-
摘要:
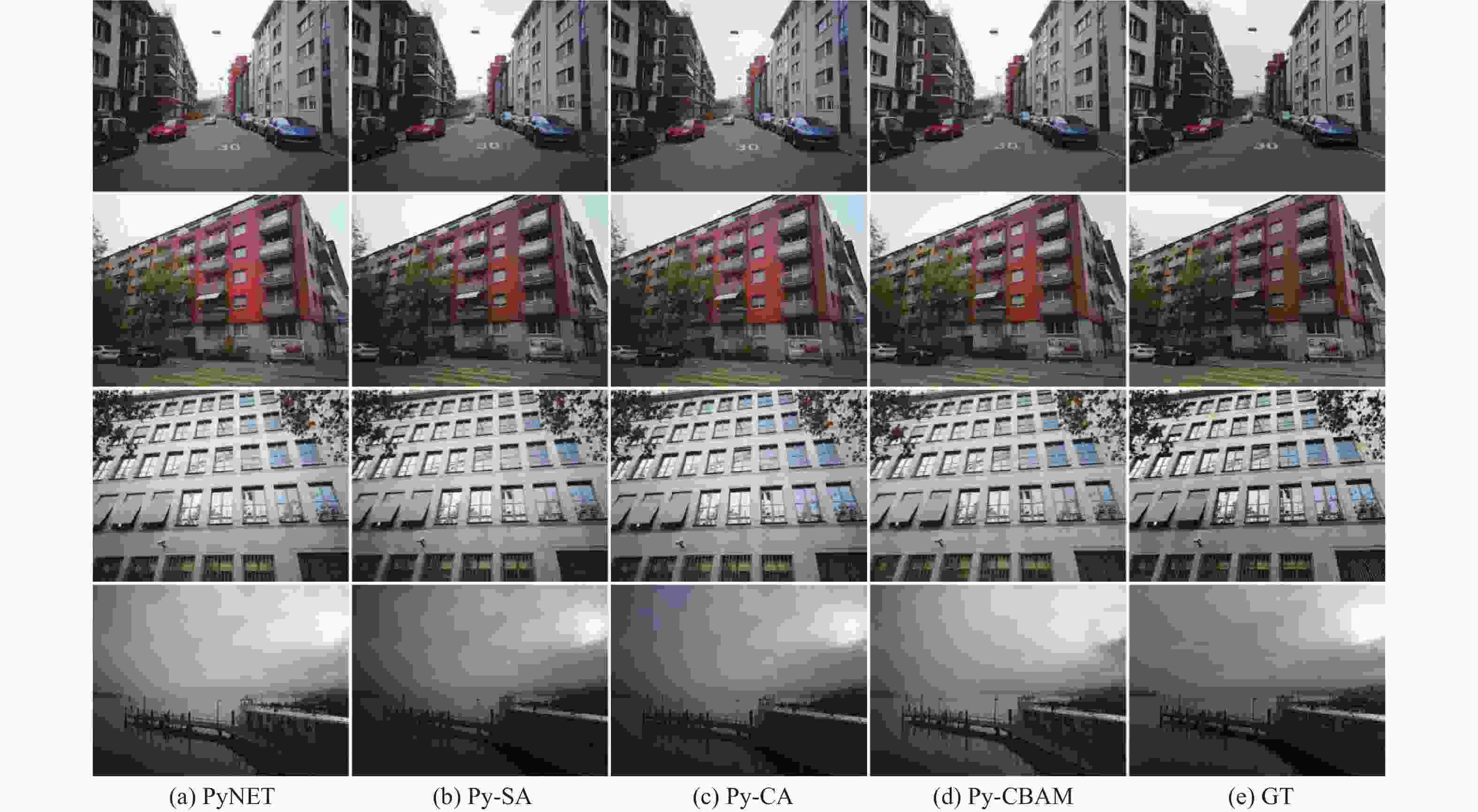
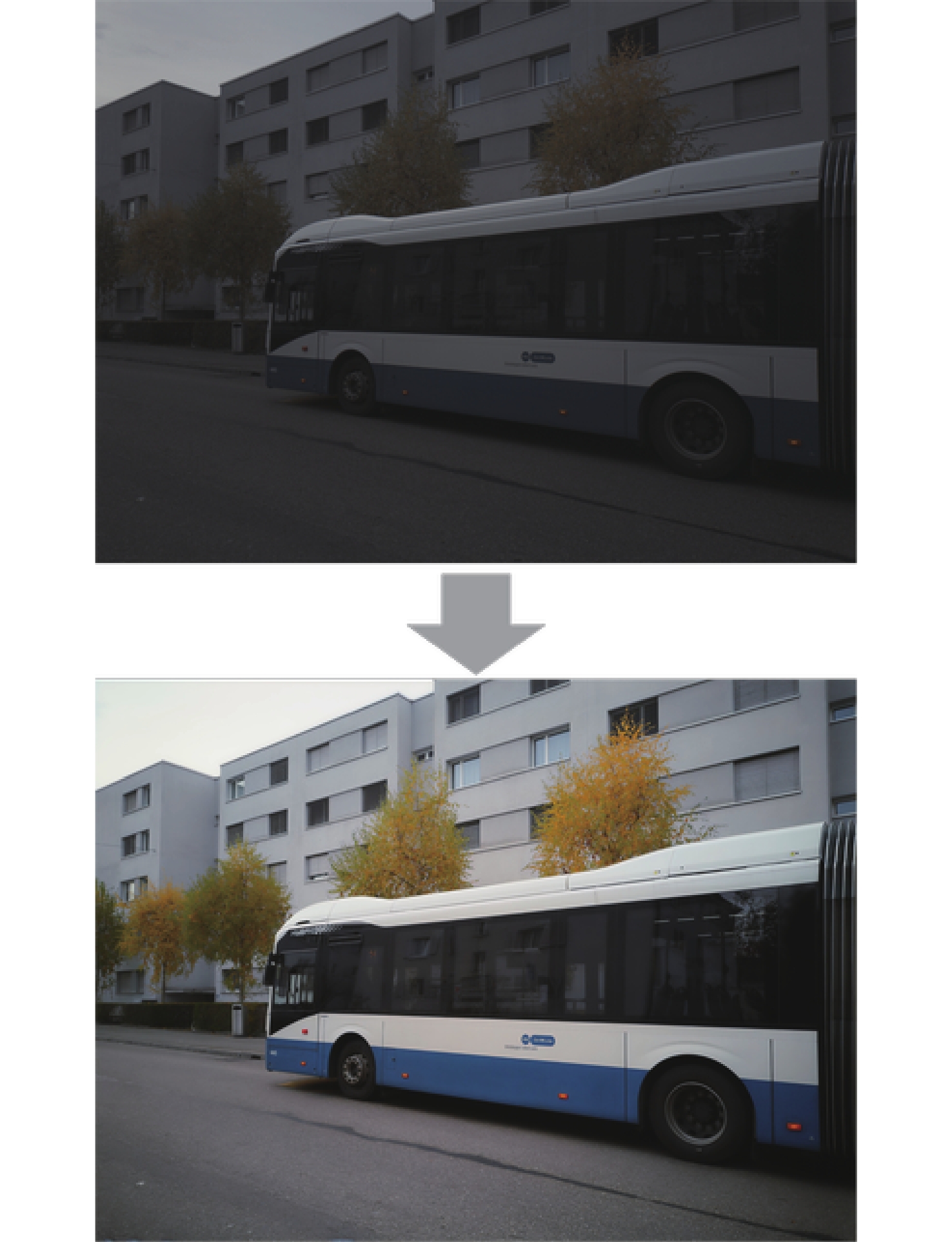
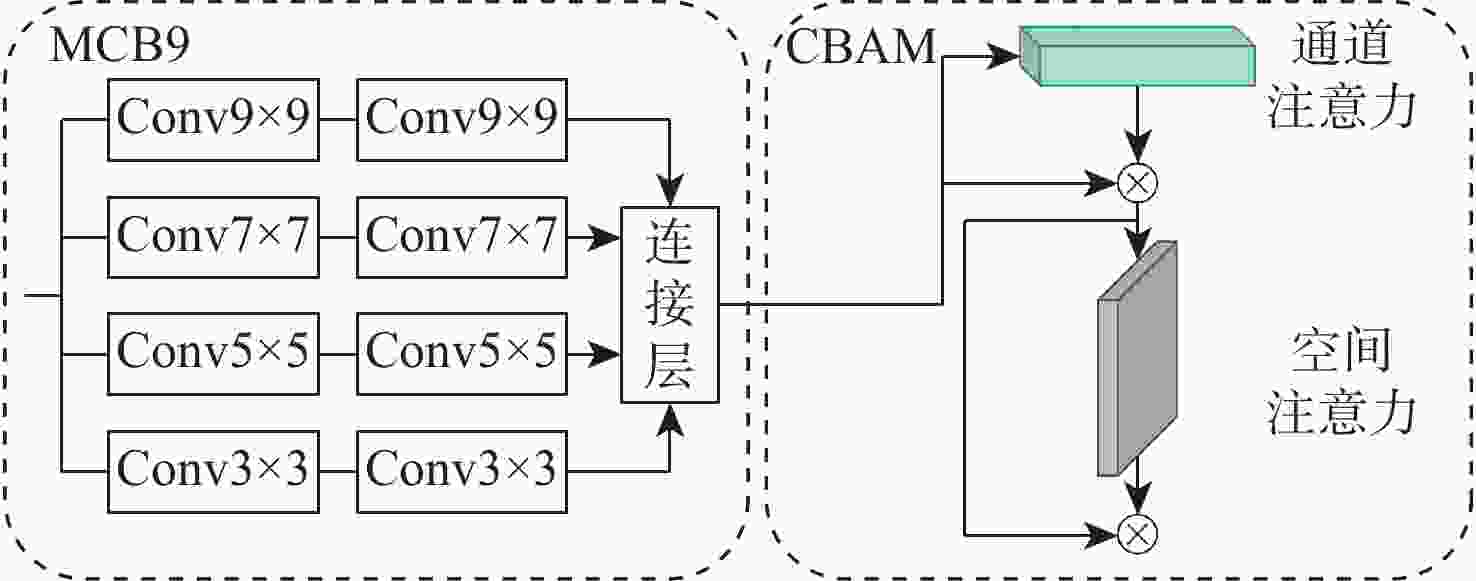
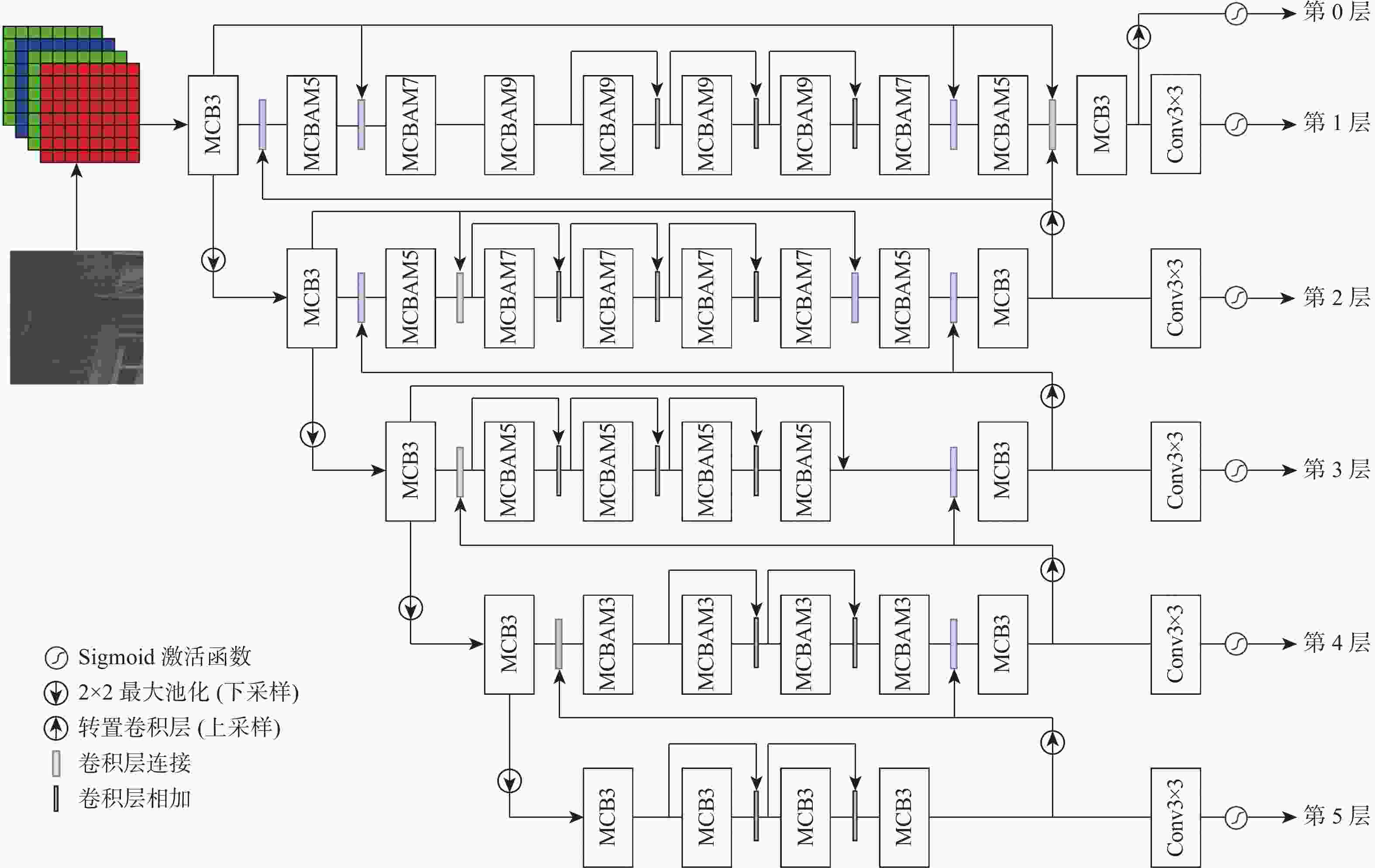
针对传统图像信号处理(ISP)算法繁琐的问题,基于可取代ISP算法的PyNET网络模型,提出一种端到端的RAW图像重建方法Py-CBAM。通过引入高效的注意力机制,并利用该机制对原有网络的多层级多尺度结构进行重设计,实现不同尺度特征的自适应加权,以较大程度提升图像重建的性能。实验结果表明,所提方法在公开的ZRR数据集上获得的峰值信噪比(PSNR)与PyNET方法相比提升了0.37 dB,结构相似度(SSIM)提升了0.001 8。将ZRR数据集和新构建的NRR数据集联合对Py-CBAM重新训练后,PSNR和SSIM分别达到25.73 dB和0.965 4。视觉效果上,所提方法解决了RAW图像重建时的噪声高与色彩失真、畸变等问题,增强模型在多场景不同光照环境条件下的重建能力;重建结果较为真实,视觉质量最优,在图像过曝和过暗区域视觉提升效果较为明显。
Abstract:Traditional image signal processing (ISP) algorithms are cumbersome. Therefore, based on the PyNET model that can replace ISP algorithms, an end-to-end RAW image reconstruction method was proposed, called Py-CBAM. This method introduced an efficient attention mechanism and used it to redesign the multi-level and multi-scale structure of the PyNET network to achieve adaptive weighting of features at different scales, so as to improve the image reconstruction performance to a large extent. The experimental results show that the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index measure (SSIM) obtained by the proposed method on the publicly available ZRR dataset improve by 0.37 dB and
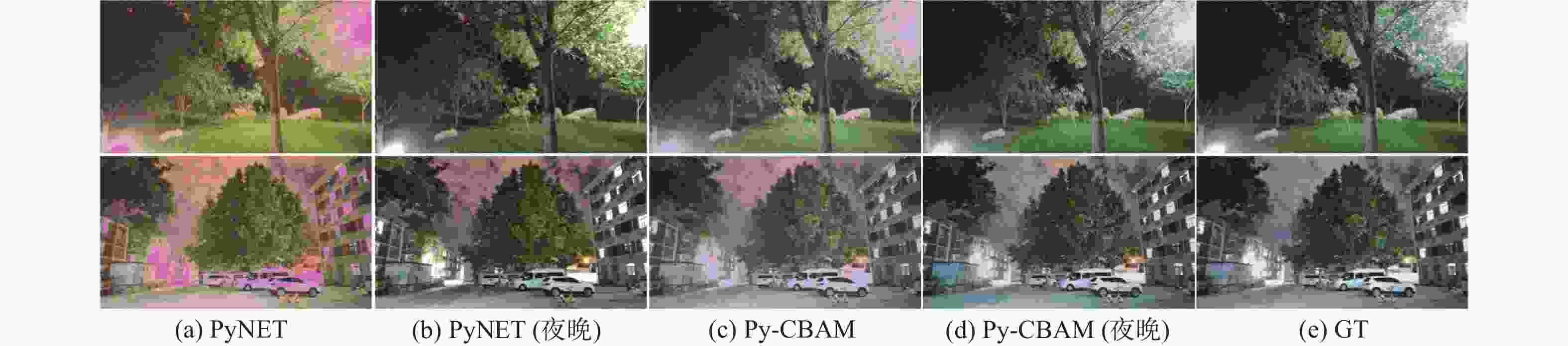
0.0018 compared with those by the PyNET method. After retraining the Py-CBAM on the ZRR dataset and the newly constructed NRR dataset, the PSNR and SSIM reach 25.73 dB and 0.965 4, respectively. Visually, the proposed method solves the problems of high noise and chromatic aberration and distortion in RAW image reconstruction. It can also enhance the reconstruction ability of the model under different lighting environment conditions in multiple scenes. The reconstruction results are more realistic and have better visual quality, especially in the overexposed and dark areas of the image. -
表 1 消融实验结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of ablation experiment results
模型 通道注意力 空间注意力 PSNR/dB SSIM PyNET 20.77 0.8601 Py-CA √ 20.89 0.8597 Py-SA √ 20.97 0.8610 Py-CBAM √ √ 21.14 0.8619 表 2 亮度方差对比实验结果
Table 2. Comparison experiments result of brightness variance
模型 方差 PyNET 1 108.6 Py-CA 1 042.0 Py-SA 1 022.2 Py-CBAM 994.3 表 3 NRR数据集测试结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of test results on NRR dataset
模型 PSNR/dB SSIM PyNET 13.67 0.5537 PyNET(夜晚) 20.22 0.7059 Py-CBAM 20.54 0.7158 Py-CBAM(夜晚) 25.73 0.9654 -
[1] SCHWARTZ E, GIRYES R, BRONSTEIN A M. DeepISP: Toward learning an end-to-end image processing pipeline[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(2): 912-923. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2872858 [2] LIANG Z T, CAI J R, CAO Z S, et al. CameraNet: A two-stage framework for effective camera ISP learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2248-2262. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3051486 [3] IGNATOV A, VAN GOOL L, TIMOFTE R. Replacing mobile camera ISP with a single deep learning model[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2275-2285. [4] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[EB/OL]. (2018-07-17)[2022-11-25]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1807.06521. [5] HEIDE F, STEINBERGER M, TSAI Y T, et al. FlexISP: A flexible camera image processing framework[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, 33(6): 231. [6] ZAMIR S W, ARORA A, KHAN S, et al. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 5718-5729. [7] LI X, GUNTURK B, ZHANG L. Image demosaicing: A systematic survey[C]//Proceedings of the Visual Communications and Image Processing. San Diego: SPIE, 2008: 6822-6837. [8] BUADES A, COLL B, MOREL J M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 60-65. [9] KWOK N M, SHI H Y, HA Q P, et al. Simultaneous image color correction and enhancement using particle swarm optimization[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 26(10): 2356-2371. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2013.07.023 [10] GIJSENIJ A, GEVERS T, VAN DE WEIJER J. Improving color constancy by photometric edge weighting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(5): 918-929. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.197 [11] SHI W Z, CABALLERO J, HUSZÁR F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1874-1883. [12] LIM B, SON S, KIM H, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1132-1140. [13] LAI W S, HUANG J B, AHUJA N, et al. Deep Laplacian pyramid networks for fast and accurate super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5835-5843. [14] LEE J Y, SUNKAVALLI K, LIN Z, et al. Automatic content-aware color and tone stylization[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 2470-2478. [15] FU X Y, ZENG D L, HUANG Y, et al. A fusion-based enhancing method for weakly illuminated images[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 129: 82-96. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.05.031 [16] GUO C L, YAN Q X, ANWAR S, et al. Image dehazing Transformer with transmission-aware 3D position embedding[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 5802-5810. [17] ZAMIR S W, ARORA A, KHAN S, et al. CycleISP: Real image restoration via improved data synthesis[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2693-2702. [18] UHM K H, KIM S W, JI S W, et al. W-Net: Two-stage U-Net with misaligned data for raw-to-RGB mapping[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3636-3642. [19] ZHANG Z L, WANG H L, LIU M, et al. Learning RAW-to-sRGB mappings with inaccurately aligned supervision[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 4328-4338. [20] MORAWSKI I, CHEN Y, LIN Y S, et al. GenISP: Neural ISP for low-light machine cognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 629-638. [21] HSYU M C, LIU C W, CHEN C H, et al. CSANet: High speed channel spatial attention network for mobile ISP[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 2486-2493. [22] DAI L H, LIU X H, LI C Q, et al. AWNet: Attentive wavelet network for image ISP[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 185-201. [23] WANG F, JIANG M Q, QIAN C, et al. Residual attention network for image classification[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6450-6458. [24] VEDALDI A, FULKERSON B. VLFeat: An open and portable library of computer vision algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the 18th ACM international conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2010: 1469-1472. -







 下载:
下载: