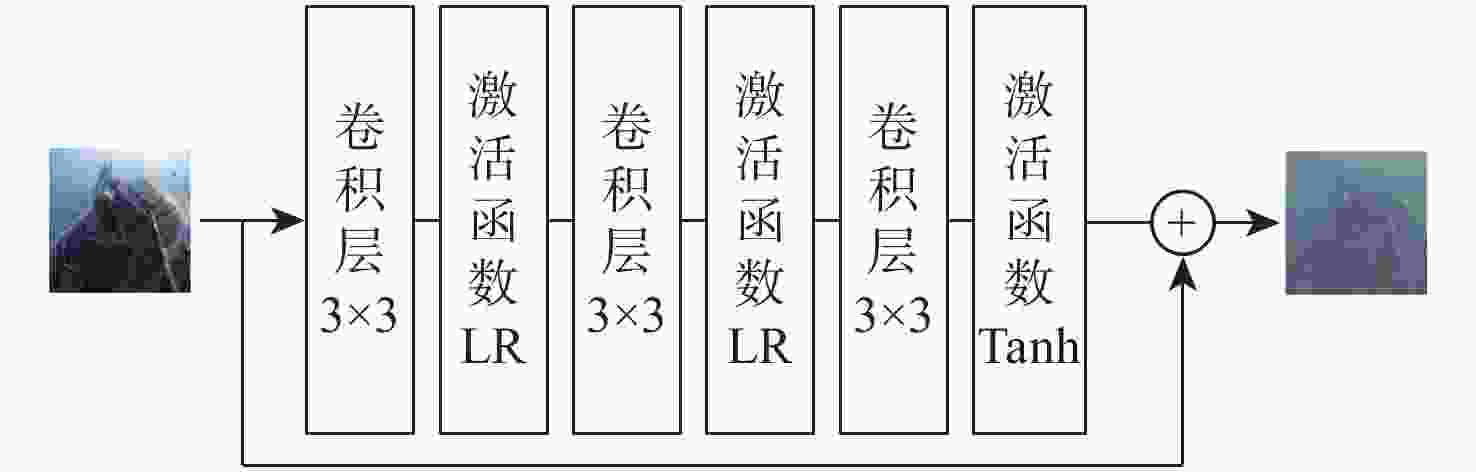
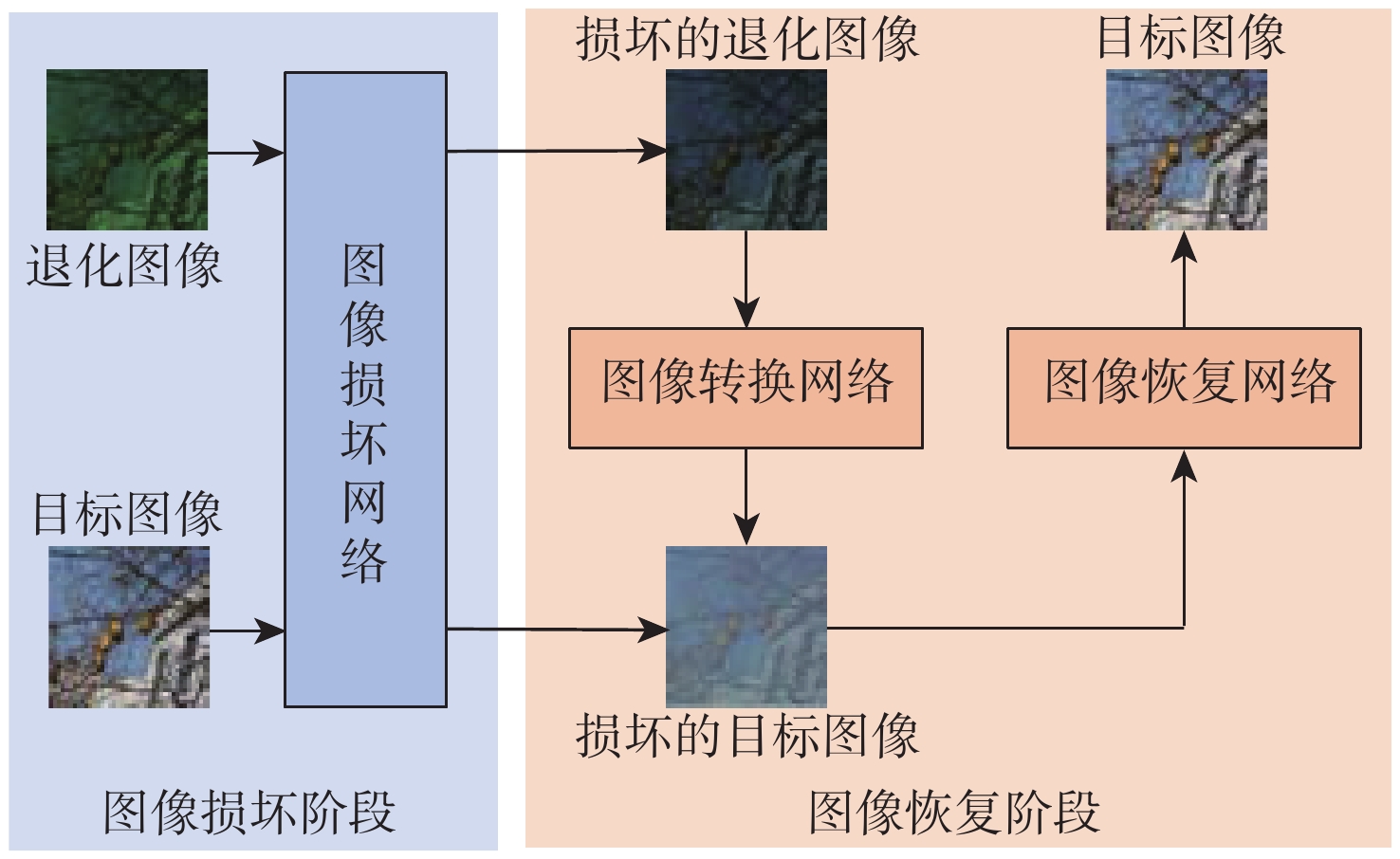
Two-stage underwater image enhancement method based on convolutional neural networks
-
摘要:
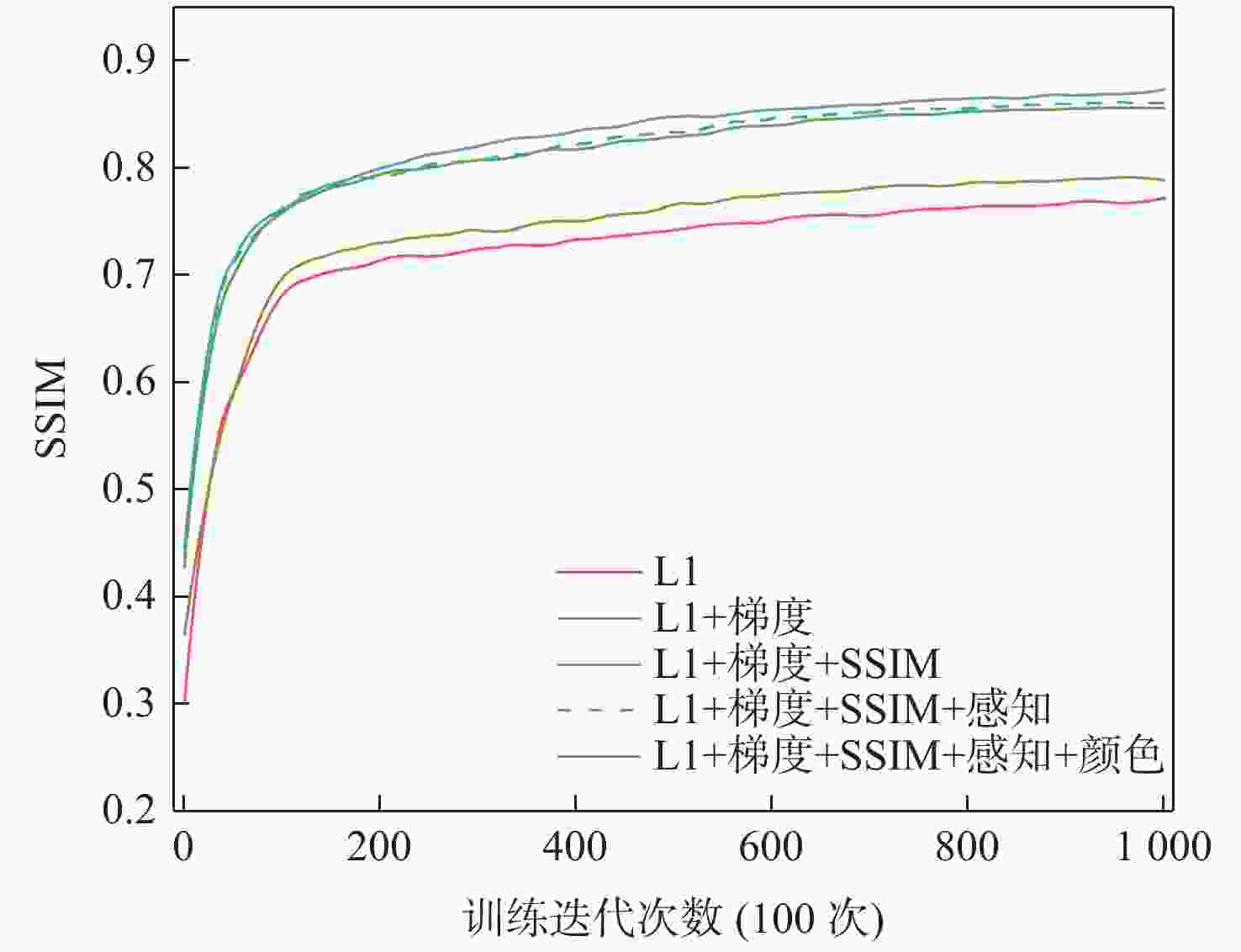
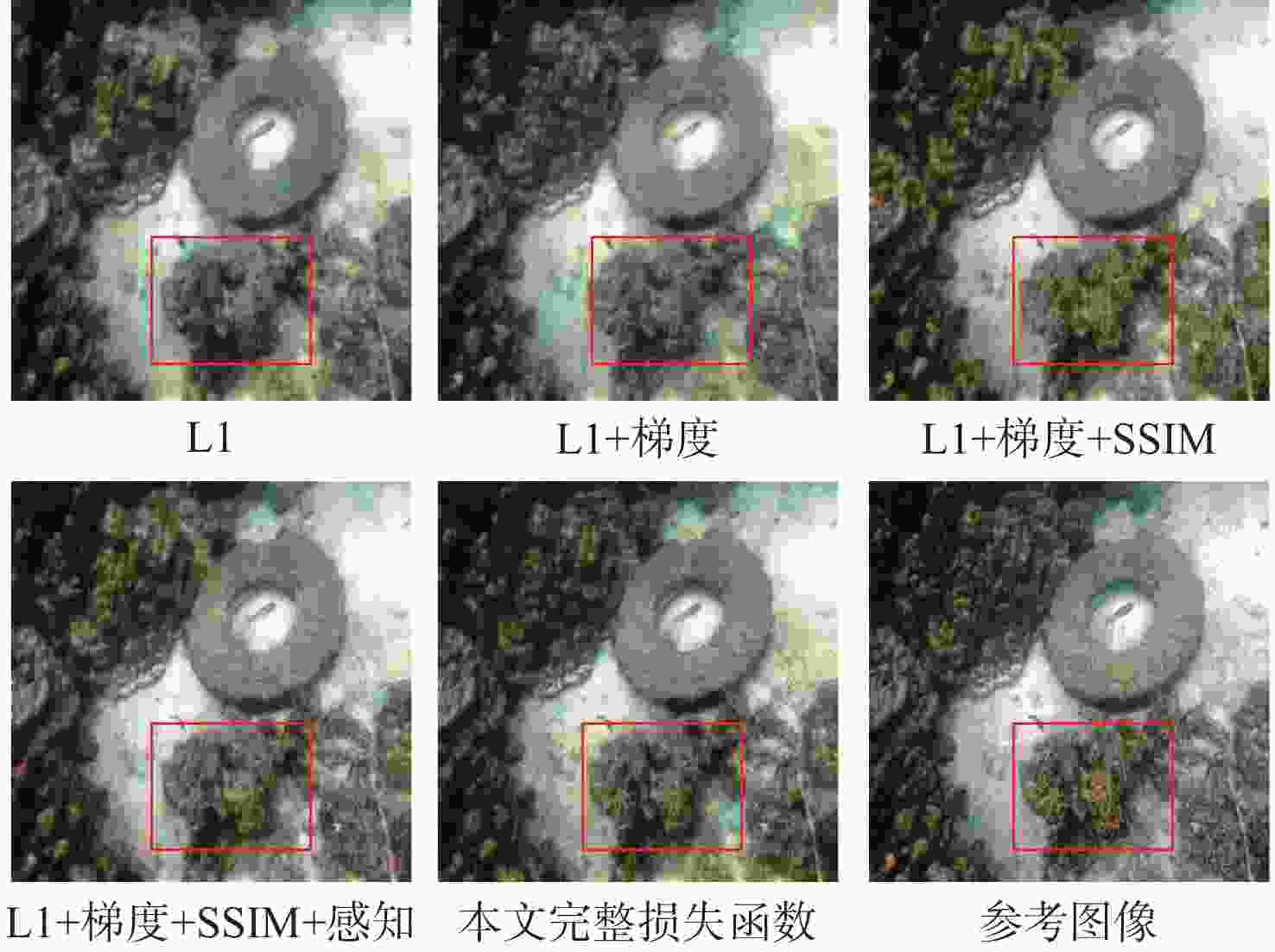
由于水体对光线不同粒子的吸收能力具有一定差异,水下采集到的图像往往存在严重的退化现象,严重影响水下机器人对环境的感知。传统的图像处理方法和基于退化模型的图像恢复算法受到水下环境的复杂性和物理参数不确定性的影响往往表现出较差的泛化能力。为提高水下图像的视觉效果,利用深度学习模型强大的学习能力,提出一种基于卷积神经网络的双阶段水下图像增强方法,通过图像损坏和图像恢复两个阶段的处理将退化的水下图像增强为视觉效果优秀的近空气图像。在Challenge60、U45、EUVP和RUIE数据集上的测试结果表明,提出的方法相比于已有水下图像复原、增强算法具有更好的增强效果,水下图像质量指标(UIQM)提升了5.18%,水下彩色图像质量评价(UCIQE)指标提升了6.64%。
Abstract:Images taken underwater frequently suffer from substantial degradation due to the varied capabilities of water particles to absorb light, which has a significant impact on how underwater robots perceive their surroundings. The intricacy of underwater environments and uncertainties in physical factors usually result in poor generalization for traditional image processing techniques and degradation model-based picture restoration systems. A two-stage underwater image enhancement technique based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is suggested to improve the quality of underwater images. This method improves degraded underwater images into visually superior near-air images through damage and restoration phases. Testing results on Challenge60, U45, EUVP, and RUIE datasets show that the proposed method achieves better enhancement compared to existing underwater image restoration and enhancement algorithms, with improvements of 5.18% and 6.64% respectively for UIQM and UCIQE scores.
-
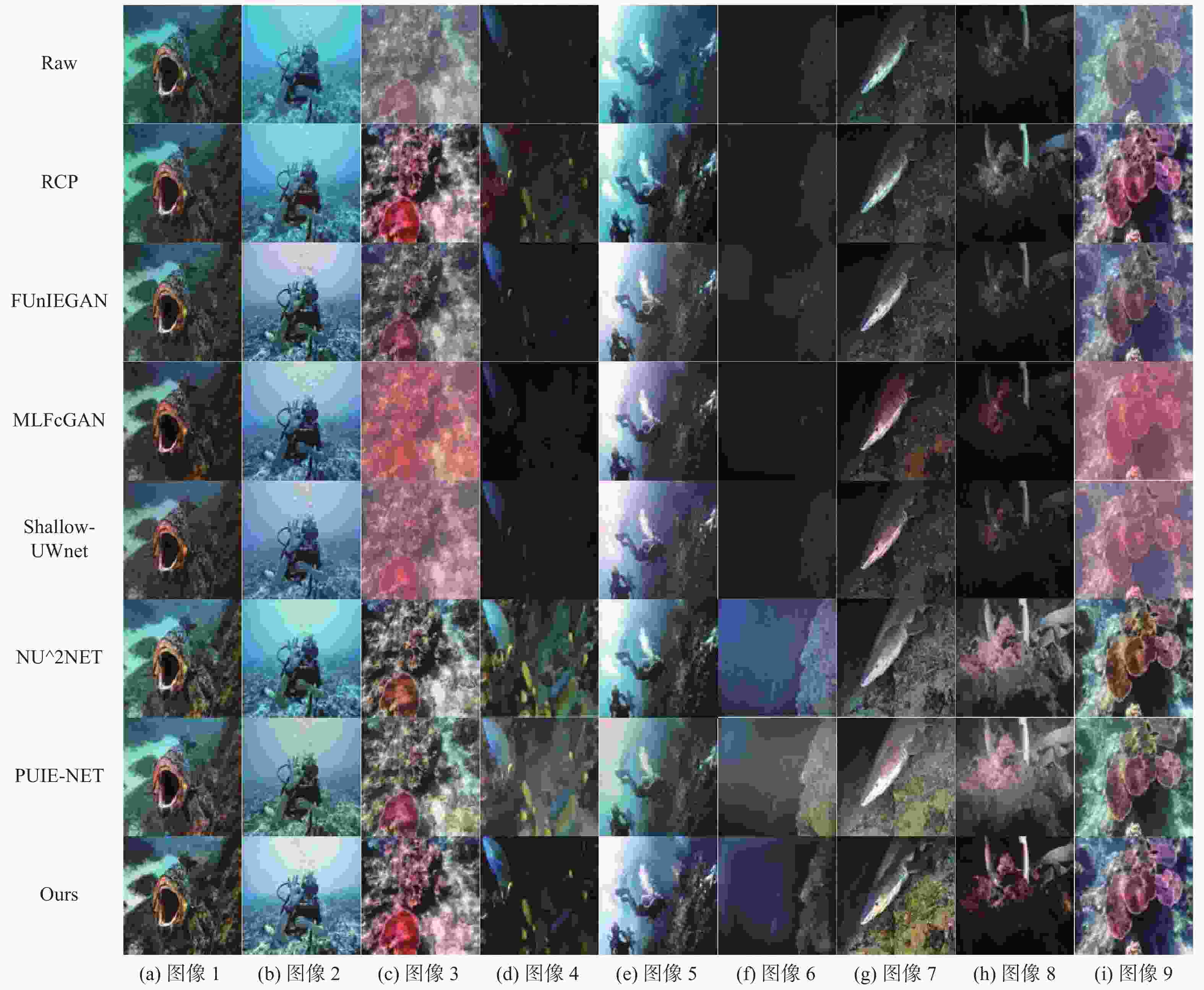
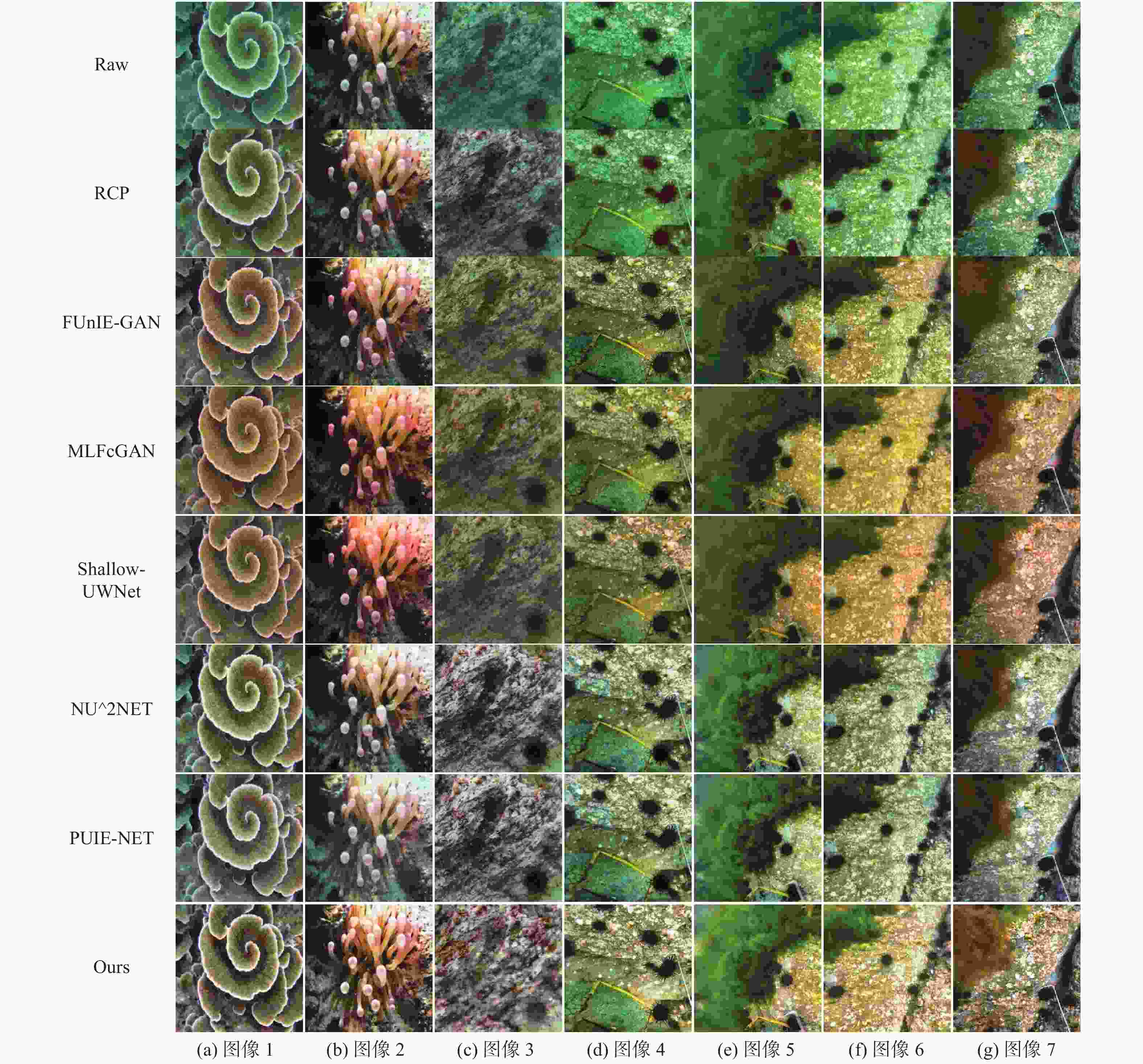
表 1 不同方法在对应图像上的UIQM指标
Table 1. UIQM metrics of different methods on the corresponding images
图像编号 图像处理方案 RCP FUnIE-GAN MLFcGAN Shallow-UWNet NU^2Net PUIE-NET Ours 图6(a) 4.633 9 4.853 3 (5.053 6) 4.948 9 4.666 4 4.730 5 5.140 2 图6(b) 1.321 9 (3.353 4) 2.826 0 3.168 7 2.599 2 3.276 7 3.382 9 图6(c) 6.109 0 5.409 3 5.562 0 5.127 4 5.719 4 5.504 4 (6.106 7) 图6(d) (5.101 8) 5.076 1 4.631 1 4.835 4 4.615 3 4.244 7 5.341 0 图6(e) 4.219 8 4.250 9 4.226 3 4.111 4 (4.273 3) 3.975 3 4.295 9 图6(f) 3.390 0 3.467 1 (3.899 2) 3.466 2 3.496 4 3.535 1 4.096 7 图6(g) 5.030 5 5.294 6 5.428 8 (5.449 9) 5.439 7 5.225 4 5.458 0 图6(h) 5.205 8 (5.351 5) 4.620 7 4.287 3 5.243 8 4.704 8 5.802 8 图6(i) 6.010 9 (5.369 2) 5.588 7 5.222 4 5.588 6 5.143 7 (5.600 2) 注:表中各列的平均值分别为4.558 2,4.713 9,4.648 5,4.513 1,4.626 9,4.482 2,5.024 9;表中粗体表示每行最优结果,()表示每行次优结果。 表 2 不同方法在对应图像上的UCIQE指标
Table 2. UCIQE metrics of different methods on the corresponding images
图像编号 图像处理方案 RCP FUnIE-GAN MLFcGAN Shallow-UWNet NU^2Net PUIE-NET Ours 图6(a) 0.468 5 0.416 7 0.439 9 0.424 7 0.442 5 0.441 8 (0.445 0) 图6(b) 0.453 8 0.378 0 0.375 0 0.348 8 (0.413 4) 0.372 3 0.352 7 图6(c) (0.515 0) 0.315 5 (0.408 0) 0.292 9 0.409 5 0.384 4 0.515 2 图6(d) 0.475 0 0.436 2 0.318 2 0.293 6 0.391 7 0.340 5 (0.442 6) 图6(e) 0.486 1 0.351 1 0.378 8 0.335 6 0.375 0 0.342 9 (0.401 4) 图6(f) 0.180 3 0.171 1 0.267 1 0.160 7 0.316 0 0.294 4 (0.297 5) 图6(g) 0.429 9 0.415 4 0.511 6 (0.507 7) 0.425 9 0.394 6 0.445 1 图6(h) (0.441 3) 0.326 7 0.422 0 0.421 7 0.380 0 0.329 7 0.537 6 图6(i) 0.438 0 0.346 7 0.409 7 0.341 8 (0.442 3) 0.408 6 0.460 6 注:表中各列的平均值分别为0.432 0,0.350 8,0.392 3,0.347 5,0.399 5,0.367 6,0.433 1;表中粗体表示每行最优结果,()表示每行次优结果。 表 3 不同方法在对应图像上的UIQM指标
Table 3. UIQM metrics of different methods on the corresponding images
图像编号 图像处理方案 RCP FUnIE-GAN MLFcGAN Shallow-UWNet NU^2NET PUIE-NET Ours 图7(a) 5.108 2 (5.818 9) 5.802 1 5.621 2 5.386 5 5.351 9 5.822 7 图7(b) 5.612 6 5.674 8 5.606 5 (5.785 0) 5.478 9 5.134 9 5.917 4 图7(c) 5.686 1 5.707 6 5.670 7 5.599 5 (5.972 9) 5.608 4 6.071 0 图7(d) 4.122 1 5.382 3 5.384 3 5.457 0 5.243 7 (5.604 7) 5.664 0 图7(e) 4.169 7 4.759 3 4.497 5 4.020 5 4.451 6 4.417 9 (4.581 2) 图7(f) 4.483 3 5.681 1 5.591 8 (5.864 9) 5.322 2 5.505 1 5.873 7 图7(g) 5.102 4 5.548 5 (5.998 2) 5.677 2 5.552 8 5.367 5 6.171 6 注:表中各列的平均值分别为4.897 7,5.510 3,5.507 3,5.432 1,5.344 0,5.284 3,5.728 8;表中粗体表示每行最优结果,()表示每行次优结果。 表 4 不同方法在对应图像上的UCIQE指标
Table 4. UCIQE metrics of different methods on the corresponding images
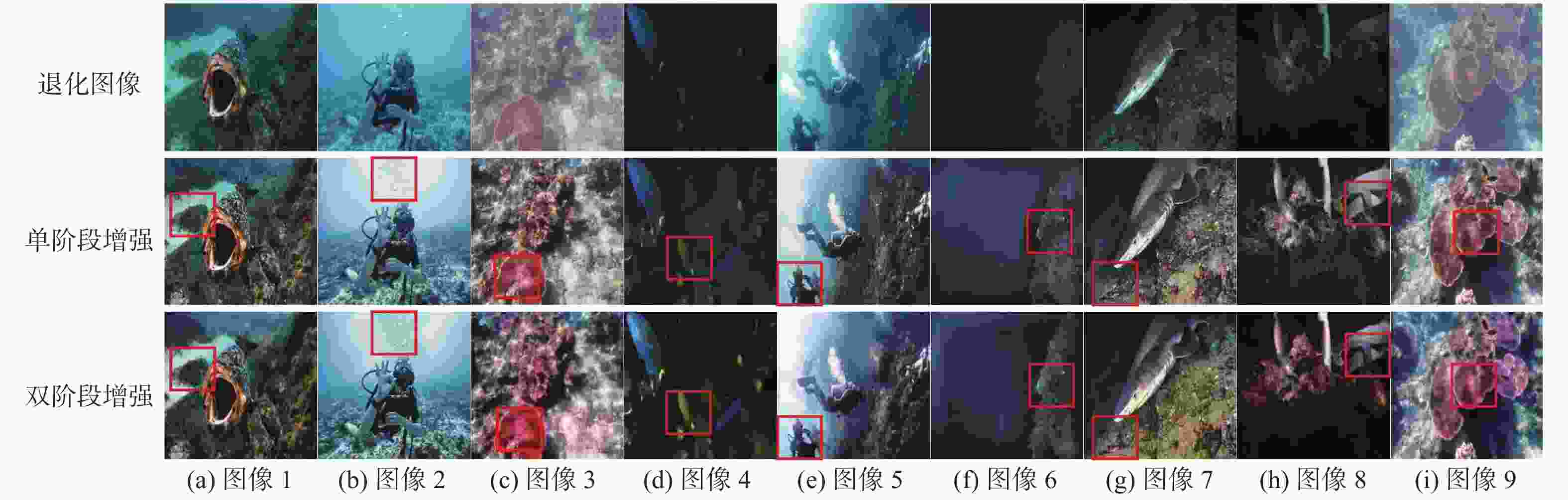
图像编号 图像处理方案 RCP FUnIE-GAN MLFcGAN Shallow-UWNet NU^2NET PUIE-NET Ours 图7(a) 0.409 8 0.450 7 (0.451 4) 0.430 0 0.416 9 0.417 5 0.456 7 图7(b) 0.476 1 0.478 7 0.481 8 (0.476 5) 0.451 1 0.401 8 0.457 1 图7(c) 0.356 9 0.293 7 0.288 3 0.260 0 0.405 0 0.347 2 (0.382 5) 图7(d) 0.403 8 0.413 3 0.410 7 0.423 2 0.398 8 (0.425 4) 0.435 3 图7(e) 0.449 0 (0.469 4) 0.459 4 0.479 8 0.421 7 0.389 9 0.466 4 图7(f) 0.406 3 0.406 2 (0.412 3) 0.404 2 0.390 2 0.386 2 0.438 7 图7(g) 0.441 2 0.419 3 0.442 0 0.451 1 0.435 7 0.406 6 (0.444 0) 注:表中各列的平均值分别为0.420 4,0.418 7,0.420 8,0.417 8,0.417 0,0.396 3,0.440 1;表中粗体表示每行最优结果,()表示每行次优结果。 表 5 单阶段增强与双阶段增强指标对比
Table 5. Comparison of single-stage enhancement and two-stage enhancement metrics
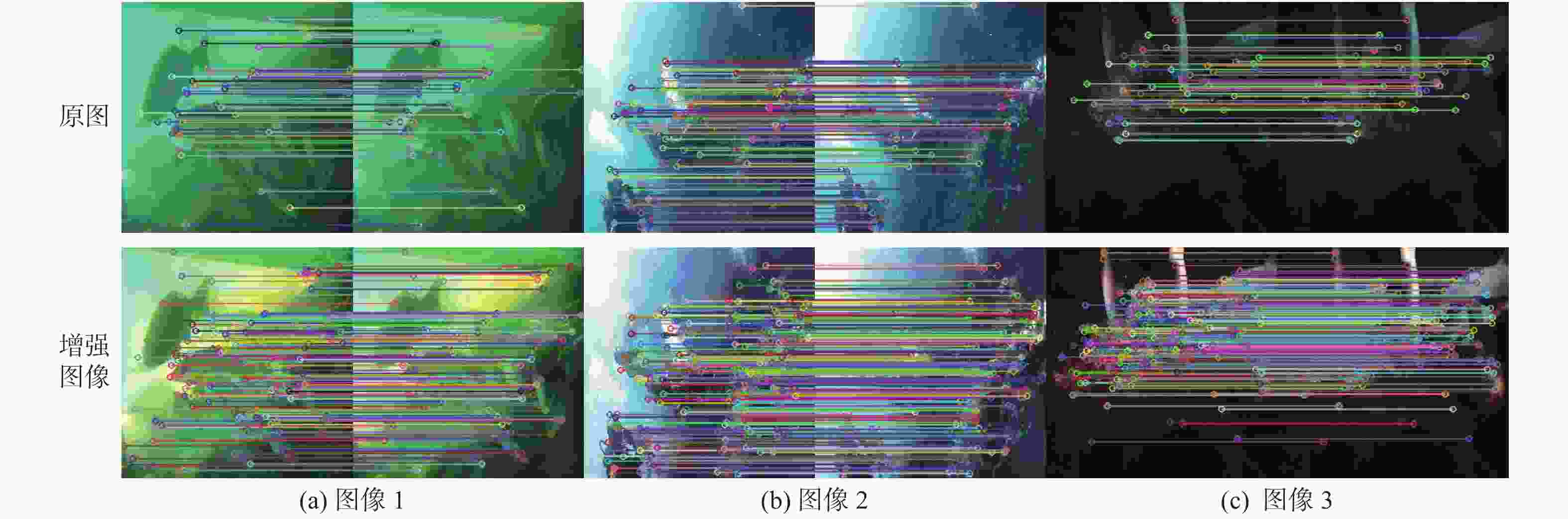
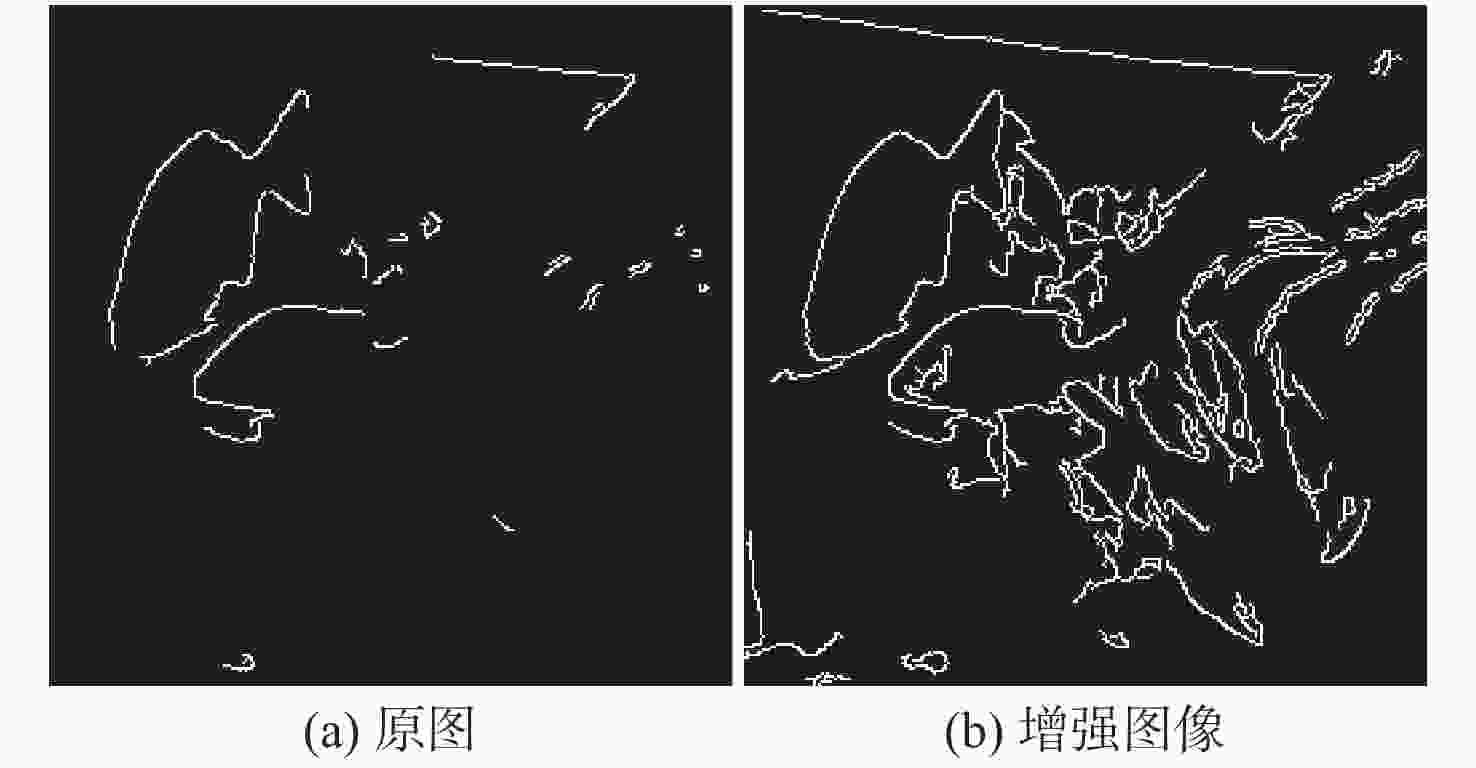
图像编号 单阶段增强 双阶段增强 UIQM UCIQE UIQM UCIQE 图8(a) 5.089 3 0.431 1 5.140 2 0.445 0 图8(b) 3.281 4 0.374 0 3.382 9 0.352 7 图8(c) 5.995 7 0.429 3 6.106 7 0.515 2 图8(d) 4.630 6 0.305 5 5.341 0 0.442 6 图8(e) 4.224 3 0.364 6 4.295 9 0.401 4 图8(f) 3.768 5 0.269 1 4.096 7 0.297 5 图8(g) 5.469 0 0.436 0 5.458 0 0.445 1 图8(h) 5.388 6 0.394 4 5.802 8 0.537 6 图8(i) 5.605 2 0.434 5 5.600 2 0.460 6 注:表中各列的平均值分别为4.828 1,0.382 1,5.024 9,0.433 1;表中粗体表示对应指标每行最优结果。 表 6 增强前后SIFT匹配点数目对比
Table 6. Comparison of the number of SIFT matching points before and after enhancement
表 7 不同方法参数量、处理速度及性能对比
Table 7. Comparison of the parameters, processing speed and performance of different methods
方法 速度/s 参数量/MB UIQM UCIQE FUnIE-GAN 0.046 4.02 5.112 1 0.384 8 MLFcGAN 0.227 45.80 5.077 9 0.406 6 Shallow-UWNet 0.032 0.21 4.972 6 0.382 7 NU^2NET 0.013 3.00 4.985 4 0.409 4 PUIE-NET 0.010 5.12 4.883 2 0.383 6 Ours 0.048 4.67 5.376 9 0.436 6 -
[1] KOCAK D M, DALGLEISH F R, CAIMI F M, et al. A focus on recent developments and trends in underwater imaging[J]. Marine Technology Society Journal, 2008, 42(1): 52-67. doi: 10.4031/002533208786861209 [2] GUO Y C, LI H Y, ZHUANG P X. Underwater image enhancement using a multiscale dense generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45(3): 862-870. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2911447 [3] LI C L, TANG S Q, KWAN H K, et al. Color correction based on CFA and enhancement based on retinex with dense pixels for underwater images[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 155732-155741. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3019354 [4] HITAM M S, AWALLUDIN E A, JAWAHIR HJ WAN YUSSOF W N, et al. Mixture contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization for underwater image enhancement[C]// 2013 International Conference on Computer Applications Technology (ICCAT). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-5. [5] TANG Z J, JIANG L Z, LUO Z H. A new underwater image enhancement algorithm based on adaptive feedback and Retinex algorithm[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(18): 28487-28499. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11095-5 [6] LI C Y, GUO J C, CONG R M, et al. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5664-5677. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2612882 [7] ZHANG S, WANG T, DONG J Y, et al. Underwater image enhancement via extended multi-scale Retinex[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 245: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.03.029 [8] CARLEVARIS-BIANCO N, MOHAN A, EUSTICE R M. Initial results in underwater single image dehazing[C]// OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 1-8. [9] YANG H Y, CHEN P Y, HUANG C C, et al. Low complexity underwater image enhancement based on dark channel prior[C]// 2011 Second International Conference on Innovations in Bio-inspired Computing and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 17-20. [10] WANG N, ZHENG H Y, ZHENG B. Underwater image restoration via maximum attenuation identification[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 18941-18952. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2753796 [11] DREWS P L J Jr, NASCIMENTO E R, BOTELHO S S C, et al. Underwater depth estimation and image restoration based on single images[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2016, 36(2): 24-35. doi: 10.1109/MCG.2016.26 [12] SHIN Y S, CHO Y, PANDEY G, et al. Estimation of ambient light and transmission map with common convolutional architecture[C]// OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-7. [13] WANG Y, ZHANG J, CAO Y, et al. A deep CNN method for underwater image enhancement[C]// 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1382-1386. [14] ANWAR S, LI C Y, PORIKLI F. Deep underwater image enhancement[C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-12. [15] HU Y, WANG K, ZHAO X, et al. Underwater image restoration based on convolutional neural network[J]. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, 2018, 95(11): 296-311. [16] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]// Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal: Curran Associates Inc. , 2014: 2672−2680. [17] KONG J H, SHEN H B, HUANG K J. DualPathGAN: facial reenacted emotion synthesis[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2021, 15(7): 501-513. doi: 10.1049/cvi2.12047 [18] RUAN C C, YUAN L C, HU H F, et al. Image translation with dual-directional generative adversarial networks[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2021, 15(1): 73-83. doi: 10.1049/cvi2.12011 [19] CHAVDAROVA T, FLEURET F. SGAN: an alternative training of generative adversarial networks[C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 9407-9415. [20] 尹诗, 侯国莲, 胡晓东, 等. 基于AC-GAN数据重构的风电机组主轴承温度监测方法[J]. 智能系统学报, 2021, 16(6): 1106-1116. doi: 10.11992/tis.202009020YIN S, HOU G L, HU X D, et al. Temperature monitoring method of the main bearing of wind turbine based on AC-GAN data reconstruction[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2021, 16(6): 1106-1116(in Chinese). doi: 10.11992/tis.202009020 [21] ZHU J Y, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]// 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2242-2251. [22] LI C Y, GUO J C, GUO C L. Emerging from water: underwater image color correction based on weakly supervised color transfer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(3): 323-327. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2792050 [23] FABBRI C, ISLAM M J, SATTAR J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks[C]// 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7159-7165. [24] LI J, SKINNER K A, EUSTICE R M, et al. WaterGAN: unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(1): 387-394. [25] ISLAM M J, XIA Y Y, SATTAR J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227-3234. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [26] LIU X D, GAO Z, CHEN B M. MLFcGAN: multilevel feature fusion-based conditional GAN for underwater image color correction[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(9): 1488-1492. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2950056 [27] NAIK A, SWARNAKAR A, MITTAL K. Shallow-UWnet: compressed model for underwater image enhancement[EB/OL]. (2021-01-06)[2022-12-09]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.02073. [28] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [29] HUANG J, ZHU P F, GENG M R, et al. Range scaling global U-net for perceptual image enhancement on mobile devices[C]// Computer Vision-ECCV 2018 Workshops. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 230-242. [30] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [31] WANG R X, ZHANG Q, FU C W, et al. Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation[C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6842-6850. [32] IGNATOV A, KOBYSHEV N, TIMOFTE R, et al. DSLR-quality photos on mobile devices with deep convolutional networks[C]// 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3297-3305. [33] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, LI F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]// European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2016: 694-711. [34] LI C, GUO C, REN W, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J/OL]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4376-4389[2022-12-01]. http://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2955241. [35] HOU G J, ZHAO X, PAN Z K, et al. Benchmarking underwater image enhancement and restoration, and beyond[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 122078-122091. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006359 [36] LI H Y, LI J J, WANG W. A fusion adversarial underwater image enhancement network with a public test dataset[J/OL]. Image and Video Processing, 2019: 1-8 [2022-12-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1906.06819. [37] LIU R S, FAN X, ZHU M, et al. Real-world underwater enhancement: challenges, benchmarks, and solutions under natural light[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(12): 4861-4875. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2963772 [38] MANDAL D, PANETTA K, AGAIAN S. Human visual system inspired object detection and recognition[C]// 2012 IEEE International Conference on Technologies for Practical Robot Applications (TePRA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 145-150. [39] YANG M, SOWMYA A. An underwater color image quality evaluation metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2015, 24(12): 6062-6071. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2491020 [40] GALDRAN A, PARDO D, PICÓN A, et al. Automatic Red-Channel underwater image restoration[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 26: 132-145. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.11.006 [41] GUO C L, WU R Q, JIN X, et al. Underwater ranker: learn which is better and how to be better[EB/OL]. (2022-11-26)[2022-12-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2208.06857. [42] FU Z Q, WANG W, HUANG Y, et al. Uncertainty inspired underwater image enhancement[M]// Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2022: 465-482. -






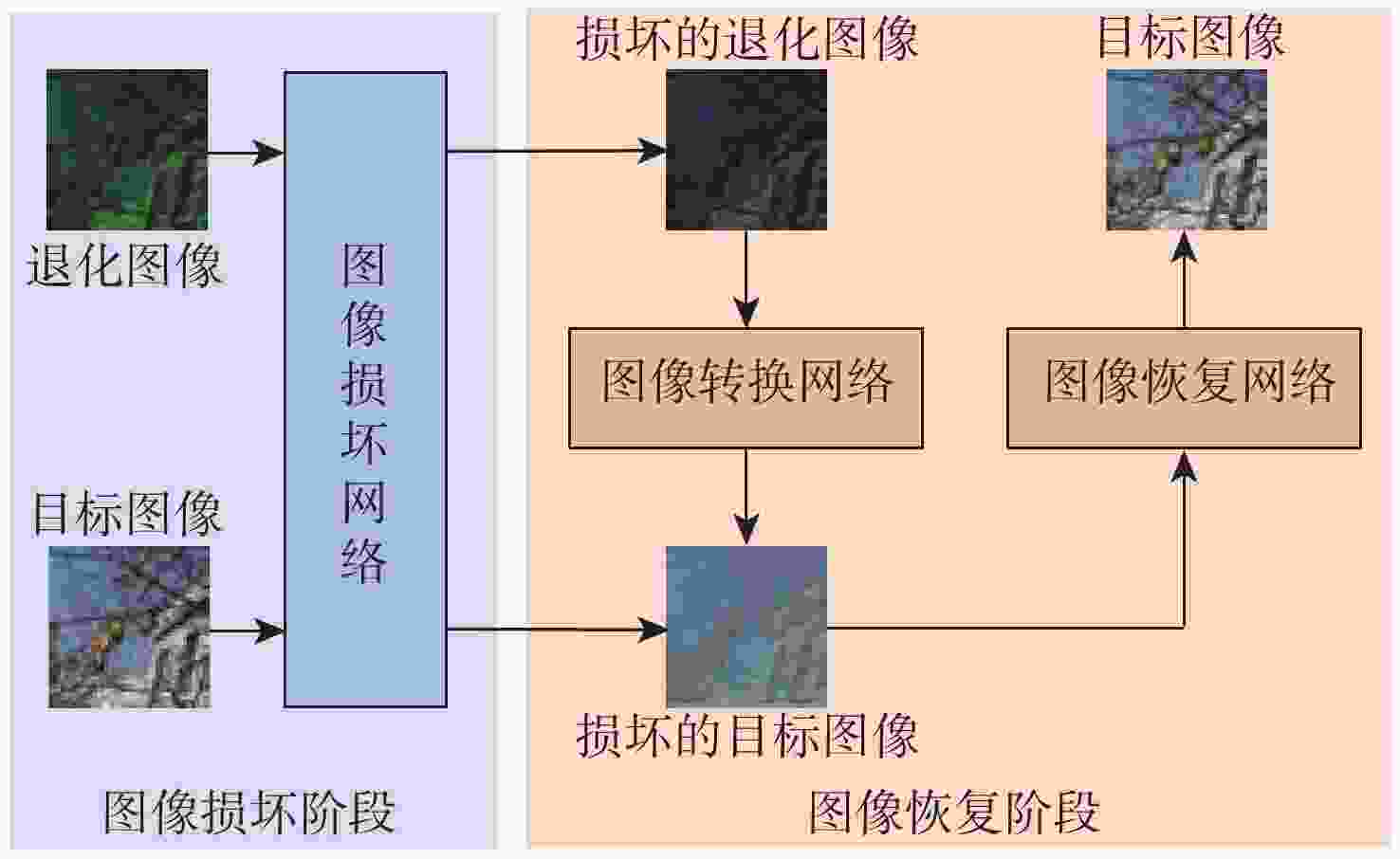
 下载:
下载: