A matching method based on improved SuperPoint and linear Transformer for optical and infrared images
-
摘要:
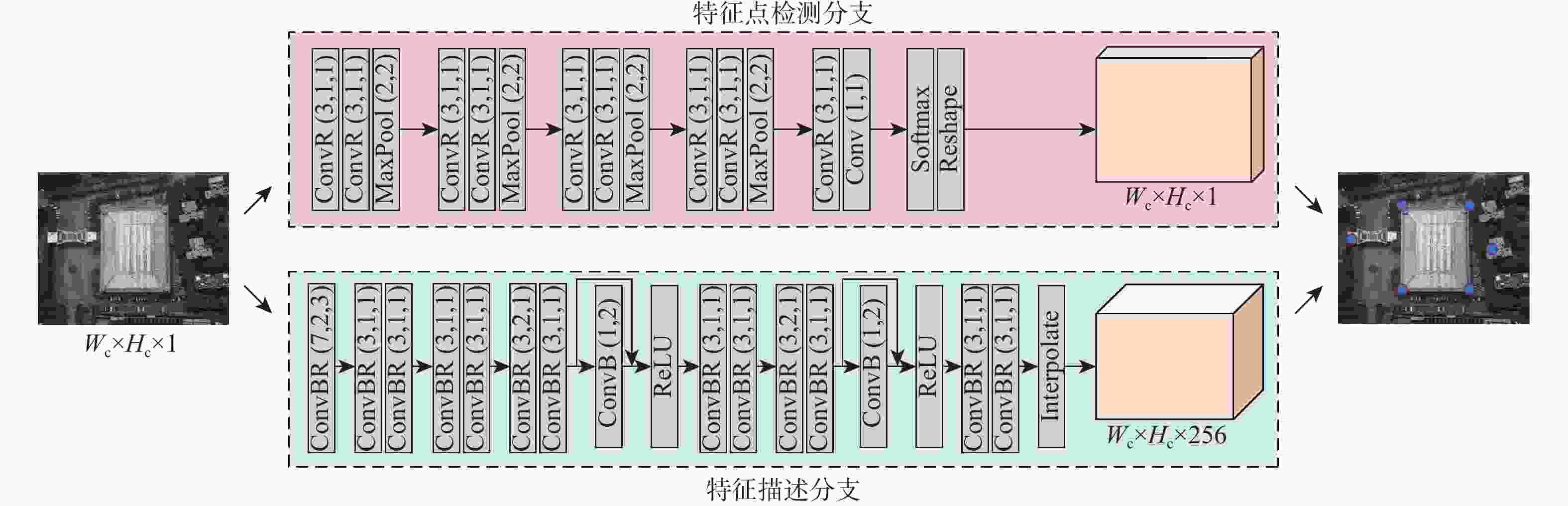
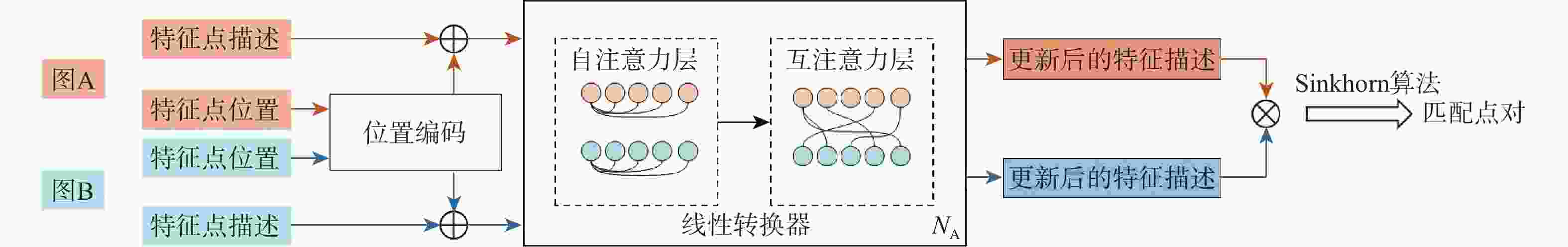
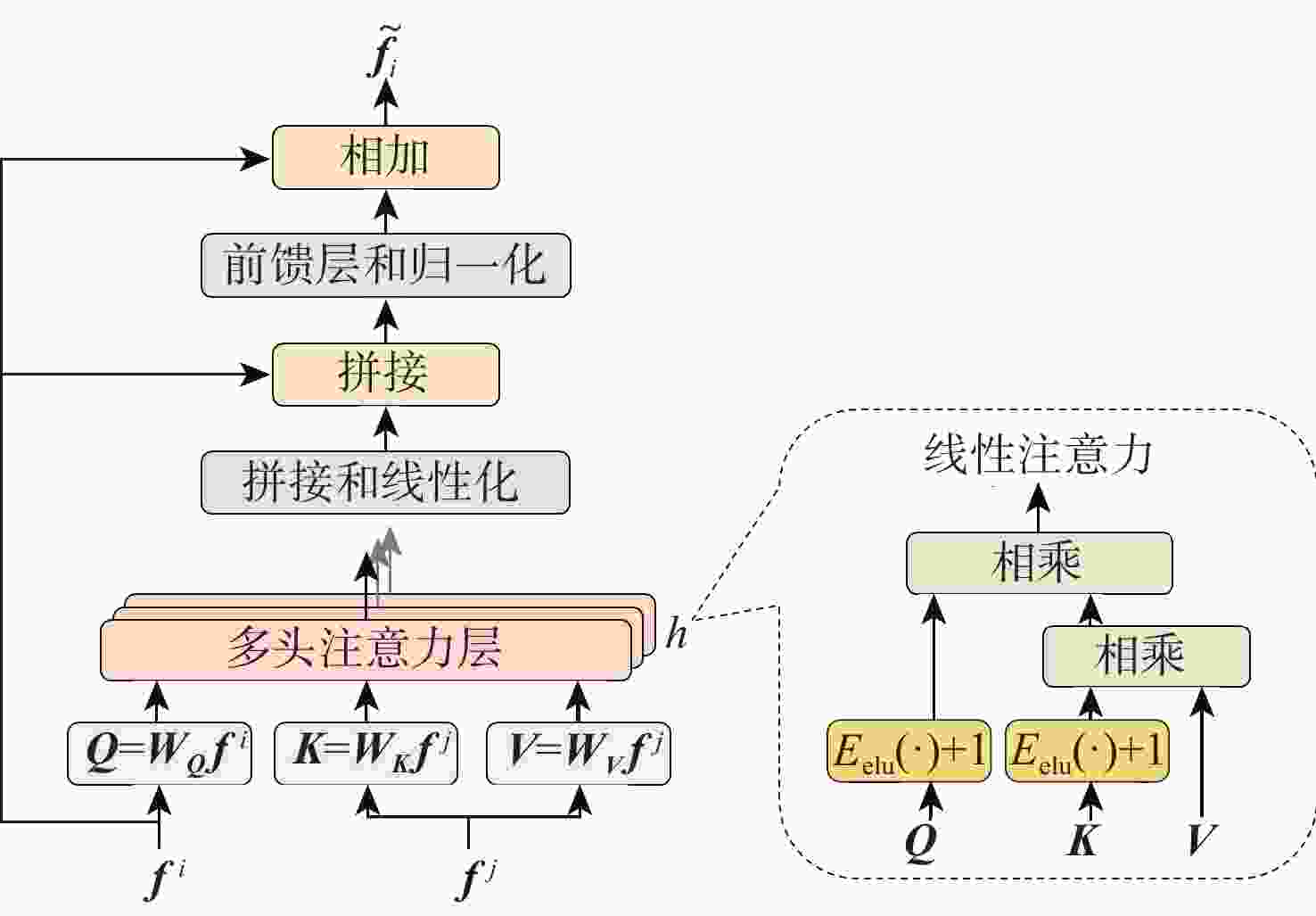
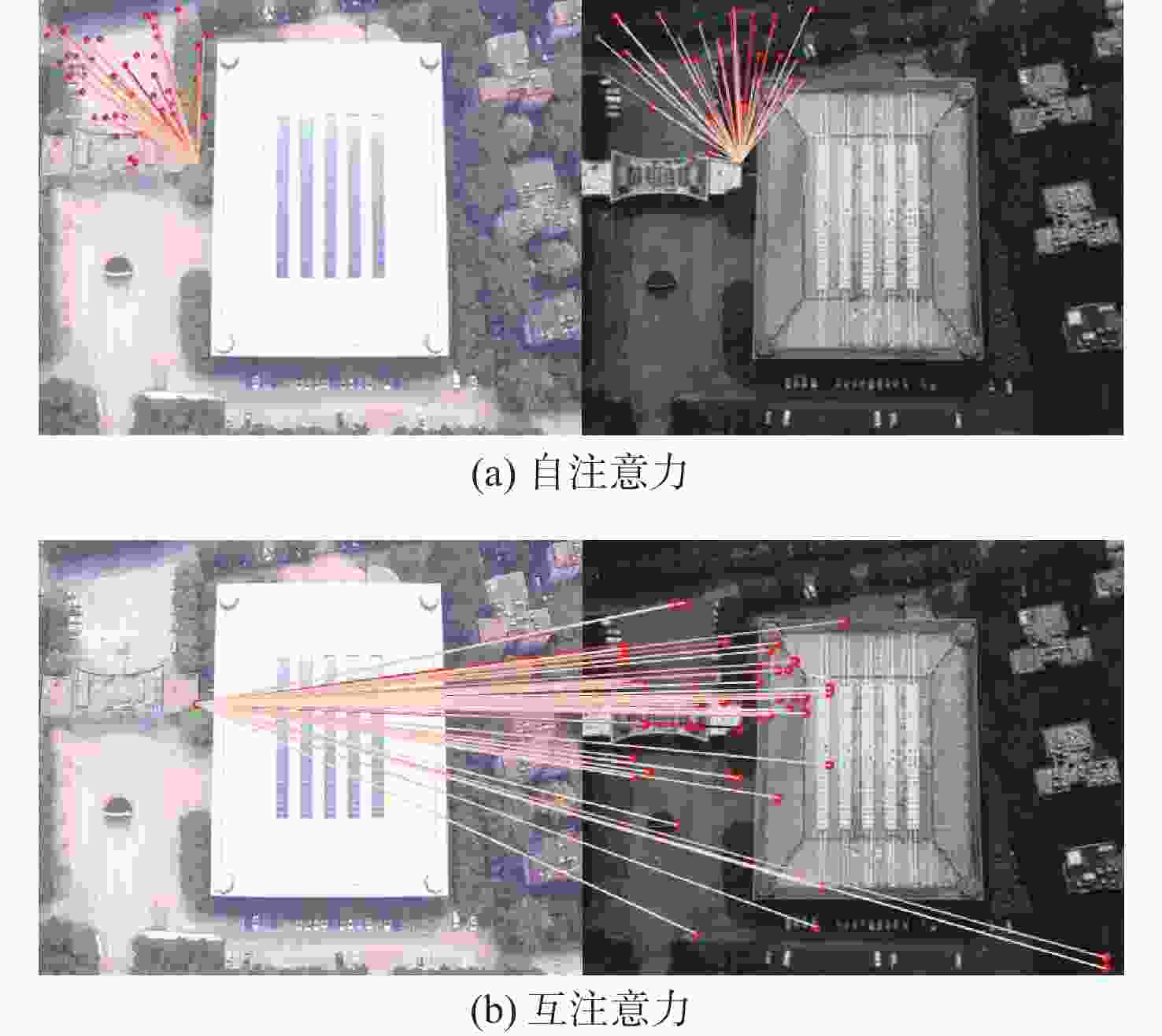
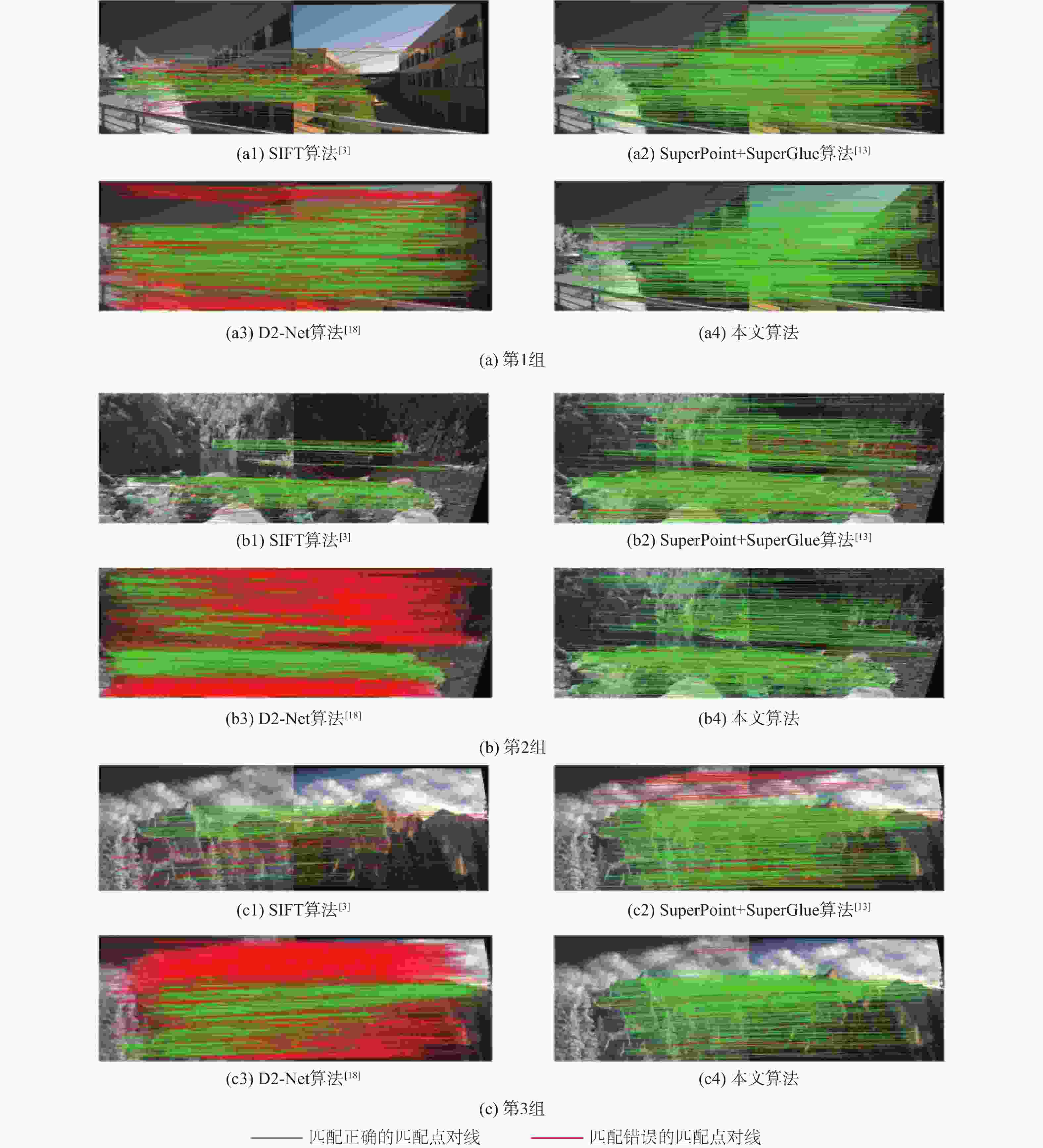
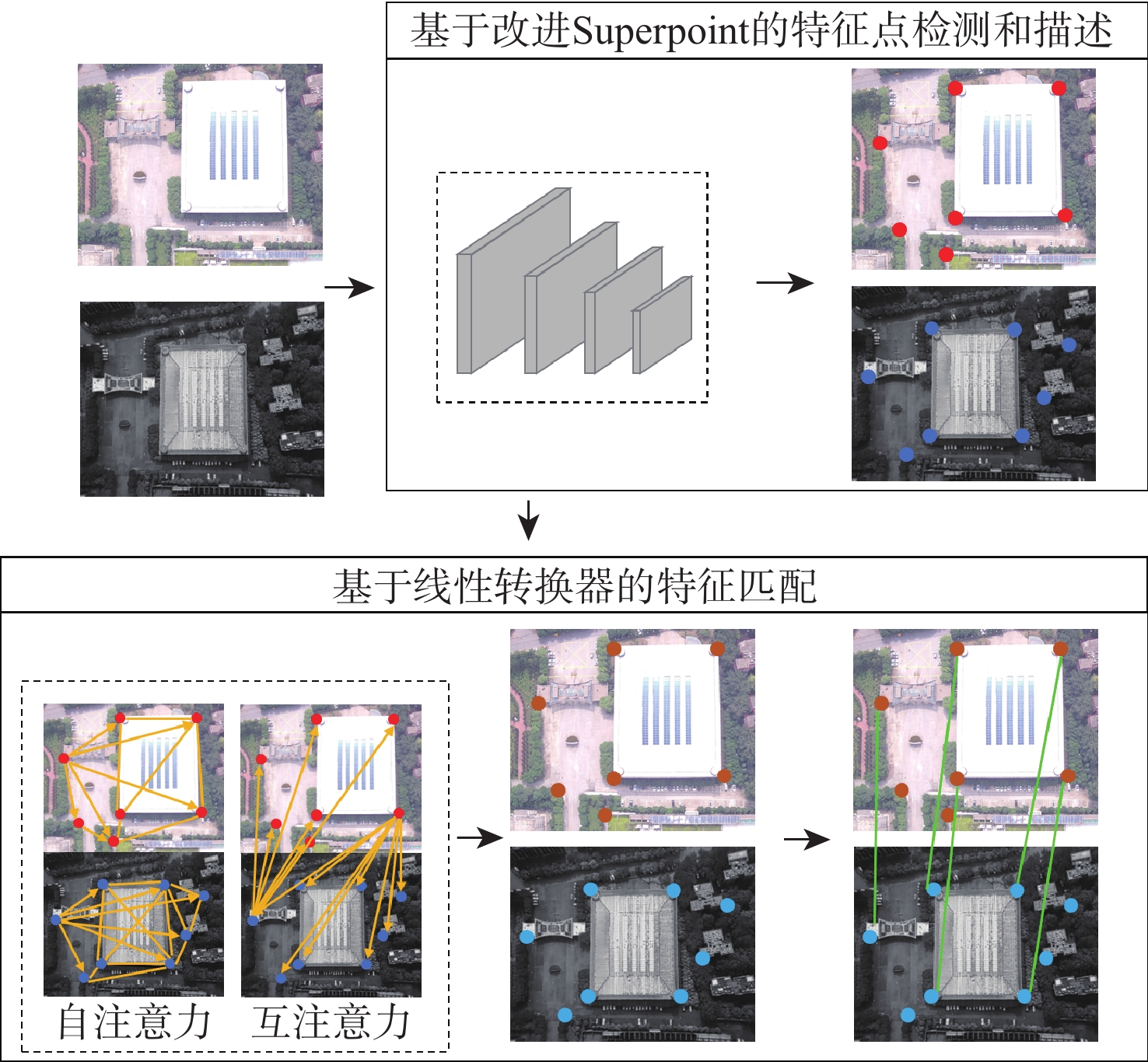
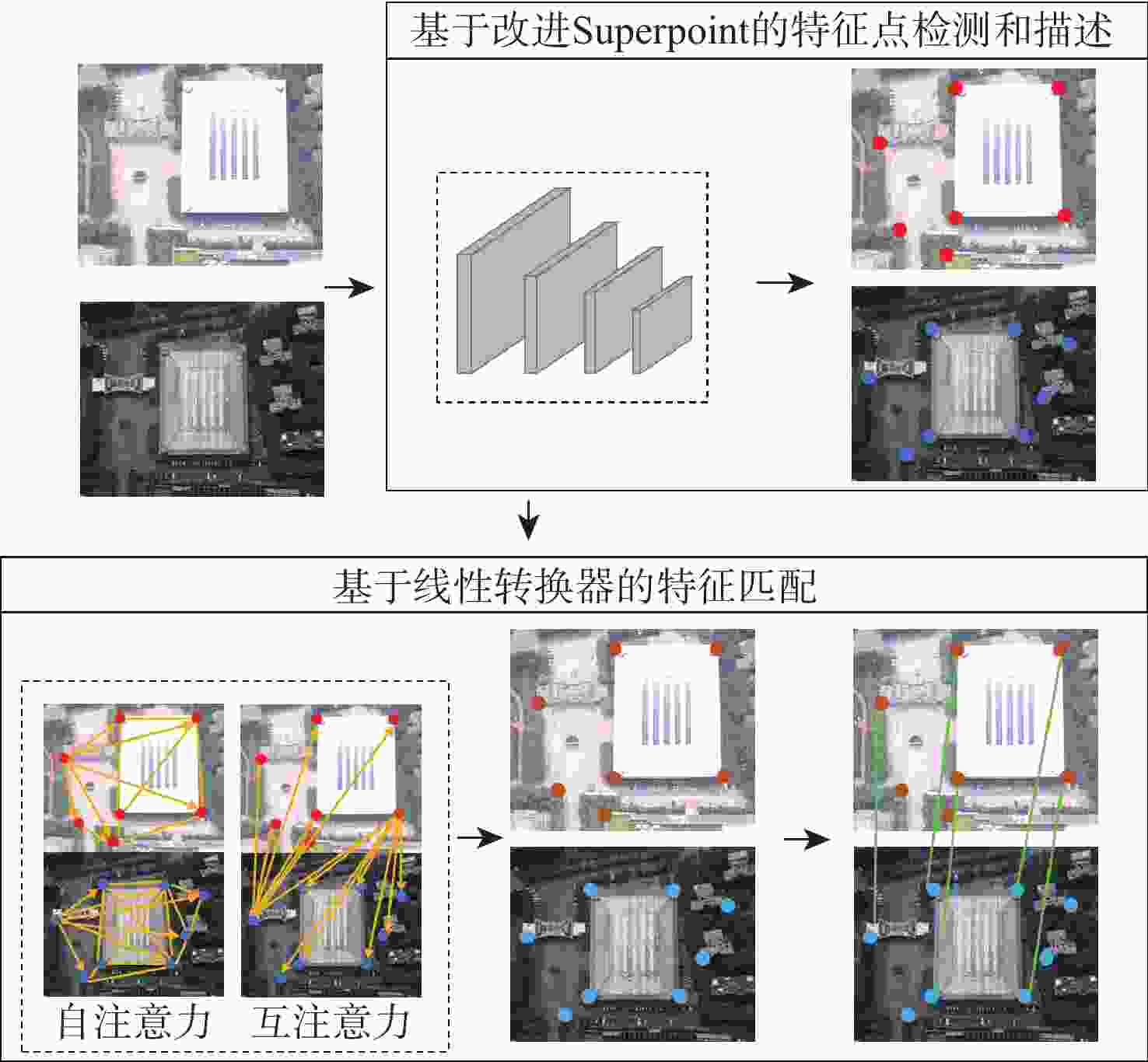
针对可见光和红外图像的异源图像匹配难度大、误匹配率高的问题,提出一种基于改进SuperPoint与线性转换器的深度学习匹配算法。首先在SuperPoint网络结构的基础上,引入特征金字塔的思想构建特征描述分支,基于铰链损失函数进行训练,从而较好地学习可见光与红外图像多尺度深层次特征,增大图像同名点对描述子的相似度;在特征匹配模块,利用线性转换器对SuperGlue匹配算法进行改进,聚合特征以提高匹配性能。在多个数据集上对所提算法进行实验验证,结果表明,与现有的算法相比,所提算法获得了更好的匹配效果,提高了匹配准确率。
Abstract:A deep learning matching algorithm based on improved SuperPoint and linear transformer was proposed to solve the problem of difficult matching and high mismatching rates between visible and infrared heterologous images. Firstly, based on the SuperPoint network structure, the algorithm introduced the idea of a feature pyramid to build a feature description branch and trained it based on the hinge loss function, so as to better learn the multi-scale deep features of visible and infrared images and increase the similarity of the image with correspondence points to the descriptor. In the feature matching module, SuperGlue was improved by adopting a linear transformer for aggregating features to obtain better matching results. Experiments conducted on multiple datasets demonstrate that the proposed method improves the matching precision and provides better matching performance in comparison with existing matching methods.
-
表 1 不同算法的实验结果对比
Table 1. Comparison experiment results of different algorithms
表 2 消融实验结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of ablation experiment results
网络结构 准确率/% 匹配误差/pixel 匹配耗时/s RGB-NIR数据集 VEDAI数据集 RGB-NIR数据集 VEDAI数据集 RGB-NIR数据集 VEDAI数据集 A 73.72 85.76 1.3818 1.3538 0.071 0.104 B 82.37 95.37 1.0767 0.9785 0.306 0.339 C 81.46 94.80 1.0867 0.9778 0.075 0.110 D 83.56 97.65 1.0745 0.9742 0.314 0.365 表 3 网络参数量对比
Table 3. Comparison of network parameters
特征提取与描述 特征匹配 SuperPoint SuperPoint -FPN SuperGlue L- SuperGlue 960000 4920000 11460000 11460000 -
[1] MA J Y, JIANG X Y, FAN A X, et al. Image matching from handcrafted to deep features: A survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(1): 23-79. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01359-2 [2] ZITOVÁ B, FLUSSER J. Image registration methods: A survey[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2003, 21(11): 977-1000. doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(03)00137-9 [3] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [4] MA J Y, ZHAO J, MA Y, et al. Non-rigid visible and infrared face registration via regularized Gaussian fields criterion[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(3): 772-784. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.09.005 [5] YE Y X, SHAN J, BRUZZONE L, et al. Robust registration of multimodal remote sensing images based on structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(5): 2941-2958. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2656380 [6] CHEN Y J, ZHANG X W, ZHANG Y N, et al. Visible and infrared image registration based on region features and edginess[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2018, 29(1): 113-123. doi: 10.1007/s00138-017-0879-6 [7] LI J Y, HU Q W, AI M Y. RIFT: Multi-modal image matching based on radiation-variation insensitive feature transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2019, 29: 3296-3310. [8] ARAR M, GINGER Y, DANON D, et al. Unsupervised multi-modal image registration via geometry preserving image-to-image translation[C]// 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 13407-13416. [9] PIELAWSKI N, WETZER E, ÖFVERSTEDT J, et al. CoMIR: Contrastive multimodal image representation for registration[C]// Proceedings of Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2020: 1-21. [10] YI K M, TRULLS E, LEPETIT V, et al. LIFT: Learned invariant feature transform[M]// Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 467-483. [11] DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, RABINOVICH A. SuperPoint: Self-supervised interest point detection and description[C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 337-33712. [12] LI K H, WANG L G, LIU L, et al. Decoupling makes weakly supervised local feature better[C]// 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 15817-15827. [13] SARLIN P E, DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, et al. SuperGlue: Learning feature matching with graph neural networks[C]// 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4937-4946. [14] SHI Y, CAI J X, SHAVIT Y, et al. ClusterGNN: Cluster-based coarse-to-fine graph neural network for efficient feature matching[C]// 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 12507-12516. [15] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 936-944. [16] CUTURI M. Sinkhorn distance: Lightspeed computation of optimal transport[C]// Proceedings of Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2013: 1-9. [17] KATHAROPOULOS A, VYAS A, PAPPAS N, et al. Transformers are RNNs: Fast autoregressive transformers with linear attention[C]//Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Machine Learing (ICML). New York: ACM Press, 2020: 1-10. [18] DUSMANU M, ROCCO I, PAJDLA T, et al. D2-net: a trainable CNN for joint description and detection of local features[C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8084-8093. [19] QUAN D, WANG S, NING H Y, et al. Element-wise feature relation learning network for cross-spectral image patch matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(8): 3372-3386. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3052756 [20] RAZAKARIVONY S, JURIE F. Vehicle detection in aerial imagery: A small target detection benchmark[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2016, 34: 187-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2015.11.002 [21] ROCCO I, ARANDJELOVIC R, SIVIC J. Convolutional neural network architecture for geometric matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(11): 2553-2567. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2865351 [22] HARTLEY R, ZISSERMAN A. Multiple view geometry in computer vision[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 117-123. -






 下载:
下载: