-
摘要:
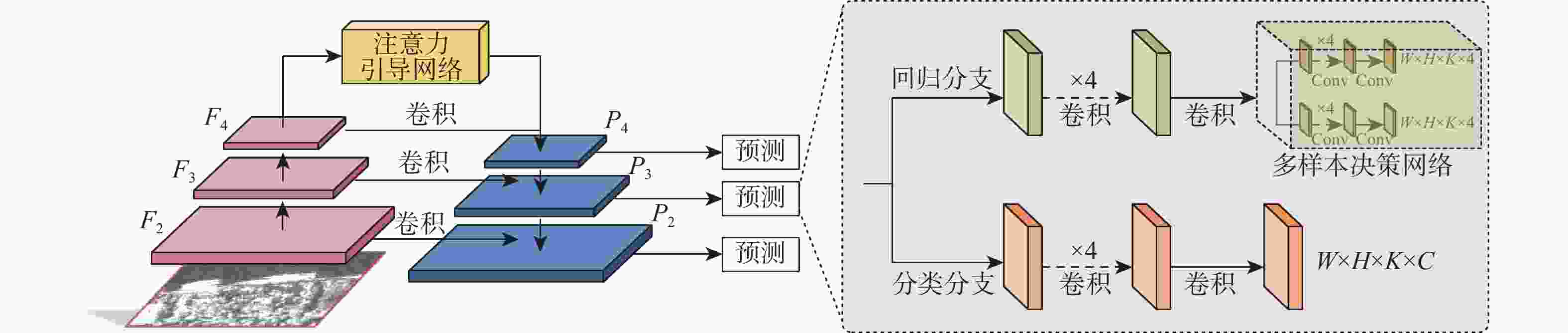
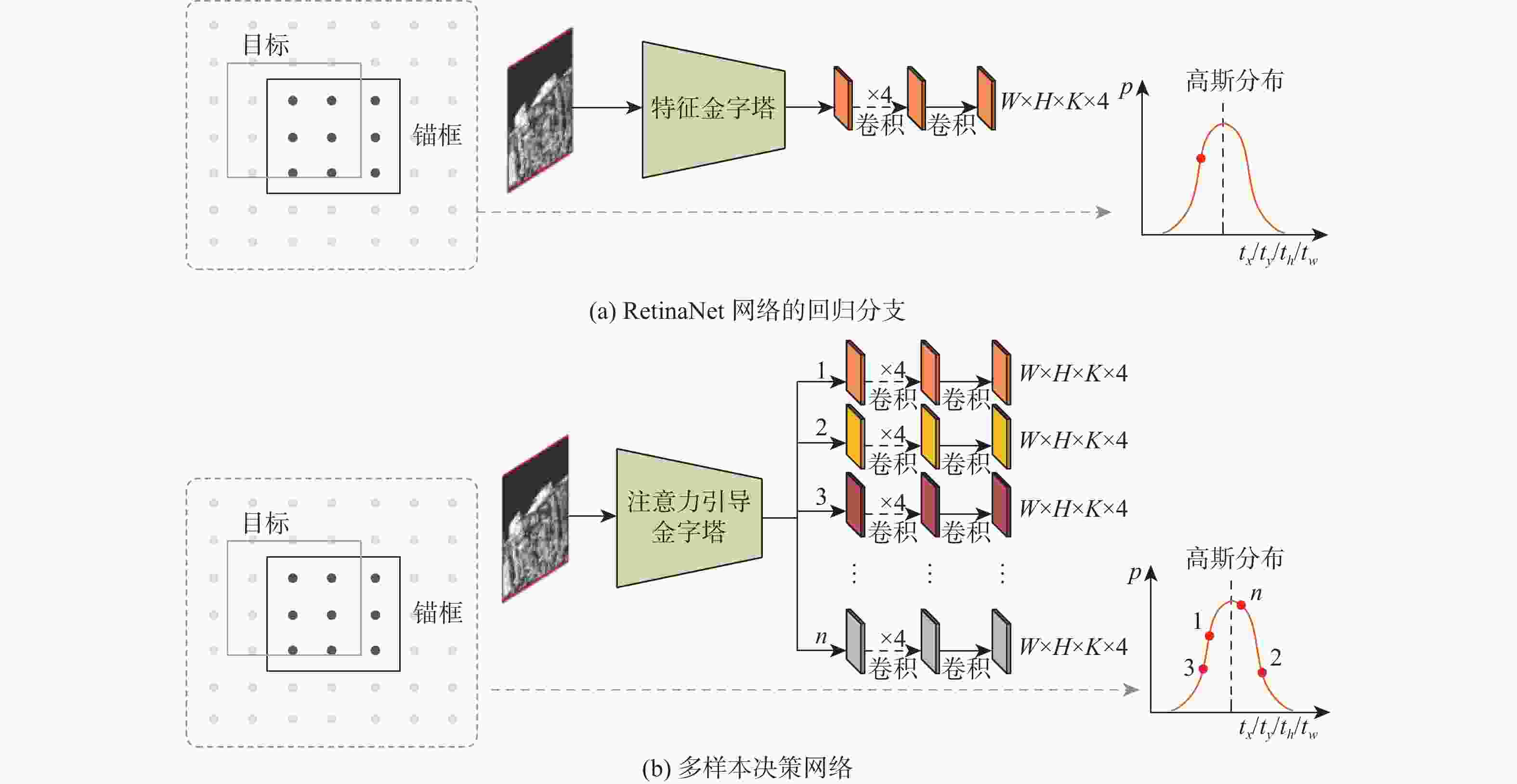
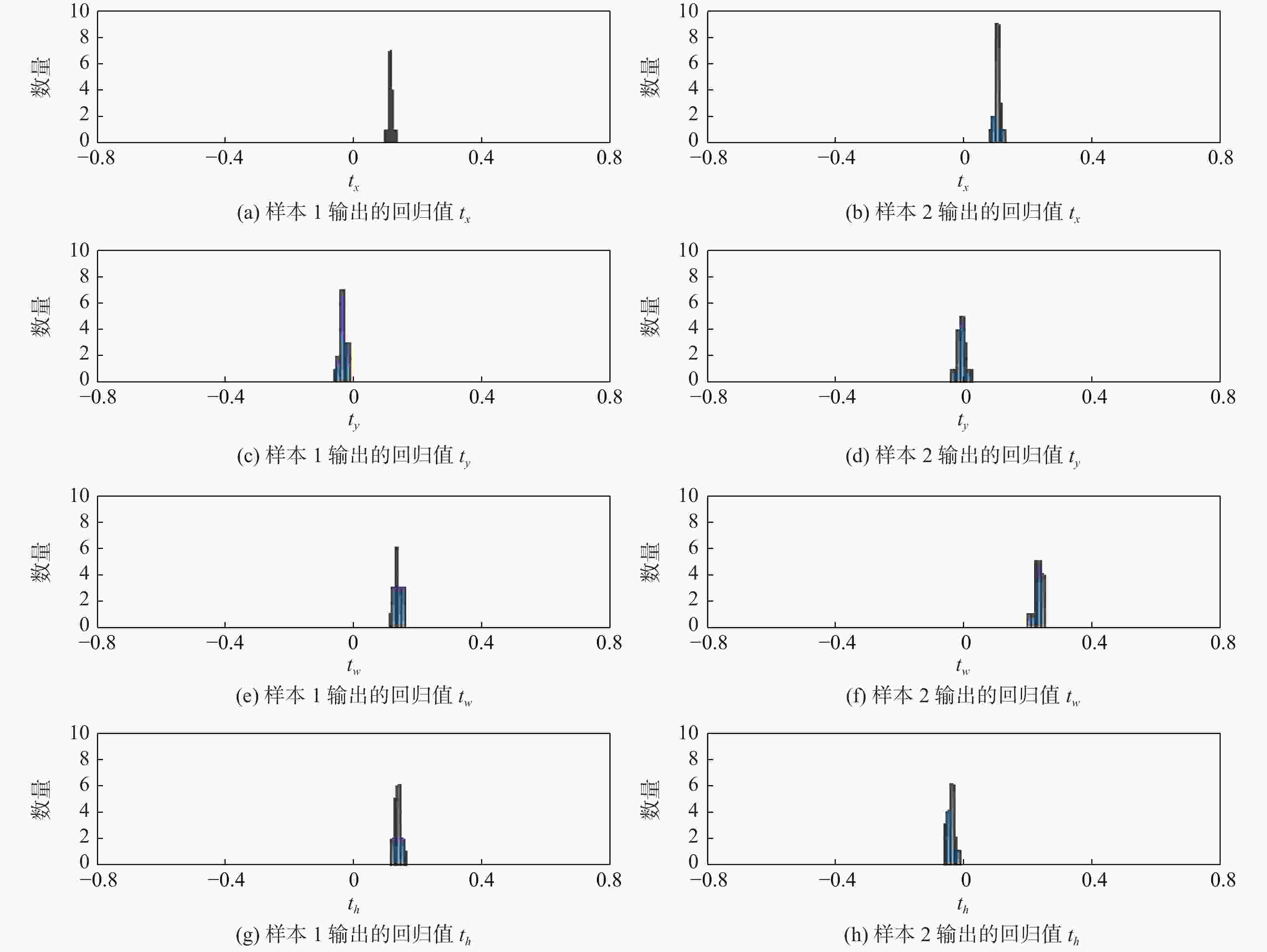
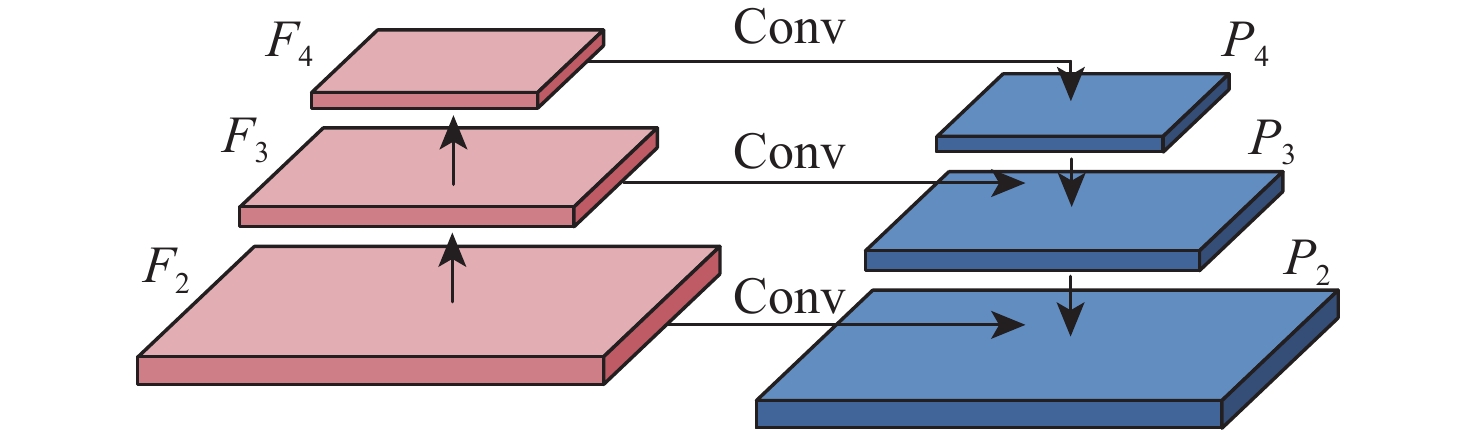
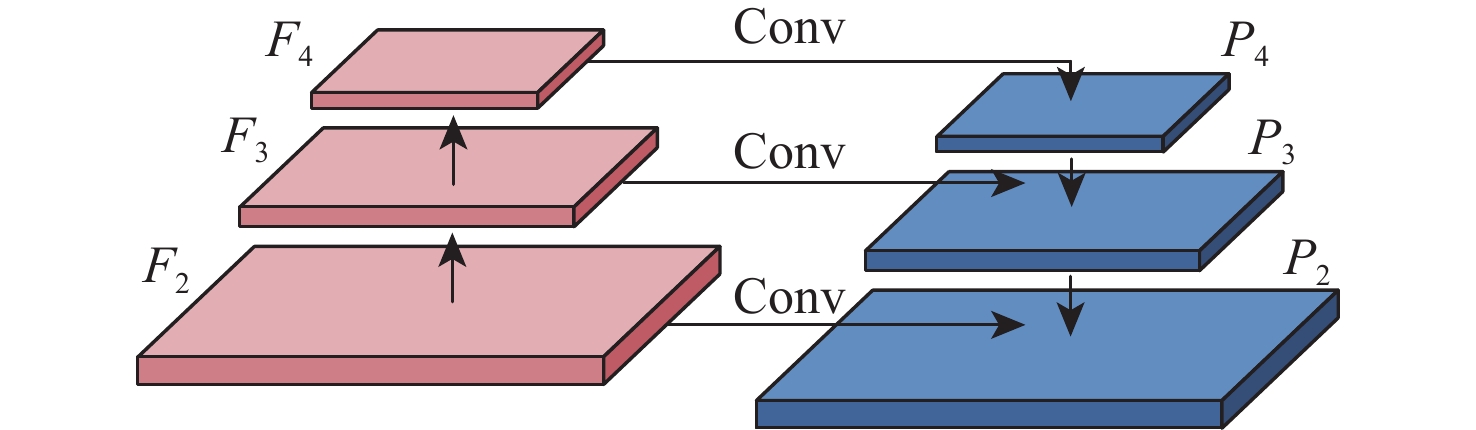
单阶段目标检测方法具有训练速度快、检测时间短的特点,然而其特征金字塔网络(FPN)难以抑制合成孔径雷达(SAR)舰船图像的背景和噪声信息,且检测头存在预测误差。针对该问题,提出一种基于注意力引导和多样本决策的检测方法,用于SAR舰船检测。提出一种注意力引导网络,将其添加至特征金字塔的最高层,使其抑制背景和噪声干扰,从而提升特征的表示能力。提出多样本决策网络,使其参与目标位置的预测。该网络通过增加回归分支中输出的样本数量,缓解预测误差对检测结果的影响。设计了一种新颖的最大似然损失函数。该损失函数利用多样本决策网络中输出的样本构造出最大似然函数,用于规范决策网络的训练,进一步提升目标定位的精度。以RetinaNet网络模型为基线方法,相较于基线方法及目前先进的目标检测方法,所提方法在舰船检测数据集SSDD上表现出最高的检测精度,AP达到52.8 %。相比基线方法,所提方法在AP评价指标上提升了3.4%~5.7%,且训练参数量仅增加2.03×106,帧率仅降低0.5帧/s。
Abstract:The ones-stage object detection method has the characteristics of fast training speed and short inference time. However, its feature pyramid network (FPN) cannot suppress the background and noise information of the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) ship image, and the detection head has a prediction bias. This paper proposes a detection model based on attention guidance and multi-sample decisions for SAR ship detection. Firstly, in order to improve feature representation, this study suggests adding an attentional guidance network to the top of the feature pyramid in order to decrease noise and background interference. Secondly, Multi-sample decision networks are proposed to participate in predicting ship locations. By increasing the amount of output samples in regression branches, the network reduces the impact of prediction bias on detection outcomes. Finally, a novel maximum likelihood loss function is designed. The loss function constructs the maximum likelihood function from the output samples of multiple decision networks, which is used to standardize the training of decision networks and further improve the accuracy of target positioning. Compared with RetinaNet and current advanced object detection methods, the proposed method shows higher detection accuracy on the SSDD dataset, with AP up to 54%. Compared with the baseline method, the SARetinaNet method improved the AP evaluation index by 3.4%~5.7%, the number of training parameters Params only increased by 2.03M, and the FPS only increased by 0.5iter/s.
-
表 1 实验硬件环境
Table 1. Experimental hardware environment
类别 环境条件 CPU intel(R) xeon(R) silver 4110 显卡 TITAN RTX (24 GB) 操作系统 Ubuntu 18.04 深度学习框架 Pytorch 1.6.0 CUDA版本 CUDA 11.2 cuDNN版本 cuDNN 7.4.2 运行环境 Pycharm 2021.01 脚本语言 Python3.7 表 2 不同样本量的影响
Table 2. Effect of different sample size
n AP 参数量 浮点运算次数 1 49.6 36.88×106 205.13×109 16 52.8 38.13×106 231.68×109 30 48 39.29×106 256.46×109 50 12.8 40.95×106 291.86×109 100 — 45.1×106 380.36×109 表 3 消融实验结果
Table 3. Results of ablation experiments
注意力
引导网络多样本
决策网络最大似然
损失函数AP 参数量 浮点运
算次数帧率/
(帧·s−1)× × × 48.8 36.1×106 204.36×109 16.2 √ × × 49.6 36.88×106 205.13×109 15.5 × √ × 50.2 37.35×106 230.91×109 15.6 × √ √ 51.3 37.35×106 230.91×109 15.7 √ √ √ 52.8 38.13×106 231.68×109 15.7 表 4 特征金字塔输出通道数对检测性能的影响
Table 4. Influence of the number of output channels of feature pyramid on the detection performance
输出通道数 AP 参数量 浮点运算次数 64 52.2 30.02×106 196.71×109 128 48.3 32.17×106 206.55×109 256 52.8 37.35×106 230.91×109 512 52 51.24×106 298.26×109 表 5 检测头卷积层数对检测性能的影响
Table 5. Influence of convolution layer number of detection head on detection performance
检测头卷积层数 AP 参数量 浮点运算次数 1 53.7 33.81×106 155.36×109 2 53.6 34.99×106 180.54×109 3 52.6 36.17×106 205.73×109 4 52.8 37.35×106 230.91×109 表 6 消融实验结果
Table 6. Results of ablation experiments
方法 骨干网络类型 训练策略 AP AP50 AP75 APS APM APL RetinaNet ResNet-50 1× 48.8 86.7 49.5 46.2 56 31.2 RetinaNet ResNet-50 2× 53.8 91.5 58.1 49.6 63 38.6 RetinaNet ResNet-101 1× 48.9 88.3 48.7 45.7 56.3 33.3 RetinaNet ResNet-101 2× 53.8 91.7 58.6 48.9 63.5 46.0 本文方法 ResNet-50 1× 52.8 89.4 57.2 50.7 58.9 41.1 本文方法 ResNet-50 2× 57.2 91.8 67.1 53.5 65.4 58.8 本文方法 ResNet-101 1× 54.6 89.5 61.8 51.3 62.0 49.9 本文方法 ResNet-101 2× 57.5 93.1 64.1 53.3 65.6 60.3 表 7 不同检测方法的对比
Table 7. Comparison of different detection methods
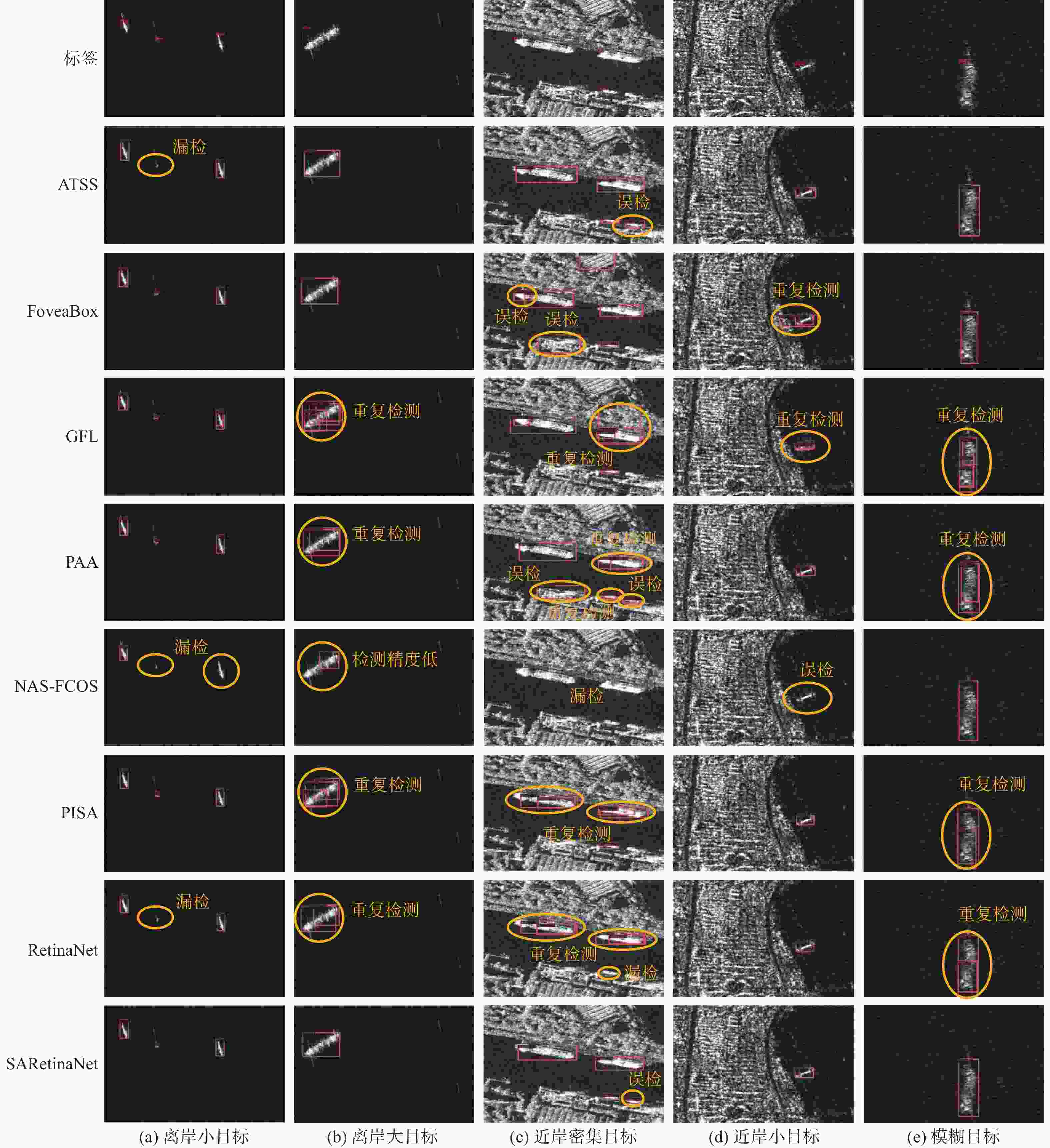
方法 骨干网络类型 训练策略 AP AP50 AP75 APS APM APL 参数量 浮点运算次数 帧率/(帧·s−1) FoveaBox ResNet-50 1× 50.0 88.0 52.9 49.0 54.3 33.5 36.01×106 202.39×109 11.4 NAS-FCOS ResNet-50 1× 46.1 84.7 47.5 47 46.9 34.5 38.66×106 191.81×109 15.3 ATSS ResNet-50 1× 52.4 89.3 58.5 52 56.6 36.8 31.89×106 201.33×109 15.6 GFL ResNet-50 1× 43.6 80.1 44.3 45 43.2 34 32.03×106 204.42×109 16.8 PISA ResNet-50 1× 50.6 88.3 56.0 47.8 57.2 29.8 36.1×106 204.36×109 16.1 PAA ResNet-50 1× 52.7 92.0 55.0 49 61.4 37 31.89×106 201.33×109 9.9 RetinaNet ResNet-50 1× 48.8 86.7 49.5 46.2 56 31.2 36.1×106 204.36×109 16.2 本文方法 ResNet-50 1× 52.8 89.4 57.2 50.7 58.9 41.1 38.13×106 231.68×109 15.7 -
[1] DU L, DAI H, WANG Y, et al. Target discrimination based on weakly supervised learning for high-resolution SAR images in complex scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(1): 461-472. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2937175 [2] SHAHZAD M, MAURER M, FRAUNDORFER F, et al. Buildings detection in VHR SAR images using fully convolution neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 1100-1116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2864716 [3] HUANG L Q, LIU B, LI B Y, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195-208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672 [4] ZHANG Z M, WANG H P, XU F, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177-7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222 [5] YANG G, LI H C, YANG W, et al. Unsupervised change detection of SAR images based on variational multivariate Gaussian mixture model and Shannon entropy[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(5): 826-830. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2879969 [6] GIERULL C H. Demystifying the capability of sublook correlation techniques for vessel detection in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(4): 2031-2042. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2870716 [7] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [8] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2999-3007. [9] TIAN Z, SHEN C H, CHEN H, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9626-9635. [10] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [11] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [12] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1800-1807. [13] XIE S N, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5987-5995. [14] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 936-944. [15] LIU S, QI L, QIN H F, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8759-8768. [16] GHIASI G, LIN T Y, LE Q V. NAS-FPN: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7029-7038. [17] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 640-651. [18] DAI X Y, CHEN Y P, XIAO B, et al. Dynamic head: Unifying object detection heads with attentions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 7369-7378. [19] 李晨瑄, 顾佼佼, 王磊, 等. 多尺度特征融合的Anchor-Free轻量化舰船要害部位检测算法[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2022, 48(10): 2006-2019.LI C X, GU J J, WANG L, et al. Warship' s vital parts detection algorithm based on lightweight Anchor-Free network with multi-scale feature fusion[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(10): 2006-2019(in Chinese). [20] 张晓玲, 张天文, 师君, 等. 基于深度分离卷积神经网络的高速高精度SAR舰船检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 841-851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111ZHANG X L, ZHANG T W, SHI J, et al. High-speed and high-accurate SAR ship detection based on a depthwise separable convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 841-851 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12000/JR19111 [21] JIAO J, ZHANG Y, SUN H, et al. A densely connected end-to-end neural network for multiscale and multiscene SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 20881-20892. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2825376 [22] ZHANG T W, ZHANG X L, SHI J, et al. Balanced feature pyramid network for ship detection in synthetic aperture radar images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-5. [23] CHEN S Q, ZHAN R H, WANG W, et al. Learning slimming SAR ship object detector through network pruning and knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 14: 1267-1282. [24] FU J M, SUN X, WANG Z R, et al. An anchor-free method based on feature balancing and refinement network for multiscale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1331-1344. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3005151 [25] 张冬冬, 王春平, 付强. 基于Anchor-Free的光学遥感舰船关重部位检测算法[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2024, 50(4): 1365-1374.ZHANG D D, WANG C P, FU Q. Ship’s critical part detection algorithm based on Anchor-Free in optical remote sensing[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(4): 1365-1374(in Chinese). [26] ZHANG T W, ZHANG X L, LI J W, et al. SAR ship detection dataset (SSDD): Official release and comprehensive data analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3690. doi: 10.3390/rs13183690 [27] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[M]// Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2014: 740-755. [28] KONG T, SUN F C, LIU H P, et al. FoveaBox: Beyound anchor-based object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7389-7398. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3002345 [29] ZHANG S F, CHI C, YAO Y Q, et al. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 9756-9765. [30] LI X, WANG W H, WU L J, et al. Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection[EB/OL]. (2020-06-08)[2022-12-10]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2006.04388. [31] CAO Y H, CHEN K, LOY C C, et al. Prime sample attention in object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11580-11588. [32] KIM K, LEE H S. Probabilistic anchor assignment with IoU prediction for object detection[M]// Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 355-371. -






 下载:
下载: