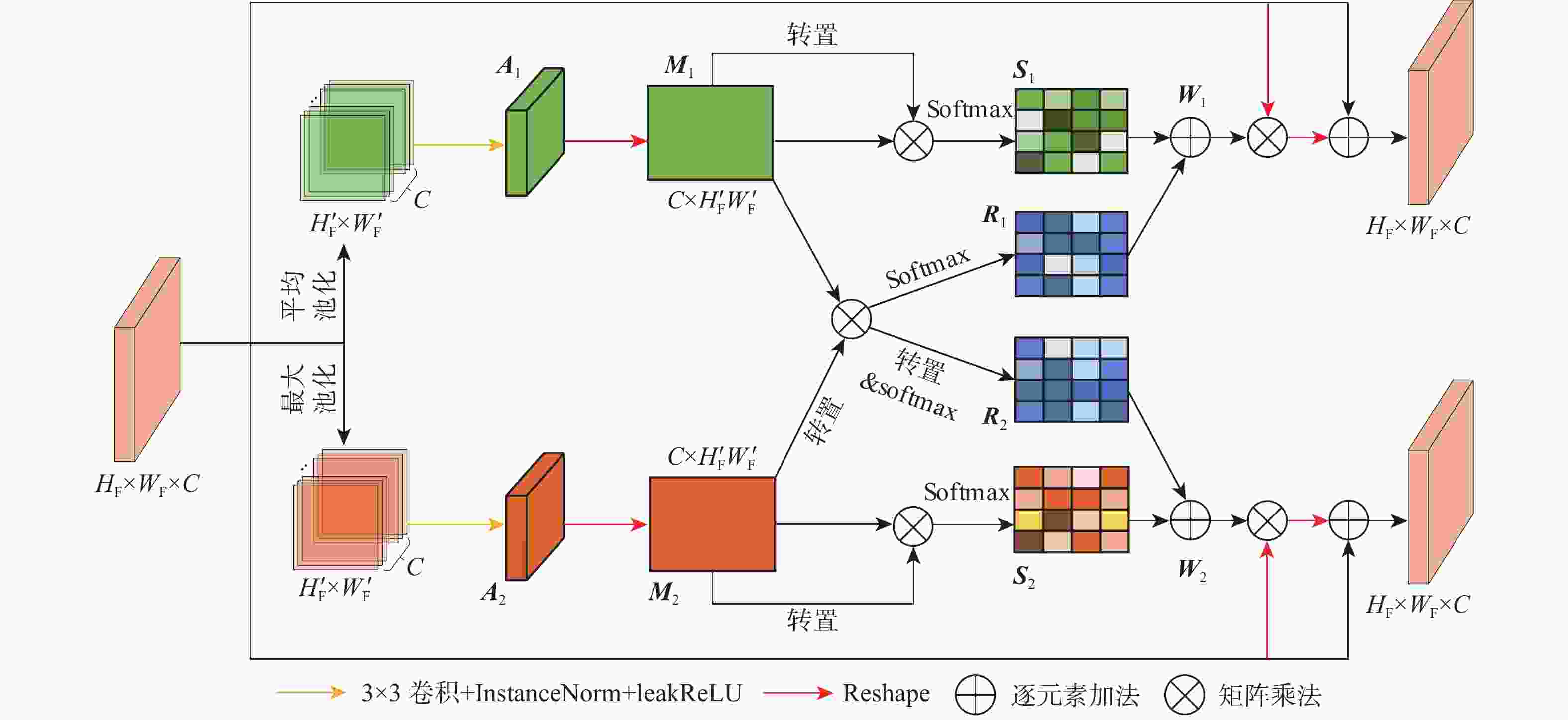
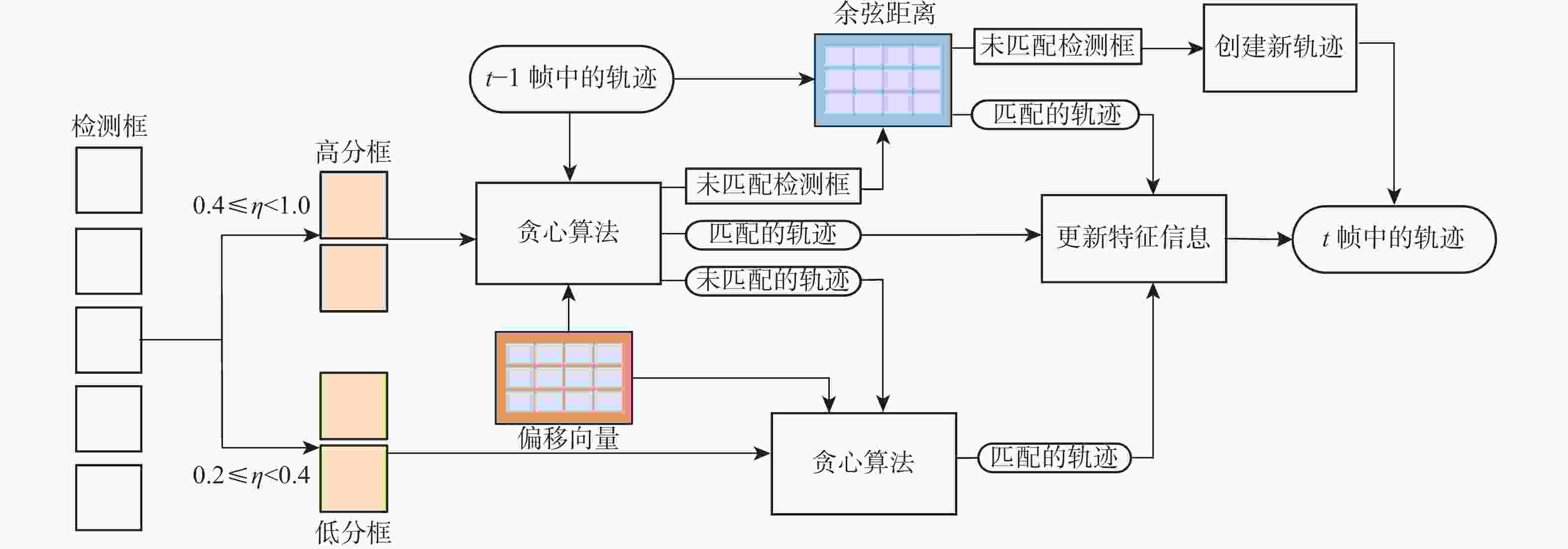
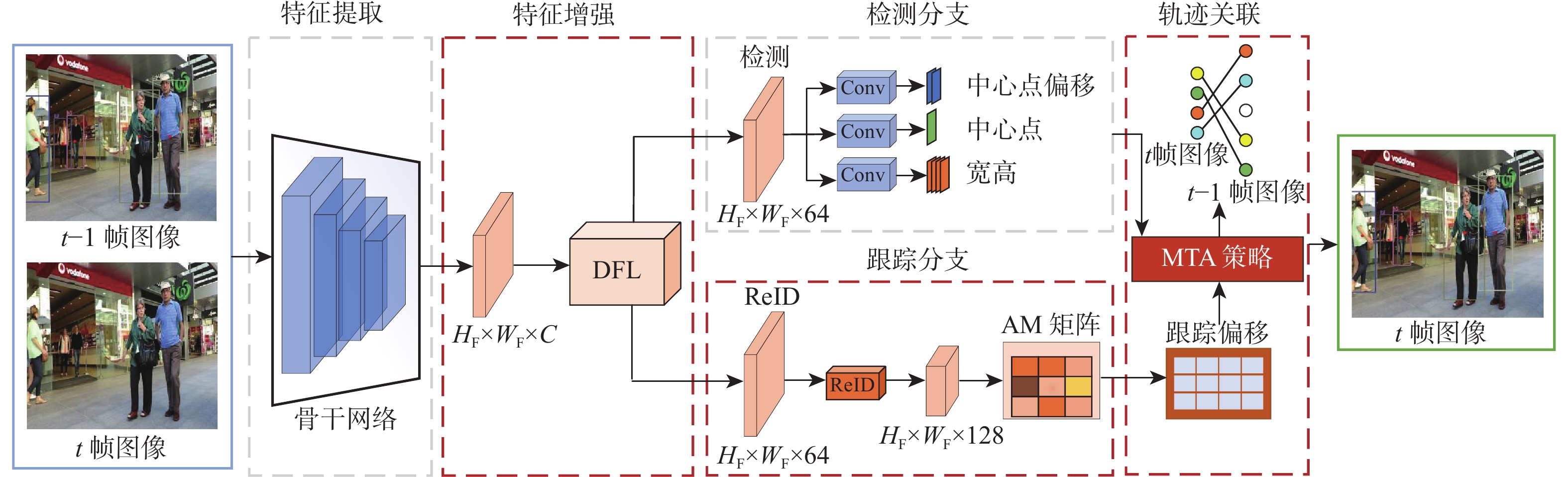
Multi-object tracking algorithm based on dual-branch feature enhancement and multi-level trajectory association
-
摘要:
在多目标跟踪(MOT)算法中,经常出现目标特征提取不足、身份切换及轨迹缺失问题,降低跟踪性能。为解决以上问题,提出一种基于双分支特征增强和多级轨迹关联(MTA)的MOT算法。采用双分支特征学习网络对检测和跟踪2种任务的特殊性和相关性进行学习,缓解了两任务之间的过度竞争,提取到充足的目标特征信息;引入关联矩阵(AM),利用更多的时序信息预测偏移向量,减少身份切换次数;采用多级轨迹关联策略,保留一部分低分检测框,并将检测框重新划分为高分框和低分框,采用不同的匹配方式与轨迹进行关联,减少轨迹缺失次数。在典型多目标跟踪数据集MOT17和MOT20上,对JDE、CenterTrack等6种相关算法进行对比实验。实验结果表明:所提算法在MOT17数据集上的多目标跟踪准确度(MOTA)和身份
F 1分数(IDF1)值分别达到68.2%和68.5%,与基准算法CenterTrack相比,分别提升了2.1%、4.3%;在MOT20数据集上,MOTA和IDF1值分别达到52.7%和48.2%,分别提升了1.4%、7.9%。所提算法在复杂场景下取得了优异的跟踪性能。Abstract:Insufficient target feature extraction and target occlusion situations frequently occur in single-stage multipal object tracking(MOT) algorithms, resulting in a large number of identity switches and degraded tracking performance. A multi-target tracking algorithm based on dual-branch feature enhancement and multi-level trajectory association(MTA) is proposed to solve this problem. In order to alleviate the excessive competition between detection and tracking branches and fully extract the target improvement features for detection and tracking, respectively, a dual-branch feature learning network is utilized to learn the specificity and relevance of both detection and tracking tasks. An association matrix(AM) is introduced to predict a more accurate offset vector for data association by learning the similarity relationship between two frames. In order to recover lost trajectories and achieve long-term target association, a hierarchical trajectory association strategy is used to divide detection frames into high-score frames and low-score frames, and different matching methods are used to associate with the trajectories. On the typical multi-target tracking datasets MOT17 and MOT20, six related algorithms, including CenterTrack and QuasiDense, are tested. The algorithms’ multipal object tracking accuracy(MOTA)and identity
F 1 score (IDF1) values on MOT17 and MOT20 are 68.2% and 68.5%, respectively, 2.1% and 4.3% higher than those of the benchmark algorithm CenterTrack. On MOT20, the MOTA and IDF1 values are 52.7% and 48.2%, respectively, 1.4% and 7.9% higher. The algorithm solves the identity switching problem better and achieves excellent tracking performance in complex scenarios. -
表 1 本文算法在MOT17测试集上的消融实验
Table 1. Ablation experiments of the proposed algorithm on MOT17 test set
基准算法 AM DFL MTA MOTA/% IDF1/% IDs/次 MT/% ML/% CenterTrack 66.1 64.2 528 41.3 21.2 √ 67.1 68.6 369 41.0 19.2 √ √ 67.4 69.1 368 40.4 18.6 √ √ 67.9 67.8 344 44.2 18.3 √ √ √ 68.2 68.5 333 44.5 16.8 表 2 不同跟踪算法实验对比
Table 2. Experimental comparison of different tracking algorithms
数据集 算法 MOTA/% IDF1/% IDs/次 FP FN speed/(帧·s−1) MOT17 CTracker[14] 63.1 60.9 755 2955 16174 6.8 JDE[8] 60.0 63.6 473 2923 18158 22.2 CenterTrack[9] 66.1 64.2 528 2442 15286 17.5 QuasiDense[15] 67.3 67.8 377 2637 14605 20.3 TransTrack[16] 67.1 68.3 254 1652 15817 10.0 MOTR[17] 64.7 67.2 346 5278 13452 7.5 本文算法 68.2 68.5 333 2062 14764 16.8 MOT20 CenterTrack[9] 51.3 40.3 7731 10080 281757 10.2 本文算法 52.7 48.2 3043 13403 274419 7.8 -
[1] 朱姝姝, 王欢, 严慧. 基于帧内关系建模和自注意力融合的多目标跟踪方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(2): 335-344.ZHU S S, WANG H, YAN H. Multi-object tracking based on intra-frame relationship modeling and self-attention fusion mechanism[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(2): 335-344(in Chinese). [2] CAO M W, ZHENG L P, JIA W, et al. Joint 3D reconstruction and object tracking for traffic video analysis under IoV environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(6): 3577-3591. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2995768 [3] SUN P, KRETZSCHMAR H, DOTIWALLA X, et al. Scalability in perception for autonomous driving: waymo open dataset[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2443-2451. [4] PEREIRA R, CARVALHO G, GARROTE L, et al. Sort and deep-SORT based multi-object tracking for mobile robotics: evaluation with new data association metrics[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(3): 1319. doi: 10.3390/app12031319 [5] 吴孙勇, 周于松, 谢芸, 等. 基于MM-GGIW-PMBM滤波的扩展目标跟踪算法[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2022, 48(12): 2356-2364.WU S Y, ZHOU Y S, XIE Y, et al. Extended target tracking algorithm based on MM-GGIW-PMBM filter[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(12): 2356-2364(in Chinese). [6] BEWLEY A, GE Z Y, OTT L, et al. Simple online and realtime tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 3464-3468. [7] WOJKE N, BEWLEY A, PAULUS D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3645-3649. [8] WANG Z D, ZHENG L, LIU Y X, et al. Towards real-time multi-object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 107-122. [9] ZHOU X Y, KOLTUN V, KRÄHENBÜHL P. Tracking objects as points[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 474-490. [10] LIANG C, ZHANG Z P, ZHOU X, et al. Rethinking the competition between detection and ReID in multiobject tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 3182-3196. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3165376 [11] ZHOU X Y, WANG D Q, KRÄHENBÜHL P. Objects as points [EB/OL]. (2019-04-16)[2023-07-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.07850. [12] WU J L, CAO J L, SONG L C, et al. Track to detect and segment: an online multi-object tracker[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 12347-12356. [13] STIEFELHAGEN R, BERNARDIN K, BOWERS R, et al. The CLEAR 2006 evaluation[C]//Proceedings of the International Evaluation Workshop on Classification of Events, Activities and Relationships. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 1-44. [14] PENG J L, WANG C G, WAN F B, et al. Chained-tracker: chaining paired attentive regression results for end-to-end joint multiple-object detection and tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 145-161. [15] PANG J M, QIU L L, LI X, et al. Quasi-dense similarity learning for multiple object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 164-173. [16] SUN P Z, CAO J K, JIANG Y, et al. Transtrack: multiple object tracking with transformer [EB/OL]. (2020-12-31)[2023-07-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2012.15460. [17] ZENG F G, DONG B, ZHANG Y A, et al. MOTR: end-to-end multiple-object tracking with transformer[C]//Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2022: 659-675. -






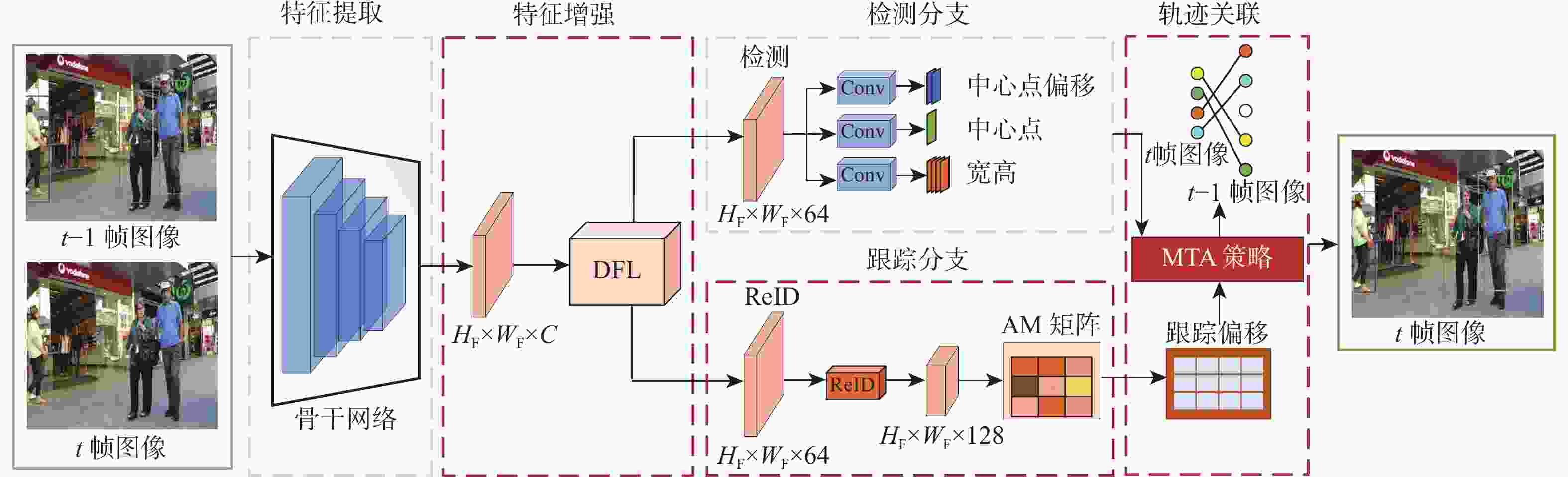
 下载:
下载: