-
摘要:
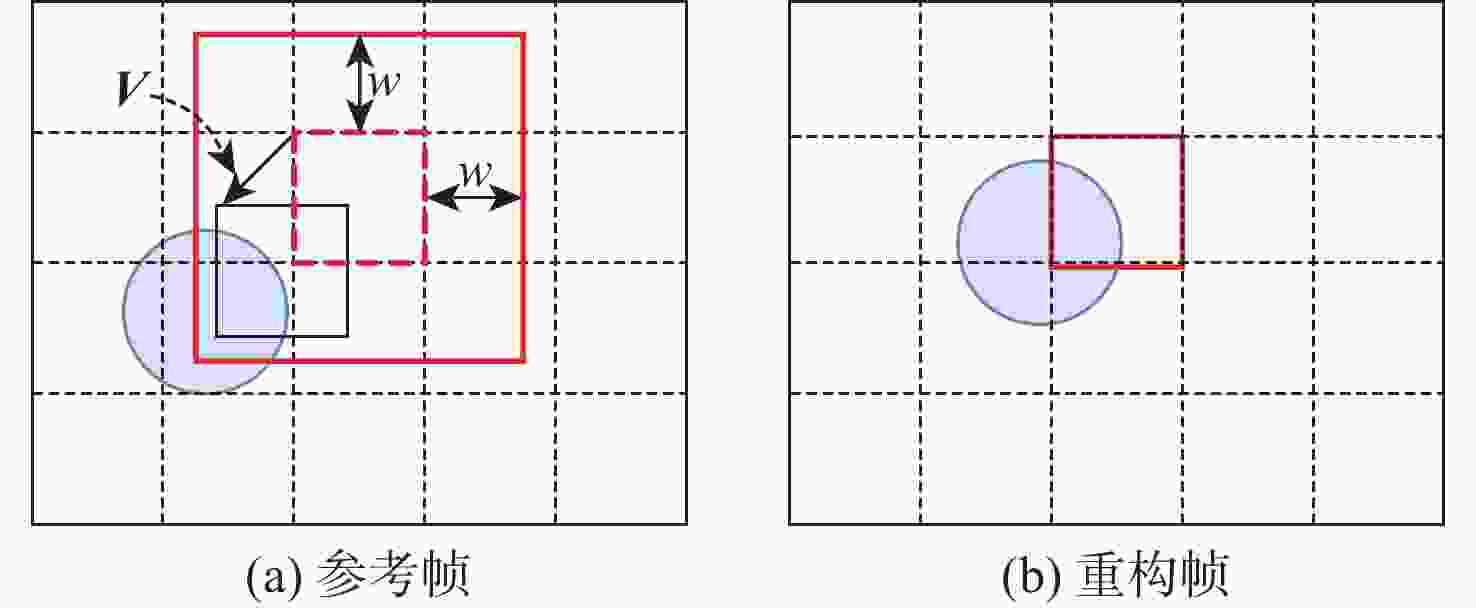
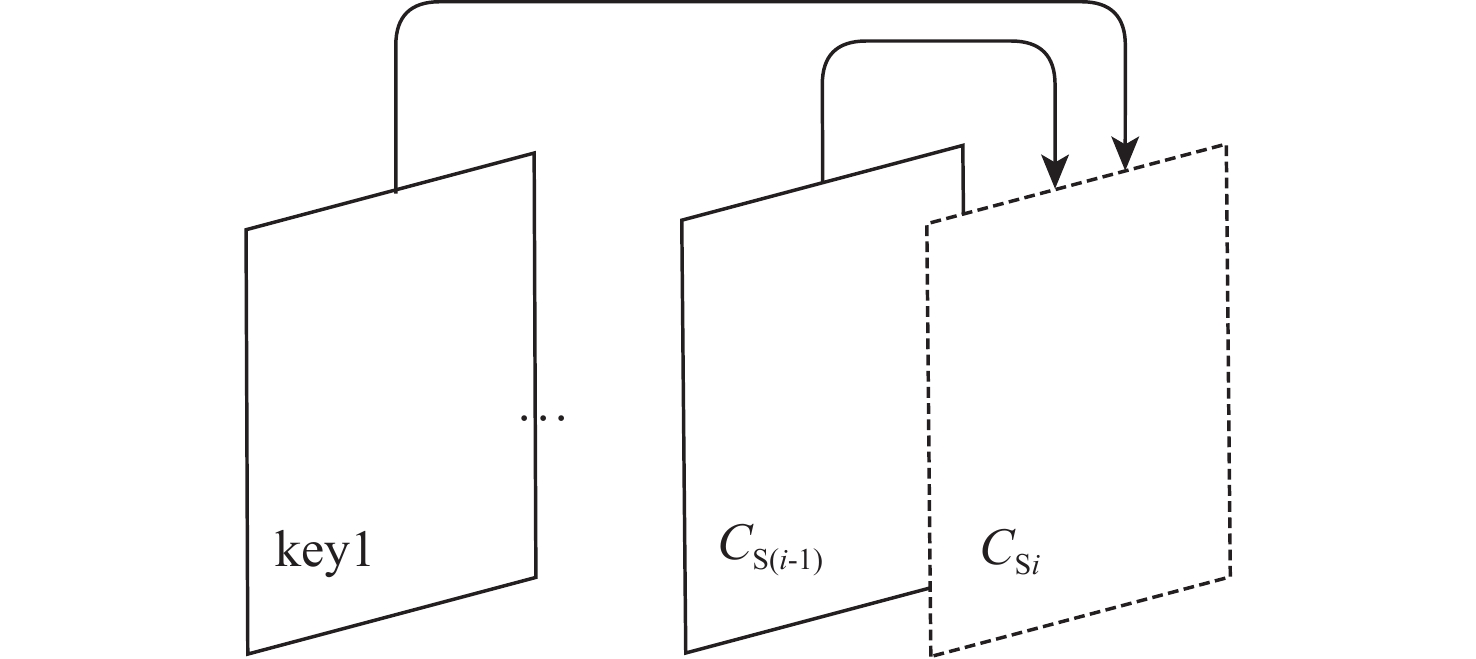
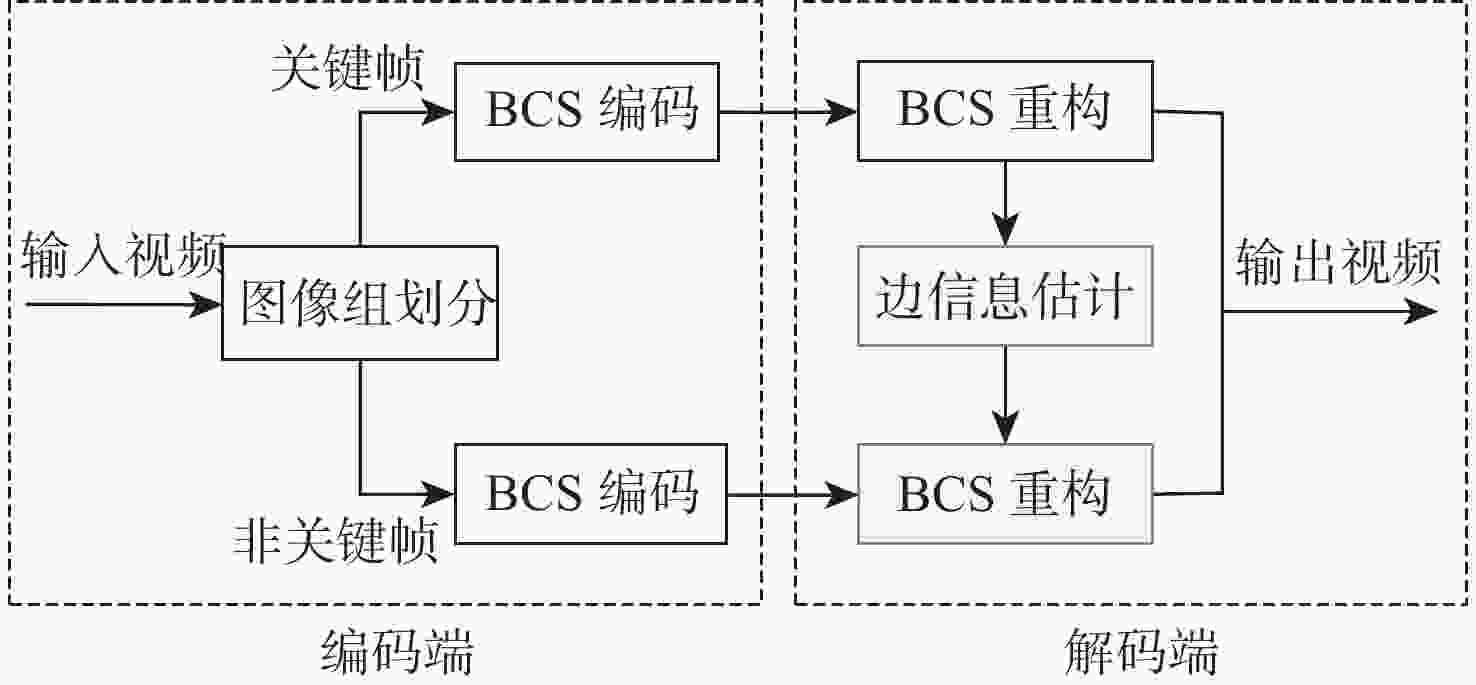
面向分布式视频压缩感知,帧间多假设预测能够降低编码端的运算量、提高解码端非关键帧的恢复质量,因此,近年来出现了很多与其相关的优化算法。然而在现有算法中,假设集的搜索窗口是大小经验固定的正方形区域。为进一步提高假设集质量、降低解码端时延,提出一种搜索窗口位置和大小自适应变化的重构算法。所提算法根据光流法快速确定相邻非关键帧之间的运动向量;联合该运动向量和前向相邻非关键帧与关键帧之间的运动信息,在关键帧中确定搜索窗口的中心块位置;由当前重构块与搜索窗口中心块的相对位置关系自适应地确定一个符合运动变化的矩形搜索窗口。在低延迟框架下对多个视频序列进行实验分析。实验结果表明:所提算法能够有效提高非关键帧的恢复质量,并减少运行时间。
Abstract:For distributed video compressive sensing, the inter-frame multi-hypothesis prediction offers low computational complexity at the encoding end and good restoration quality for non-key frames at the decoding end. In recent years, many optimization algorithms related to it have been proposed. However, in existing algorithms, the search window of the hypothesis set is a square area whose size is empirically fixed. To further improve the quality of the hypothesis set and reduce the delay at the decoding end, this paper proposed a reconstruction algorithm that adaptively adjusted the position and size of the search window. The proposed algorithm first quickly determined the motion vector between adjacent non-key frames using the optical flow method. Then, by combining the motion vector and the motion information between the forward adjacent non-key frame and the key frame, the central block position of the search window in the key frame was determined. Finally, based on the relative position relationship between the current reconstruction block and the central block of the search window, a rectangular search window that aligned with motion changes could be determined adaptively. In the paper, several video sequences were experimentally analyzed within a low-delay framework. The results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the restoration quality of non-key frames and reduce the runtime.
-
Key words:
- adaptively /
- optical flow method /
- motion vector /
- low-delay framework /
- rectangular search window
-
表 1 不同窗口尺寸下块匹配过程的CPU运行时间
Table 1. CPU runtime of block matching process under different window sizes
窗口尺寸/
像素CPU运行时间/s 采样率
为0.10采样率
为0.15采样率
为0.20采样率
为0.25采样率
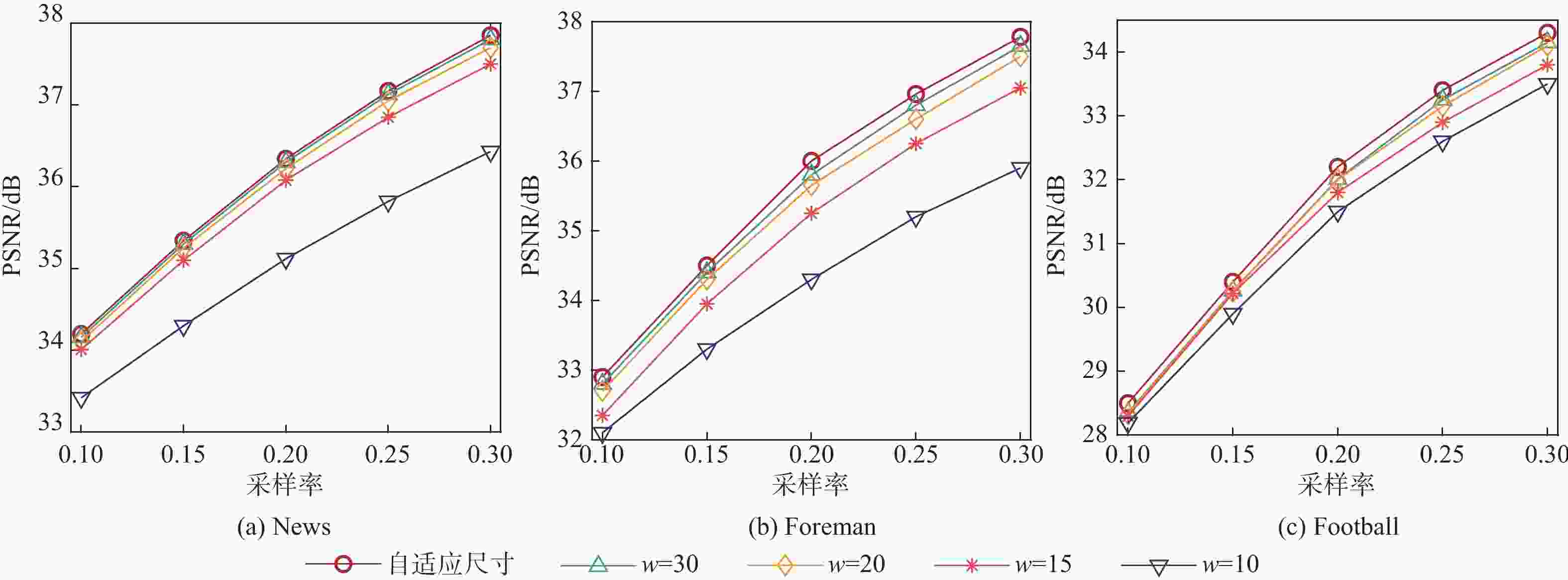
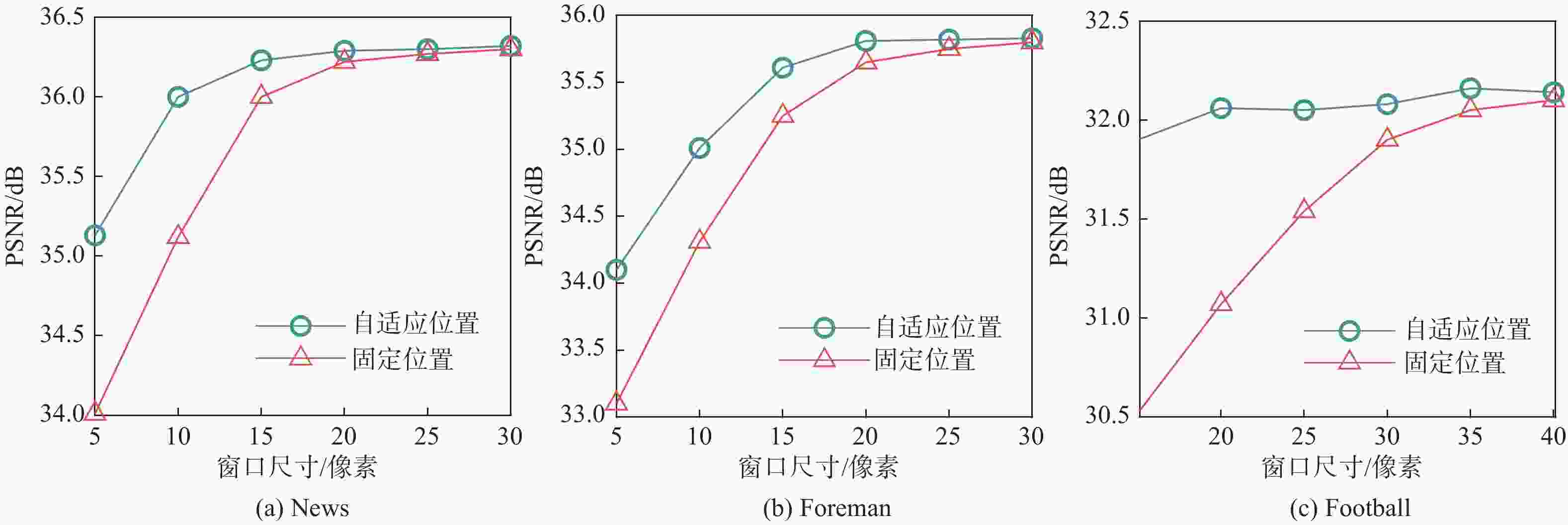
为0.3010 33.5 37.5 42.3 45.2 47.3 20 49.3 52.3 57.3 64.3 74.6 30 70.2 76.4 82.4 86.6 95.3 自适应尺寸 42.2 46.9 51.6 59.1 63.1 表 2 不同运动程度视频序列上不同算法的PSNR
Table 2. PSNR of different algorithms on video sequences with different motion degrees
视频 算法 PSNR/dB 采样率为0.10 采样率为0.15 采样率为0.20 采样率为0.25 采样率为0.30 均值 News MC[9] 31.19 32.26 33.38 34.24 34.97 33.21 NMH[18] 33.92 34.86 36.04 36.88 37.24 35.79 IPH[19] 34.12 35.02 36.46 37.32 37.63 36.11 WMR 34.35 35.29 36.72 37.56 37.94 36.37 Foreman MC[9] 31.49 32.57 34.12 34.78 35.79 33.75 NMH[18] 33.52 34.70 36.35 37.04 38.14 35.95 IPH[19] 33.77 34.97 36.65 37.36 38.48 36.25 WMR 34.11 35.42 36.94 37.66 38.76 36.58 Football MC[9] 25.34 27.11 28.63 29.93 31.10 28.42 NMH[18] 27.35 29.16 30.83 32.26 33.45 30.61 IPH[19] 27.61 29.43 31.10 32.57 33.77 30.90 WMR 27.83 29.67 31.35 32.84 34.06 31.15 -
[1] CANDES E J, ROMBERG J, TAO T. Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489-509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 [2] 刘浩, 郑浩然, 黄荣. 面向量化分块CS的区域层次化预测编码[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2022, 48(8): 1376-1382.LIU H, ZHENG H R, HUANG R. Region-hierarchical predictive coding for quantized block compressive sensing[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(8): 1376-1382(in Chinese). [3] JI Y, KANG Z, ZHANG X, et al. Model recovery for multi-input signal-output nonlinear systems based on the compressed sensing recovery theory[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2022, 359(5): 2317-2339. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2022.01.032 [4] CANDES E J, WAKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21-30. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 [5] WANG S W, YU L, XIANG S. A low complexity compressed sensing-based codec for consumer depth video sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2019, 65(4): 434-443. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2019.2929586 [6] GAN L. Block compressed sensing of natural images[C]//Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 403-406. [7] DO T T, CHEN Y, NGUYEN D T, et al. Distributed compressed video sensing[C]//Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 1393-1396. [8] KANG L W, LU C S. Distributed compressive video sensing[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 1169-1172. [9] MUN S, FOWLER J E. Residual reconstruction for block-based compressed sensing of video[C]//Proceedings of the Data Compression Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 183-192. [10] CHEN C, TRAMEL E W, FOWLER J E. Compressed-sensing recovery of images and video using multihypothesis predictions[C]// Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 45th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1193-1198. [11] TRAMEL E W, FOWLER J E. Video compressed sensing with multihypothesis[C]//Proceedings of the Data Compression Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 193-202. [12] FOWLER J E. Block-based compressed sensing of images and video[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(4): 297-416. [13] TROCAN M, TRAMEL E W, FOWLER J E, et al. Compressed-sensing recovery of multiview image and video sequences using signal prediction[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2014, 72(1): 95-121. doi: 10.1007/s11042-012-1330-7 [14] KUO Y H, WU K, CHEN J. A scheme for distributed compressed video sensing based on hypothesis set optimization techniques[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 28(1): 129-148. doi: 10.1007/s11045-015-0337-4 [15] CHEN J, CHEN Y Z, QIN D, et al. An elastic net-based hybrid hypothesis method for compressed video sensing[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2015, 74(6): 2085-2108. doi: 10.1007/s11042-013-1743-y [16] ZHAO C, MA S W, GAO W. Image compressive-sensing recovery using structured Laplacian sparsity in DCT domain and multi-hypothesis prediction[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-6. [17] ZHENG S, ZHANG X P, CHEN J, et al. A high-efficiency compressed sensing-based terminal-to-cloud video transmission system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(8): 1905-1920. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2891415 [18] ZHENG S, CHEN J, ZHANG X P, et al. A new multihypothesis-based compressed video sensing reconstruction system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 23: 3577-3589. [19] LIU H, SUN R H. Iterative progressive-hypothesis prediction for forward interframe reconstruction of video compressive sensing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 24th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1-6. [20] 刘浩, 黄荣, 袁浩东. 面向上行流媒体的CS视频流技术前沿[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(7): 1545-1557. doi: 10.11834/jig.200487LIU H, HUANG R, YUAN H D. Survey on compressive sensing video stream for uplink streaming media[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(7): 1545-1557(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.200487 [21] 刘泉洋, 刘云清, 史俊, 等. 视频图像运动估计中的一维块匹配算法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2021, 33(3): 424-430.LIU Q Y, LIU Y Q, SHI J, et al. One-dimensional block matching algorithm in video image motion estimation[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2021, 33(3): 424-430(in Chinese). [22] LIU Q P, XI U, ZHANG W C, et al. Improved image matching algorithm based on LK optical flow and grid motion statistics[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications in Technology, 2022, 68(1): 49-57. doi: 10.1504/IJCAT.2022.123238 -






 下载:
下载: