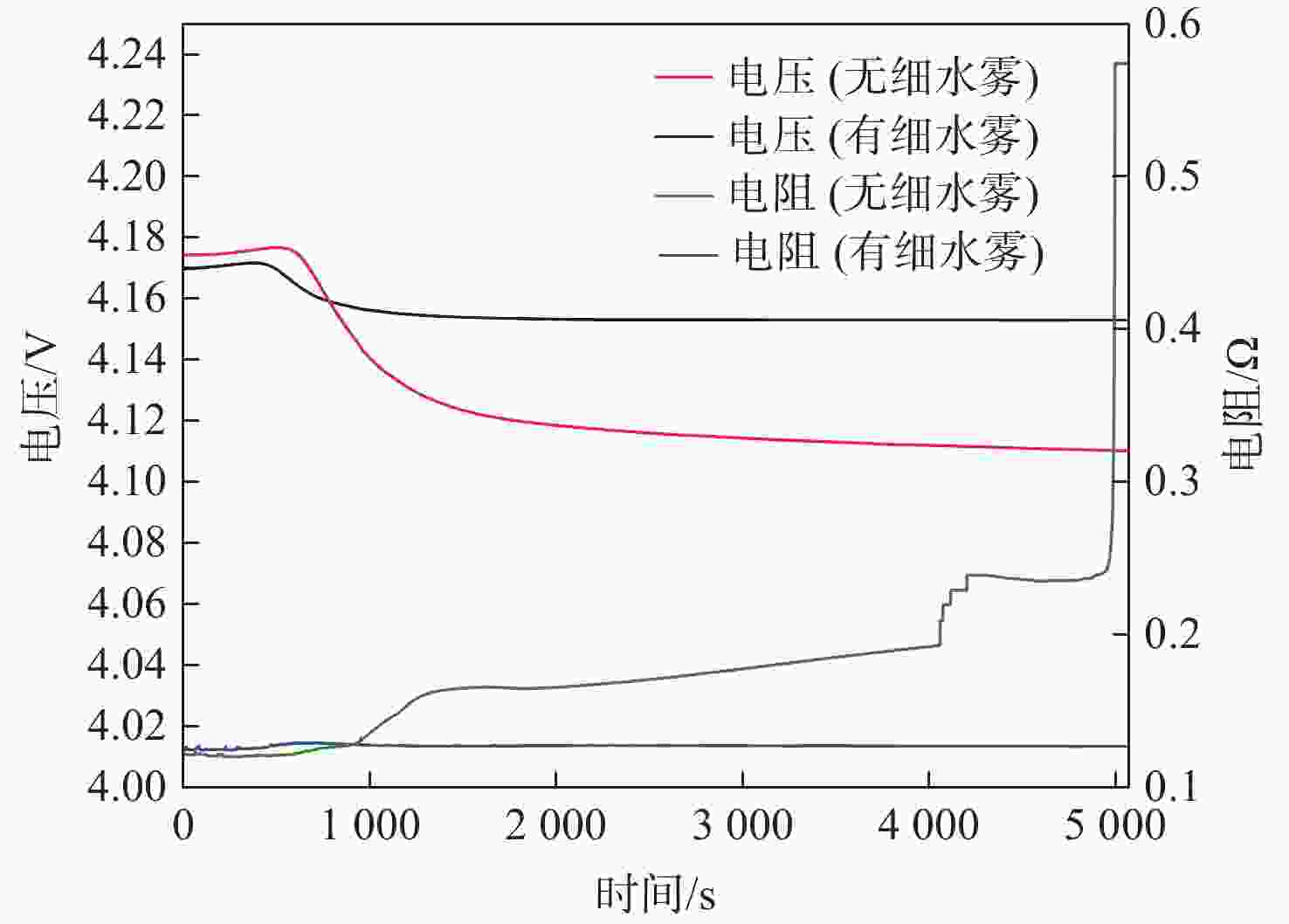
为削减气体、高压细水雾等灭火剂抑灭锂离子电池火灾导致二次灾害的短板问题,研究低压双流体细水雾抑灭锂离子电池燃爆技术。以中小型储能系统常用的三元锂离子电池为对象,研究了低压双流体细水雾对锂离子电池在热失控前不同温度下(90 ℃、145 ℃和200 ℃)的外观形貌变化、产热过程抑制和电性能防护的影响。结果表明:在施加低压双流体细水雾情况下,锂离子电池极耳附近鼓包厚度分别减小了0 cm、0.01 cm和0.15 cm,电池直接受热大面的受损状况有所减小;电池非直接受热大面温度降低幅度很大,分别降低了38 ℃、43 ℃和31 ℃;电池充电容量分别提高了487.54 mAh、4116.69 mAh和6 230.06 mAh,放电容量分别提高了565.07 mAh、4 325.11 mAh和6297.45 mAh。因此,低压双流体细水雾不仅可有效防护遭遇热失控锂离子电池的外观形貌、热量抑制和电性能,而且可有效防止锂离子电池热失控灾害传统抑灭技术导致的二次灾害。
Abstract:To address the shortcomings of gas, high-pressure water mist, and other fire extinguishing agents in suppressing lithium battery fires, this paper investigated the low-pressure dual-fluid water mist for ternary lithium-ion battery fire suppression. The effects of low-pressure dual-fluid water mist on the appearance, heat generation inhibition, and electrical performance protection of lithium batteries at different temperatures (90 °C, 145 °C, and 200 °C) before thermal runaway were examined. The results show that under the application of low-pressure dual-fluid water mist, the thickness of the bulge near the pole lugs decreased by 0 cm, 0.01 cm, and 0.15 cm, and the extent of damage to the battery surface was reduced. The temperature of the non-heated surface of the battery decreases the most, by 38 °C, 43 °C, and 31 °C. The battery’s charging capacity increases by 487.54 mAh、4116.69 mAh and 6230.06 mAh, and the discharge capacity increases by 565.07 mAh、4325.11 mAh and 6297.45 mAh. These findings demonstrate that low-pressure dual-fluid water mist not only effectively protects the appearance, morphology, heat suppression, and electrical properties of lithium batteries, but also proves its reliability in inhibiting the thermal runaway process during the early stages.
-
表 1 锂离子电池物性参数
Table 1. Physical property parameters of lithium-ion batteries
参数 状态/数值 正极材料 NCM523 负极材料 石墨 电池质量/g 151.4±1 额定容量/mAh 10000 标定电压/V 4.2 荷电状态/% 100 电池尺寸/(mm×mm×mm) 7.0×65×115 表 2 不同受热程度有无细水雾电池充放电性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of charge and discharge performance of batteries with or without water mist at different heating degrees
温度/℃ 实验阶段 充电容量/
mAh放电容量/
mAh充放电效率/
%90 无细水雾 9492.52 9347.47 98.47 有细水雾 9980.06 9912.54 99.32 145 无细水雾 5860.34 5538.01 94.50 有细水雾 9977.03 9863.12 98.86 200 无细水雾 1818.20 1707.12 93.89 有细水雾 8048.26 8004.57 99.46 -
[1] 王鹏博, 郑俊超. 锂离子电池的发展现状及展望[J]. 自然杂志, 2017, 39(4): 283-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.04.006WANG P B, ZHENG J C. The present situation and expectation of lithium-ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2017, 39(4): 283-289(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.04.006 [2] 徐晓楠. 灭火剂与应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006: 81-82.XU X N. Fire extinguishing agent and application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006: 81-82(in Chinese). [3] WANG Q S, PING P, ZHAO X J, et al. Thermal runaway caused fire and explosion of lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 208: 210-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.02.038 [4] FENG X N, OUYANG M G, LIU X, et al. Thermal runaway mechanism of lithium ion battery for electric vehicles: a review[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 10: 246-267. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2017.05.013 [5] WHITTINGHAM M S. History, evolution, and future status of energy storage[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(SI): 1518-1534. [6] HENRIKSEN M, VAAGSAETHER K, LUNDBERG J, et al. Explosion characteristics for Li-ion battery electrolytes at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 371: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.108 [7] CHEN S C, WANG Z R, WANG J H, et al. Lower explosion limit of the vented gases from Li-ion batteries thermal runaway in high temperature condition[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2020, 63: 103992. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2019.103992 [8] LIU X, WU Z B, STOLIAROV S I, et al. Heat release during thermally-induced failure of a lithium ion battery: impact of cathode composition[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2016, 85: 10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2016.08.001 [9] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 消防设施通用规范: GB 55036—2022[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2022: 12-19.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. General code for fire protection facilities: GB 55036—2022[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2022: 12-19(in Chinese). [10] MENG X D, YANG K, ZHANG M J, et al. Experimental study on combustion behavior and fire extinguishing of lithium iron phosphate battery[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 30: 101532. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2020.101532 [11] WANG Q, CHEN J Z, LI M, et al. Eltoprazine prevents levodopa-induced dyskinesias by reducing causal interactions for theta oscillations in the dorsolateral striatum and substantia nigra pars reticulate[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2019, 148: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.12.027 [12] LI Y L, LIN Z L. A generalized piecewise quadratic Lyapunov function approach to estimating the domain of attraction of a saturated system[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(11): 120-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.09.170 [13] WANG Q S, SHAO G Z, DUAN Q L, et al. The efficiency of heptafluoropropane fire extinguishing agent on suppressing the lithium titanate battery fire[J]. Fire Technology, 2016, 52(2): 387-396. doi: 10.1007/s10694-015-0531-9 [14] SI R J, LIU D Q, XUE S Q. Experimental study on fire and explosion suppression of self-ignition of lithium ion battery[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2018, 211: 629-634. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2017.12.057 [15] HYNES R. Inhibition of premixed hydrogen-air flames by 2-H heptafluoropropane[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1998, 113(4): 554-565. doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(97)00267-8 [16] 张乃平, 马永飞, 杨孟霖, 等. 锂电池火灾灭火技术研究综述[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(7): 47-53.ZHANG N P, MA Y F, YANG M L, et al. Review on fire extinguishing technology research of lithium battery[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(7): 47-53(in Chinese). [17] 胡振恺, 李勇琦, 彭鹏. 电池储能系统火灾预警与灭火系统设计[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2020, 39(10): 1434-1438. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.10.027HU Z K, LI Y Q, PENG P. Design of fire warning system and fire extinguishing system of battery energy storage system[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2020, 39(10): 1434-1438(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.10.027 [18] LARSSON F, ANDERSSON P, BLOMQVIST P, et al. Characteristics of lithium-ion batteries during fire tests[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 271: 414-420. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.08.027 [19] ZHANG L, DUAN Q L, LIU Y J, et al. Experimental investigation of water spray on suppressing lithium-ion battery fires[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2021, 120: 103117. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2020.103117 [20] 韩路豪, 王子阳, 何骁龙, 等. 细水雾释放策略对大容量三元锂离子电池热失控火灾抑制效果的实验研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1664-1674.HAN L H, WANG Z Y, HE X L, et al. The effect of water mist strategies on thermal runaway fire suppression of large-capacity NCM lithium-ion battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1664-1674(in Chinese). [21] 丰汉军, 邹丽, 张宇航. 高压细水雾抑制磷酸铁锂电池模块火灾试验研究及设计讨论[J]. 给水排水, 2022, 58(11): 114-119.FENG H J, ZOU L, ZHANG Y H. Experimental research on fire suppression of lithium iron phosphate battery module by high pressure water mist and discussion on design[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2022, 58(11): 114-119(in Chinese). [22] LIU T, TAO C F, WANG X S. Cooling control effect of water mist on thermal runaway propagation in lithium ion battery modules[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 267: 115087. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115087 [23] 赵军超, 付阳阳, 薛峰, 等. 低压细水雾系统扑救锂电池箱火灾的试验研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(4): 1897-1903.ZHAO J C, FU Y Y, XUE F, et al. Experimental study on suppressing lithium battery package fires by low-pressure water mist system[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(4): 1897-1903(in Chinese). [24] KRITZER P, DORING H, EMERMACHER B. Improved safety for automotive lithium batteries: an innovative approach to include an emergency cooling element[J]. Advances in Chemical Engineering and Science, 2014, 4(2): 197-207. doi: 10.4236/aces.2014.42023 [25] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 电动汽车用动力蓄电池安全要求: GB 38031—2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020: 5-6.State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration. Electric vehicles traction battery safety requirements: GB 38031—2020[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2020: 5-6(in Chinese). [26] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 细水雾灭火系统技术规范: GB 50898—2013[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2013: 10-11.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for water mist fire extinguishing system: GB 50898—2013[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2013: 10-11(in Chinese). [27] 王雪峰, 纪小刚. 软包锂电池铝塑膜热封强度工艺参数研究[J]. 实验力学, 2023, 38(2): 222-230. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-22-130WANG X F, JI X G. Study on the heat-sealing process parameters of aluminum plastic film for pouch lithium battery[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2023, 38(2): 222-230(in Chinese). doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-22-130 [28] LU L G, HAN X B, LI J Q, et al. A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 226: 272-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.10.060 [29] JIANG J, DAHN J R. ARC studies of the thermal stability of three different cathode materials: LiCoO2; Li[Ni0.1Co0.8Mn0.1]O2; and LiFePO4, in LiPF6 and LiBoB EC/DEC electrolytes[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2004, 6: 39-43. [30] 王淮斌, 李阳, 王钦正, 等. 三元锂离子动力电池热失控及蔓延特性实验研究[J]. 工程科学学报, 2021, 43(5): 663-675.WANG H B, LI Y, WANG Q Z, et al. Experimental study on the thermal runaway and its propagation of a lithium-ion traction battery with NCM cathode under thermal abuse[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2021, 43(5): 663-675(in Chinese). [31] GRANT G, BRENTON J, DRYSDALE D. Fire suppression by water sprays[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2000, 26(2): 79-130. doi: 10.1016/S0360-1285(99)00012-X -






 下载:
下载: