Longitudinal autonomous separation control of aircraft in random wind fields based on MPC
-
摘要:
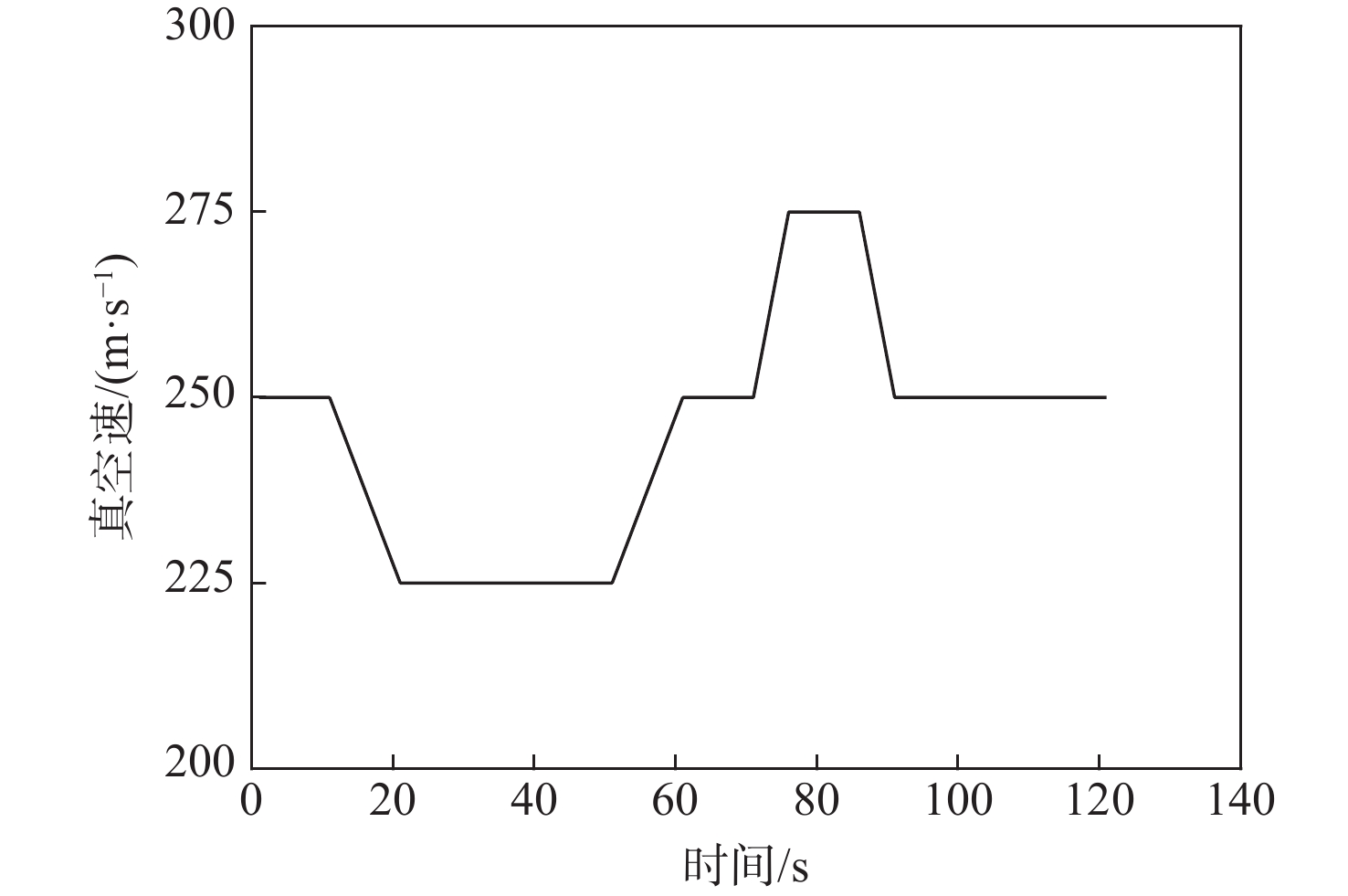
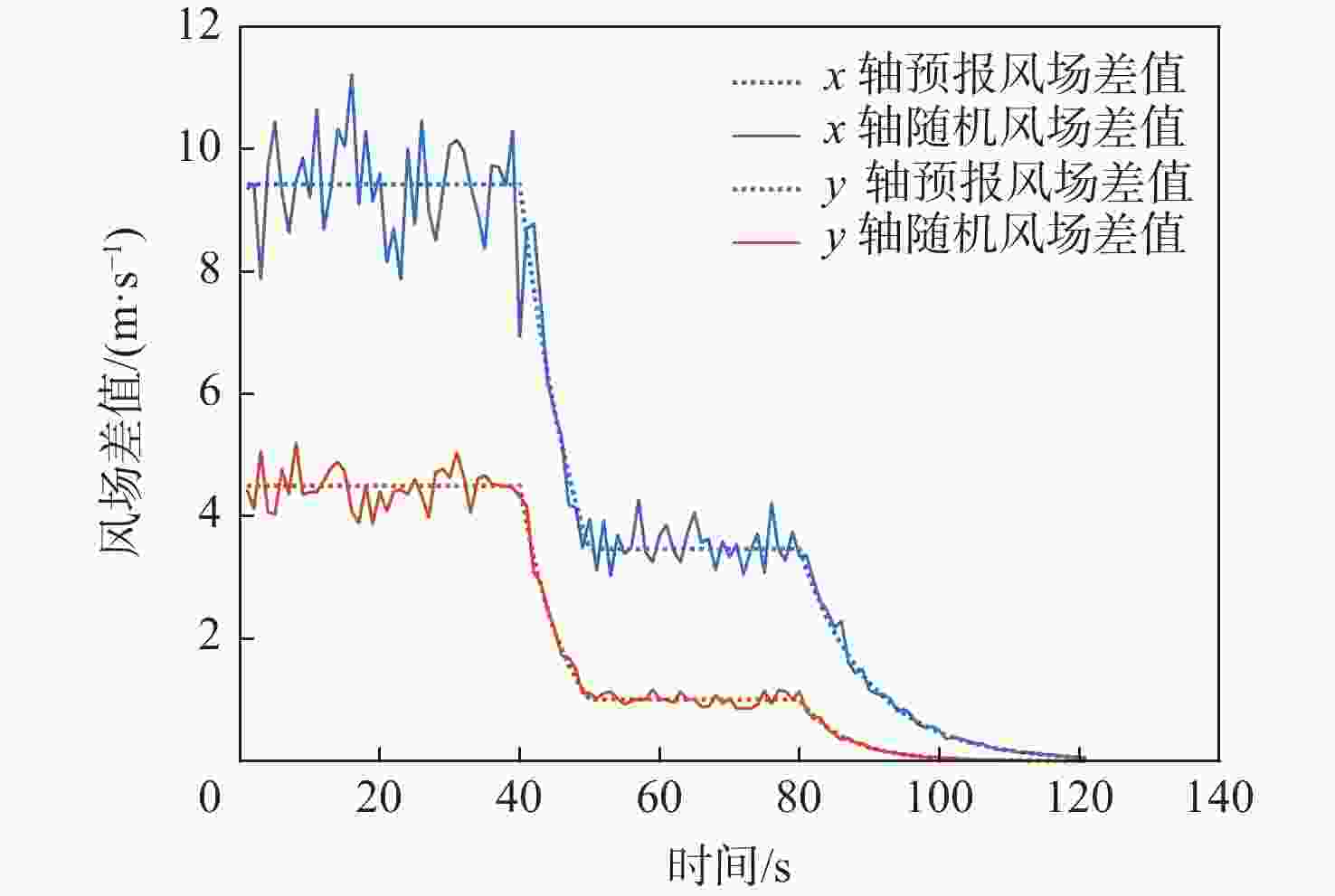
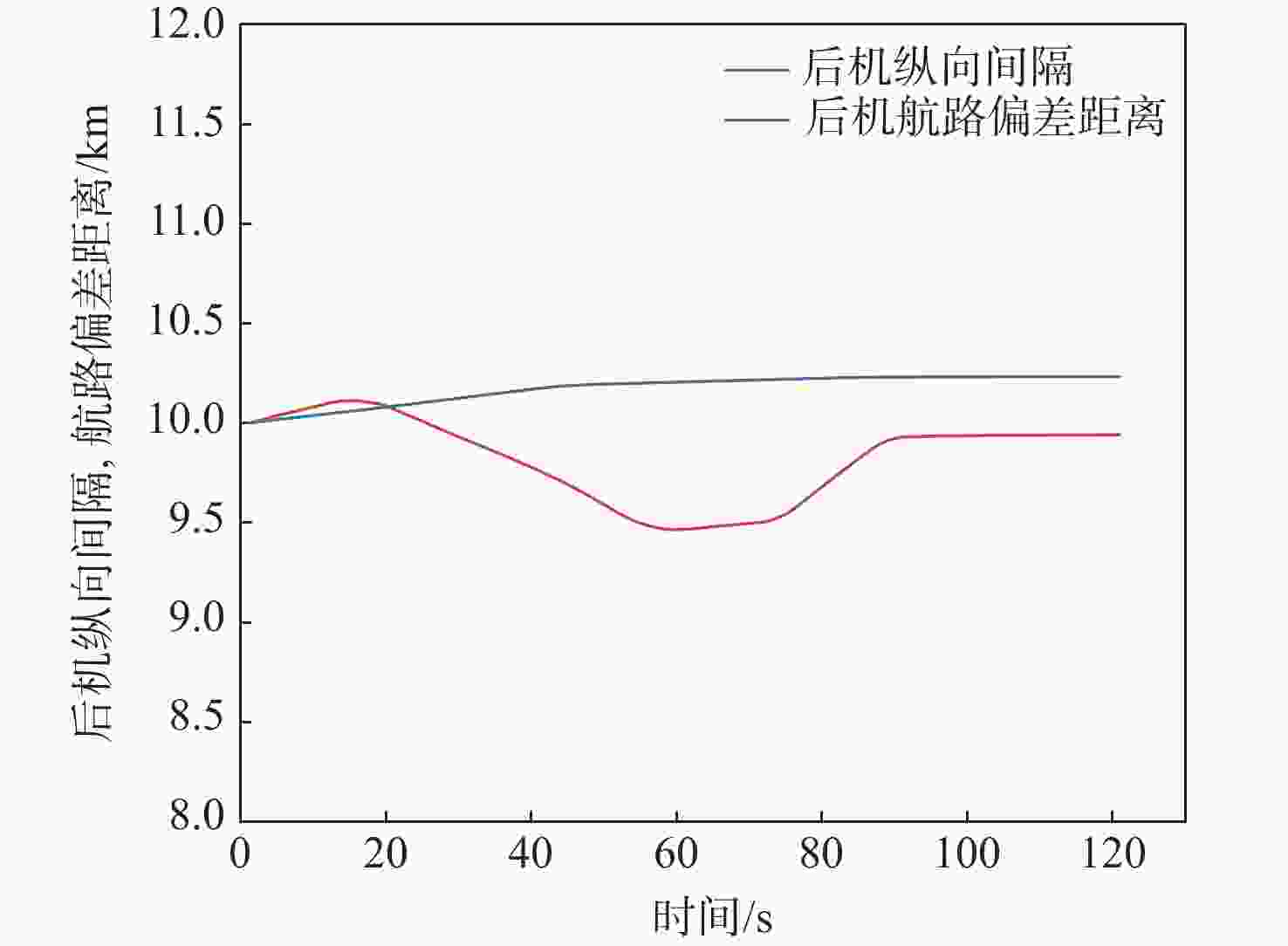
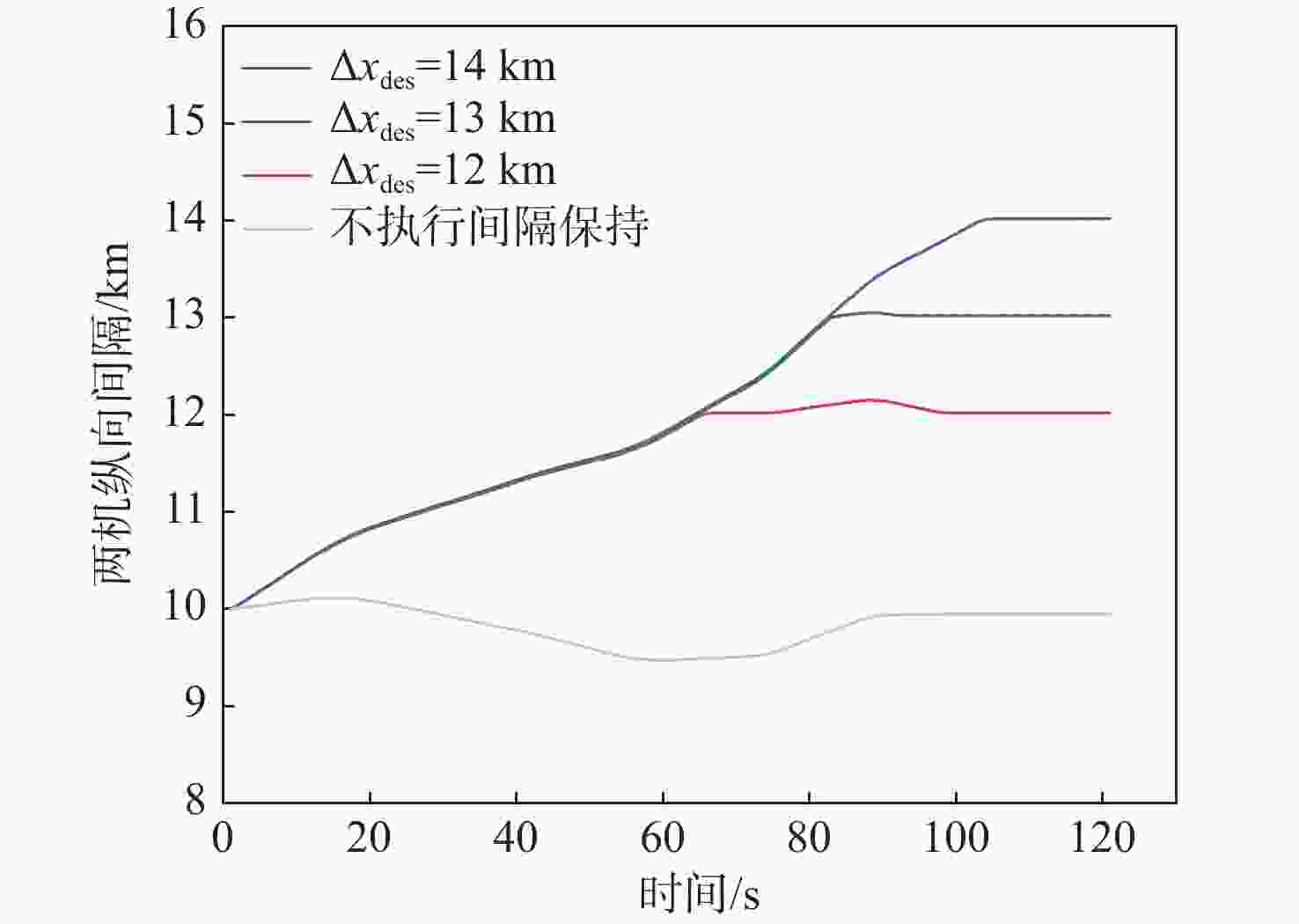
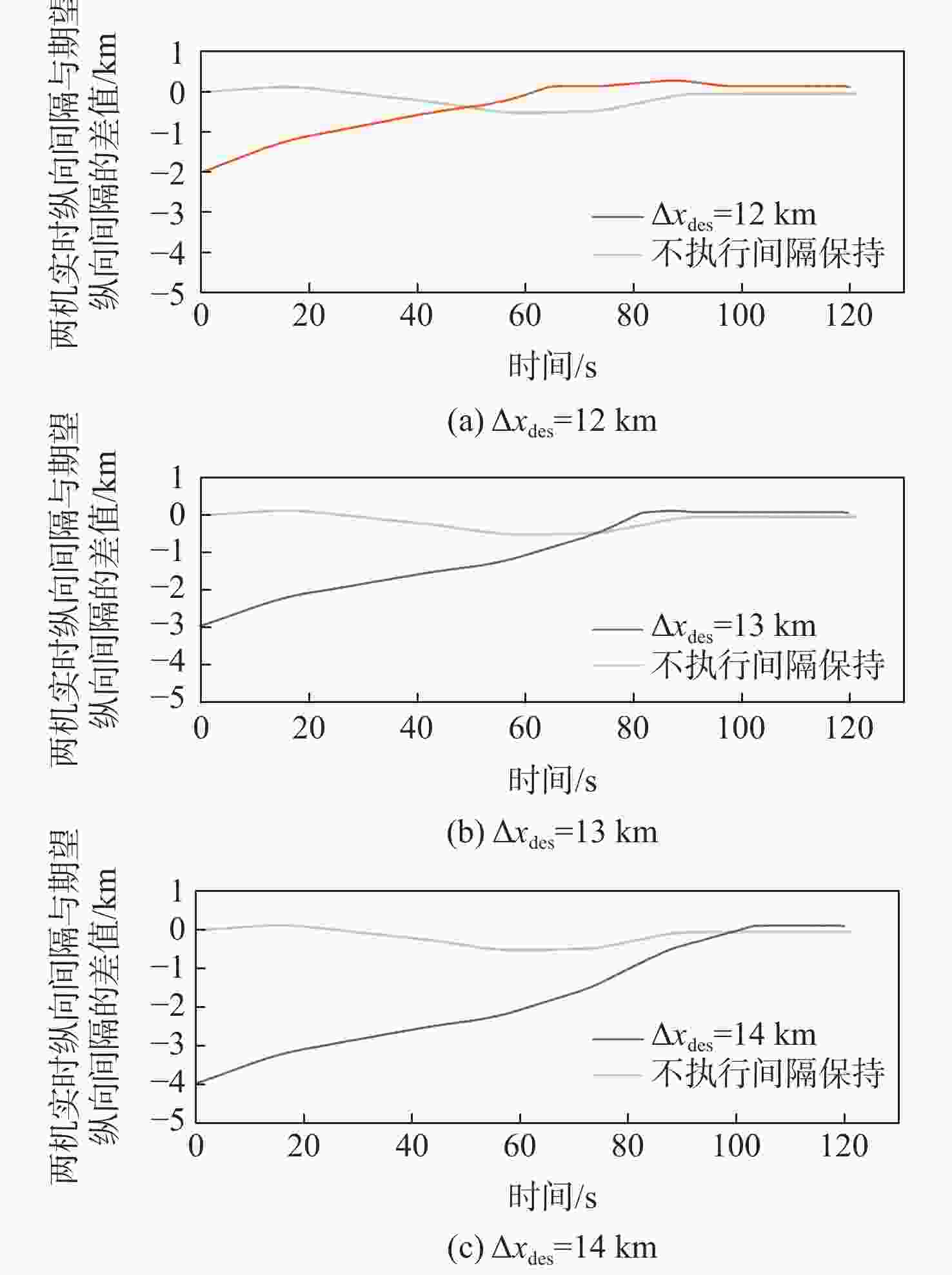
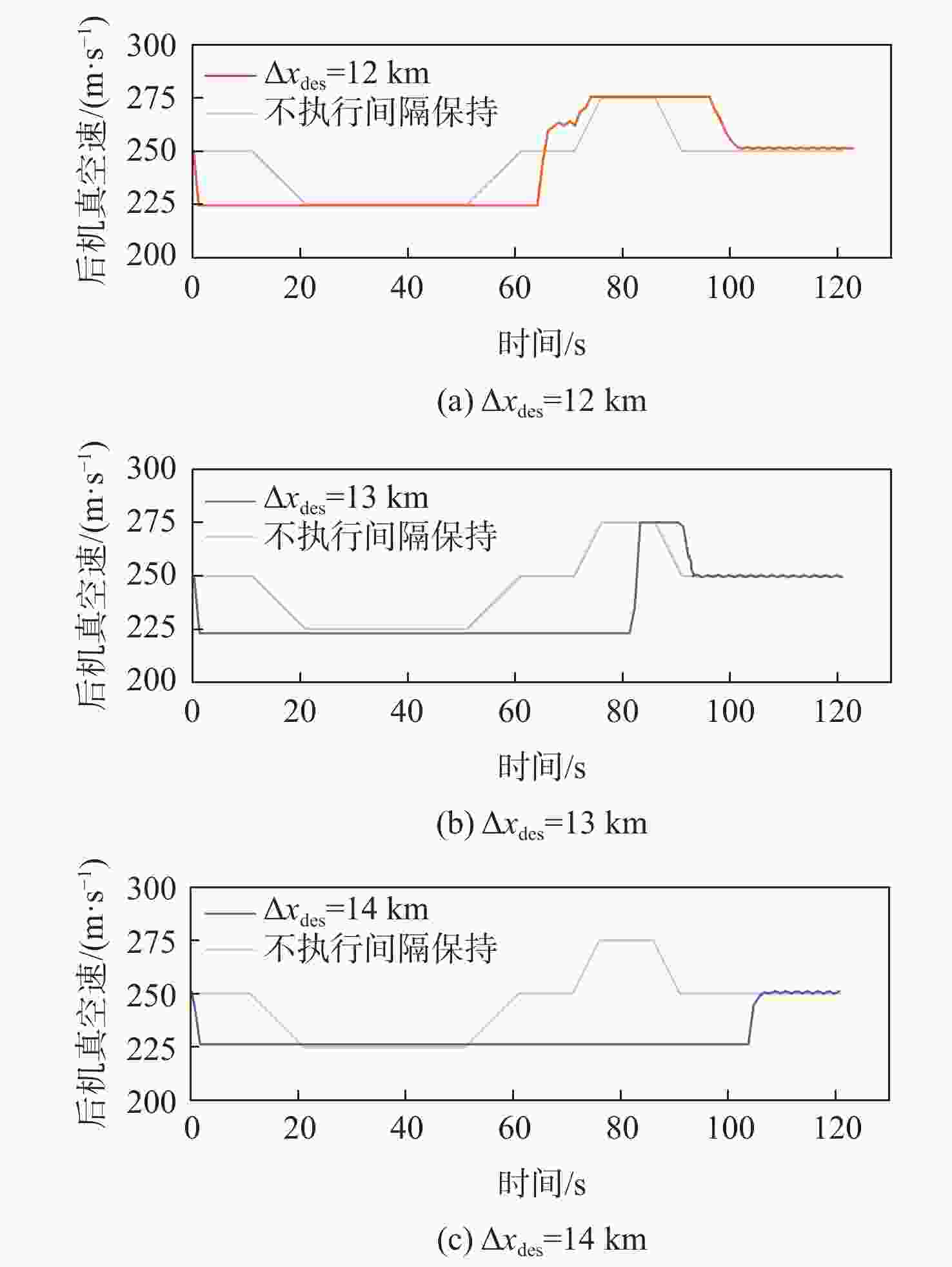
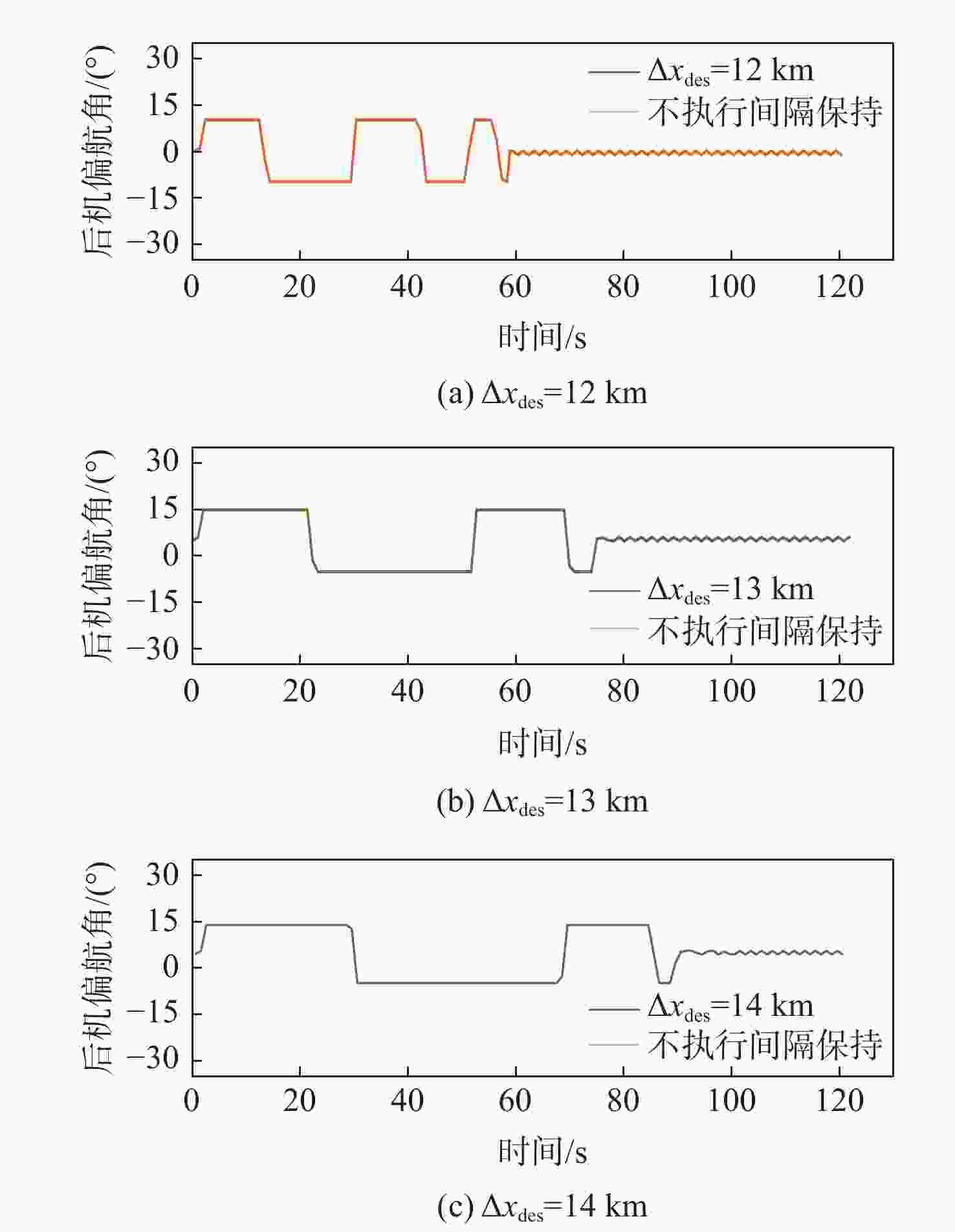
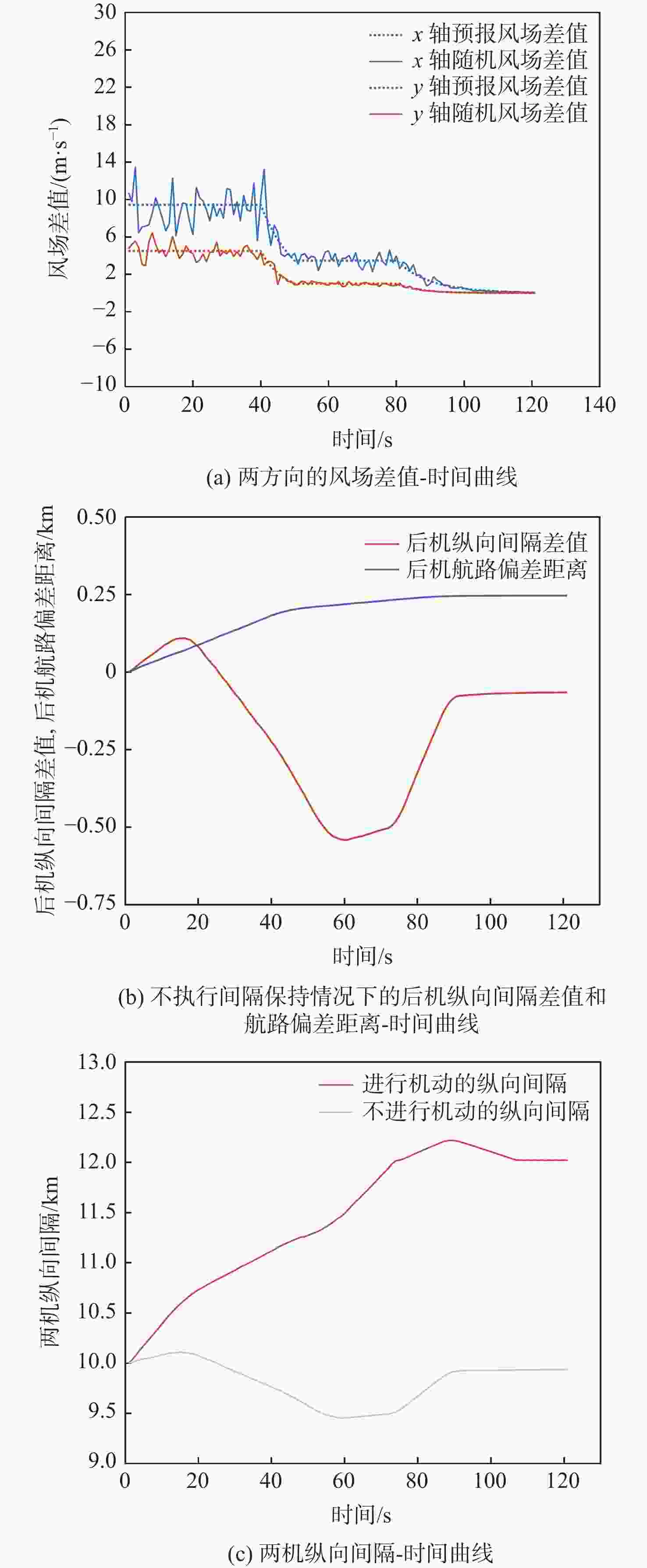
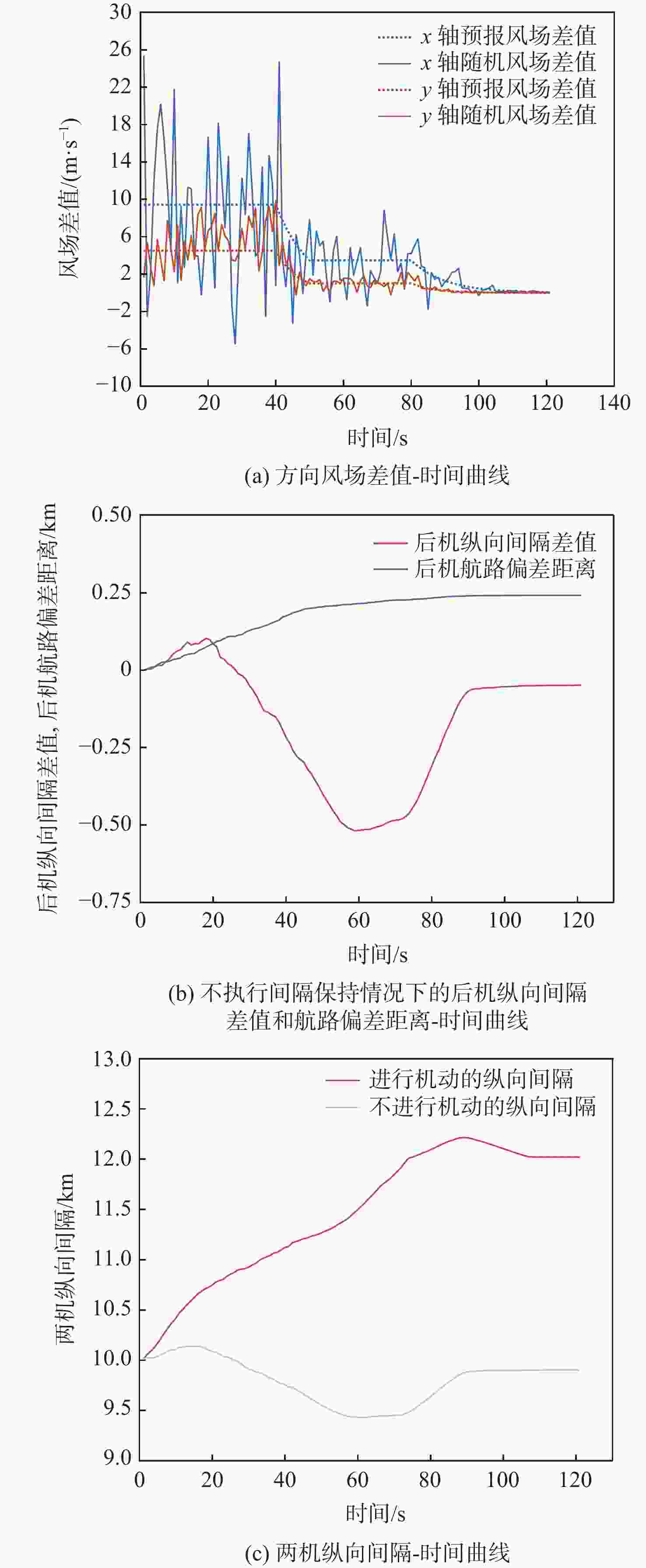
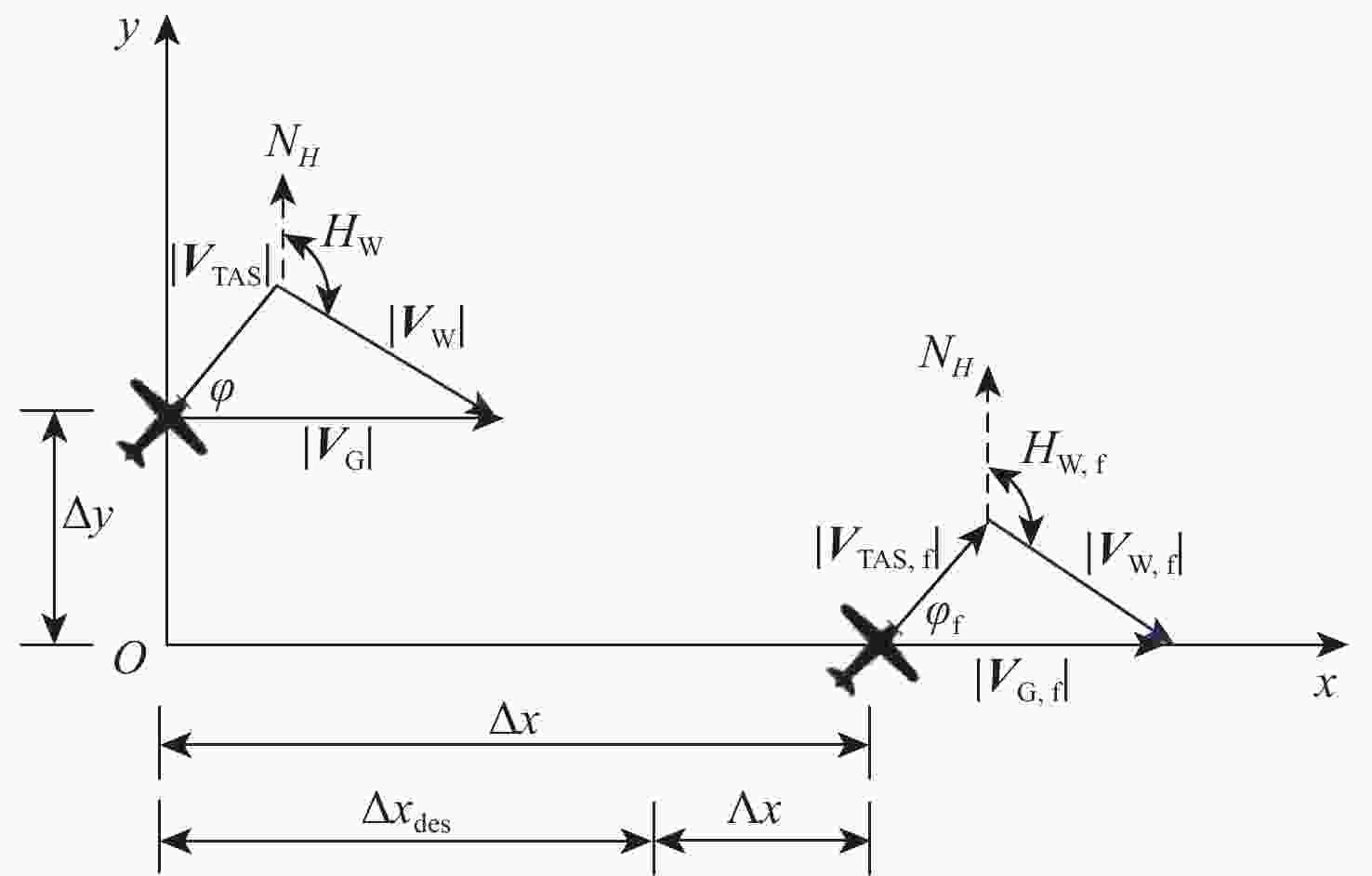
针对航迹随机扰动下的纵向自主间隔保持问题,高空风这一随机因素往往导致两机纵向间隔鲁棒性较差的情况,基于此,提出基于模型预测控制(MPC)的航空器纵向自主间隔控制方法。建立两机所受风场差值与纵向间隔的非线性运动学微分方程,推导线性时变预测模型,选取两机的纵向间隔和航路偏差距离为优化目标,高空风为随机扰动量,前机的真空速和偏航角作为观测量,并在空中安全和航空器性能约束中加入终端等式约束保持系统的稳定性。为验证所提方法的有效性,在规定的120 s仿真时间内,设置3组不同期望纵向间隔分别为12,13,14 km,通过设计的MPC控制器,在滚动时域周期内通过控制后机真空速和偏航角,两机纵向间隔曲线较为平滑且始终不低于最小安全间隔10 km,分别在第74,90,118 s稳定在期望的目标纵向间隔,在第58,74,95 s开始回归航路,最终回到航路中心线;设置了2组风场对照组,一组为预报风强度增大2倍,另一组为紊流风的扰动强度增大8倍,均能分别在第61,72 s平滑且稳定地建立期望的纵向间隔12 km。
Abstract:In view of the fact that the high altitude wind, a random factor, often leads to poor robustness of the longitudinal separation between two aircraft in the longitudinal autonomous separation maintenance problem under the random disturbance of track, this paper proposed a longitudinal autonomous separation control method based on model predictive control (MPC). Firstly, the linear time-varying prediction model was developed by establishing the nonlinear kinematics differential equation of the longitudinal separation and the wind field difference between the two aircraft. The longitudinal separation and route deviation distance of the two aircraft was selected as the optimization objectives, the vacuum speed and yaw angle of the front aircraft were taken as the measurable disturbances, and the high-altitude wind was the random disturbance. Terminal equality constraints were added to the air safety and aircraft performance constraints to maintain the stability of the system. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, within the specified 120-second simulation time, this article set three sets of different expected separations of 12 km, 13 km, and 14 km. Through the design of an MPC controller, the vacuum speed and yaw angle of the following aircraft were controlled during the rolling time domain cycle. The separation curve between the two aircraft is relatively smooth and always not less than the minimum safety separation of 10 km. It stabilized at the expected target separation in the 74th second, 90th second, and 118th second, and returned to the route starting from the 58th second, 74th second, and 95th second. Two sets of wind field control groups were set up. Two times as much wind was forecast in one group, while eight times as much turbulent wind was disturbed in the other. Both groups were able to establish the expected interval of 12 km smoothly and stably in the 61th second and 72th second, respectively.
-
表 1 随机风场模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of random wind model
参数 x轴 y轴 平均风预报风差值/(m·s−1) 9.4286 4.4983 紊流风的概率分布 $ R_{x}^{n}\sim N(0,1) $ $ {R}_{y}^{n}\sim N(0,1) $ 紊流风的相对误差水平 0.1 0.08 起始峰值强度 9.4286 4.4983 衰减系数 0.1 0.15 衰减时间/s 40~50,80~120 40~50,80~120 表 2 MPC控制器参数
Table 2. Model predictive controller parameters
参数 设定值 状态量个数$ N_{{\boldsymbol{x}}} $ 2 控制量个数$ N_{{\boldsymbol{u}}} $ 2 输出量个数$ N_{{\boldsymbol{y}}} $ 2 随机扰动量个数$ N_{{\mathrm{w}}} $ 2 可测扰动量个数$ N_{{\mathrm{f}}} $ 1 仿真步长 120 采样周期$ \Delta T $/s 1 滚动时域周期$ N $/s 10 跟踪项加权系数矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{Q}} $ [0.8,0.2] 终端项加权系数矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{P}} $ [0.8,0.2] 表 3 控制量约束和输出量约束范围
Table 3. Control quantity and output quantity constraint range
系统量 参数 约束范围 控制量 真空速/(m·s−1) [220,280] 偏航角/(°) [−10,10] 输出量 纵向间隔/km [10,15] 航路偏差距离/km [−10,10] 表 4 纵向间隔保持仿真结果
Table 4. Simulation results of longitudinal separation maintenance
期望纵向
间隔/km建立纵向
间隔时间/s开始回归
航路时间/s最大航路
偏差距离/km达到最大航路
偏差距离时间/s12 74 58 0.88046 14 13 90 74 1.53811 23 14 118 95 2.12746 31 表 5 随机风场对照组参数
Table 5. Parameters of random wind field control groups
对照组序号 平均风预报风数值/(m·s−1) 紊流风相对误差水平 前机 后机 x轴 y轴 1 40 30 0.1 0.08 2 80 60 0.1 0.08 3 40 30 0.8 0.64 -
[1] BALLIN M, WING D, HUGHES M, et al. Airborne separation assurance and traffic management-research of concepts and technology[C]//Proceedings of the Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 1999. [2] 章学锋, 李洪伟, 冯涛. 机载间隔保持系统建模及仿真[J]. 中国民航飞行学院学报, 2020, 31(1): 51-55.ZHANG X F, LI H W, FENG T. Model and simulation of airborne separation assurance system[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation Flight University of China, 2020, 31(1): 51-55(in Chinese). [3] 中国民用航空局空中交通管理局. 中国民航现代化空中交通管理系统体系架构: IB-TM-2016-003[S]. 北京: 中国民用航空局空中交通管理局, 2016.Civil Aviation Administration of China Air Traffic Management Bureau. Architecture of CAAC modern air traffic management system: IB-TM-2016-003[S]. Beijing: Civil Aviation Administration of China Air Traffic Management Bureau, 2016(in Chinese). [4] 王莉莉, 朱博, 位放. 近距平行跑道配对进近微观跟驰模型研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(3): 985-988.WANG L L, ZHU B, WEI F. Microscopic tracing model for the paired approach to the narrow-spaced parallel runways[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(3): 985-988(in Chinese). [5] 王莉莉, 王坤. 飞机流宏观与微观同高度纵向间隔研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2016, 16(5): 78-82.WANG L L, WANG K. Study of the longitudinal interval for the airplanes to keep away at the same height both from the macro- and micro point of view[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2016, 16(5): 78-82(in Chinese). [6] 王超, 朱明. 空中交通流微观尾随时距分布模型[J]. 计算机仿真, 2018, 35(5): 55-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.05.012WANG C, ZHU M. Microscopic aircraft-following headway distribution model of air traffic flow[J]. Computer Simulation, 2018, 35(5): 55-59(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.05.012 [7] HUA M Z, ZHANG M, TANG X M, et al. Structural modelling and deceleration algorithm for a follow aircraft on performance-based navigation airway based on multi-agent technique[J]. Cybernetics and Information Technologies, 2015, 15(6): 46-56. doi: 10.1515/cait-2015-0066 [8] TAKEICHI N, NAKAMURA Y, FUKUOKA K. Fundamental characteristics of decentralized air traffic flow control in high density corridor[C]//Proceedings of the 28th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences. [S. l. ]: ICAS, 2012. [9] NAKAMURA Y, TAKEICHI N, KAGEYAMA K. A self-separation algorithm using relative speed for a high-density air corridor[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2014, 57(6): 336-342. doi: 10.2322/tjsass.57.336 [10] TAKEICHI N, NAKAMURA Y, KAGEYAMA K. Aircraft self-separation algorithm for high density air corridor operation based on flight intent[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2014, 57(3): 179-185. doi: 10.2322/tjsass.57.179 [11] FUKUOKA K, TAKEICHI N, NAKAMURA Y. A self-separation algorithm in a high density air corridor feasible for a human pilot control[J]. Journal of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2014, 62(3): 107-115. doi: 10.2322/jjsass.62.107 [12] 汤新民, 郑鹏程. 航路序贯飞行条件下的航空器自主间隔控制[J]. 南京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2019, 51(6): 742-748.TANG X M, ZHENG P C. Aircraft autonomous separation control under sequential flying conditions[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2019, 51(6): 742-748(in Chinese). [13] TIAN Y, DONG Y L, YE B J, et al. A framework for the assessment of distributed self-separation procedures for air traffic in flow corridors[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 123544-123557. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937655 [14] 王瑜嘉, 王永国, 鲁鹏. 翼身融合飞机在风场中的建模与Simulink仿真[J]. 科技风, 2021(29): 4-6.WANG Y J, WANG Y G, LU P. Modeling and Simulink simulation of blended wing body aircraft in wind field[J]. Science and Technology Wind, 2021(29): 4-6(in Chinese). [15] 龚建伟, 姜岩, 徐威. 无人驾驶车辆模型预测控制[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014: 49-50.GONG J W, JIANG Y, XU W. Model predictive control for unmanned vehicles[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 49-50(in Chinese). [16] 陈虹. 模型预测控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 1-3.CHEN H. Model predictive control[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013: 1-3(in Chinese). [17] 万兵, 苏析超, 汪节, 等. 基于模型预测控制算法的精确着舰控制方法[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2024, 50(4): 1197-1207. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0383WAN B, SU X C, WANG J, et al. Research on accurate landing control based on model predictive control algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(4): 1197-1207(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0383 [18] 徐哲, 胡趁义, 龙永文, 等. 车辆纵向跟车舒适性模型预测控制算法研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2022, 36(12): 9-17.XU Z, HU C Y, LONG Y W, et al. Research on model predictive control algorithm for longitudinal vehicle following comfort[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 36(12): 9-17(in Chinese). [19] 中国民用航空局. 运输类飞机适航标准: CCAR-25-R4[S]. 北京: 中国民用航空局, 2016.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Airworthiness standards for transport aircraft: CCAR-25-R4[S]. Beijing: Civil Aviation Administration of China, 2016(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: