Influence analysis of flexure support characteristics on performance of inertial reference unit
-
摘要:
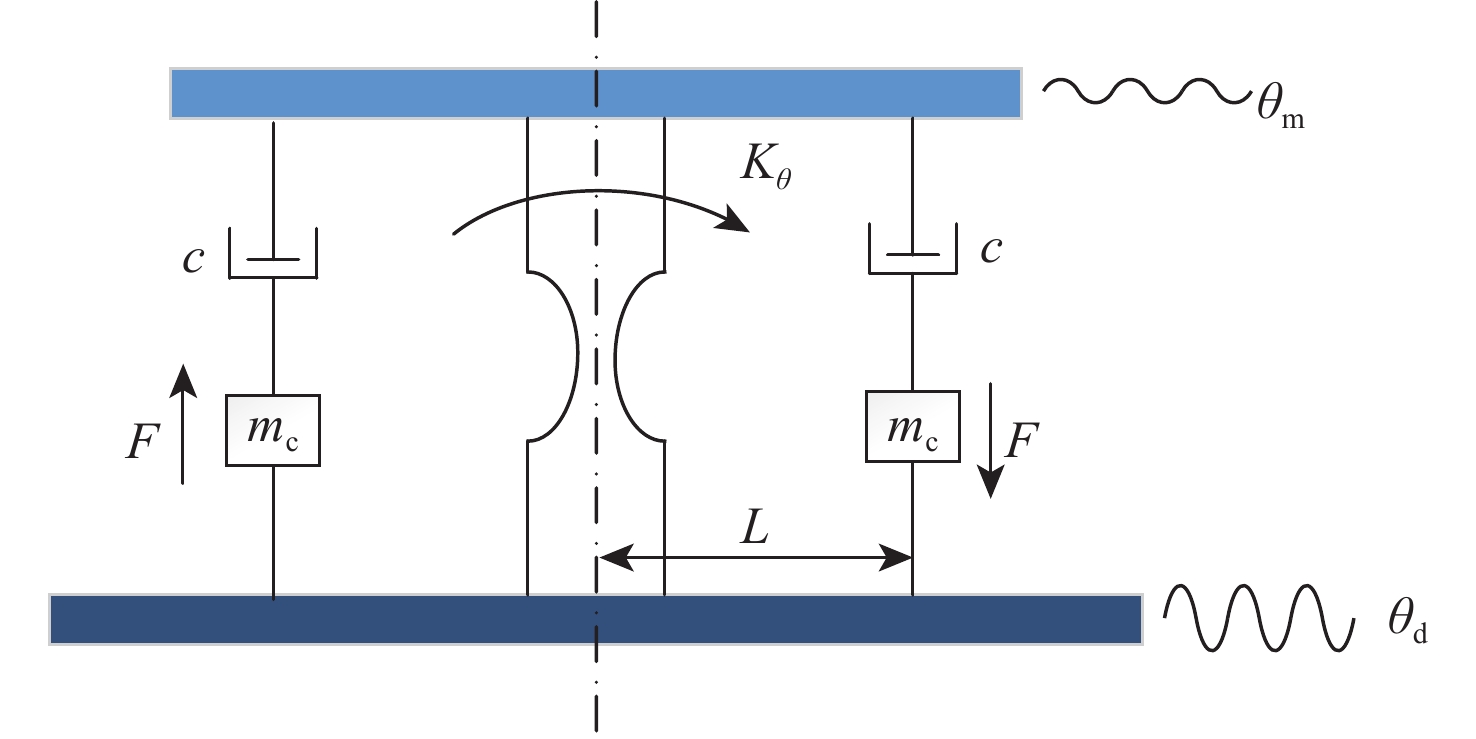
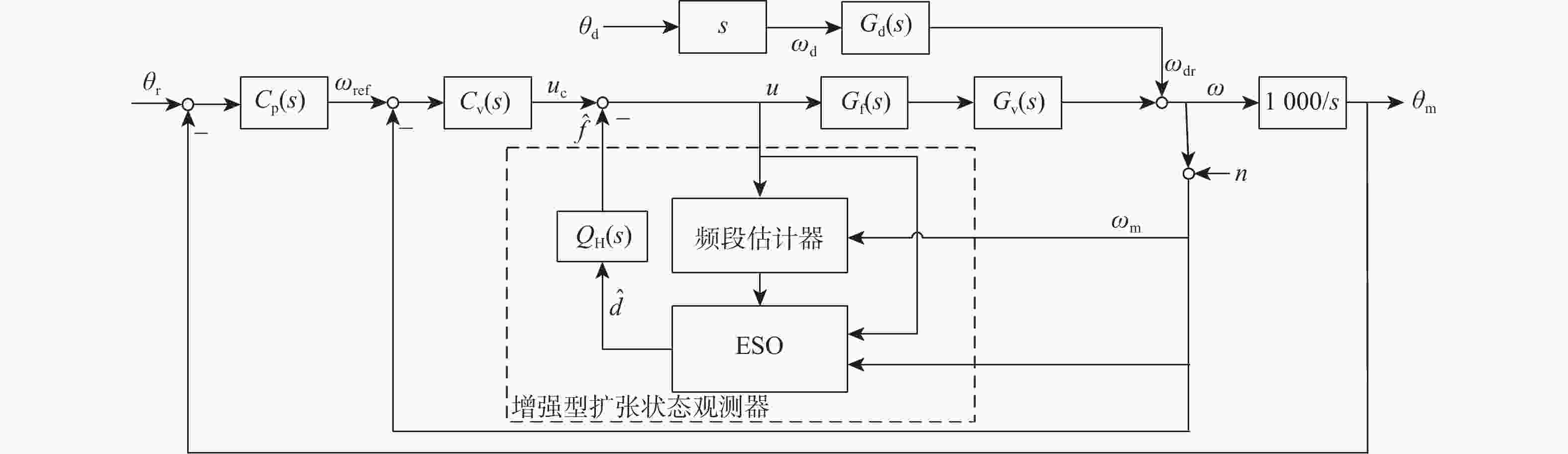
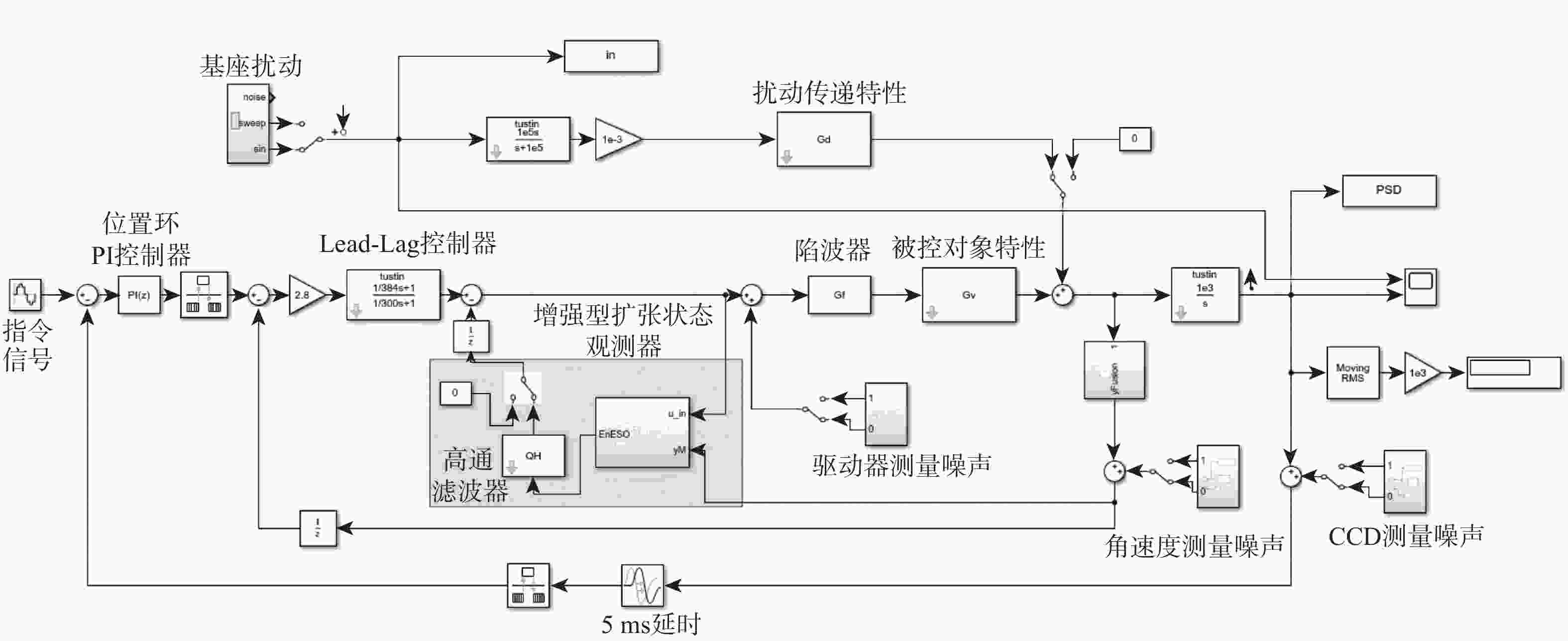
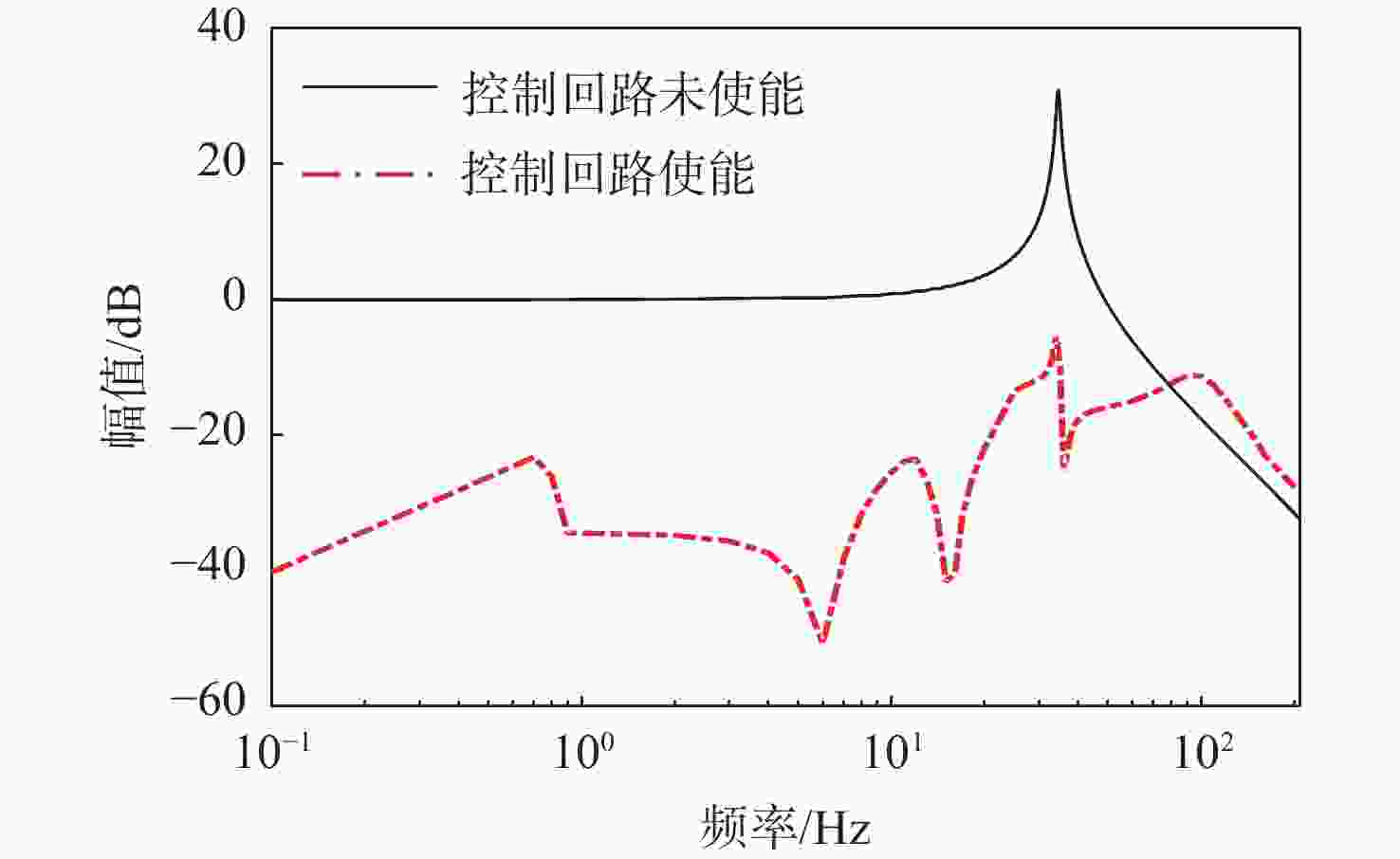
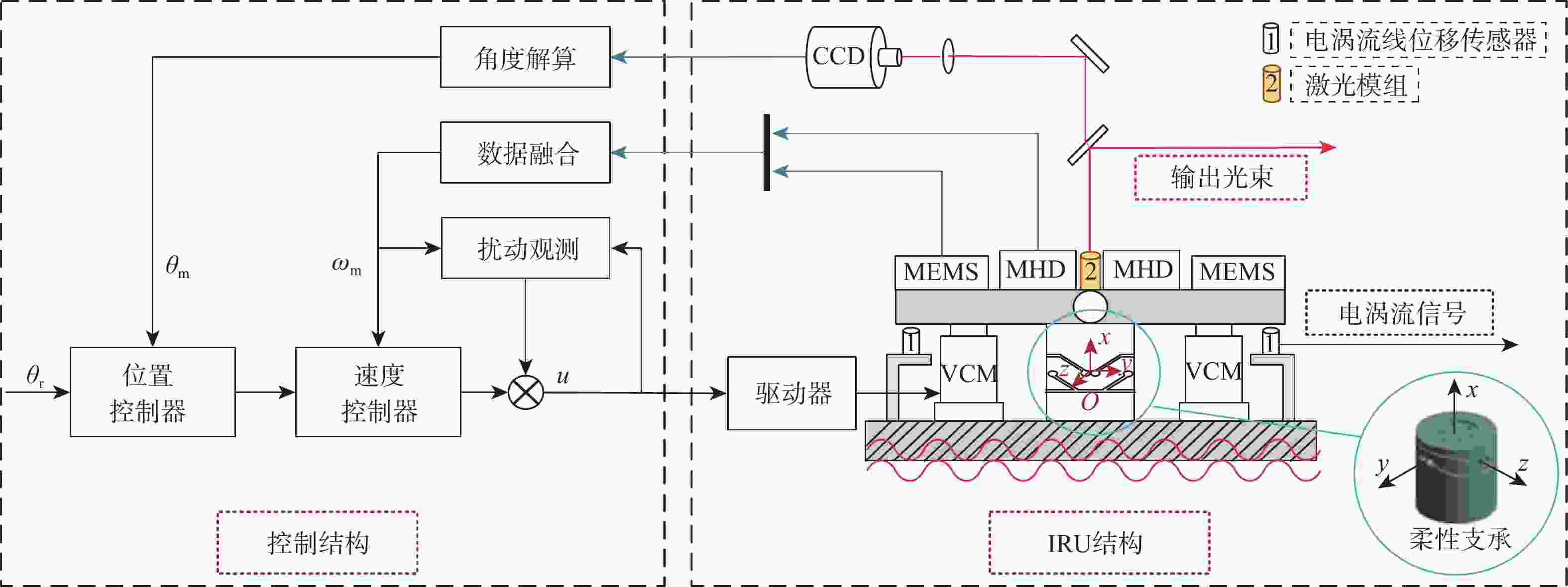
复合轴跟瞄与惯性参考单元(IRU)相结合的方式是当前抑制运动平台振动干扰、提升跟瞄精度的主要技术手段。IRU通常采用柔性支承结构,以规避框架式结构转动惯量大的缺陷,柔性支承特性是决定IRU扰动抑制带宽的关键因素。基于此,针对柔性支承特性对IRU性能的影响进行量化分析,基于质量-刚度-阻尼模型建立IRU系统的传递函数模型,并验证其准确性;利用参数分析方法研究柔性支承扰动传递特性和物理参数对IRU系统扰动抑制能力的影响;搭建IRU“速度内环-位置外环”双闭环控制系统的Simulink仿真模型,通过仿真分析给定振动环境下柔性支承转动刚度特性对IRU扰动抑制能力和稳定精度的影响。结果表明:柔性支承的扰动传递特性决定了系统对高频扰动的抑制能力,降低柔性支承的转动刚度能够有效提升IRU系统的扰动抑制能力,但会加剧传感器静态测量噪声、驱动器纹波对IRU系统稳定精度的负面影响。
Abstract:The combination of compound axis tracking and aiming with an inertial reference unit (IRU) is the main technical means to reject vibration interference of moving platform and improve tracking and aiming accuracy. IRU usually adopts flexure support structure to avoid the defect of large moment of inertia of frame structure. The characteristics of the flexure support structure are the key factors to determine the bandwidth of IRU disturbance rejection. The influence of flexure support characteristics on IRU performance was quantitatively analyzed. Firstly, based on the mass-stiffness-damping model, the transfer function model of IRU system was established, and its accuracy was verified. Then, the parametric analysis method was used to study the influence of disturbance transmission characteristics and physical parameters of flexure support on the disturbance rejection ability of IRU system. Finally, a Simulink simulation model of IRU double-loop (velocity inner loop-position outer loop) control system was built. The influences of flexure support stiffness characteristics on IRU disturbance rejection ability and stabilization precision under a given vibration environment were simulated and analyzed. The results show that the disturbance transmission characteristics of the flexure support determine the ability of the system to reject high-frequency disturbance. Reducing the rotational stiffness of the flexure support can effectively improve the disturbance rejection ability of the IRU system but aggravate the negative impact of sensor noise and driver ripple on the stabilization precision of the IRU system.
-
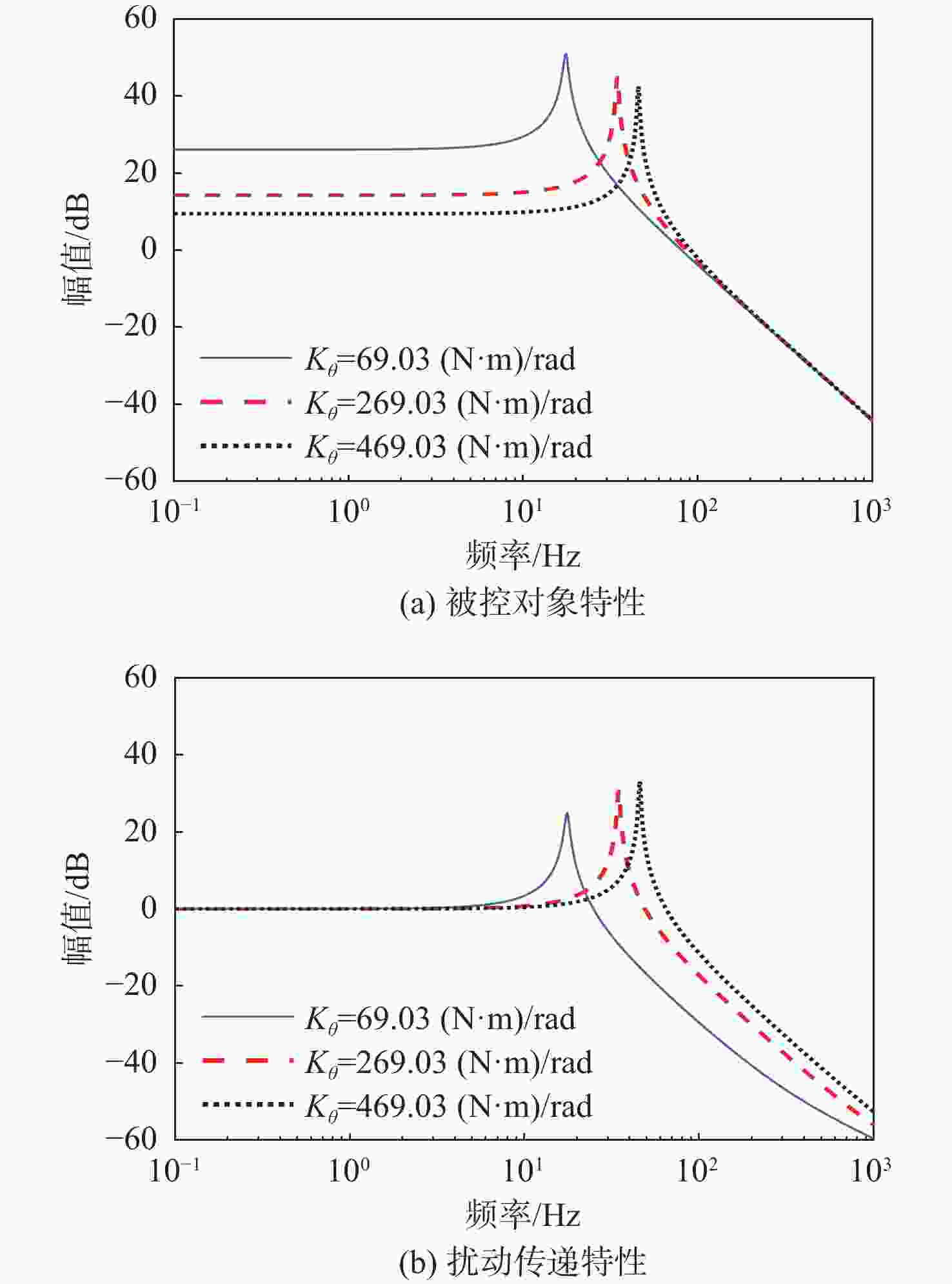
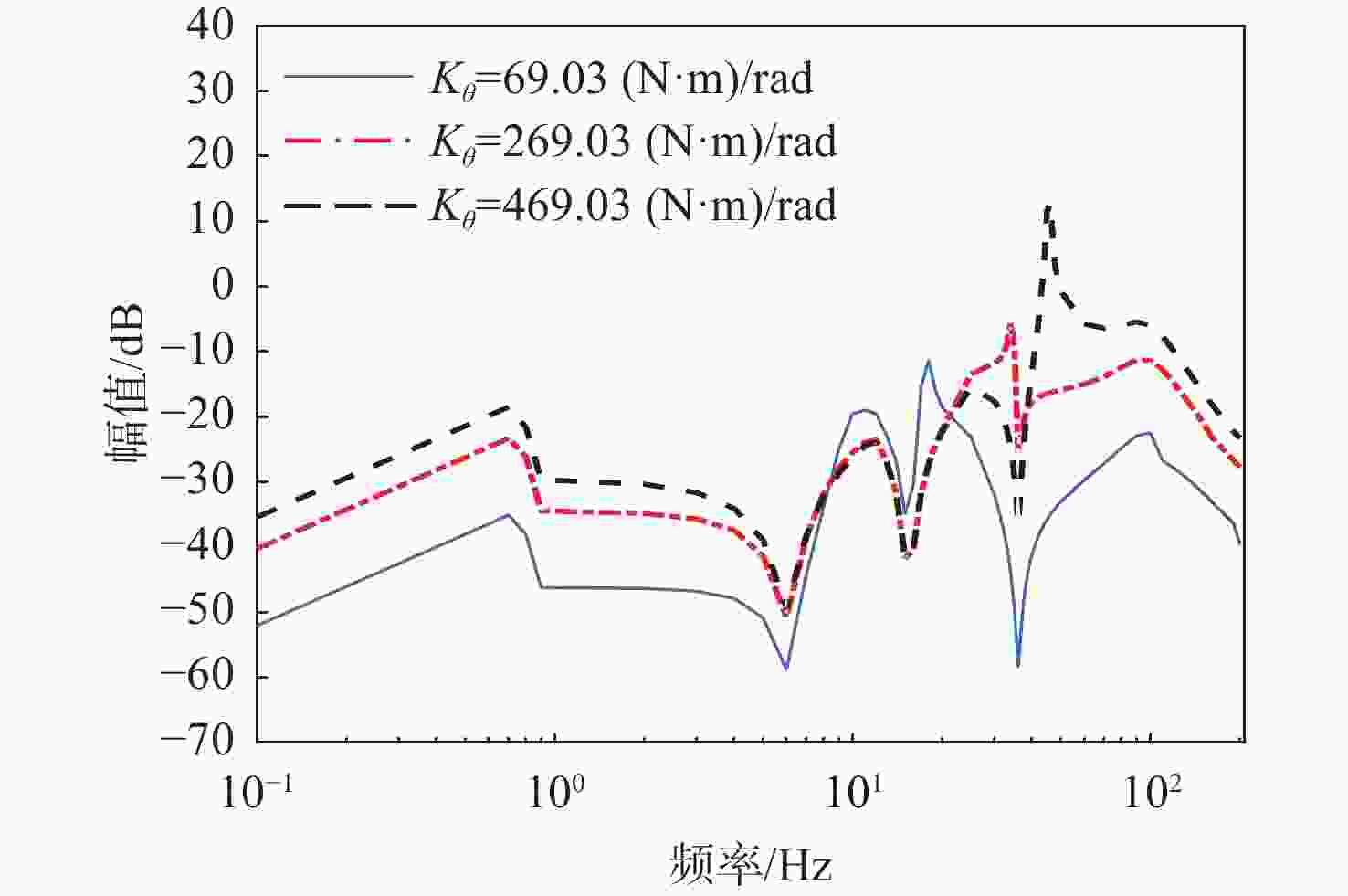
表 1 不同转动刚度时IRU系统扰动抑制能力的影响
Table 1. Influence of different rotational stiffness on disturbance rejection ability of IRU system
转动刚度/
(N·m·rad−1)谐振频率/Hz 扰动频率/Hz 扰动抑制比/dB 69.03 17.47 1 −46.25 17.47 −10.18 100 −22.45 269.03 34.52 1 −34.5 34.52 −4.49 100 −11.34 469.03 45.78 1 −29.76 45.78 14.314 100 −5.93 表 2 不同转动刚度下传感器静态测量噪声对稳定精度的影响
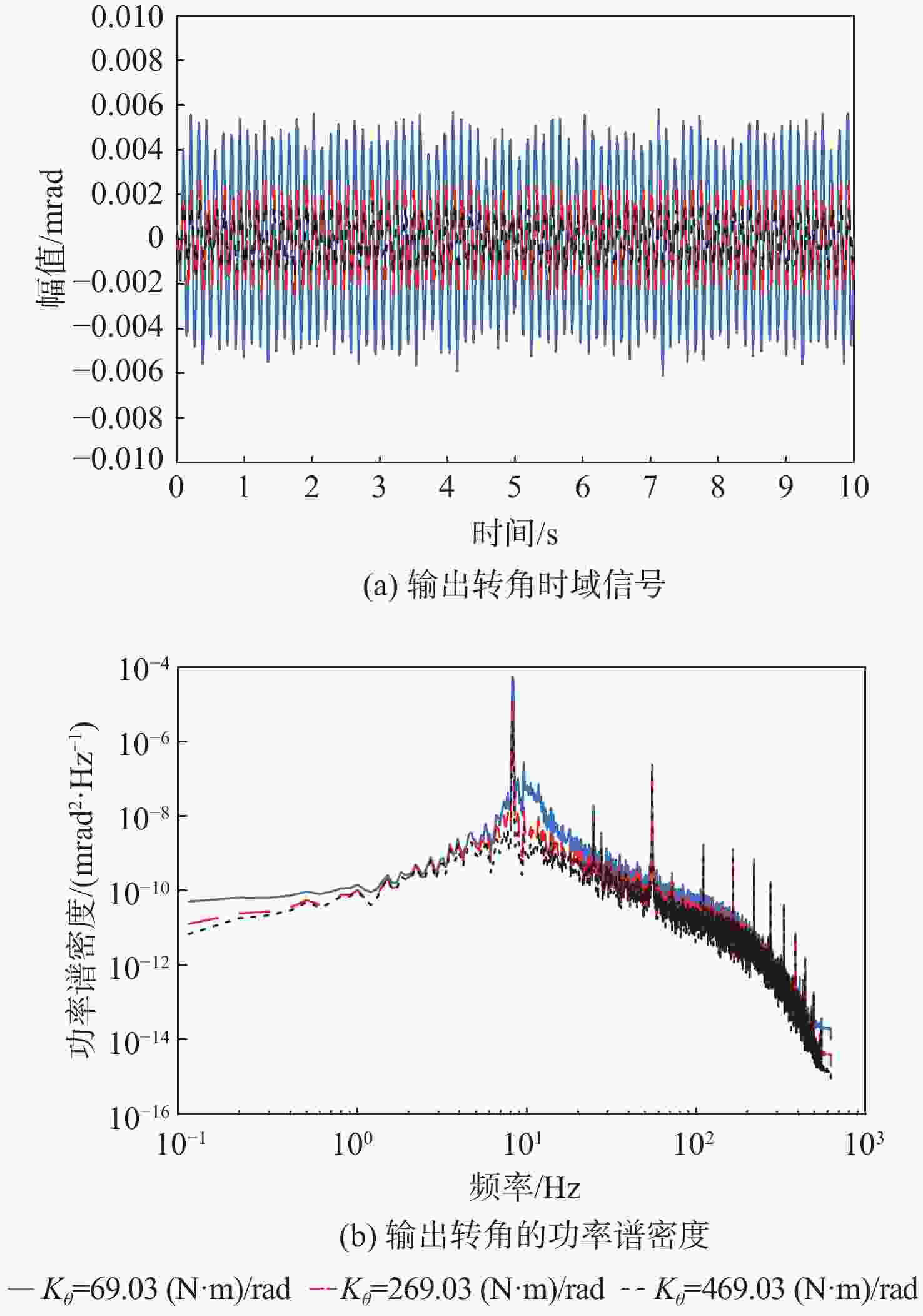
Table 2. Influence of sensor static measurement noise on stabilization precision under different rotational stiffness
转动刚度/( N·m·rad−1) 输出转角均方根/μrad 等效角位移/μrad 69.03 15.975 15.975 269.03 7.442 7.4371 469.03 5.5367 5.5306 表 3 不同转动刚度下驱动器纹波对稳定精度的影响
Table 3. Influence of driver ripple on stabilization precision under different rotational stiffness
转动刚度/( N·m·rad−1) 输出转角均方根/μrad 等效角位移/μrad 69.03 3.2992 3.2993 269.03 1.4495 1.4495 469.03 0.8466 0.8467 -
[1] 马佳光. 捕获跟踪与瞄准系统的基本技术问题[J]. 光学工程, 1989, 16(3): 1-42.MA J G. The basic technologies of the acquisition, tracking and pointing systems[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 1989, 16(3): 1-42(in Chinese). [2] LI Q, LIU L, YANG H J. High accuracy and multi-target acquisition, pointing and tracking under satellite micro-vibrations[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2020, 32(4): 715-727. doi: 10.1007/s12217-020-09804-0 [3] 任彦, 刘正华, 周锐. 滑模干扰观测器在低速光电跟踪系统中的应用[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2013, 39(6): 835-840.REN Y, LIU Z H, ZHOU R. Application of low speed opto-electronic tracking systems based on sliding mode distutbance observer[J]. [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(6): 835-840(in Chinese). [4] 王伟, 刘云清, 董岩, 等. 空间激光通信中复合跟踪技术研究[J]. 激光与红外, 2020, 50(4): 403-406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.04.003WANG W, LIU Y Q, DONG Y, et al. Research on composite tracking technology in space laser communication[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2020, 50(4): 403-406(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.04.003 [5] 唐涛, 马佳光, 陈洪斌, 等. 光电跟踪系统中精密控制技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(10): 200315.TANG T, MA J G, CHEN H B, et al. A review on precision control methodologies for optical-electric tracking control system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2020, 47(10): 200315(in Chinese). [6] BURNSIDE J W, CONRAD S D, PILLSBURY A D, et al. Design of an inertially stabilized telescope for the LLCD[C]//Proceedings of the Free-Space Laser Communication Technologies XXIII. Bellingham: SPIE, 2011. [7] BURNSIDE J W, MURPHY D V, KNIGHT F K, et al. A hybrid stabilization approach for deep-space optical communications terminals[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2007, 95(10): 2070-2081. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2007.905101 [8] LUNIEWICZ M F, GILMORE J P, CHIEN T T, et al. Comparison of wideband inertial line-of-sight stabilization reference mechanizations[C]//Proceedings of the Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing VI. Bellingham: SPIE, 1992: 378-398. [9] XIA X Q, ZHANG B, LI X T. High precision low-speed control for permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(5): 1526. doi: 10.3390/s20051526 [10] 谢航. 动基座光电稳定平台视轴稳定技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2022.XIE H. Research on line-of-sight stabilization technology of photoelectric stabilization platform with moving base[D]. Changchun: University Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2022(in Chinese). [11] LUNIEWICZ M F, MURPHY J, O’NEIL E, et al. Testing the inertial pseudo-star reference unit[C]//Proceedings of the Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing VIII. Bellingham: SPIE, 1994: 638-649. [12] ECKELKAMP-BAKER D, SEBESTA H R, BURKHARD K. Magnetohydrodynamic inertial reference system[C]//Proceedings of the Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing XIV. Bellingham: SPIE, 2000: 99-110. [13] HARUNA M, KODEKI K, SHIMIZU S, et al. Evaluation of developing inertial stabilization unit[C]//Proceedings of the Free-Space Laser Communication and Atmospheric Propagation XXVII. Bellingham: SPIE, 2015. [14] BLUEHALO. Optical inertial reference units (OIRU) [EB/OL]. (2022-02-27)[2023-07-01]. http://bluehalo.com/product/optical-inertial-reference-unit-oiru. [15] DENG J Q, XUE W C, ZHOU X, et al. On dual compensation to disturbances and uncertainties for inertially stabilized platforms[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2022, 20(5): 1521-1534. doi: 10.1007/s12555-021-0022-3 [16] TUO W X, LI X F, JI Y, et al. Mechanical design and determination of bandwidth for a two-axis inertial reference unit[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 172: 108962. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2022.108962 [17] ZHOU Z, LI X F, TUO W X. Design of disturbance suppression controller for optical inertial reference unit[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology: Optoelectronic Measurement Technology and Systems. Bellingham: SPIE, 2022. [18] 胡浩军. 运动平台捕获、跟踪与瞄准系统视轴稳定技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2005.HU H J. Research on line-of-sight stabilization technology of acquisition, tracking and aiming system of moving platform[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2005(in Chinese). [19] JACKA N, WALTER R, LAUGHLIN D, et al. Design of stabilized platforms for deep space optical communications (DSOC) [C]//Proceedings of the Free-Space Laser Communication and Atmospheric Propagation XXIX. Bellingham: SPIE, 2017. [20] XIAO R J, XU M L, SHAO S B, et al. Design and wide-bandwidth control of large aperture fast steering mirror with integrated-sensing unit[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 126: 211-226. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.02.028 [21] SUN J J, DING Y L, ZHANG H W, et al. Conceptual design and image motion compensation rate analysis of two-axis fast steering mirror for dynamic scan and stare imaging system[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(19): 6441. doi: 10.3390/s21196441 [22] ZHANG W F, YUAN J, YAN C X, et al. Multi-objective optimization design of natural frequency of two-degree-of-freedom fast steering mirror system[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 33689-33703. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3061473 [23] 夏笠城, 王姝旸, 张晶, 等. 基于双频扩张状态观测器的无人机抗扰控制[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2023, 49(5): 1201-1208.XIA L C, WANG S Y, ZHANG J, et al. Bi-bandwidth extended state observer based disturbance rejection control method and its application on UAV[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(5): 1201-1208(in Chinese). [24] LI J, ZHANG L Y, LUO L, et al. Extended state observer based current-constrained controller for a PMSM system in presence of disturbances: design, analysis and experiments[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2023, 132: 105412. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2022.105412 -






 下载:
下载: