-
摘要:
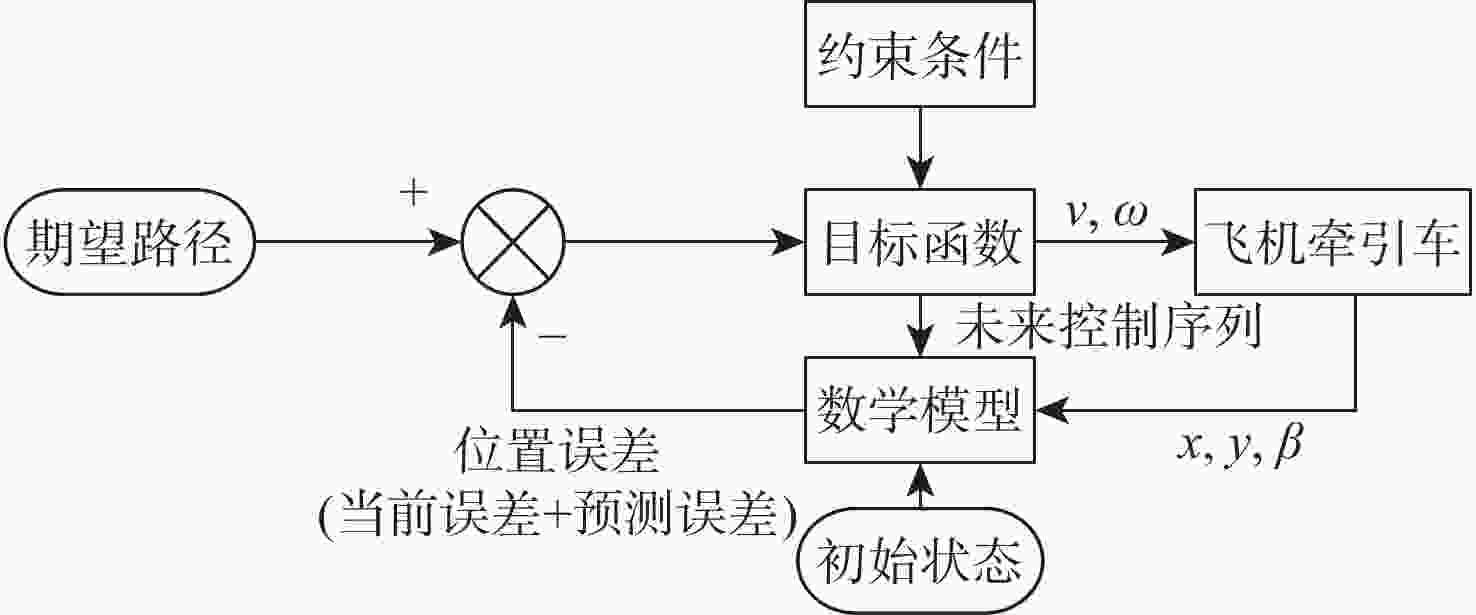
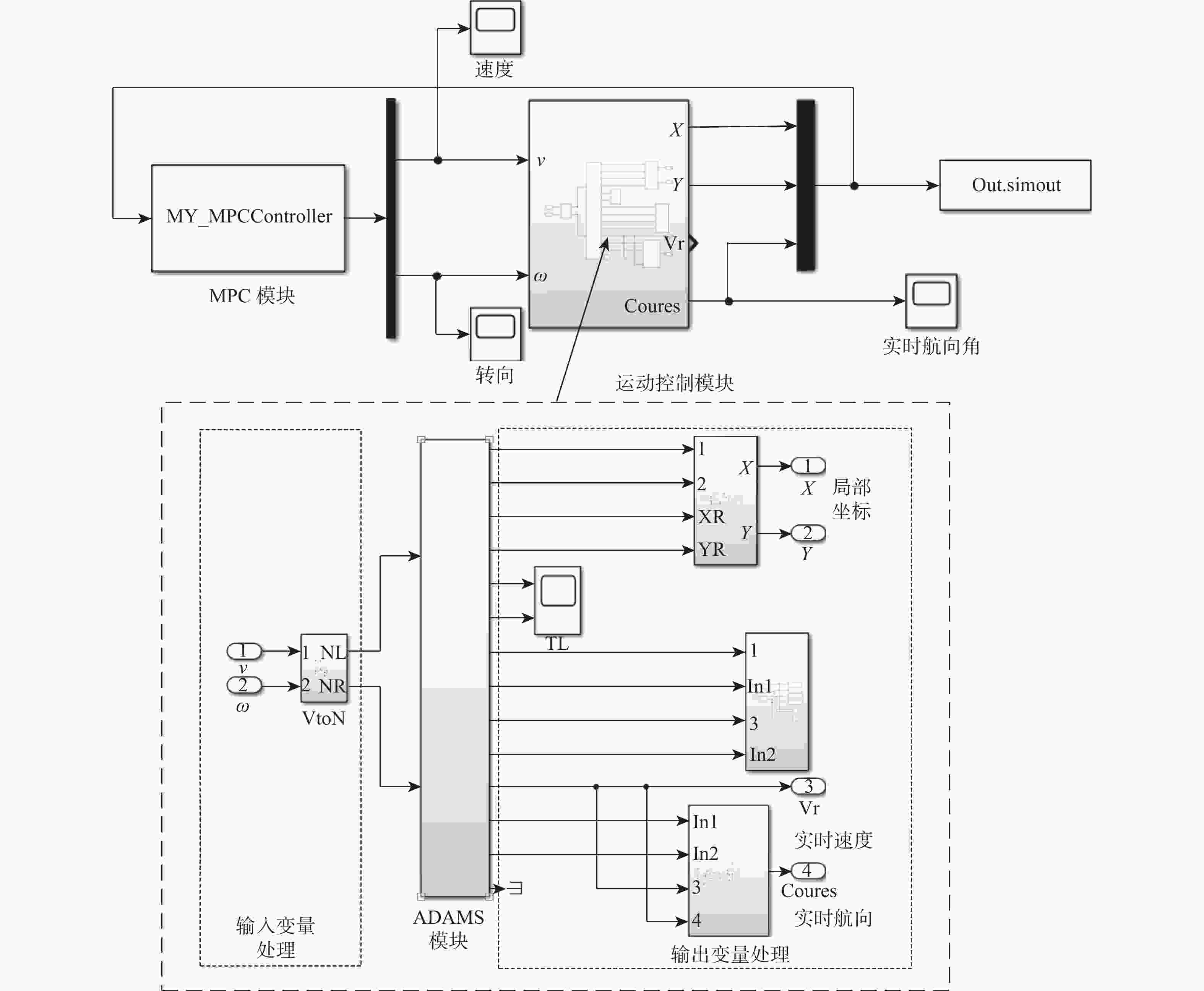
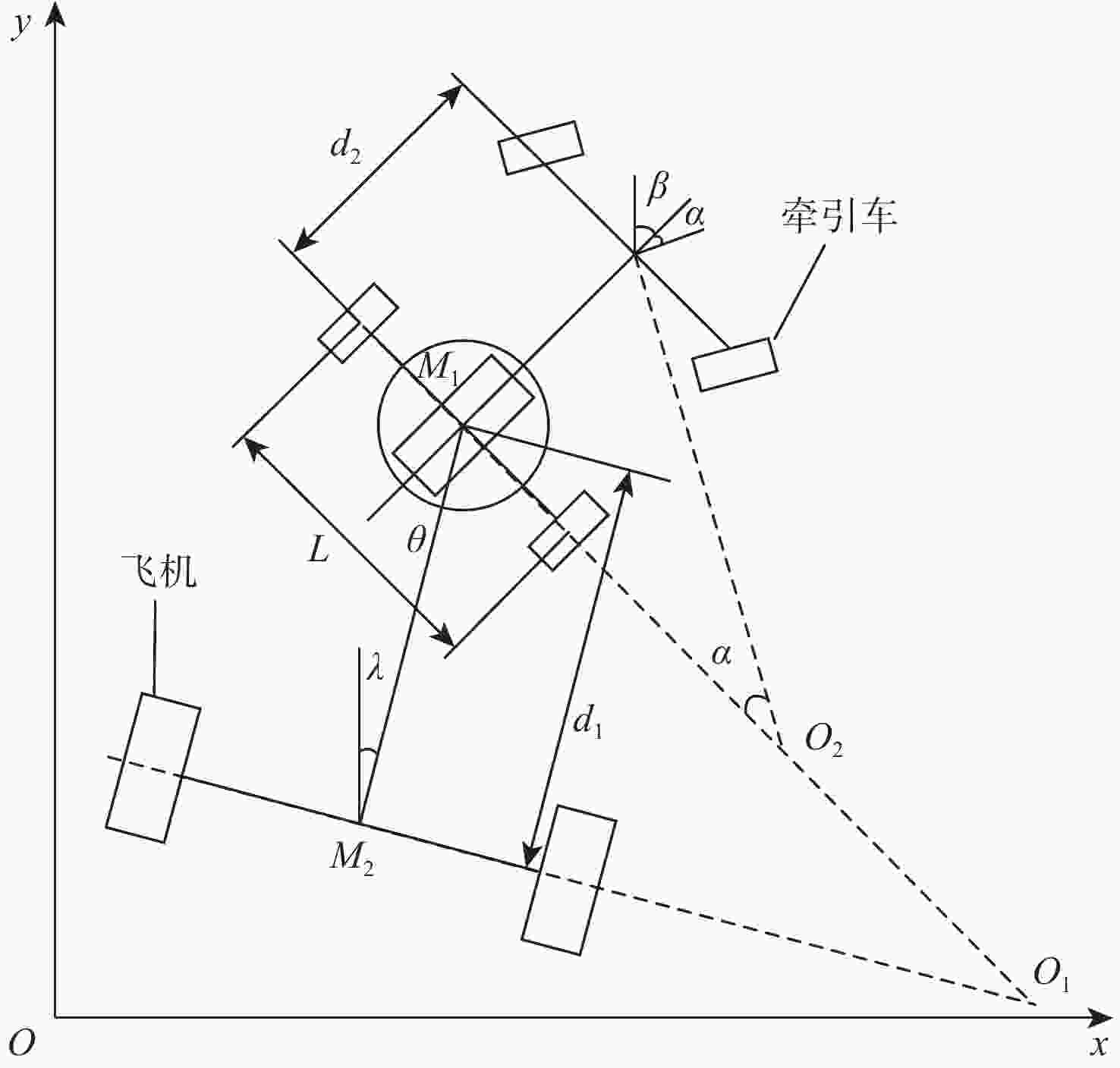
为能满足物流机场短时间、高频次的快捷飞机牵引需求,提出了基于无人驾驶技术的快速牵引方法。采用“理论建模-算法设计-算例测试和仿真优化-样机实验”的技术路线和方法,以10 t飞机牵引车为对象,构建牵引车的运动学模型,确定牵引车的约束条件和控制量,通过增加防碰撞处理、最小转弯半径和路径平滑的方式改进A*算法,生成牵引车运动轨迹;设计模型预测控制(MPC)的轨迹跟踪控制器,构建MATLAB/Simulink和ADAMS联合仿真模型,通过轨迹跟踪仿真实验优化MPC的控制参数,并在改造的电传动飞机牵引车样机上开展轨迹跟踪实验。结果表明:改进的A*算法满足飞机牵引车工作路径规划和最小转弯半径要求,联合仿真方法优化了MPC控制器,在样机上实现了较好的跟踪精度,弯道和直线跟踪误差的标准差分别为0.362 m和0.128 m,实现了飞机牵引车的无人驾驶功能,为智慧物流机场的无人牵引飞机奠定技术基础。
Abstract:To meet the short and high frequency demands of quick aircraft towing at logistics airports, a rapid towing method based on unmanned driving technology is proposed. Using the technical route and method of “theoretical modeling-algorithm design-case test and simulation optimization-prototype experiment”, a kinematic model of the towing vehicle is constructed for a 10-ton aircraft towing vehicle, the vehicle’s constraint conditions and control quantities are determined, and the A* algorithm is improved by adding collision avoidance processing, minimum turning radius, and path smoothing to generate the motion trajectory of the towing vehicle. A trajectory tracking controller based on model predictive control (MPC) is designed, and a joint simulation model of MATLAB/Simulink and ADAMS is constructed. The control parameters of MPC are optimized through trajectory tracking simulation experiments, and trajectory tracking experiments are carried out on the modified electric aircraft towing vehicle prototype. The results show that the improved A* algorithm meets the requirements of aircraft towing vehicle work path planning and minimum turning radius, the joint simulation method optimizes the MPC controller, achieves good tracking accuracy on the prototype, with standard deviation of tracking errors for curve paths and straight paths being 0.362 m and 0.128 m respectively, realizes the unmanned driving function of the aircraft towing vehicle, and lays the technical foundation for unmanned aircraft towing at smart logistics airports.
-
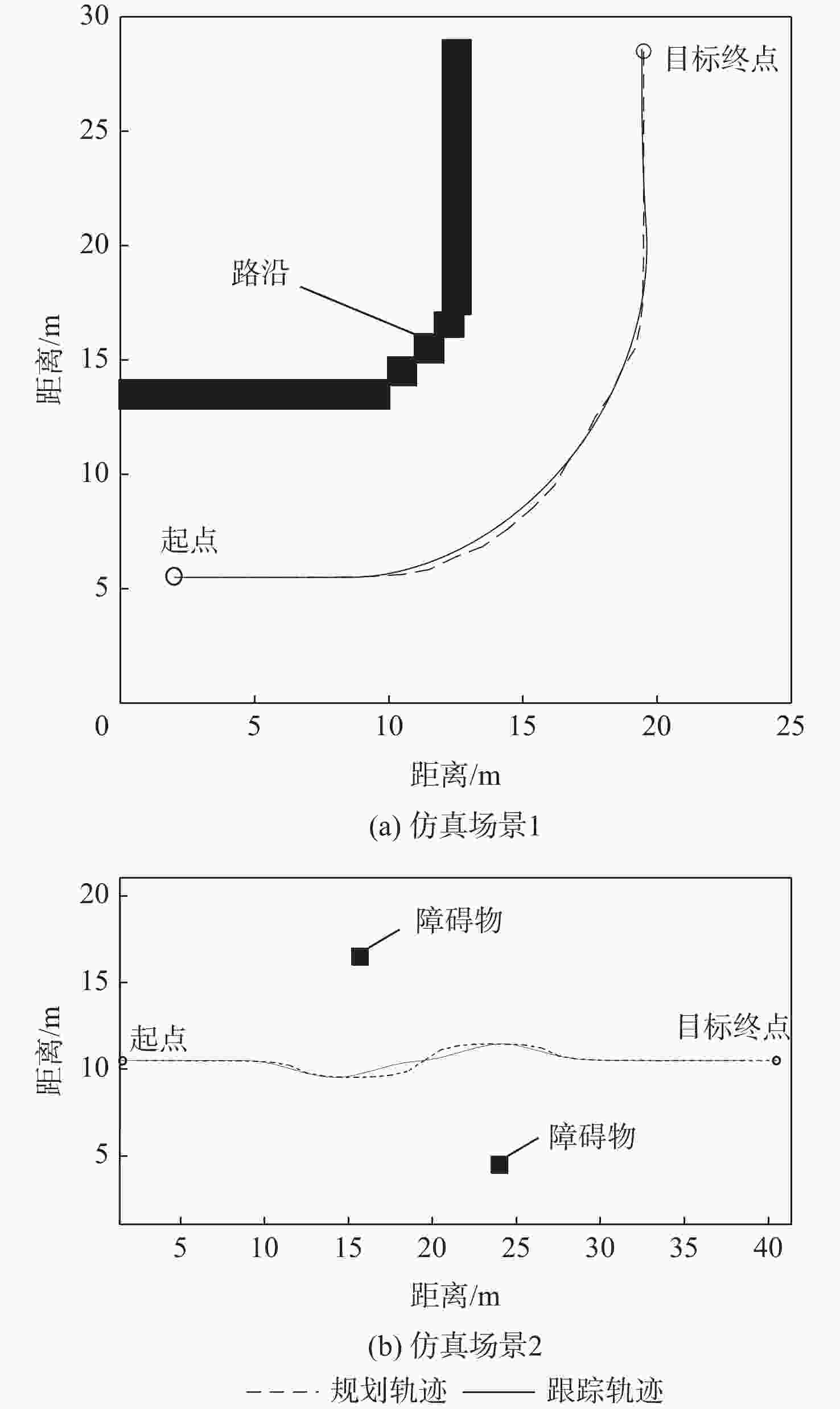
表 1 路径平滑仿真结果
Table 1. Path smoothing simulation results
场景 方法 方差/m2 标准差/m 平滑性 仿真场景1 最小二乘法 1.851 1.360 一般 梯度下降法 0.015 0.126 好 仿真场景2 最小二乘法 0.026 0.161 一般 梯度下降法 0.012 0.111 好 表 2 不同控制参数下的MPC控制效果对比
Table 2. Compared results at different MPC control parameters
参数组合 $ {N_{\rm c}} $ $ {N_{\rm p}} $ 标准差/m 仿真时间/s 1 30 60 0.267 6.95 2 30 50 0.247 6.39 3 30 40 0.231 6.23 4 30 30 0.218 5.92 5 20 20 0.204 5.07 6 10 10 0.182 3.73 7 5 10 0.183 2.83 8 5 5 0.157 2.78 表 3 联合仿真轨迹结果
Table 3. Joint simulation trajectory results
场景 方差/m2 标准差/m 仿真场景1 0.021 0.146 仿真场景2 0.016 0.128 表 4 轨迹跟踪误差分析
Table 4. Track tracking error analysis
场景 方差/m2 标准差/m 实验场景1 0.131 0.362 实验场景2 0.016 0.128 -
[1] 李永丹, 马天力, 陈超波, 等. 无人驾驶车辆路径规划算法综述[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2019, 38(6): 72-79.LI Y D, MA T L, CHEN C B, et al. Review of path planning algorithm for unmanned vehicles[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2019, 38(6): 72-79(in Chinese). [2] 刘军, 冯硕, 任建华. 移动机器人路径动态规划有向D*算法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2020, 54(2): 291-300.LIU J, FENG S, REN J H. Directed D* algorithm for dynamic path planning of mobile robots[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2020, 54(2): 291-300(in Chinese). [3] 陈秋莲, 蒋环宇, 郑以君. 机器人路径规划的快速扩展随机树算法综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(16): 10-17. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1905-0061CHEN Q L, JIANG H Y, ZHENG Y J. Summary of rapidly-exploring random tree algorithm in robot path planning[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(16): 10-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1905-0061 [4] NOREEN I, KHAN A, HABIB Z. Optimal path planning using RRT* based approaches: a survey and future directions[J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2016, 7(11): 97-107. [5] KARAMAN S, WALTER M R, PEREZ A, et al. Anytime motion planning using the RRT[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1478-1483. [6] 孙家玮, 余明晖, 杨大鹏, 等. 基于CL-RRT与MPC的舰载机牵引系统路径规划[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(5): 1745-1755.SUN J W, YU M H, YANG D P, et al. Path planning of carrier based aircraft traction system based on CL-RRT and MPC[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronic Technology, 2024, 46(5): 1745-1755(in Chinese). [7] 张智, 林圣琳, 邱兵, 等. 舰载机牵引系统甲板调运避碰路径规划[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(8): 1551-1557. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.08.17ZHANG Z, LIN S L, QIU B, et al. Collision avoidance path planning of carrier aircraft traction system indispatching on deck[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(8): 1551-1557(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.08.17 [8] MENG X L, WANG N J, LIU Q H. Aircraft parking trajectory planning in semistructured environment based on kinodynamic safety RRT[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 3872248. [9] LIU J, DONG X Z, WANG J Y, et al. A novel EPT autonomous motion control framework for an off-axle hitching tractor-trailer system with drawbar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2021, 6(2): 376-385. [10] LIU J, HAN W, PENG H J, et al. Trajectory planning and tracking control for towed carrier aircraft system[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 84: 830-838. [11] 张震男. 牵引系统路径规划与路径跟踪控制策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021.ZHANG Z N. Research on path planning and path tracking control strategy of traction system[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2021(in Chinese). [12] WALLACE R, STENTZ A, THORPE C, et al. First results in robot road-following[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 1985: 1089-1095. [13] 黄海洋, 张建, 王宇, 等. 基于多点预瞄最优控制的智能车辆路径跟踪[J]. 汽车技术, 2018(10): 6-9.HUANG H Y, ZHANG J, WANG Y, et al. Path traking for intelligent vehicle based on the optimal multipoint preview control[J]. Automobile Technology, 2018(10): 6-9(in Chinese). [14] CHENG S, LI L, CHEN X, et al. Model-predictive-control-based path tracking controller of autonomous vehicle considering parametric uncertainties and velocity-varying[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(9): 8698-8707. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3009585 [15] 张攀, 柳阳, 刘新杰, 等. 改进的智能飞机牵引车路径导航纯追踪算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2019, 45(5): 267-271.ZHANG P, LIU Y, LIU X J, et al. Improved pure pursuit algorithm for intelligent aircraft tractor path navigation[J]. Computer Engineering, 2019, 45(5): 267-271(in Chinese). [16] YU M H, GONG X, FAN G W, et al. Trajectory planning and tracking for carrier aircraft-tractor system based on autonomous and cooperative movement[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 2020: 6531984. [17] WERNER R, KORMANN G, MUELLER S. Systematic model based path tracking control of actively steered implements in simulation and experiment[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2013, 46(18): 85-90. [18] BIN Y, SHIM T, FENG N L, et al. Path tracking control for backing-up tractor-trailer system via model predictive control[C]//Proceedings of the 24th Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 198-203. [19] BACKMAN J, OKSANEN T, VISALA A. Navigation system for agricultural machines: nonlinear model predictive path tracking[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2012, 82: 32-43. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2011.12.009 [20] 张军, 文川, 阳星, 等. 基于ADRC的电传动飞机牵引车控制系统设计[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2023, 49(5): 1017-1026.ZHANG J, WEN C, YANG X, et al. Design of an electric driveaircraft tug control system based on ADRC[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(5): 1017-1026(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: