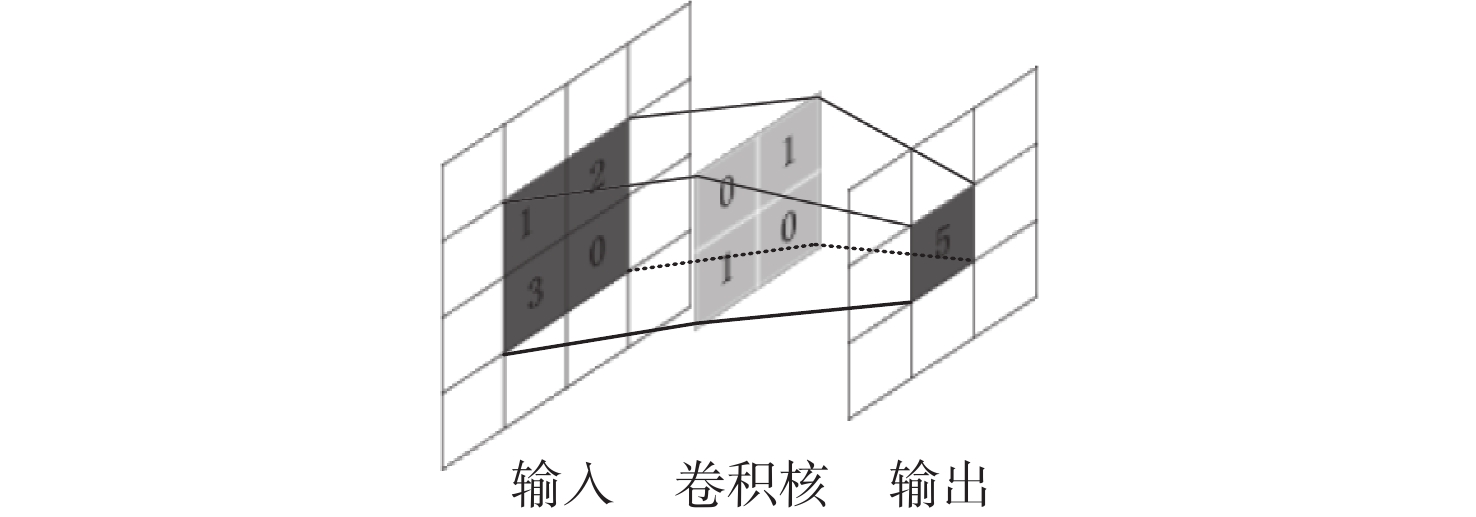
-
摘要:
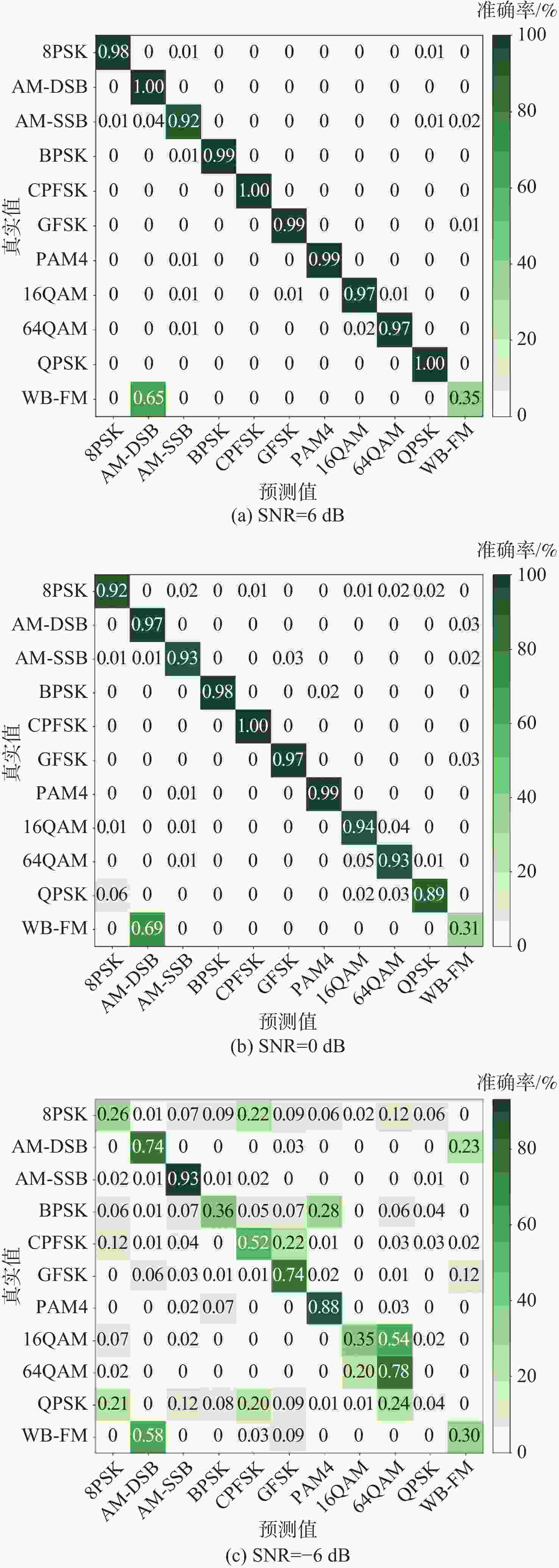
信号调制波形识别是空间频谱认知领域的关键技术之一,是实现低轨卫星频谱资源监测与管控的重要手段。针对现阶段基于深度学习的调制波形识别方法存在的参数量多、计算复杂度高等问题,提出一种基于空时融合网络(STF-Net)的轻量级信号调制波形识别方法。将信号预处理为时域-频域形式的双通道数据,通过卷积神经网络(CNN)提取信号空间特征并减少特征冗余,进而利用长短时记忆网络(LSTM)提取时序信息,输出识别结果。实验结果表明:所提方法在信噪比大于0 dB时,调制波形的平均识别准确率达到91.79%;与同等方法相比,所提方法参数量降低了96%,效率提升了2.7倍。
Abstract:Signal modulation waveform recognition is one of the key technologies in the field of spectrum cognition and an important means to achieve monitoring and control of spectrum resources for low-orbit satellites. To address the issues of high parameter count and computational complexity in existing deep learning-based modulation waveform recognition methods, a lightweight signal modulation waveform recognition method based on space-time fusion network (STF-Net) is proposed. The method first preprocesses the signals into dual-channel data in the time-frequency domain. It then utilizes convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract signal spatial features and reduce feature redundancy. Long short-term memory (LSTM) is employed to capture temporal information and output recognition results. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves an average recognition accuracy of 91.79% for modulation waveforms when the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 0dB. Compared with equivalent methods, the proposed method reduces the parameter count by 96% and improves efficiency by 2.7 times.
-
Key words:
- modulation waveform recognition /
- deep learning /
- STF-Net /
- CNN /
- LSTM
-
表 1 STF-Net网络层数据结构
Table 1. Data structures of STF-Net network layers
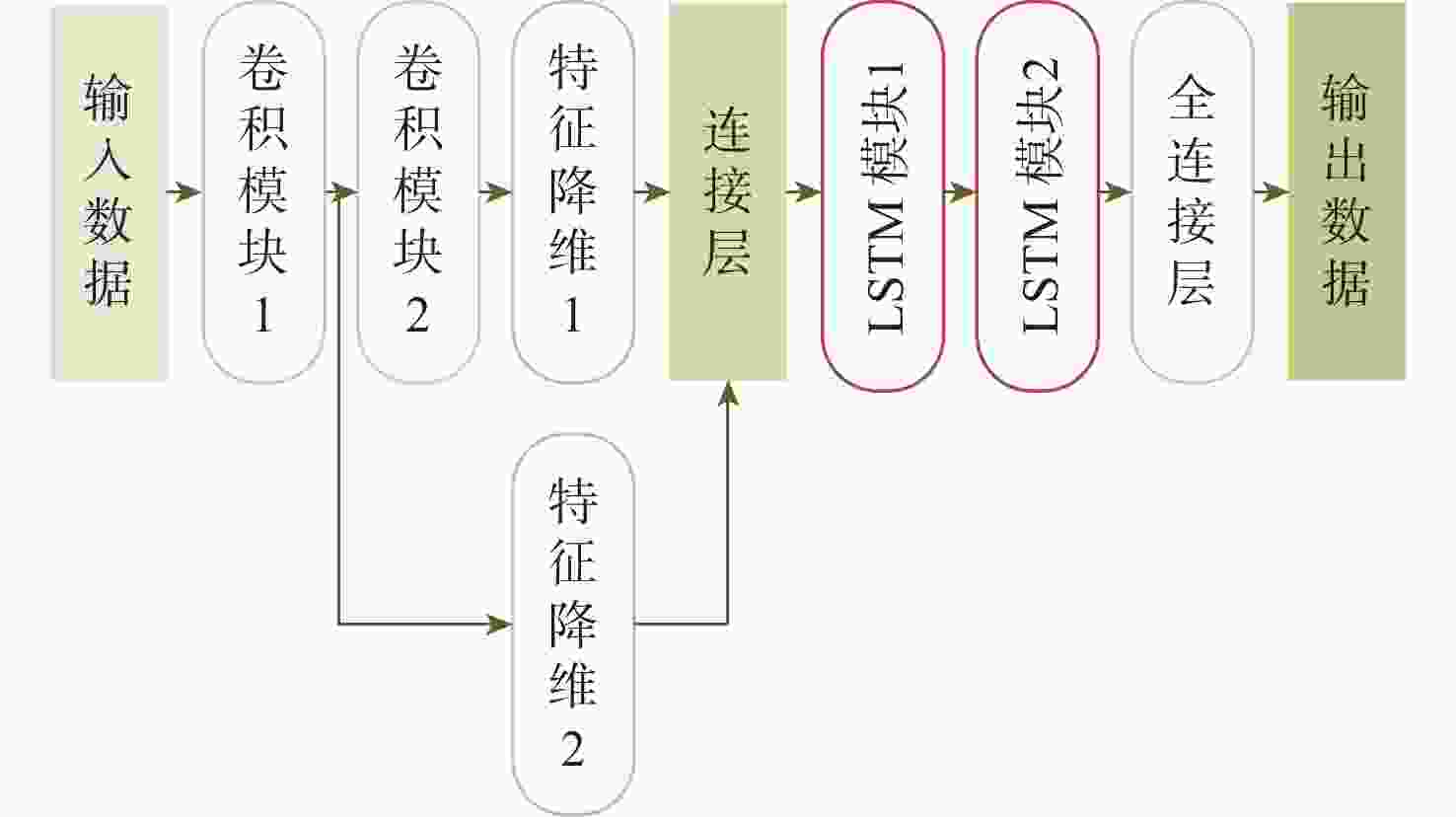
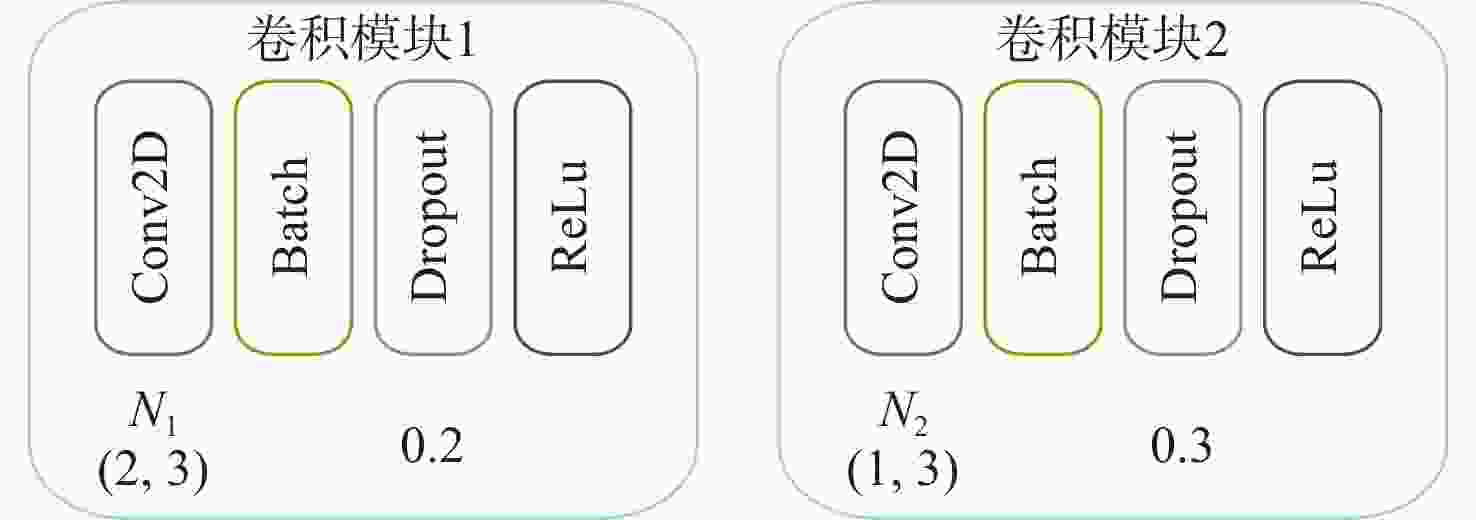
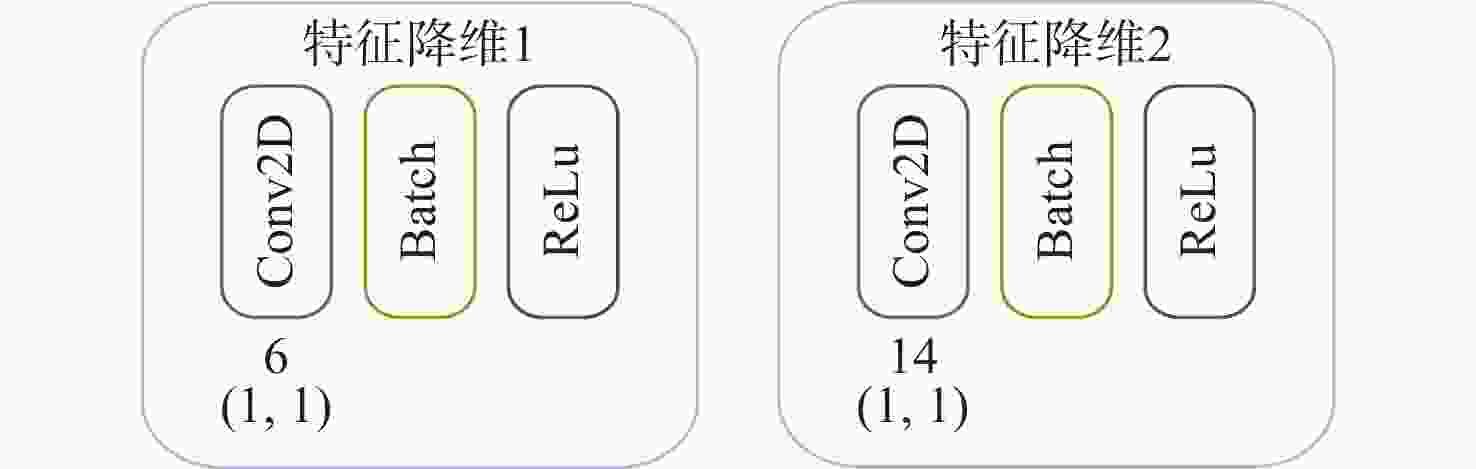
网络层 输入数据结构 输出数据结构 卷积模块1 (1,2,128) (N1,1,130) 卷积模块2 (N1,1,130) (N2,1,130) 特征降维1 (N1,1,130) (6,1,130) 特征降维2 (N2,1,130) (14,1,130) 连接层 (6,1,130), (14,1,130) (20,130) LSTM模块1 (20,130) (50,130) LSTM模块2 (50,130) (20,130) 全连接层 20 11 表 2 数据集参数
Table 2. Dataset parameters
采样
频率/kHz采样频率
标准差/Hz最大采样
频率偏移量/Hz载波频率
偏移标准差/Hz最大载波
频率偏移/Hz频率选择性
衰落中使用的
正弦波个数衰落中使用
的最大多
普勒频率/Hz衰落
模型莱斯
因子功率时延
谱的部分
样本延迟每个延迟
时间对应
的大小插入功率
时延谱的
滤波器长度200 0.01 50 0.01 500 8 1 Rician 4 [0, 0.9, 1.7] [1, 0.8, 1.3] 8 表 3 不同卷积核数的平均识别准确率
Table 3. Average recognition accuracy for different numbers of convolutional kernels
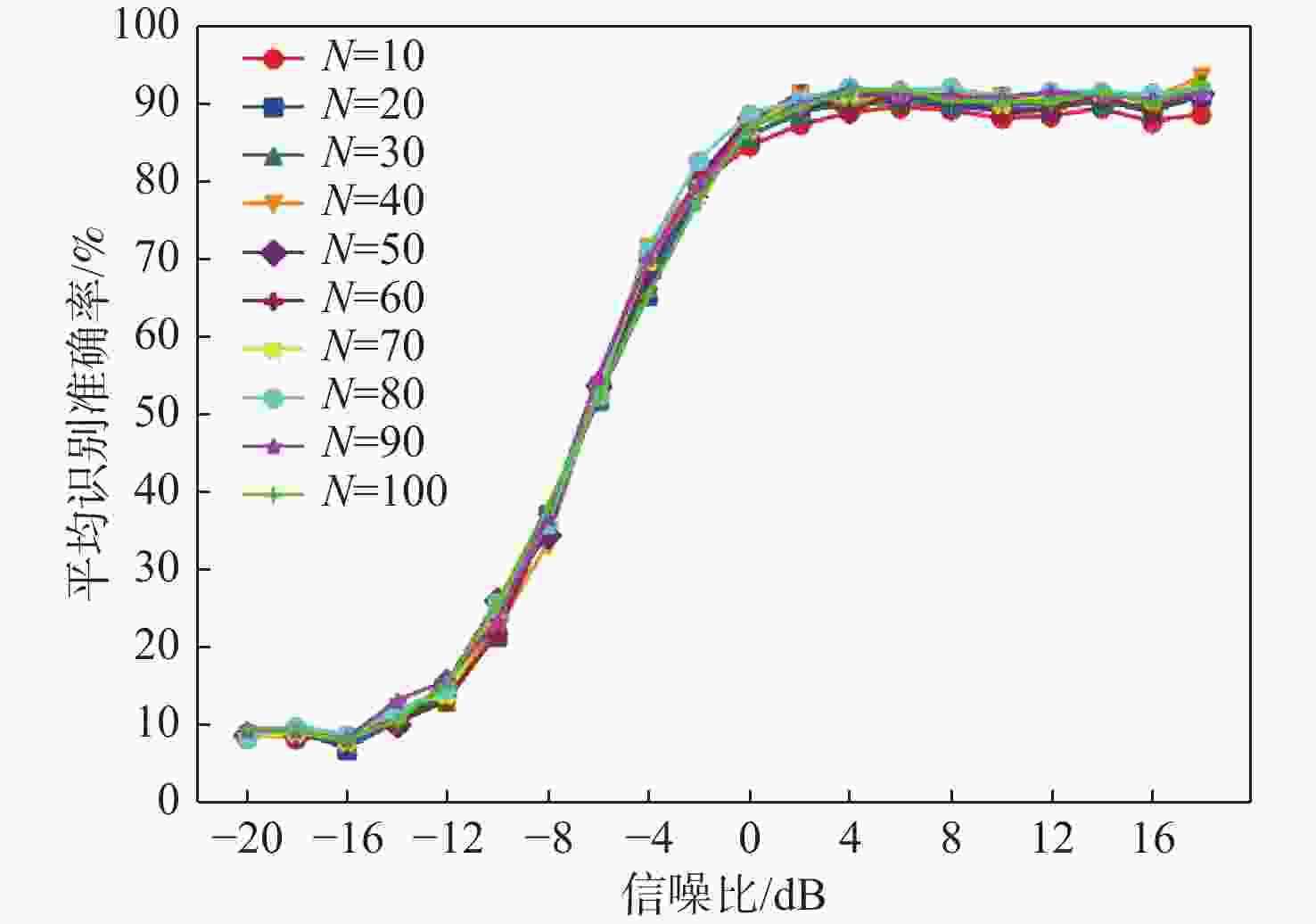
卷积核数目N 平均识别准确率/% [−20,0) dB [0,18] dB [−20,18] dB 10 30.99 88.03 59.51 20 30.35 89.36 59.85 30 30.80 89.45 60.12 40 31.19 90.78 60.98 50 31.31 90.51 60.91 60 30.07 89.96 60.52 70 31.30 90.62 60.96 80 32.08 91.04 61.56 90 31.90 90.43 61.16 100 31.02 90.35 60.68 表 4 不同数目卷积核的平均识别准确率
Table 4. Average recognition accuracy with different numbers of convolutional kernels
卷积核数目(N1,N2) 平均识别准确率/% [−20,0) dB [0,18] dB [−20,18] dB (80,80) 32.08 91.04 61.56 (81,79) 32.30 91.35 61.83 (82,78) 32.41 91.16 61.79 (83,77) 32.65 91.35 61.95 表 5 不同表示形式数据的平均识别准确率
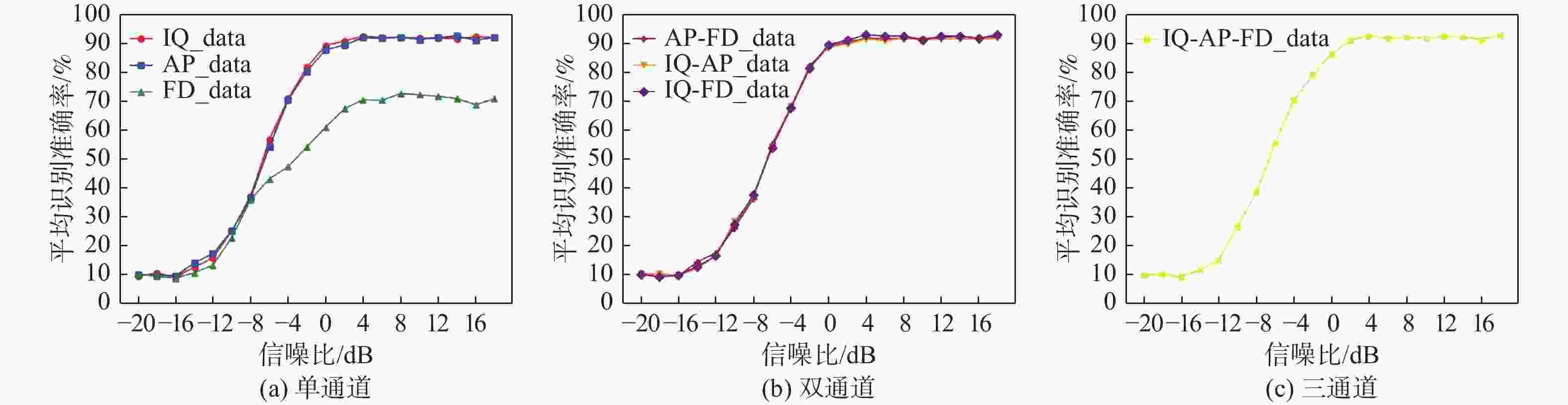
Table 5. Average recognition accuracy of different data representations
输入数据形式 平均识别准确率/% [−20,0) dB [0,18] dB [−20,18] dB IQ_data 32.65 91.35 61.95 AP_data 32.46 90.89 61.68 FD_data 25.33 69.32 47.33 IQ-AP_data 32.57 90.79 61.68 IQ-FD_data 32.33 91.79 62.06 AP-FD_data 32.70 91.26 61.98 IQ-AP-FD_data 32.32 91.27 61.80 表 6 不同方法的网络结构
Table 6. Network structures of different methods
表 7 不同方法的平均识别准确率
Table 7. Average recognition accuracy of different methods
-
[1] 李高, 王威, 吴启晖. 面向低轨卫星的频谱认知智能管控[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2021, 27(5): 7-11. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202105003LI G, WANG W, WU Q H. Cognitive intelligent spectrum management and control for low earth orbit satellite system[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2021, 27(5): 7-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202105003 [2] 古相平. 浅谈通信信号调制样式自动识别方法[J]. 无线互联科技, 2011, 8(2): 22-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6944.2011.02.007GU X P. Discussion on automatic identification method of communication signal modulation pattern[J]. Wireless Internet Technology, 2011, 8(2): 22-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6944.2011.02.007 [3] 张海燕, 闫文君, 张立民, 等. 通信信号调制识别综述[J]. 海军航空大学学报, 2022, 37(1): 126-132.ZHANG H Y, YAN W J, ZHANG L M, et al. An overview of communication signal modulation recognition[J]. Journal of Naval Aviation University, 2022, 37(1): 126-132(in Chinese). [4] 林冲, 闫文君, 张立民, 等. 通信信号调制识别综述[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2021, 16(11): 1074-1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2021.11.002LIN C, YAN W J, ZHANG L M, et al. An overview of communication signals modulation recognition[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2021, 16(11): 1074-1085(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2021.11.002 [5] HASSAN K, DAYOUB I, HAMOUDA W, et al. Automatic modulation recognition using wavelet transform and neural network[C]// Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Transport Systems Telecommunications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 234-238. [6] 闫文康, 闫毅, 范亚楠, 等. 基于小波变换熵值及高阶累积量联合的卫星信号调制识别算法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(6): 968-975. doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.06.968YAN W K, YAN Y, FAN Y N, et al. A modulation recognition algorithm based on wavelet transform entropy and high-order cumulant for satellite signal modulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(6): 968-975(in Chinese). doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.06.968 [7] 李世平, 陈方超, 王隆, 等. 多径信道下基于循环谱特征的调制识别算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2012, 32(8): 2123-2127.LI S P, CHEN F C, WANG L, et al. Modulation identification algorithm based on cyclic spectrum characteristics in multipath channel[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2012, 32(8): 2123-2127(in Chinese). [8] DONG S L, LI Z P, ZHAO L F. A modulation recognition algorithm based on cyclic spectrum and SVM classification[C]// Proceeding of the IEEE 4th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2123-2127. [9] FLOHBERGER M, GAPPMAIR W, KOUDELKA O. Modulation classifier for signals used in satellite communications[C]// Proceeding of the 5th Advanced Satellite Multimedia Systems Conference and the 11th Signal Processing for Space Communications Workshop. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 198-202. [10] 李跃, 郭兴吉, 赵欣. 基于高阶累积量的调制方式识别研究[J]. 西南科技大学学报, 2018, 33(3): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2018.03.013LI Y, GUO X J, ZHAO X. Study on modulation recognition based on higher-order cumulants[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2018, 33(3): 64-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2018.03.013 [11] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [12] TOKOZUME Y, HARADA T. Learning environmental sounds with end-to-end convolutional neural network[C]// Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2721-2725. [13] GAN C Q, WANG L, ZHANG Z F, et al. Sparse attention based separable dilated convolutional neural network for targeted sentiment analysis[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 188: 104827. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.06.035 [14] WANG D S, ZHANG M, LI Z, et al. Modulation format recognition and OSNR estimation using CNN-based deep learning[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(19): 1667-1670. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2742553 [15] PENG S L, JIANG H Y, WANG H X, et al. Modulation classification based on signal constellation diagrams and deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(3): 718-727. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2850703 [16] DOAN V S, HUYNH-THE T, HUA C H, et al. Learning constellation map with deep CNN for accurate modulation recognition[C]// Proceeding of the IEEE Global Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-6. [17] TENG C F, LIAO C C, CHEN C H, et al. Polar feature based deep architectures for automatic modulation classification considering channel fading[C]// Proceeding of the IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 554-558. [18] TENG C F, CHOU C Y, CHEN C H, et al. Accumulated polar feature-based deep learning for efficient and lightweight automatic modulation classification with channel compensation mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 15472-15485. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3041843 [19] KARRA K, KUZDEBA S, PETERSEN J. Modulation recognition using hierarchical deep neural networks[C]// Proceeding of the IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-3. [20] O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, CLANCY T C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks[C]// Proceeding of the Engineering Applications of Neural Networks. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 213-226. [21] YASHASHWI K, SETHI A, CHAPORKAR P. A learnable distortion correction module for modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(1): 77-80. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2855749 [22] WEST N E, O’SHEA T. Deep architectures for modulation recognition[C]// Proceeding of the IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [23] WU Y L, LI X J, FANG J. A deep learning approach for modulation recognition via exploiting temporal correlations[C]// Proceeding of the IEEE 19th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-5. [24] ZHANG Z F, LUO H, WANG C, et al. Automatic modulation classification using CNN-LSTM based dual-stream structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 13521-13531. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3030018 [25] REN Y, JIANG W, LIU Y. Complex-valued parallel convolutional recurrent neural networks for automatic modulation classification [C]// Proceeding of the IEEE 25th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 804-809. [26] ZHANG F X, LUO C B, XU J L, et al. An autoencoder-based I/Q channel interaction enhancement method for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(7): 9620-9625. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3248625 [27] XU J L, LUO C B, PARR G, et al. A spatiotemporal multi-channel learning framework for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1629-1632. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2999453 [28] LECUN Y, BOSER B, DENKER J S, et al. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition[J]. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(4): 541-551. doi: 10.1162/neco.1989.1.4.541 [29] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. -







 下载:
下载: