-
摘要:
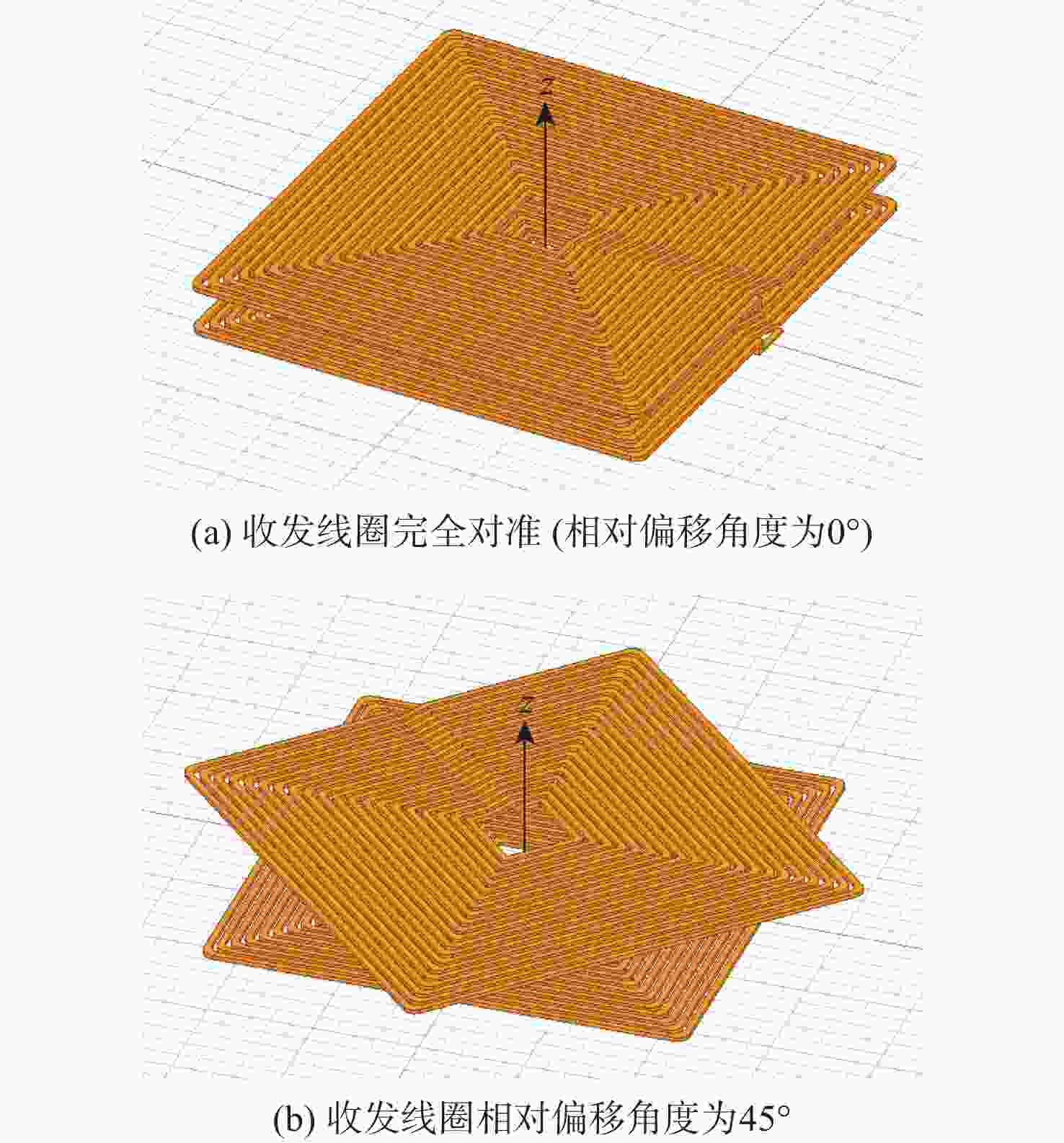
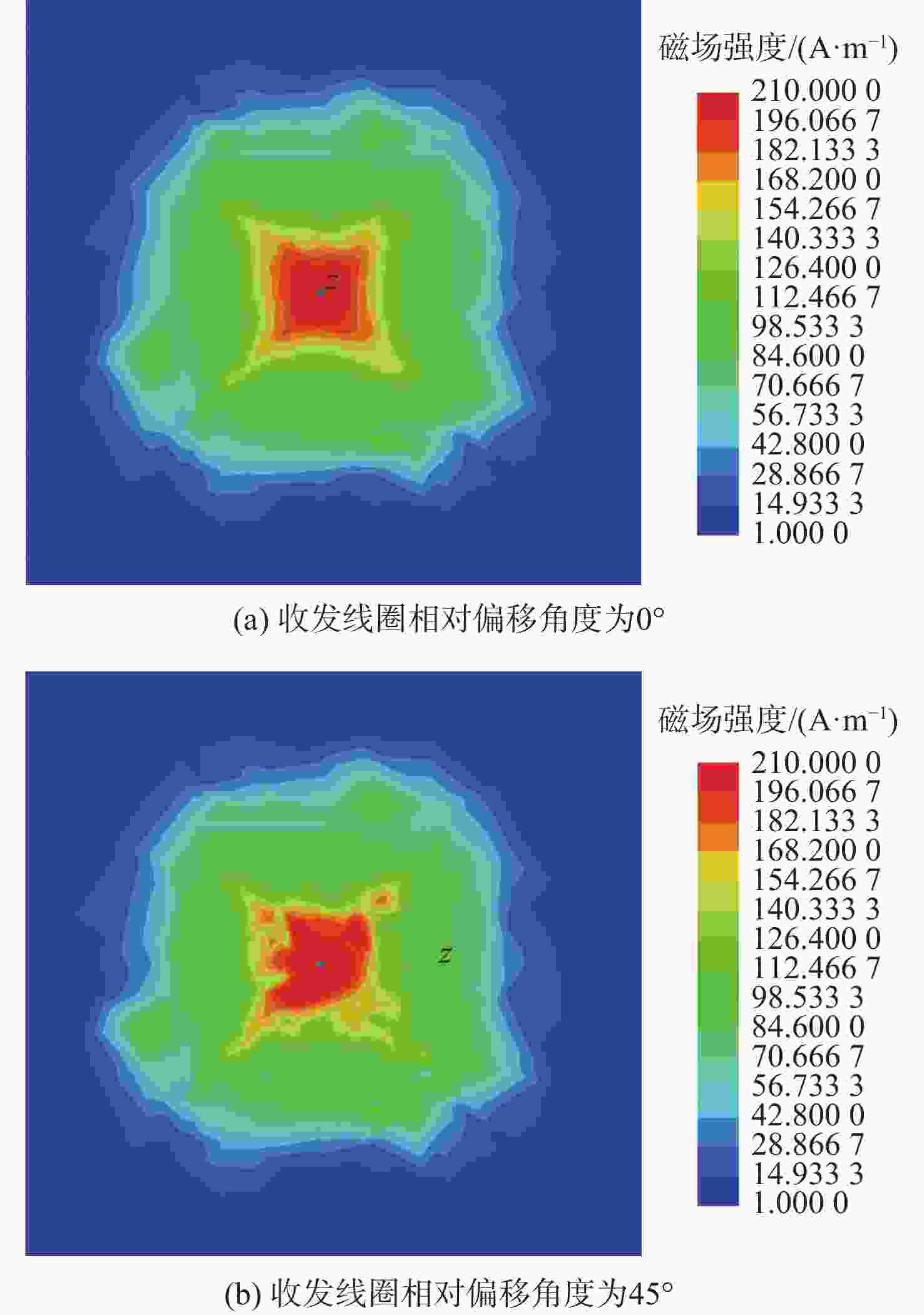
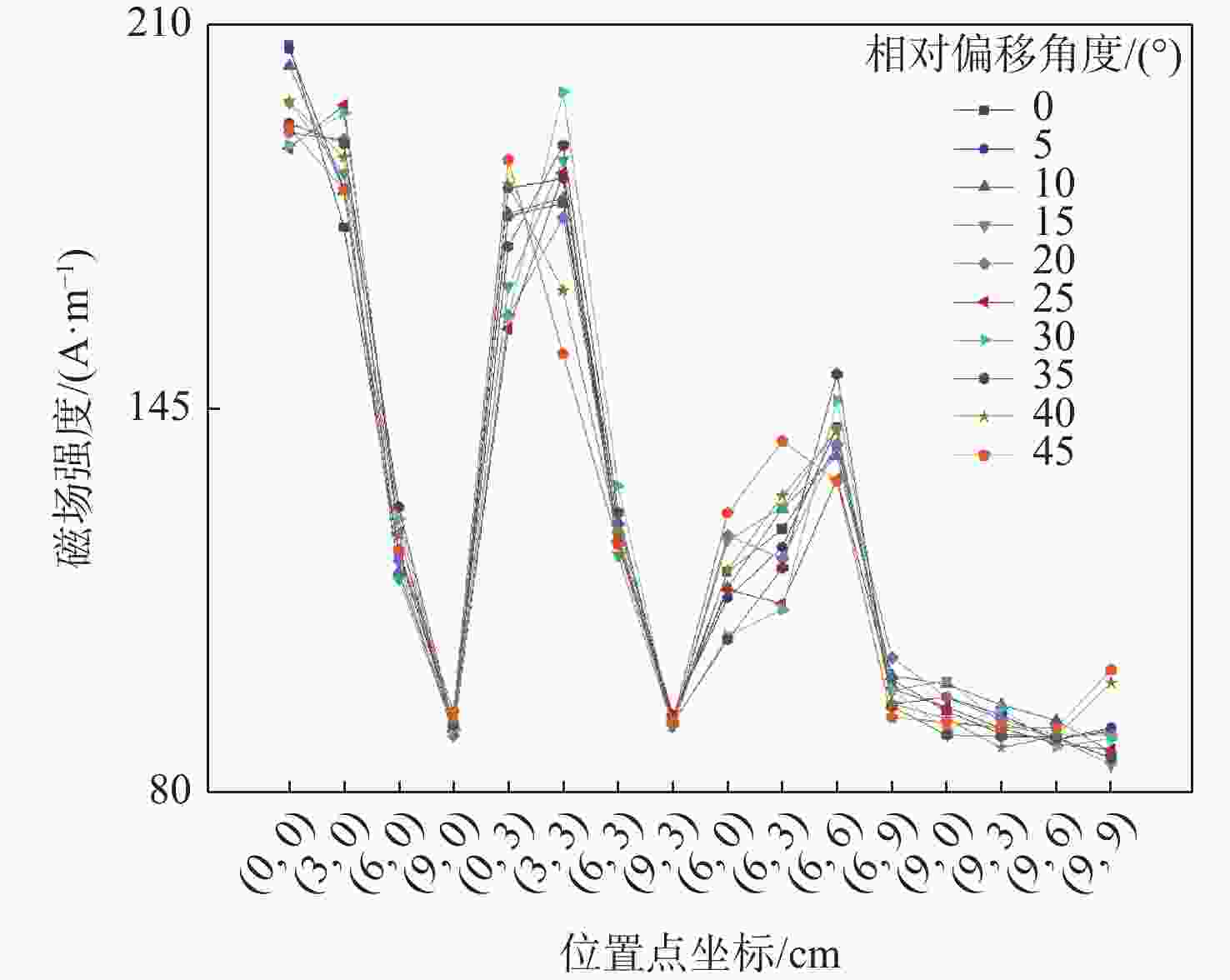
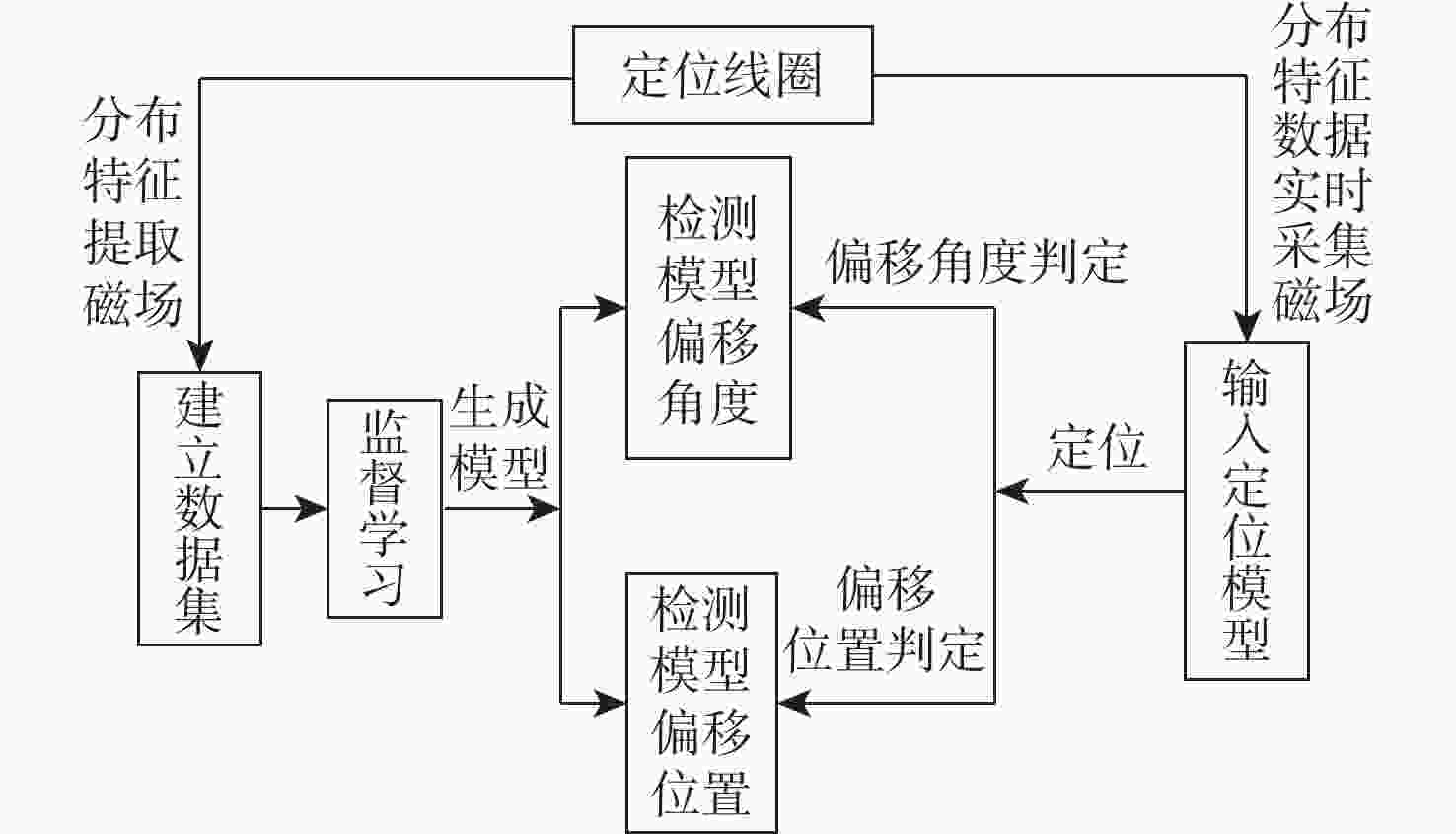
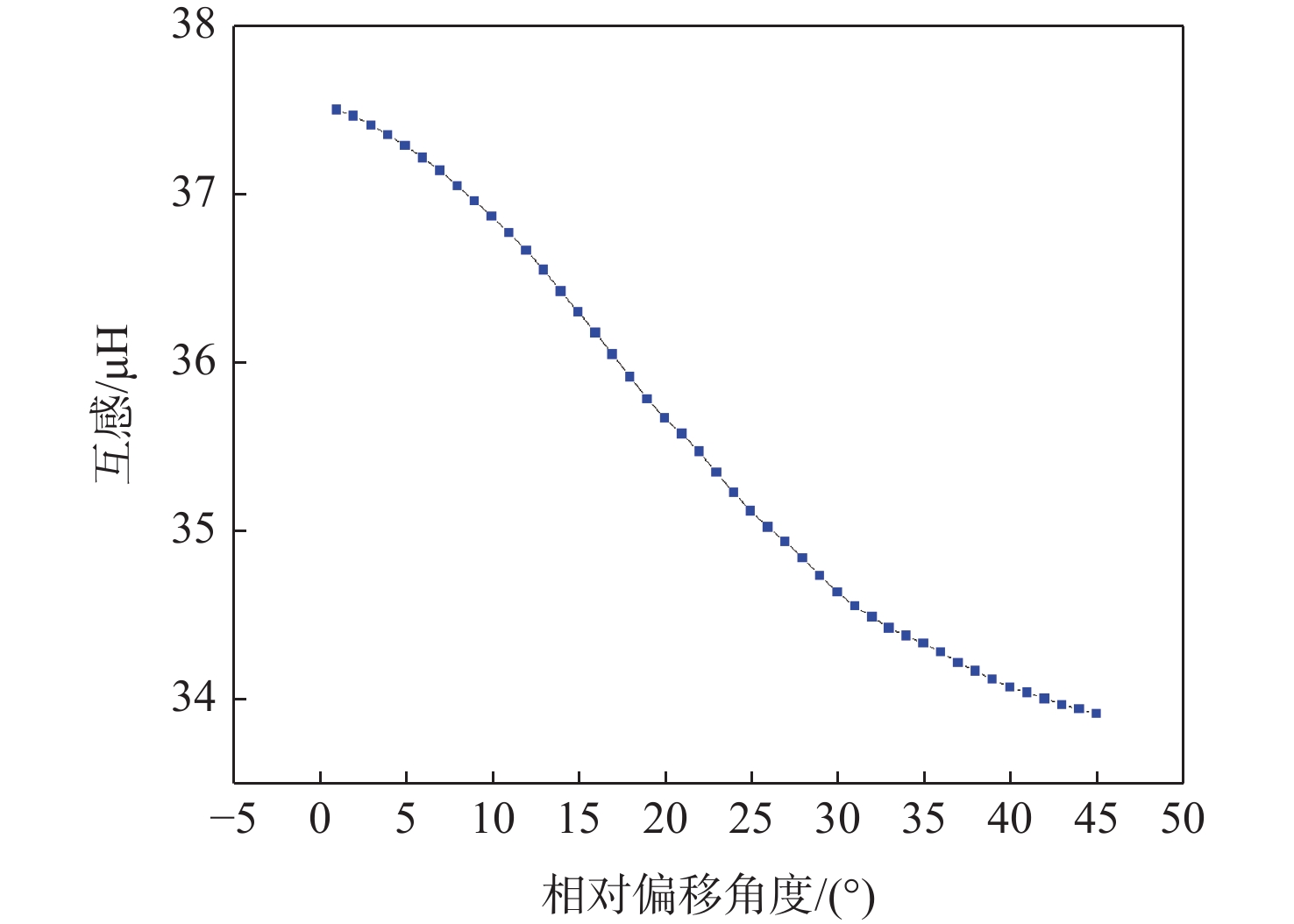
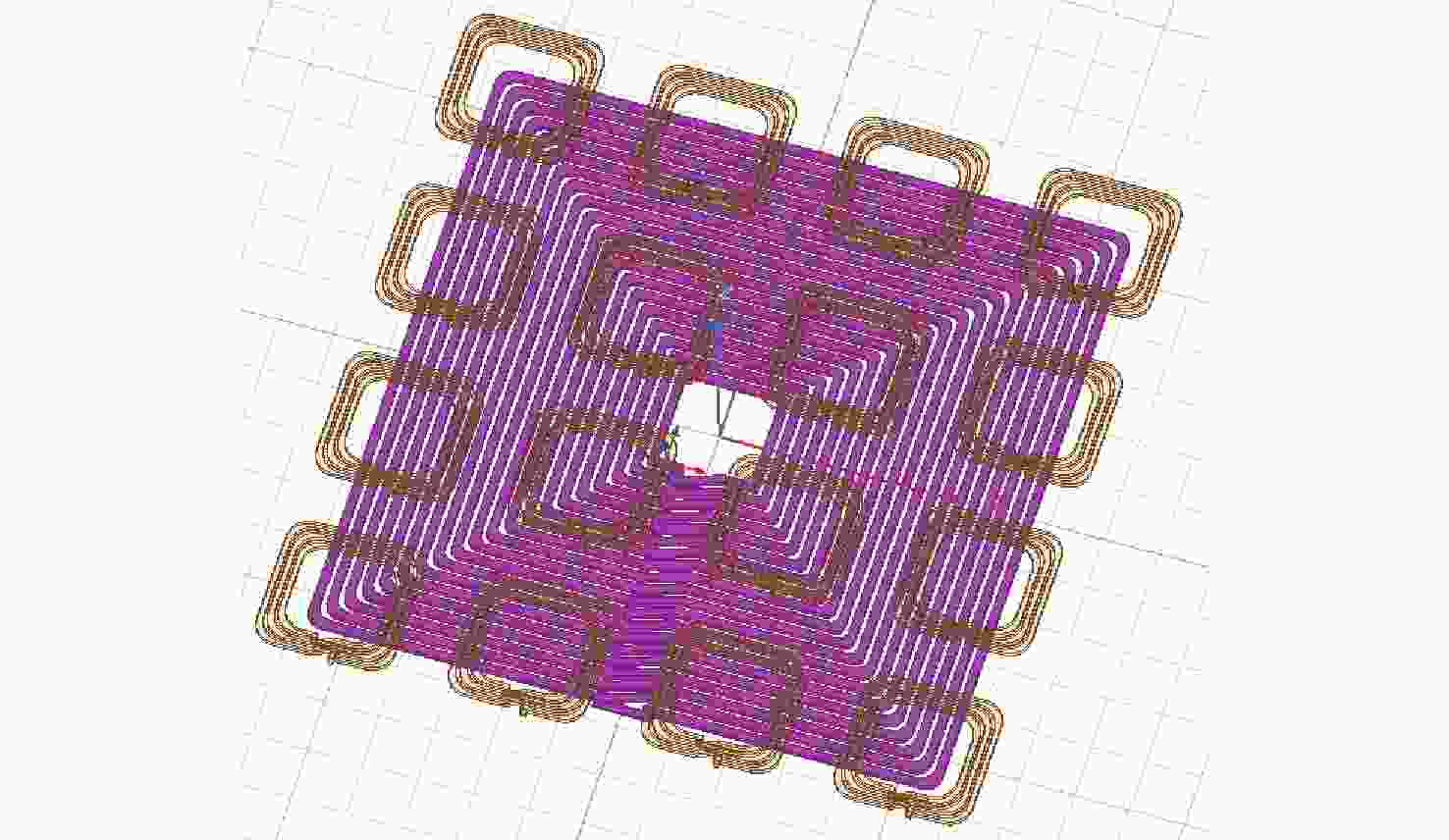
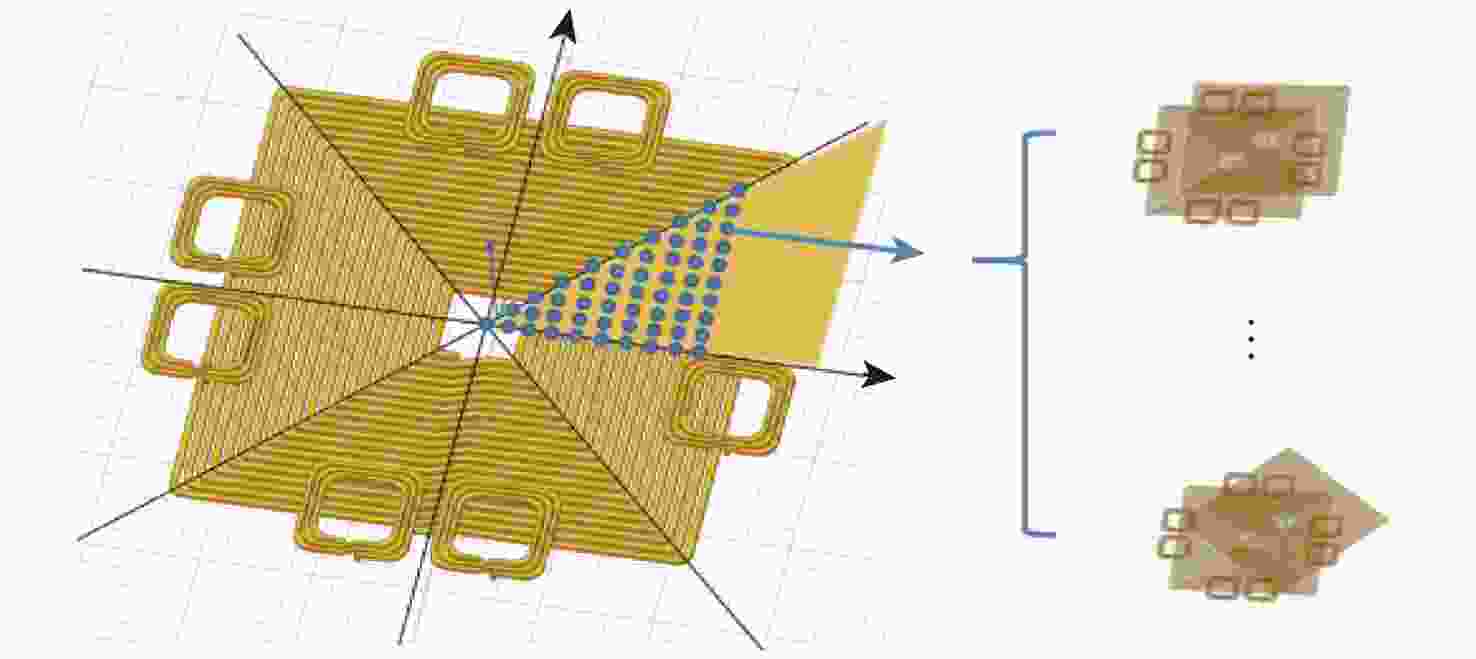
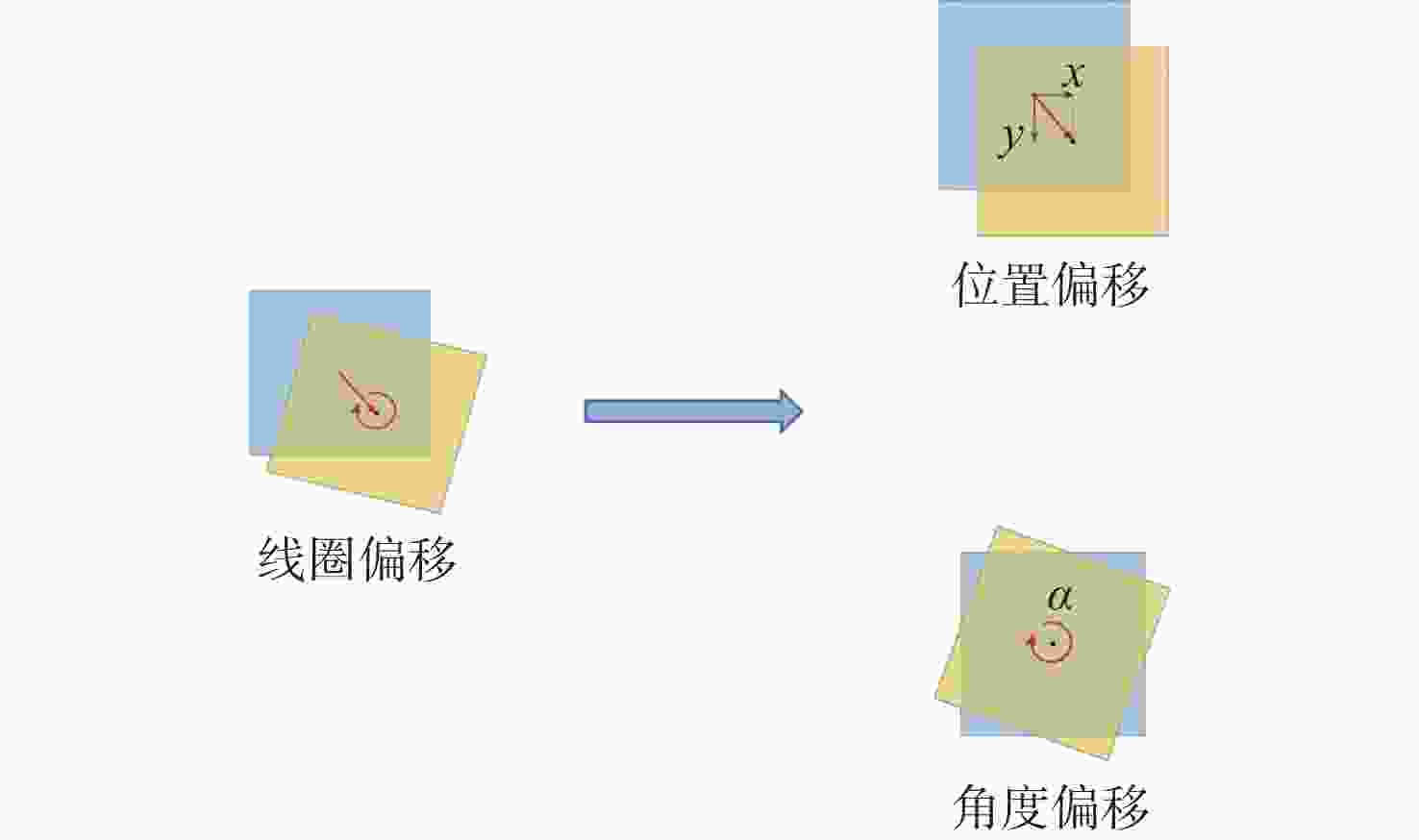
磁耦合谐振式无线电能传输技术广泛应用于无人机充电,其充电线圈定位精度直接影响充电效率。针对现有方法忽略无人机角度偏移的问题,提出一种基于监督式机器学习的线圈定位方法,可同时检测位置偏移和角度偏移。所提方法通过建立辅助线圈电压与线圈相对位置/角度标签的数据集,利用监督学习回归算法训练定位模型。经仿真和试验验证:位置偏移检测精度达1 cm,角度偏移检测精度达1°。结合停机坪的机械调节装置移动/旋转发射线圈,可有效实现线圈对准,提升充电效率。
Abstract:Magnetically coupled resonant wireless power transfer technology is widely used in drone charging, where the positioning accuracy of charging coils directly affects charging efficiency. To address the limitation of existing methods that neglect angular misalignment of drones, this paper proposes a coil positioning method based on supervised machine learning, capable of simultaneously detecting positional and angular offsets. The method establishes a dataset using auxiliary coil voltages as features and relative positional/angular offsets as labels, then trains a positioning model via supervised learning regression algorithms. Simulation and experimental validation demonstrate a positional detection accuracy of 1 cm and angular detection accuracy of 1°. By integrating mechanical adjustment mechanisms on the charging pad to translate or rotate the transmitter coil, precise coil alignment is achieved, enhancing system charging efficiency.
-
Key words:
- UAV /
- wireless charging /
- coil location /
- angle offset /
- supervised learning
-
表 1 仿真模型参数
Table 1. Simulation model parameters
仿真参数 数值 线圈材料 铜 线圈尺寸/(mm×mm) 230×230 线圈匝数/匝 20 线径/mm 3 线圈匝间距/mm 2 收发线圈间距/mm 20 原边线圈激励电流幅值/A 2 激励频率/kHz 110 表 2 定位线圈仿真参数
Table 2. Positioning coil simulation parameters
仿真参数 数值 线圈材料 铜 线圈尺寸/(mm×mm) 50×50 线圈匝数/匝 3 线径/mm 2 线圈匝间距/mm 1 表 3 定位模型泛化性测试集
Table 3. Positioning model generalization test set
参数 数值 位置偏移坐标/cm {(5.1,6.1),(6.2,7.2),(7.3,8.3)
(8.4,9.4)(9.5,5.5)}角度偏移量/(°) {5.2,6.1,12.4,16.6,19.1,20.2,
26.6,30.8,31.1,31.2,32.4,41.6,
43.1,47.8,49.2,53.4,59.6,65.4,
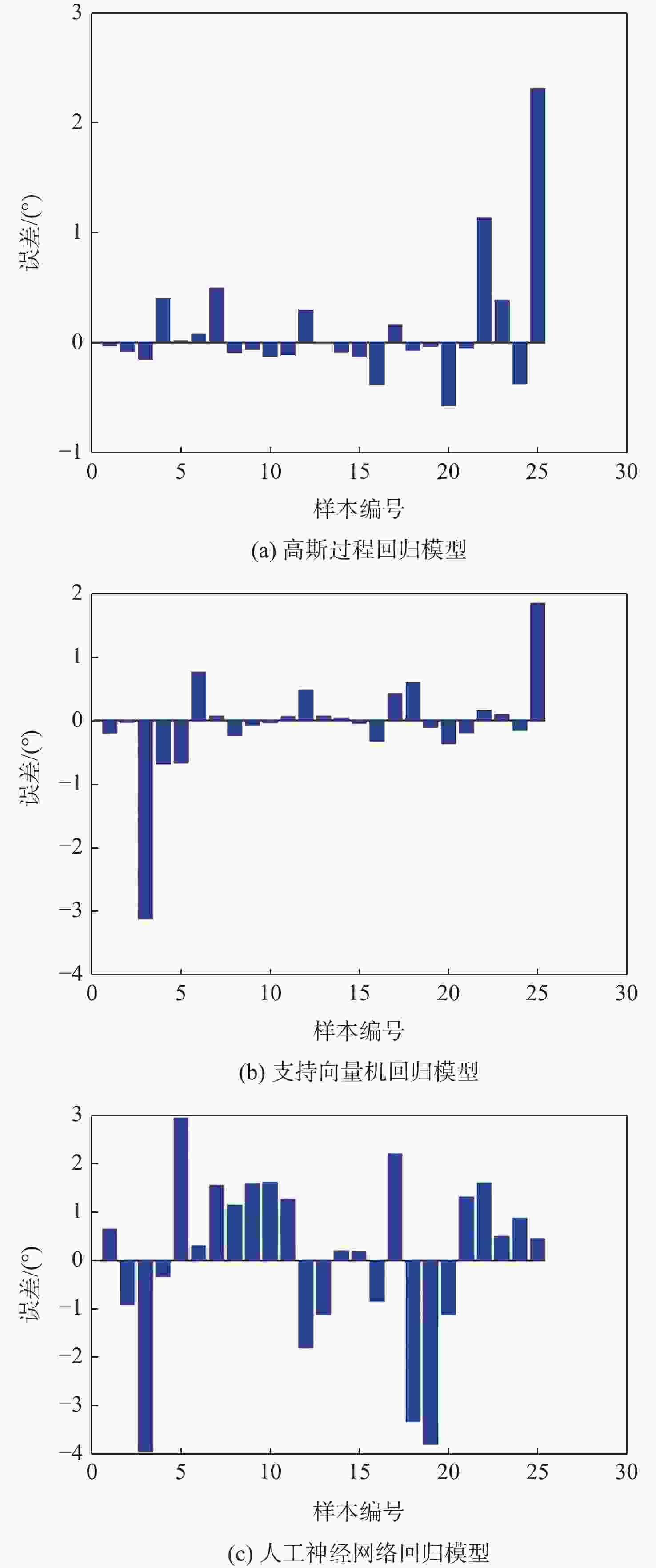
68.8,71.8,73.1,78.4,81.6,84.2,87.8}表 4 仿真测试结果
Table 4. Simulation test results
检测模型 MSE MAE 位置偏
移/cm2角度偏
移/(°)位置偏
移/cm2角度偏
移/(°)高斯过程回归模型 0.0428 1.628×10−5 0.1096 0.0028 支持向量机回归模型 0.0887 0.0011 0.2968 0.0334 人工神经网络回归模型 0.1431 1.1668 0.6502 0.8170 表 5 模型泛化性对比
Table 5. Comparison of model generalization
检测模型 MSE MAE 位置
偏移/cm2角度
偏移/(°)位置
偏移/cm2角度
偏移/(°)高斯过程回归模型 2.8161 0.6901 1.4656 0.4830 支持向量机回归模型 3.5701 0.6354 1.9828 0.4345 人工神经网络
回归模型6.0068 1.0831 2.1307 0.8050 表 6 试验平台系统参数
Table 6. Experimental platform system parameters
参数 数值 发射线圈尺寸/(mm×mm) 230×230 接收线圈尺寸/(mm×mm) 175×250 定位线圈尺寸/(mm×mm) 31×44 发射线圈自感/μH 96.2 接收线圈自感/μH 79.7 定位线圈自感/μH 30 发射线圈补偿电容/μF 0.036 接收线圈补偿电容/μF 0.044 激励电压/V 48 激励电压频率/kHz 110 表 7 试验测试结果
Table 7. Experimental test results
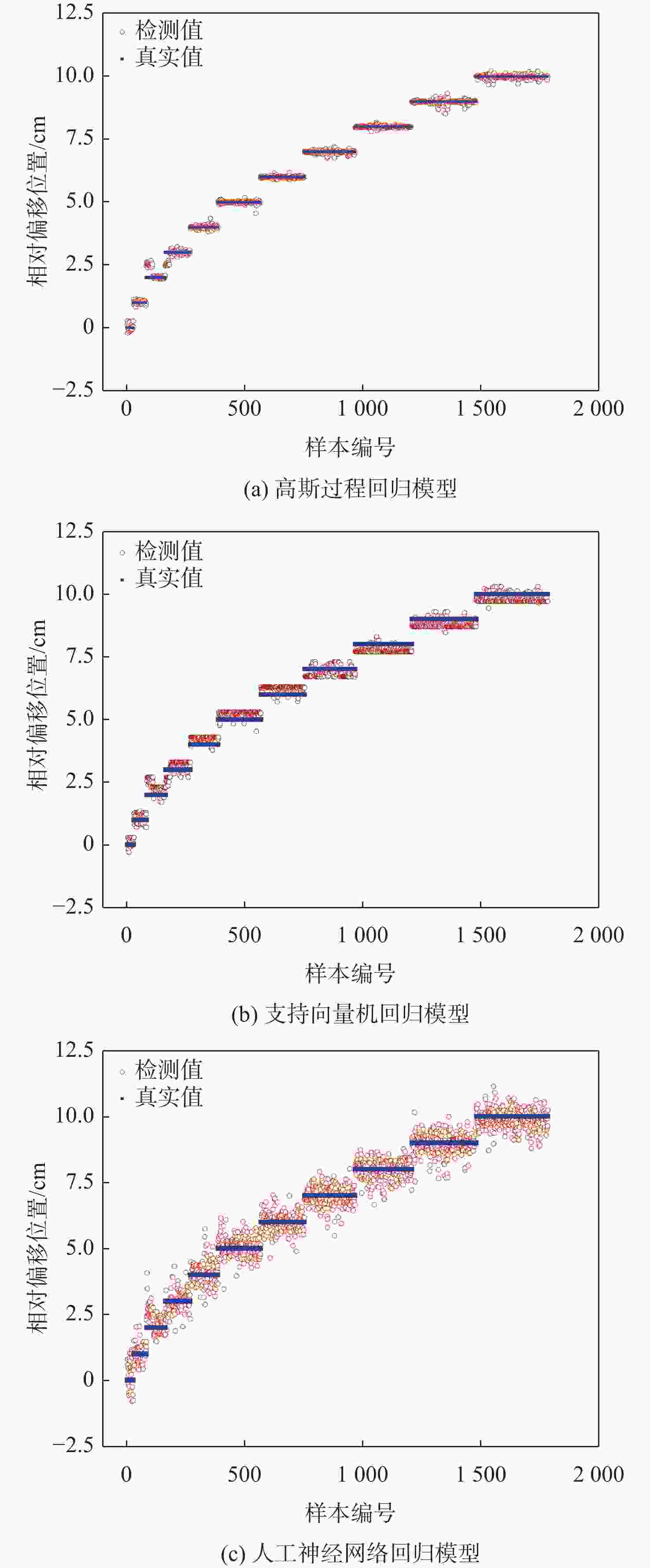
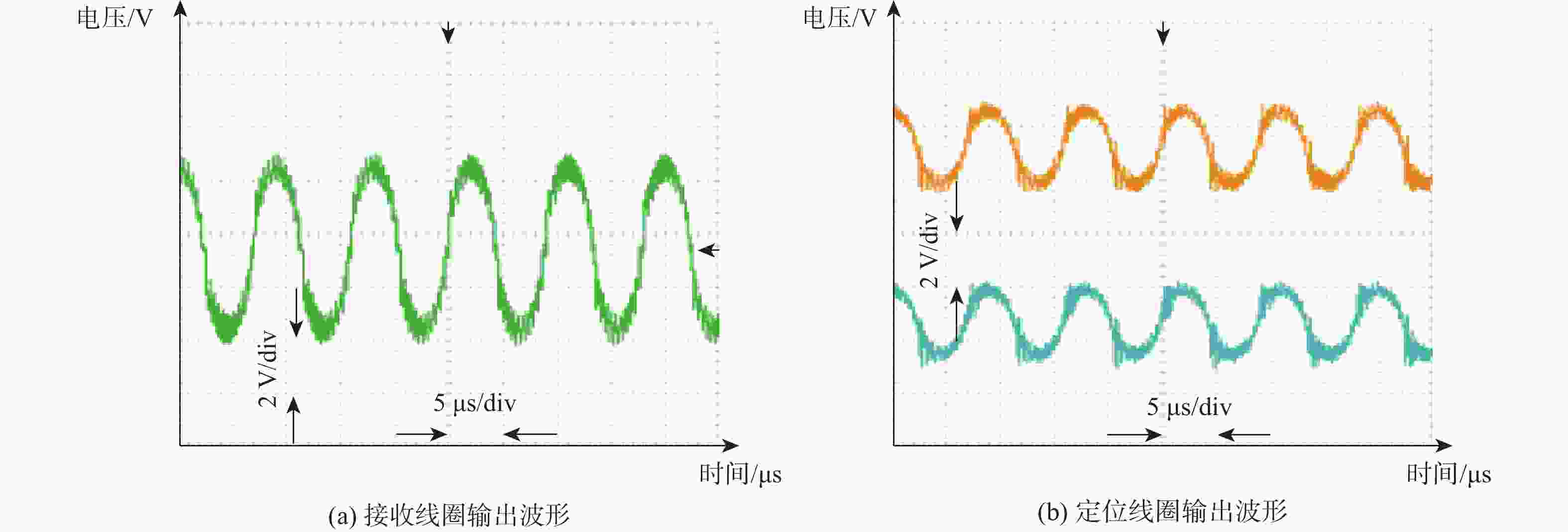
偏移检测模型 相对偏移角度/(°) 相对偏移位置/cm 第1组 第2组 第3组 第4组 第5组 第1组 第2组 第3组 第4组 第5组 高斯过程回归模型 6.58 19.47 31.15 45.87 80.69 0.57 1.07 3.44 4.17 3.66 支持向量机回归模型 6.53 19.40 31.77 45.79 81.11 0.74 0.71 1.58 2.17 3.62 人工神经网络回归模型 5.65 16.97 31.94 43.76 81.51 1.21 0.70 1.35 4.45 4.18 注:实际相对偏移角度分别为7°、19°、32°、45°、80°;实际相对偏移位置分别为0 cm、1 cm、2 cm、3 cm、4 cm。 -
[1] 马秀娟, 武帅, 蔡春伟, 等. 应用于无人机的无线充电技术研究[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2019, 23(8): 1-9.MA X J, WU S, CAI C W, et al. Research on wireless charging technology applied to UAVs[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2019, 23(8): 1-9(in Chinese). [2] 王云哲, 徐国宁, 王生, 等. 蜂群无人机充电排队优化方法[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(10): 323928.WANG Y Z, XU G N, WANG S, et al. Optimization of charging queuing of UAV swarming[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(10): 323928(in Chinese). [3] ZHANG Z, PANG H L, GEORGIADIS A, et al. Wireless power transfer: an overview[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(2): 1044-1058. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2835378 [4] 薛明, 杨庆新, 章鹏程, 等. 无线电能传输技术应用研究现状与关键问题[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(8): 1547-1568.XUE M, YANG Q X, ZHANG P C, et al. Application status and key issues of wireless power transmission technology[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(8): 1547-1568(in Chinese). [5] 武帅, 蔡春伟, 陈轶, 等. 多旋翼无人机无线充电技术研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(3): 555-565.WU S, CAI C W, CHEN Y, et al. Research progress and development trend of multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicles wireless charging technology[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(3): 555-565(in Chinese). [6] 章晨. 基于磁传感的电动汽车无线充电线圈高精度对准关键技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2021: 4-9.ZHANG C. Research on key technologies of high precision alignment of wireless charging coil of electric vehicle based on magnetic sensing[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021: 4-9(in Chinese). [7] 程泽乾. 基于数据驱动技术的无线充电系统定位/异物检测研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021: 17-23.CHENG Z Q. Research on location/foreign body detection of wireless charging system based on data-driven technology[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021: 17-23(in Chinese). [8] 潘志新, 杨晓梅, 王成亮, 等. 基于BP神经网络的线圈定位技术研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 2024, 61(2): 197-203.PAN Z X, YANG X M, WANG C L, et al. Research on coil positioning technology based on BP neural network[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2024, 61(2): 197-203(in Chinese). [9] BAI T H, MEI B Q, ZHAO L, et al. Machine learning-assisted wireless power transfer based on magnetic resonance[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 109454-109459. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2933679 [10] SHEN H, TAN P G, SONG B, et al. Receiver position estimation method for multitransmitter WPT system based on machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58(1): 1231-1241. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2021.3103489 [11] WANG R Y, HUANG X L, LI J C, et al. Accurate offset angle detection strategy for wireless charging coils based on electronic compasses[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 58579-58588. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3071755 [12] 徐诗卉, 张欢, 姚辰, 等. 电动汽车无线充电系统的精确定位方法[J]. 仪表技术与传感器, 2020(11): 59-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2020.11.013XU S H, ZHANG H, YAO C, et al. Fine positioning method for wireless charging system of electric vehicles[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2020(11): 59-63(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2020.11.013 [13] ZHANG K H, DU L N, ZHU Z B, et al. A normalization method of delimiting the electromagnetic hazard region of a wireless power transfer system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2018, 60(4): 829-839. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2017.2752300 [14] 高昊天, 陈云霞. 基于机器学习的锂离子电池健康状态分类与预测[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2023, 49(12): 3467-3475.GAO H T, CHEN Y X. A machine learning based method for lithium-ion battery state of health classification and prediction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(12): 3467-3475(in Chinese). [15] 朱琼锋, 李家腾, 乔骥, 等. 人工智能技术在新能源功率预测的应用及展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(8): 3027-3048.ZHU Q F, LI J T, QIAO J, et al. Application and prospect of artificial intelligence technology in renewable energy forecasting[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(8): 3027-3048(in Chinese). [16] 李金金, 蔡俊飞, 韩彦强, 等. 基于机器学习的电化学能源电池宏微观设计[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2023, 51(2): 438-451.LI J J, CAI J F, HAN Y Q, et al. Macro-/micro-design of electrochemical energy battery based on machine learning[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 51(2): 438-451(in Chinese). [17] 余柏杨, 吕宏强, 周岩, 等. 基于机器学习的高速复杂流场流动控制效果预测分析[J]. 实验流体力学, 2022, 36(3): 44-54. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20210168YU B Y, LV H Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Predictive analysis of flow control in high-speed complex flow field based on machine learning[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2022, 36(3): 44-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.11729/syltlx20210168 [18] 戚兴怡, 胡耀峰, 王若愚, 等. 机器学习在新材料筛选方面的应用进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 158-174. doi: 10.6023/A22110446QI X Y, HU Y F, WANG R Y, et al. Recent advance of machine learning in selecting new materials[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 158-174(in Chinese). doi: 10.6023/A22110446 [19] 王方成, 刘玉敏, 崔庆安. 基于高斯过程回归的混合型参数建模及优化[J]. 统计与决策, 2023, 39(1): 34-39.WANG F C, LIU Y M, CUI Q A. Hybrid parameter modeling and optimization based on gaussian process regression[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2023, 39(1): 34-39(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: