-
摘要:
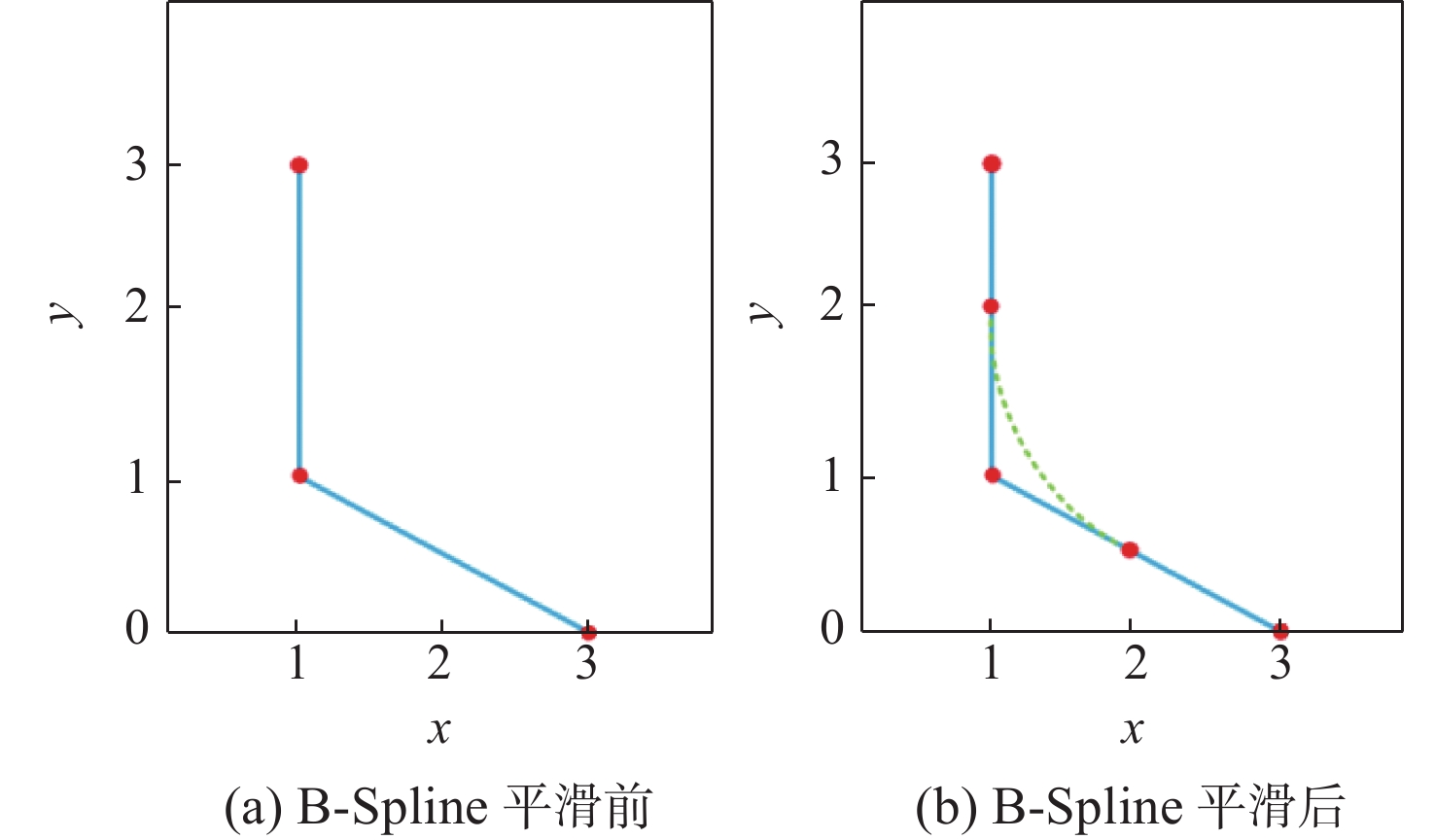
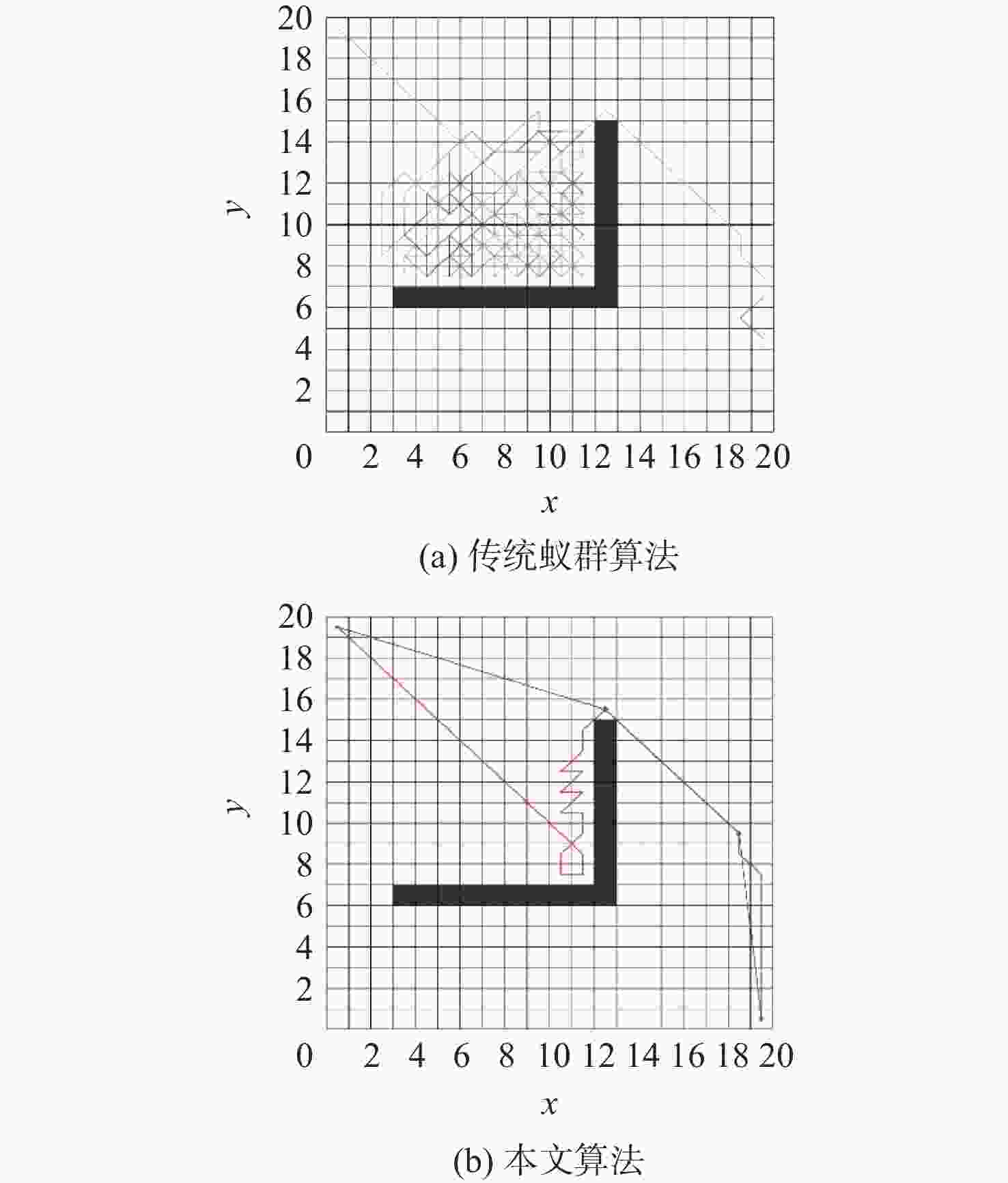
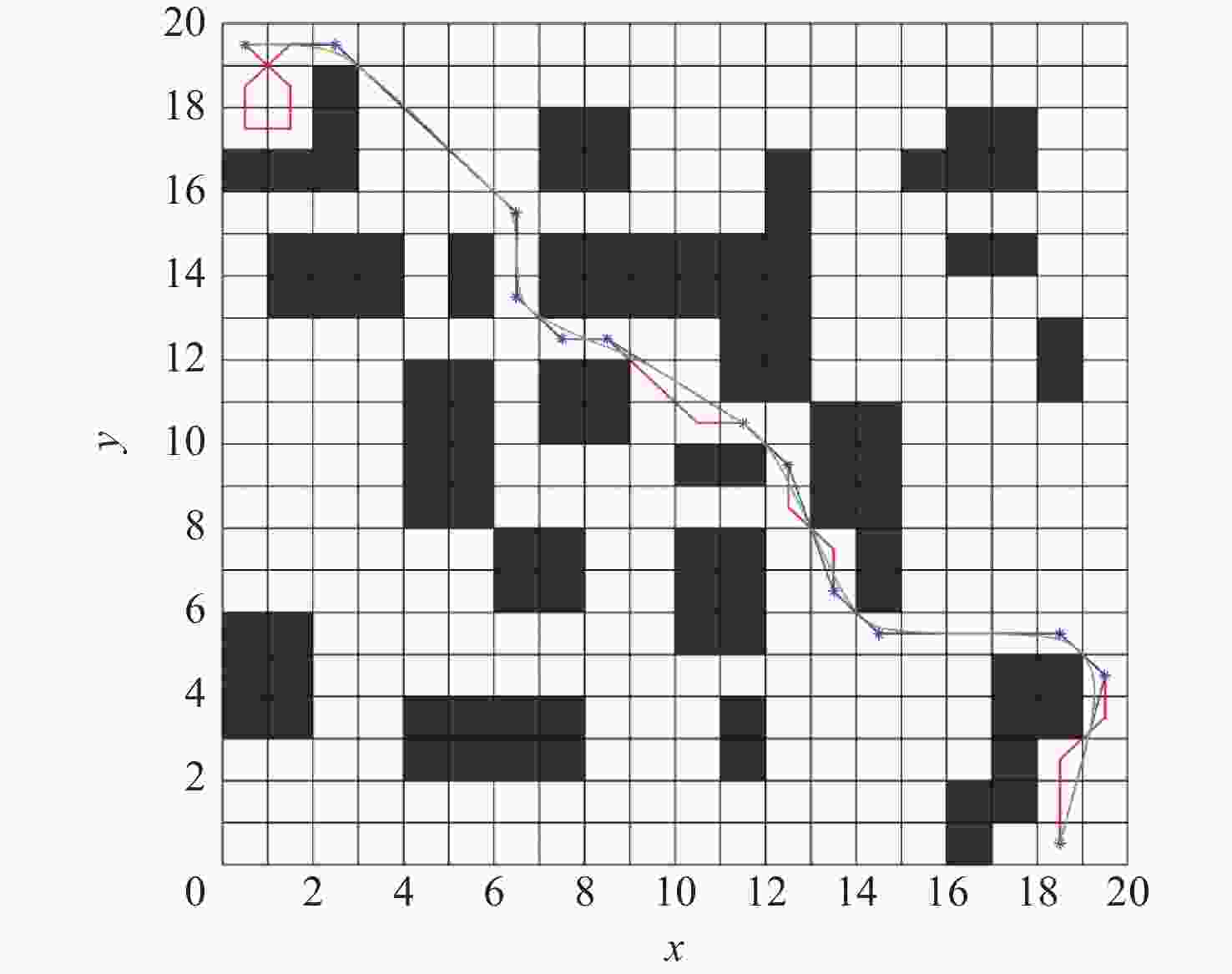
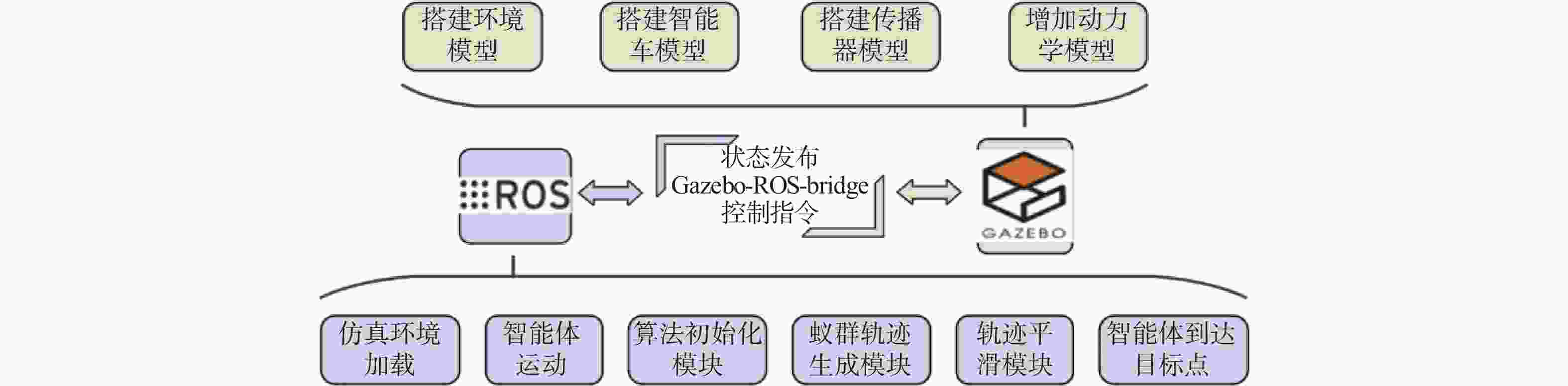
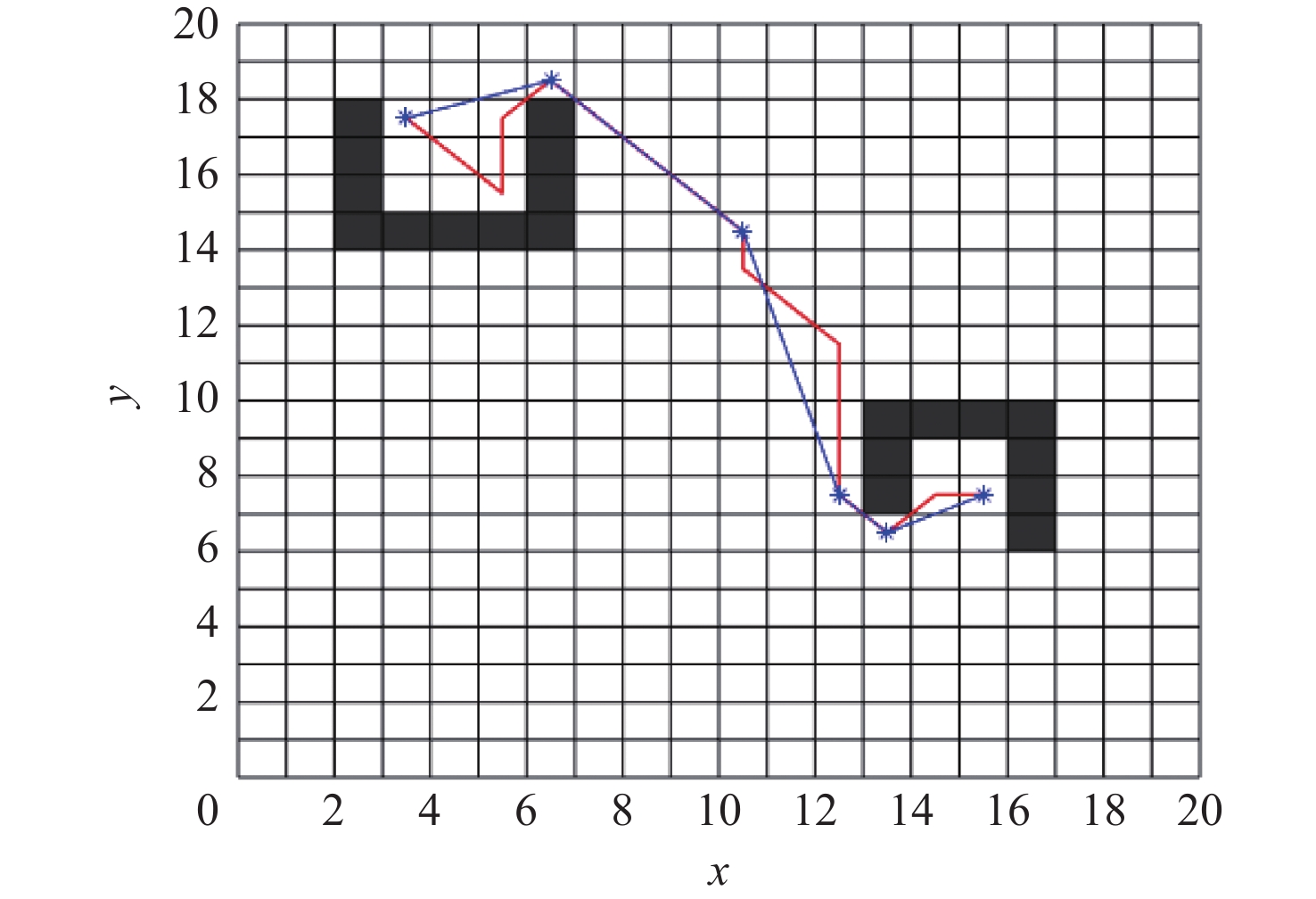
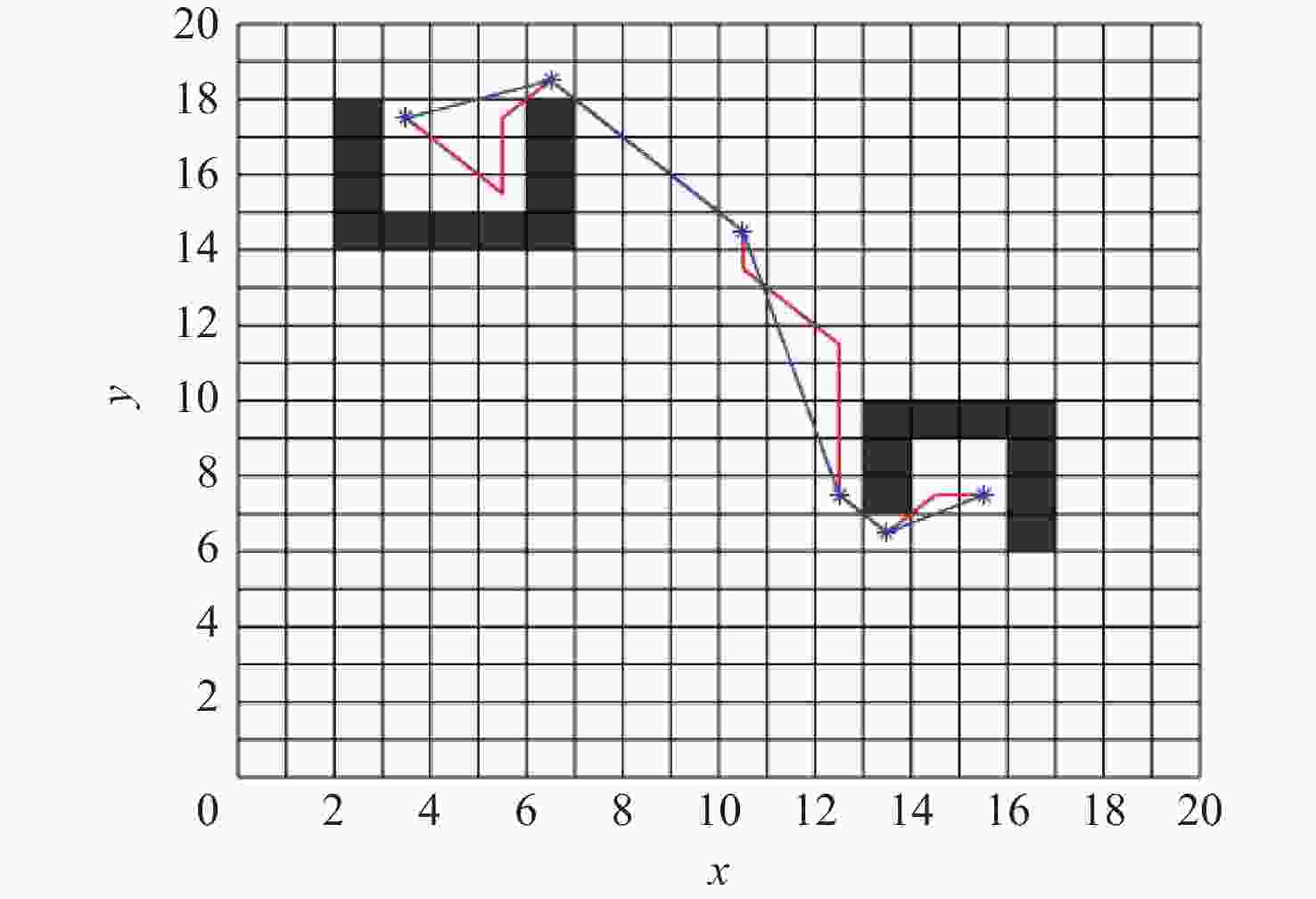
在智能体路径规划中,蚁群算法是较为流行的路径求解策略,且得到了广泛的应用。然而,传统蚁群算法存在局部最优和多余拐点问题。基于此,提出自适应多态蚁群优化算法,通过多群体划分和协作机制,极大的提高了搜索和收敛速度,有助于增强全局搜索能力,避免陷入局部最优解。改进的信息素更新策略和路径选择记录表构造进一步提高路径规划的准确性。通过3次B样条平滑曲线对路径进行处理,有效减少拐点,实现路径的平滑化。经过MATLAB和机器人操作系统(ROS)-Gazebo仿真验证,结果表明:所提算法在复杂环境下具有良好的可行性。综上所述,所提算法为智能体全局搜索带来了显著的优化和改进。
Abstract:In the realm of intelligent agent path planning, the ant colony algorithm stands as a prominent path-solving strategy that has garnered extensive adoption. However, conventional ant colony algorithms exhibit issues pertaining to local optima and excessive inflection points. The adaptive polymorphic ant colony optimization algorithm, through the mechanism of multi-colony partitioning and collaboration, remarkably enhances the search and convergence velocities, thereby bolstering global search capabilities and circumventing entrapment within local optima. To significantly increase the accuracy of path planning, this research proposes an enhanced pheromone updating technique and path selection record table building. Lastly, the adoption of trice B-Spline smoothing curves facilitates an effective reduction in inflection points, achieving path smoothness. Substantiated by MATLAB and robot operating system (ROS)-Gazebo simulations, the results demonstrate the algorithm's sound feasibility in complex environments. In conclusion, the global search of the intelligent agent is greatly optimized and enhanced by the suggested enhanced adaptive polymorphic ant colony method.
-
Key words:
- path planning /
- adaptive polymorphic ant colony algorithm /
- B-Spline /
- robot operating system /
- Gazebo
-
表 1 实验参数设置表
Table 1. Experimental Parameter Setting Table
参数 数值 起点 381 终点 18 蚂蚁个数$m$ 50 最大迭代次数$N$ 100 信息素因子$\alpha $ 1 启发函数因子$\beta $ 5 信息素挥发因子$\rho $ 0.6 信息素增加强度系数$Q$ 1 折扣系数$ (1 - \lambda ) $ 0.7 -
[1] 王梓强, 胡晓光, 李晓筱, 等. 移动机器人全局路径规划算法综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(10): 19-29.WANG Z Q, HU X G, LI X X, et al. Overview of global path planning algorithms for mobile robots[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(10): 19-29(in Chinese). [2] ZHANG L, ZHANG Y J, LI Y F. Mobile robot path planning based on improved localized particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(5): 6962-6972. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3039275 [3] 霍凤财, 迟金, 黄梓健, 等. 移动机器人路径规划算法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(信息科学版), 2018, 36(6): 639-647.HUO F C, CHI J, HUANG Z J, et al. Review of path planning for mobile robots[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Information Science Edition), 2018, 36(6): 639-647(in Chinese). [4] SANG H Q, YOU Y S, SUN X J, et al. The hybrid path planning algorithm based on improved A* and artificial potential field for unmanned surface vehicle formations[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 223: 108709. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108709 [5] ZANG X N, JIANG L, DING B, et al. A hybrid ant colony system algorithm for solving the ring star problem[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51(6): 3789-3800. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-02072-w [6] YI G H, FENG Z L, MEI T C, et al. Multi-AGVs path planning based on improved ant colony algorithm[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2019, 75(9): 5898-5913. doi: 10.1007/s11227-019-02884-9 [7] 张松灿, 普杰信, 司彦娜, 等. 蚁群算法在移动机器人路径规划中的应用综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(8): 10-19.ZHANG S C, PU J X, SI Y N, et al. Survey on application of ant colony algorithm in path planning of mobile robot[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(8): 10-19(in Chinese). [8] SONG J, HAO C, SU J C. Path planning for unmanned surface vehicle based on predictive artificial potential field[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2020, 17(2): 172988142091846. [9] ZHOU Y L, HUANG N N. Airport AGV path optimization model based on ant colony algorithm to optimize Dijkstra algorithm in urban systems[J]. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 2022, 35: 100716. doi: 10.1016/j.suscom.2022.100716 [10] LIU G Q, LI T J, PENG Y Q, et al. The ant algorithm for solving robot path planning problem[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information Technology and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 25-27. [11] ZHANG Y, CAO Y, HAN Z. Path planning of vehicle based on improved ant colony algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 797-801. [12] YUAN Z R, YU H Y, HUANG M H. Improved ant colony optimization algorithm for intelligent vehicle path planning[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Informatics-Computing Technology, Intelligent Technology, Industrial Information Integration. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-4. [13] BRAND M, MASUDA M, WEHNER N, et al. Ant colony optimization algorithm for robot path planning[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Design and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: V3-436-V3-440. [14] AKKA K, KHABER F. Mobile robot path planning using an improved ant colony optimization[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2018, 15(3): 1729881418774673. [15] WU L, HUANG X D, CUI J G, et al. Modified adaptive ant colony optimization algorithm and its application for solving path planning of mobile robot[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 215: 119410. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119410 [16] 甄然, 张春悦, 矫阳, 等. 基于自适应多态融合蚁群算法的无人机航迹规划[J]. 河北科技大学学报, 2019, 40(6): 526-532.ZHEN R, ZHANG C Y, JIAO Y, et al. Research on UAV route planning based on adaptive polymorphic ant colony algorithm[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2019, 40(6): 526-532(in Chinese). [17] MIAO C W, CHEN G Z, YAN C L, et al. Path planning optimization of indoor mobile robot based on adaptive ant colony algorithm[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 156: 107230. [18] JIAO Z Q, MA K, RONG Y L, et al. A path planning method using adaptive polymorphic ant colony algorithm for smart wheelchairs[J]. Journal of Computational Science, 2018, 25: 50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2018.02.004 [19] LAN X, LV X F, LIU W, et al. Research on robot global path planning based on improved A-star ant colony algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 613-617. -






 下载:
下载: