Coordinate-aware attention-based multi-frame self-supervised monocular depth estimation
-
摘要:
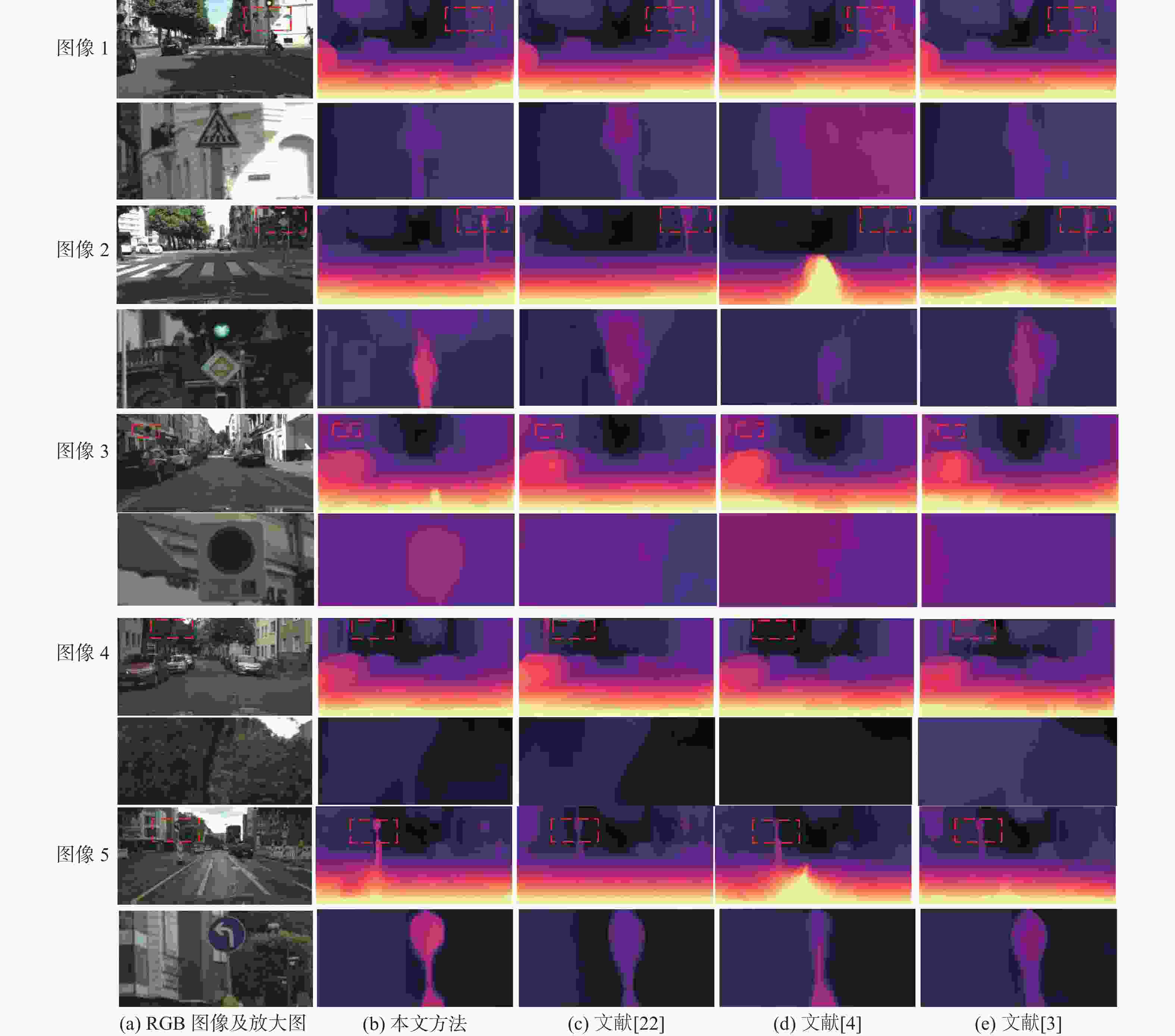
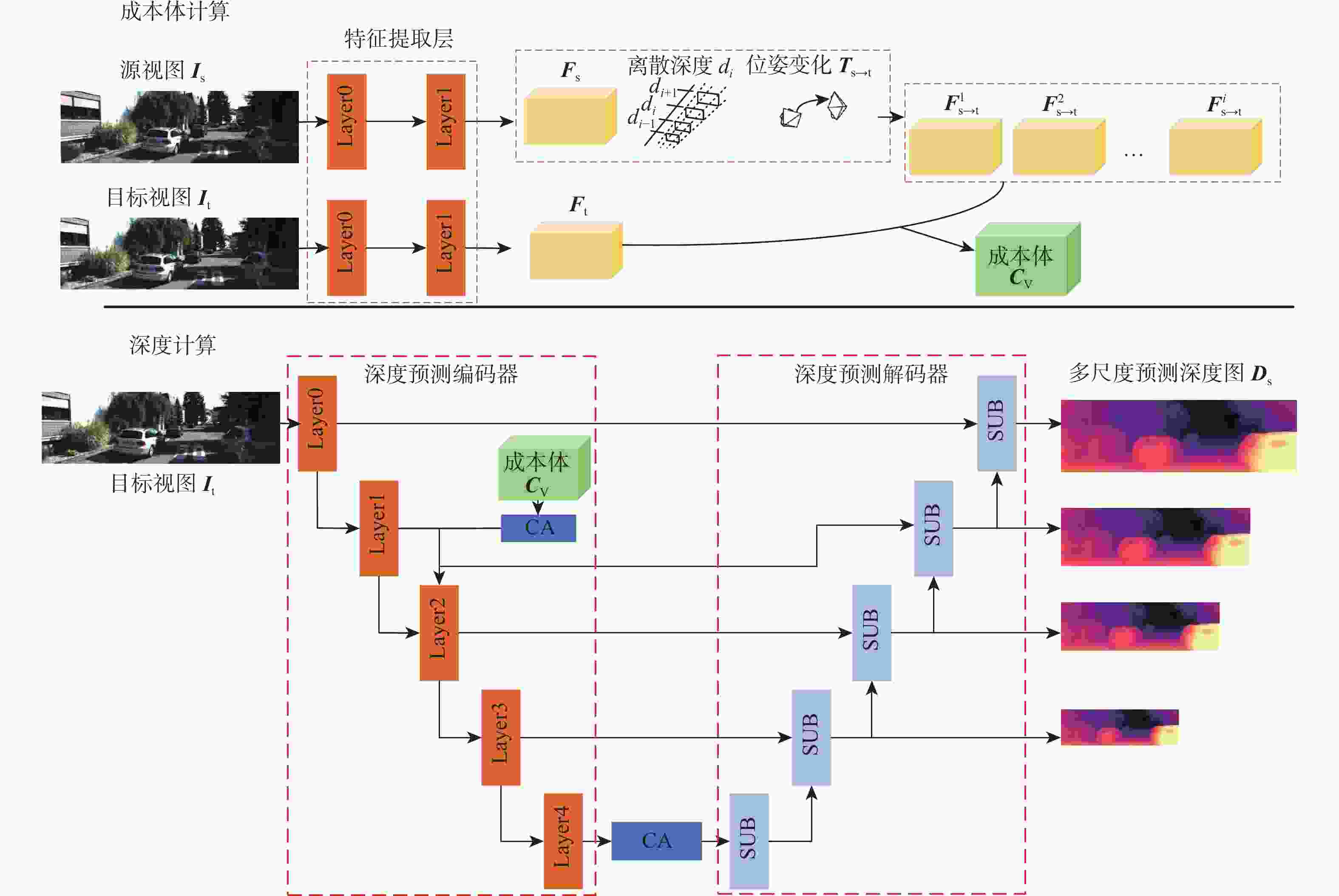
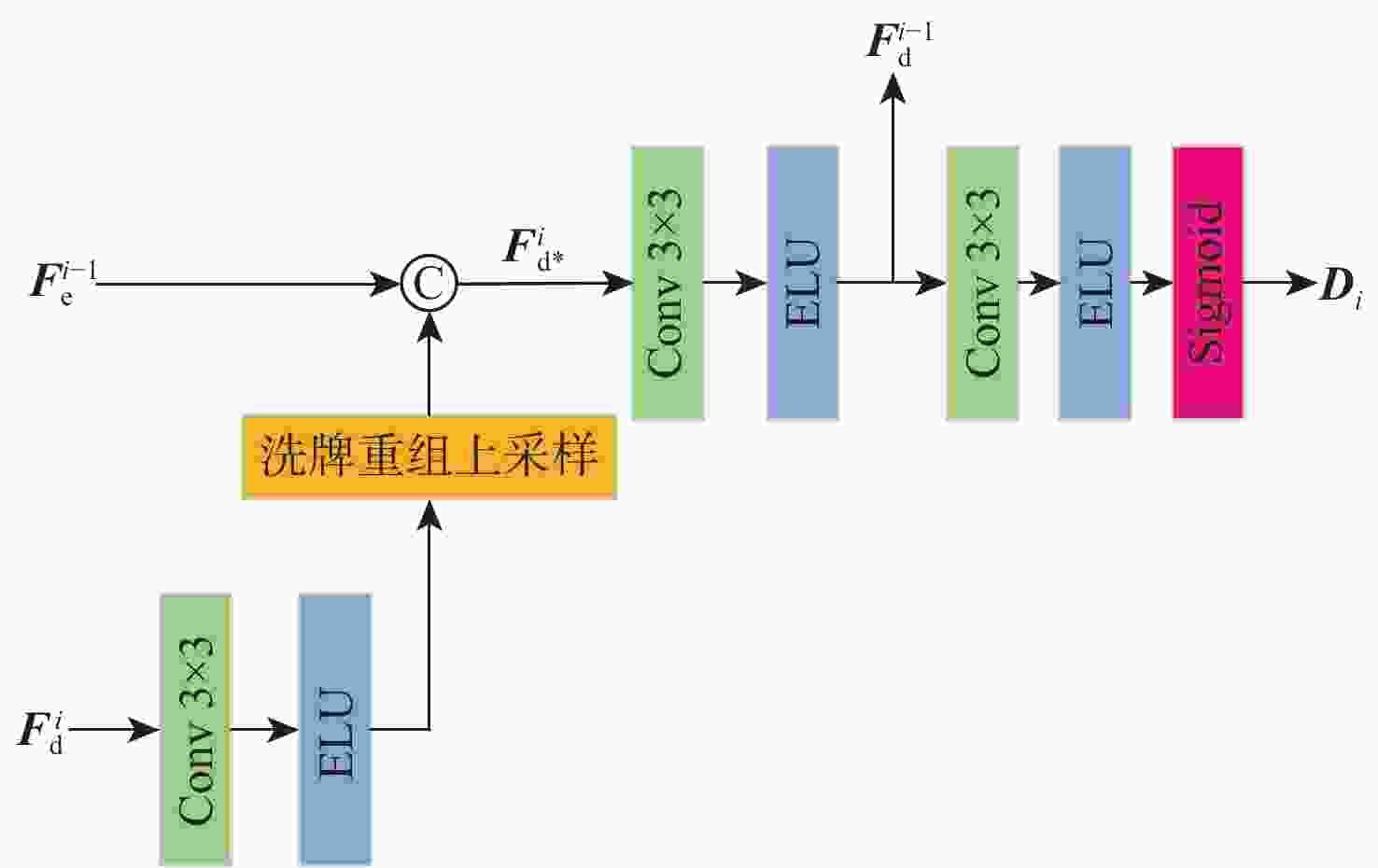
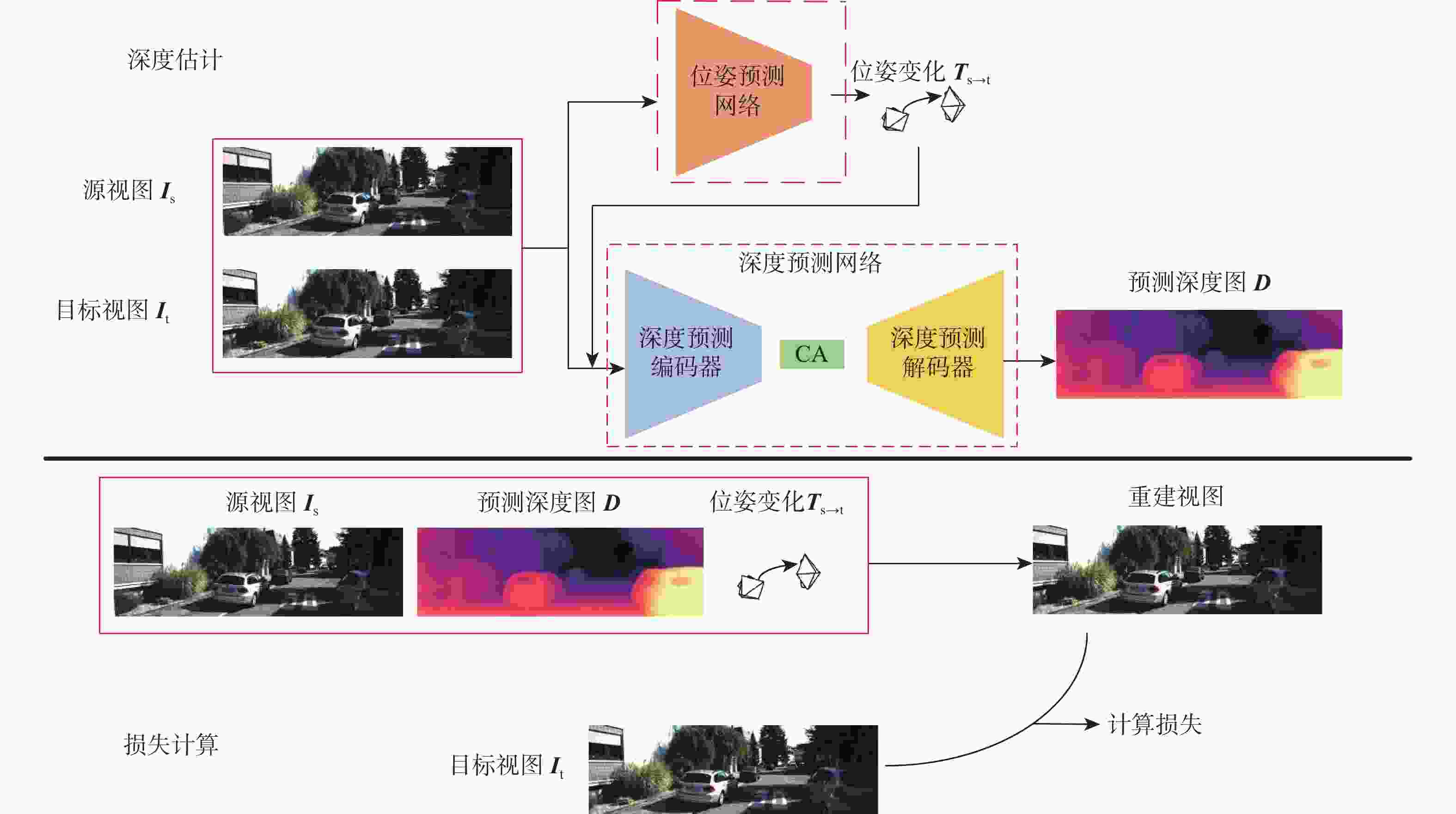
为解决单目深度估计方法中物体细节边缘深度预测模糊不清的问题,提出了一种基于坐标感知注意的多帧自监督单目深度估计方法。提出了一种坐标感知注意模块,以增强编码器最下层输出特征,并加强成本体的特征利用;提出了一种基于像素洗牌的深度预测解码器,可有效分离低分辨编码器特征中的多物体融合特征,以细化深度估计结果中的物体边缘。在KITTI和Cityscapes数据集上的实验测试结果表明:所提方法优于目前主流方法,显著提升了主观视觉效果和客观评价指标,尤其在物体边缘细节上具有更好的深度估计性能。
Abstract:A novel multi-frame self-supervised single-image depth estimation technique based on coordinate-aware attention has been presented to tackle the issue of hazy depth prediction near object edges in single-image depth estimation methods. Firstly, a coordinate-aware attention module is proposed to enhance the output features of the bottom layer of the encoder and improve the feature utilization of the cost volume. To improve the object edges in depth prediction results, a new pixel-shuffle-based depth prediction decoder is also suggested. This decoder can efficiently separate the multi-object fusion features in low-resolution encoder features. Experimental results on the KITTI and Cityscapes datasets demonstrate that the proposed method is superior to current mainstream methods, significantly improving subjective visual effects and objective evaluation indicators, especially with better depth prediction performance in object edge details.
-
Key words:
- image processing /
- deep learning /
- depth estimation /
- self-supervised learning /
- attention mechanism
-
方法 训练方法 LAbs LSq LRMS LRMSlog $ \delta<1.25 $ $ \delta < 1.25^{2} $ $ \delta < 1.25^{3} $ 文献[3] M 0.114 0.864 4.817 0.192 0.877 0.959 0.981 文献[12] M 0.115 0.871 4.778 0.191 0.874 0.963 0.984 文献[13] M 0.120 0.896 4.869 0.198 0.868 0.957 0.981 文献[14] M+Se 0.113 0.835 4.693 0.191 0.879 0.961 0.981 文献[15] M+Se 0.112 0.777 4.772 0.191 0.872 0.959 0.982 文献[16] M 0.111 0.863 4.756 0.188 0.881 0.961 0.982 文献[17] M 0.111 0.821 4.650 0.187 0.883 0.961 0.982 文献[18] M+Se 0.112 0.788 4.582 0.187 0.878 0.963 0.983 文献[19] M 0.109 0.792 4.632 0.185 0.884 0.962 0.983 文献[20] M 0.110 0.812 4.686 0.187 0.882 0.962 0.983 文献[21] M+Se 0.105 0.722 4.547 0.182 0.886 0.964 0.984 文献[22] M 0.107 0.765 4.561 0.183 0.886 0.961 0.982 文献[23] M 0.113 0.851 4.809 0.191 0.877 0.959 0.981 文献[24] M 0.100 0.805 4.678 0.187 0.879 0.961 0.983 文献[25] M 0.111 0.829 4.393 0.185 0.883 0.961 0.983 文献[26] M 0.100 0.747 4.455 0.177 0.895 0.966 0.984 文献[27] M 0.102 0.757 4.493 0.178 0.896 0.965 0.984 文献[4] M 0.098 0.770 4.459 0.176 0.900 0.965 0.983 本文 M 0.094 0.703 4.349 0.174 0.907 0.966 0.984 注:粗体表示最优结果,下划线表示次优结果。M表示以单目视频为训练集训练,Se表示使用语义标签作为监督训练。 表 2 消融实验结果
Table 2. Ablation study results
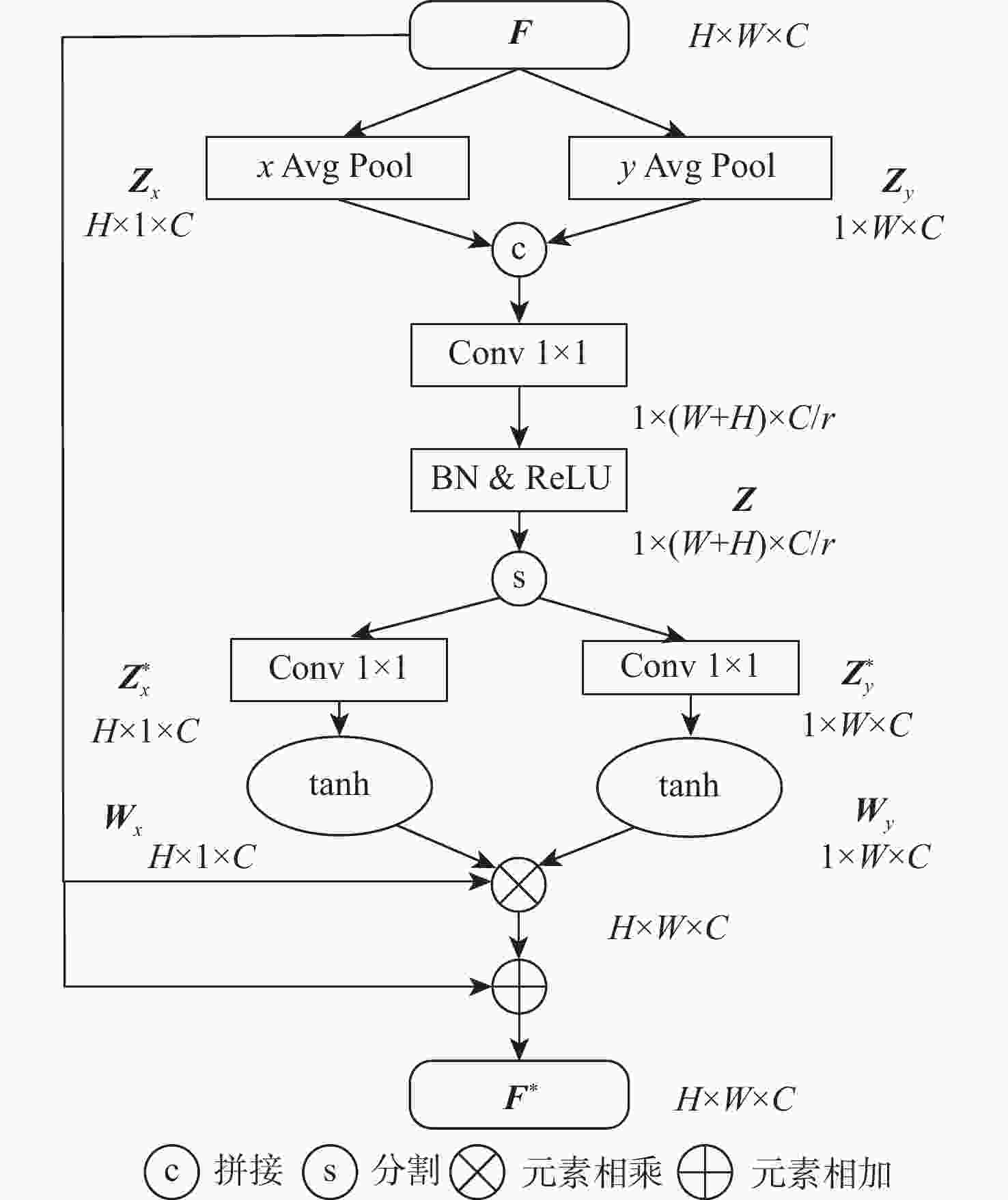
方法 CA(E) CA(C) SUB LAbs LSq LRMS LRMSlog $ \delta < 1.25 $ $ \delta < 1.25^2 $ $ \delta < 1.25^3 $ 基线模型 0.098 0.770 4.459 0.176 0.900 0.965 0.984 基线模型+Densenet 101 0.096 0.760 4.441 0.175 0.902 0.965 0.984 CAMD √ 0.100 0.781 4.466 0.176 0.905 0.965 0.983 √ 0.094 0.747 4.405 0.175 0.903 0.965 0.983 √ 0.094 0.723 4.429 0.175 0.904 0.965 0.983 √ √ 0.095 0.762 4.501 0.173 0.904 0.965 0.983 √ √ 0.094 0.738 4.496 0.177 0.904 0.965 0.983 √ √ 0.105 0.780 4.486 0.176 0.906 0.966 0.984 √ √ √ 0.094 0.703 4.349 0.174 0.907 0.966 0.984 注:CA(E)表示本文坐标注意力模块用来增强编码器最下层的输出特征,CA(C)表示本文坐标注意力模块用来增强成本体的特征利用。 表 3 不同结构的坐标感知注意模块结果
Table 3. Results of different structure of coordinate-aware attention modules
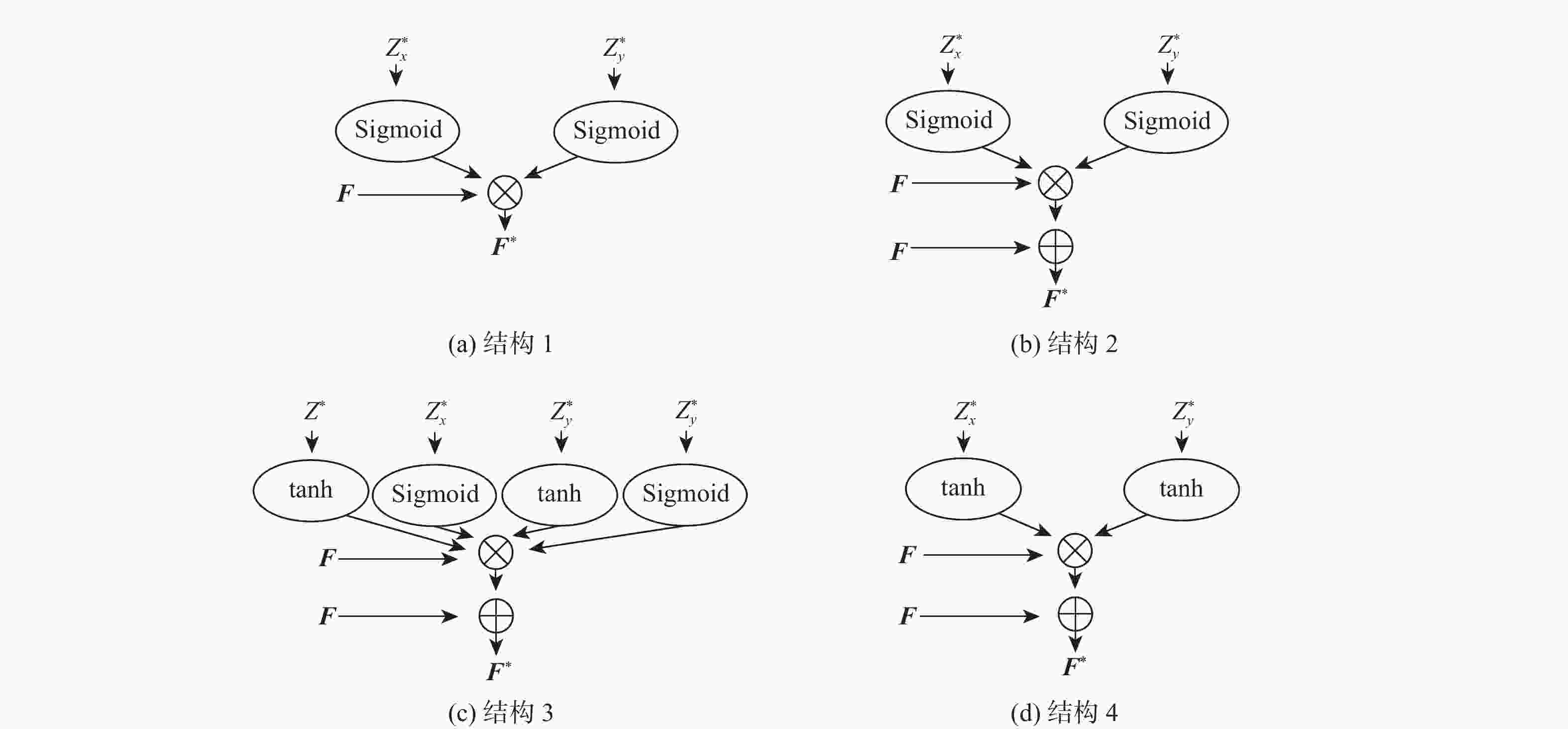
结构 LAbs LSq LRMS LRMSlog $ \delta < 1.25 $ $ \delta < 1.25^2 $ $ \delta < 1.25^{3} $ 结构1 0.098 0.761 4.401 0.181 0.904 0.965 0.984 结构2 0.097 0.748 4.436 0.181 0.904 0.965 0.984 结构3 0.095 0.750 4.415 0.181 0.905 0.965 0.984 结构4 0.094 0.703 4.349 0.174 0.907 0.966 0.984 表 4 Cityspaces数据集上迁移结果
Table 4. Transfer results on Cityspaces dataset
-
[1] 李杰, 李一轩, 吴天生, 等. 基于FPGA无人机影像快速低功耗高精度三维重建[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2021, 47(3): 486-499.LI J, LI Y X, WU T S, et al. Fast, low-power and high-precision 3D reconstruction of UAV images based on FPGA[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(3): 486-499(in Chinese). [2] ZHOU T H, BROWN M, SNAVELY N, et al. Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from video[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6612-6619. [3] GODARD C, MAC AODHA O, FIRMAN M, et al. Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3827-3837. [4] WATSON J, MAC AODHA O, PRISACARIU V, et al. The temporal opportunist: self-supervised multi-frame monocular depth[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1164-1174. [5] GUIZILINI V, AMBRUŞ R, CHEN D, et al. Multi-frame self-supervised depth with Transformers[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 160-170. [6] SHI W Z, CABALLERO J, HUSZÁR F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1874-1883. [7] GEIGER A, LENZ P, STILLER C, et al. Vision meets robotics: the KITTI dataset[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11): 1231-1237. doi: 10.1177/0278364913491297 [8] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [9] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [10] HOU Q B, ZHOU D Q, FENG J S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13708-13717. [11] EIGEN D, PUHRSCH C, FERGUS R. Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network[EB/OL]. (2014-06-09)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2283v1. [12] ZOU Y L, JI P, TRAN Q H, et al. Learning monocular visual odometry via self-supervised long-term modeling[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 710-727. [13] GUIZILINI V, HOU R, LI J, et al. Semantically-guided representation learning for self-supervised monocular depth[EB/OL]. (2020-02-27)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2002.12319v1. [14] KLINGNER M, TERMÖHLEN J A, MIKOLAJCZYK J, et al. Self-supervised monocular depth estimation: solving the dynamic object problem by semantic guidance[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 582-600. [15] LEE S, IM S, LIN S, et al. Learning monocular depth in dynamic scenes via instance-aware projection consistency[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(3): 1863-1872. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i3.16281 [16] POGGI M, ALEOTTI F, TOSI F, et al. On the uncertainty of self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 3224-3234. [17] PATIL V, VAN GANSBEKE W, DAI D X, et al. Don’t forget the past: recurrent depth estimation from monocular video[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(4): 6813-6820. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3017478 [18] CHOI J, JUNG D, LEE D, et al. SAFENet: self-supervised monocular depth estimation with semantic-aware feature extraction[EB/OL]. (2020-11-29)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02893v3. [19] WANG J D, SUN K, CHENG T H, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(10): 3349-3364. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2983686 [20] YAN J X, ZHAO H, BU P H, et al. Channel-wise attention-based network for self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 464-473. [21] JUNG H, PARK E, YOO S. Fine-grained semantics-aware representation enhancement for self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 12622-12632. [22] ZHANG N, NEX F, VOSSELMAN G, et al. Lite-Mono: a lightweight CNN and transformer architecture for self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 18537-18546. [23] SURI Z K. Pose constraints for consistent self-supervised monocular depth and ego-motion[C]//Proceedings of the Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis. Berlin: Springer, 2023: 340-353. [24] BOULAHBAL H, VOICILA A, COMPORT A. STDepthFormer: predicting spatio-temporal depth from video with a self-supervised transformer model[EB/OL]. (2023-05-02)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.01196v1. [25] LIU Y X, XU Z H, HUANG H Y, et al. FSNet: redesign self-supervised MonoDepth for full-scale depth prediction for autonomous driving[EB/OL]. (2023-04-21)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2304.10719v1. [26] SAUNDERS K, VOGIATZIS G, MANSO L J. Self-supervised monocular depth estimation: let’s talk about the weather[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 8873-8883. [27] WANG B Y, WANG S, YE D, et al. Deep neighbor layer aggregation for lightweight self-supervised monocular depth estimation[EB/OL]. [2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2309.09272v2. -






 下载:
下载: