Robust semi-supervised video object segmentation based on dynamic embedding feature
-
摘要:
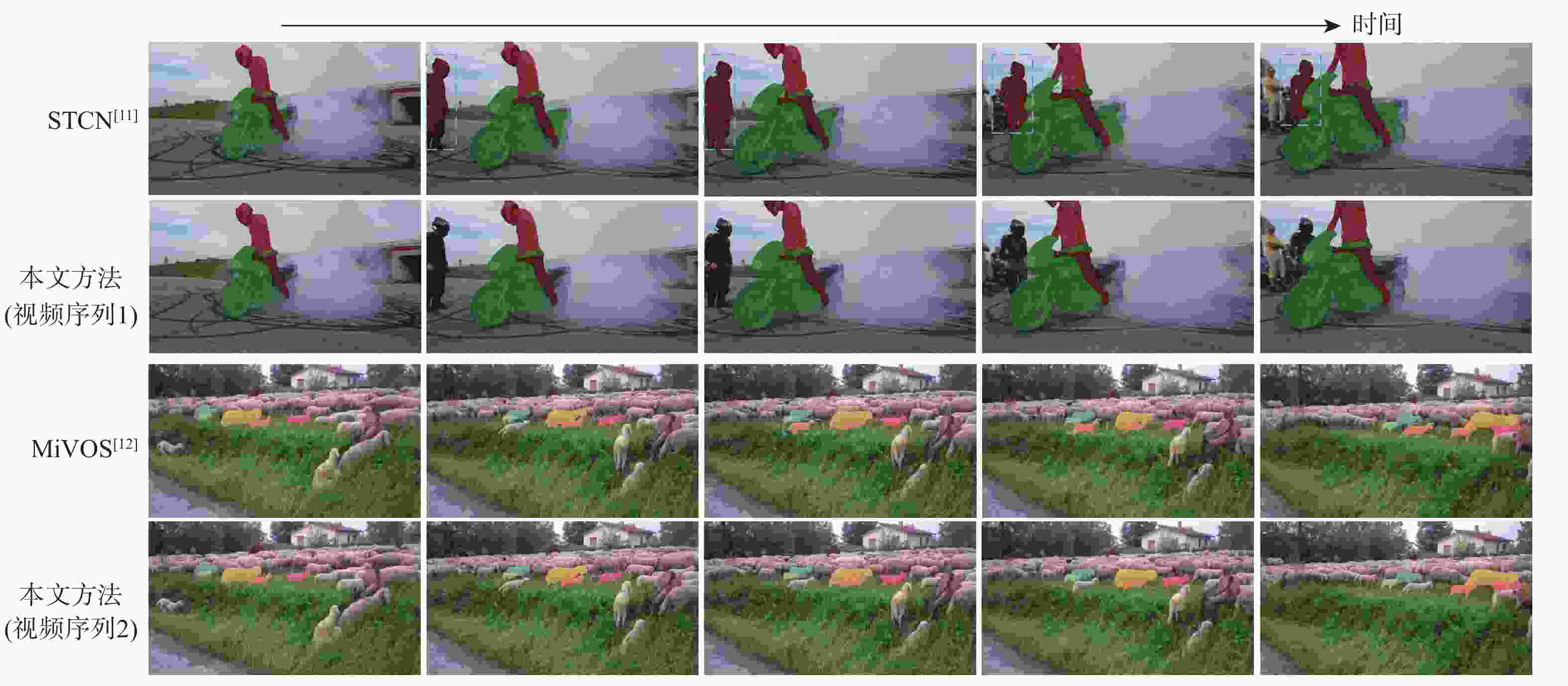
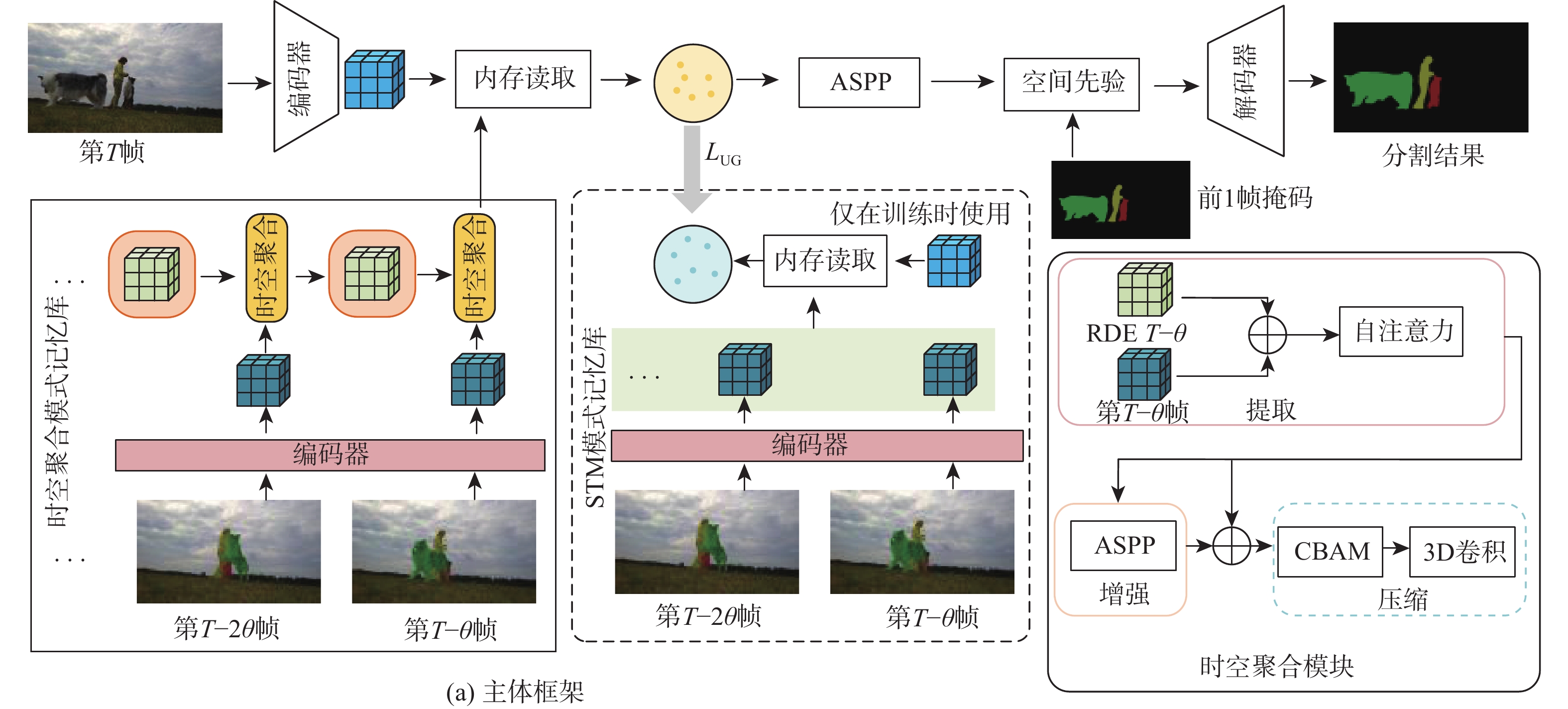
针对半监督视频目标分割(VOS)方法存在推理时内存占用不断增加及仅依赖低级像素特征训练困难的问题,提出一种基于动态嵌入特征和辅助损失函数的半监督视频目标分割方法。使用动态嵌入特征建立恒定大小的记忆库;通过时空聚合方法,利用历史信息生成和更新动态嵌入特征;使用内存更新感应器来自适应控制记忆库的更新间隔,适应不同视频的运动模式;使用辅助损失函数,在高级语义特征层面上给网络提供辅助指导,并通过在多重特征层面多方面指导,提高模型精度和训练效率;针对视频前背景中相似目标误匹配的问题,设计一种时空约束模块,以利用视频的时间连续性特性更好地捕获前一帧掩码信息与当前帧之间的关联。实验结果表明:所提方法在DAVIS 2017验证集上达到84.5%
J &F 的精度,在YouTube-VOS 2019验证集达到82.4%J &F 的精度。Abstract:A semi-supervised video object segmentation (VOS) method was proposed to address the issues of increasing memory consumption during inference and the difficulty of training relying solely on low-level pixel features. The method is based on dynamic embedding features and an auxiliary loss function. First, a dynamic embedding feature was employed to establish a constant-sized memory bank. Through spatiotemporal aggregation, historical information was utilized to generate and update dynamic embedding features. Simultaneously, a memory update sensor was employed to adaptively control the update interval of the memory bank, accommodating different motion patterns in various videos. Second, an auxiliary loss function was utilized to provide the network with guidance at the high semantic feature level, enhancing model accuracy and training efficiency by offering diverse guidance across multiple feature levels. Finally, to address the issue of misalignment between similar objects in the foreground and background of videos, a spatial constraint module was designed, which leveraged the temporal continuity of videos to better capture the correlation between the mask from the previous frame and the current frame. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves an accuracy of 84.5%
J &F on the DAVIS 2017 validation set and 82.4%J &F on the YouTube-VOS 2019 validation set. -
表 1 DAVIS 2017验证集上的实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results on DAVIS 2017 validation set
% 方法 OL CC J&F J F MiVOS[12] × 84.5 81.7 87.4 QDMN[24] × 84.6 81.8 87.3 HMMN[8] × 84.7 81.9 87.5 STCN[11] × 85.3 82.0 88.6 XMem[25] × 86.2 82.9 89.5 OnAVOS[2] √ √ 65.3 61.6 69.1 OSVOS[3] √ √ 60.2 56.6 63.9 GCNet[16] √ 71.4 69.3 73.5 文献[18] √ 74.6 73.0 76.1 PReMVOS[21] √ √ 77.8 73.9 81.7 SwiftNet[17] √ 81.1 78.3 83.9 SSTVOS[22] √ 82.5 79.9 85.1 文献[23] √ 82.7 80.2 85.3 SITVOS[26] √ 83.5 80.4 86.5 RDE[9] √ 84.2 80.8 87.5 本文 √ 84.5 81.2 87.7 注:OL表示基于在线微调的方法,“√”表示使用在线微调的方法。CC表示该方法占用恒定内存,“√”表示内存占用保持不变,“×”表示内存占用会逐渐增加。 表 2 DAVIS 2017测试集上的实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results on DAVIS 2017 test set
% 方法 600p CC J&F J F KMN[7] √ × 77.2 74.1 80.3 STCN[11] × × 76.1 72.7 79.6 MiVOS[12] × × 76.0 72.6 79.3 QDMN[24] × × 77.7 74.2 81.2 XMem[25] × × 81.0 77.4 84.5 CFBI[4] × √ 74.8 71.1 78.5 文献[23] × √ 75.2 72,0 78.3 CFBI+[5] × √ 75.6 71.6 79.6 RDE[9] × √ 77.4 73.6 81.2 本文 × √ 78.0 74.3 81.6 注: 600p表示使用600分辨率视频进行推理,“√”表示使用,“×”表示不使用。CC表示该方法占用恒定内存,其中“√”表示内存占用保持不变,“×”表示内存占用会逐渐增加。 表 3 YouTube-VOS 2019验证集上的实验结果
Table 3. Experimental results on YouTube-VOS 2019 validation set
% 方法 CC Jseen/unseen&Fseen/unseen $ {F_{{\mathrm{unseen}}}} $ $ {F_{{\mathrm{seen}}}} $ $ {J_{{\mathrm{unseen}}}} $ $ {J_{{\mathrm{seen}}}} $ STM[10] × 79.2 79.6 83.6 73.0 80.6 MiVOS[12] × 80.3 79.3 83.7 75.3 82.8 STCN[11] × 82.7 81.1 85.4 78.2 85.9 XMem[25] × 85.5 84.3 88.6 80.3 88.6 CFBI+[5] √ 81.0 80.6 85.1 75.2 83.0 SSTVOS[22] √ 81.8 80.9 76.6 RDE[9] √ 81.9 81.1 85.5 76.2 84.8 本文 √ 82.4 81.3 85.4 77.2 85.7 注: CC表示该方法占用恒定内存,“√”表示内存占用保持不变,“×”表示内存占用会逐渐增加。 表 4 DAVIS 2016验证集上的实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results on DAVIS 2016 validation set
% 方法 CC J&F J F STM[10] × 89.3 88.7 89.9 KMN[7] × 90.5 89.5 91.5 HMMN[8] × 90.8 89.6 92.0 MiVOS[12] × 91.0 89.7 92.4 QDMN[24] × 91.0 90.2 91.7 STCN[11] × 91.7 90.4 93.0 XMem[25] × 91.5 90.4 92.7 GCNet[16] √ 86.6 87.6 85.7 CFBI+[5] √ 89.9 88.7 91.1 SwiftNet[17] √ 90.4 90.7 90.3 SITVOS[26] √ 90.5 89.5 91.4 RDE[9] √ 91.1 89.7 92.5 本文 √ 91.2 89.8 92.5 注:CC表示该方法占用恒定内存,“√”表示内存占用保持不变,“×”表示内存占用会逐渐增加。 表 5 时空约束模块和高层语义辅助损失消融实验结果
Table 5. Ablation experiment results on spatial constraint modules and high-level semantic auxiliary losses
% 消融项 J&F J F 不使用时空约束 84.0 80.6 87.3 不使用辅助损失 83.3 80.2 86.4 同时使用时空约束和辅助损失 84.5 81.2 87.7 表 6 内存更新感应器消融实验结果
Table 6. Ablation experiment results on memory update sensor
% 内存更新方式 J&F Jseen/unseen&Fseen/unseen 固定间隔(3帧) 84.5 81.9 固定间隔(4帧) 84.2 82.4 使用内存更新感应 84.5 82.4 注:Jseen/unseen&Fseen/unseen表示在YouTube-VOS 2019验证集上的结果。 -
[1] PERAZZI F, KHOREVA A, BENENSON R, et al. Learning video object segmentation from static images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3491-3500. [2] VOIGTLAENDER P, LEIBE B. Online adaptation of convolutional neural networks for video object segmentation[EB/OL]. (2017-08-01)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09364v2. [3] CAELLES S, MANINIS K K, PONT-TUSET J, et al. One-shot video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5320-5329. [4] YANG Z X, WEI Y C, YANG Y. Collaborative video object segmentation by foreground-background integration[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 332-348. [5] YANG Z X, WEI Y C, YANG Y. Collaborative video object segmentation by multi-scale foreground-background integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(9): 4701-4712. [6] ZHANG P, HU L, ZHANG B, et al. Spatial consistent memory network for semi-supervised video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the DAVIS Challenge on Video Object Segmentation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-4. [7] SEONG H, HYUN J, KIM E. Kernelized memory network for video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 629-645. [8] SEONG H, OH S W, LEE J Y, et al. Hierarchical memory matching network for video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 12869-12878. [9] LI M X, HU L, XIONG Z W, et al. Recurrent dynamic embedding for video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1322-1331. [10] OH S W, LEE J Y, XU N, et al. Video object segmentation using space-time memory networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9226-9235. [11] CHENG H K, TAI Y W, TANG C K. Rethinking space-time networks with improved memory coverage for efficient video object segmentation[EB/OL]. (2021-10-08)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.05210?context=cs.CV. [12] CHENG H K, TAI Y W, TANG C K. Modular interactive video object segmentation: interaction-to-mask, propagation and difference-aware fusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 5555-5564. [13] XIE H Z, YAO H X, ZHOU S C, et al. Efficient regional memory network for video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1286-1295. [14] 季传俊, 陈亚当, 车洵. 融合视觉词与自注意力机制的视频目标分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2022, 27(8): 2444-2457.JI C J, CHEN Y D, CHE X. Visual words and self-attention mechanism fusion based video object segmentation method[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2022, 27(8): 2444-2457(in Chinese). [15] 征煜, 陈亚当, 郝川艳. 特征一致性约束的视频目标分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(8): 1558-1566. doi: 10.11834/jig.190571ZHENG Y, CHEN Y D, HAO C Y. Video object segmentation algorithm based on consistent features[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(8): 1558-1566(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.190571 [16] LI Y, SHEN Z R, SHAN Y. Fast video object segmentation using the global context module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conferenceon Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 735-750. [17] WANG H C, JIANG X L, REN H B, et al. SwiftNet: real-time video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1296-1305. [18] LIANG Y Q, LI X, JAFARI N, et al. Video object segmentation with adaptive feature bank and uncertain-region refinement[EB/OL]. (2020-10-15)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.07958v1. [19] CHEN Y D, HAO C Y, YANG Z X, et al. Fast target-aware learning for few-shot video object segmentation[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(8): 182104. doi: 10.1007/s11432-021-3396-7 [20] CHO S, LEE H, LEE M, et al. Tackling background distraction in video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2022: 446-462. [21] LUITEN J, VOIGTLAENDER P, LEIBE B. PReMVOS: proposal-generation, refinement and merging for video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 565-580. [22] DUKE B, AHMED A, WOLF C, et al. SSTVOS: sparse spatiotemporal Transformers for video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 5908-5917. [23] GE W B, LU X K, SHEN J B. Video object segmentation using global and instance embedding learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16831-16840. [24] LIU Y, YU R, YIN F, et al. Learning quality-aware dynamic memory for video object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2022: 468-486. [25] CHENG H K, SCHWING A G. XMem: long-term video object segmentation with an Atkinson-Shiffrin memory model[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2022: 640-658. [26] LAN M, ZHANG J, HE F X, et al. Siamese network with interactive Transformer for video object segmentation[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 36(2): 1228-1236. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20009 [27] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [28] 陈亚当, 陈柳任, 余文斌, 等. 多尺度特征融合的知识蒸馏异常检测方法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2022, 34(10): 1542-1549.CHEN Y D, CHEN L R, YU W B, et al. Knowledge distillation anomaly detection with multi-scale feature fusion[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2022, 34(10): 1542-1549(in Chinese). [29] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. -







 下载:
下载: