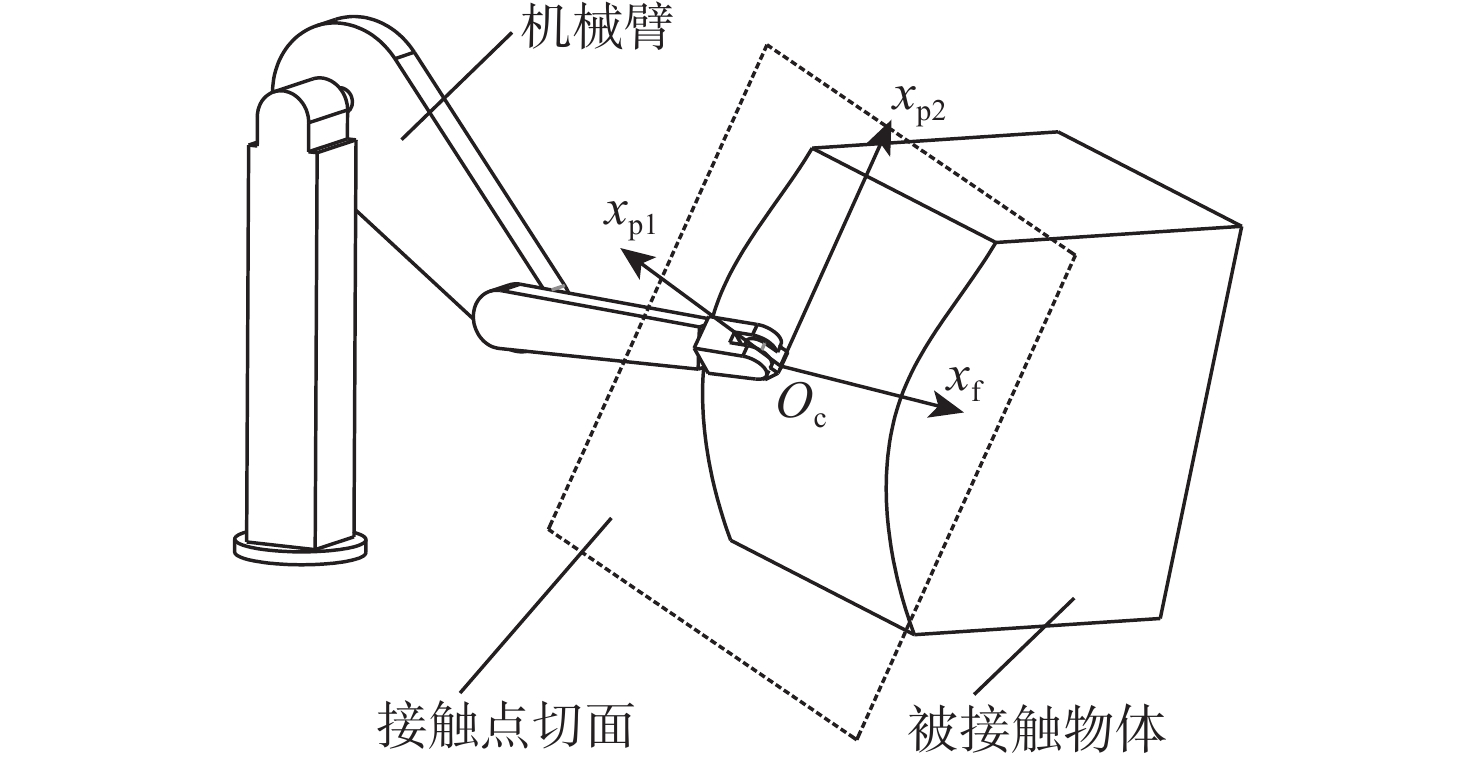
-
摘要:
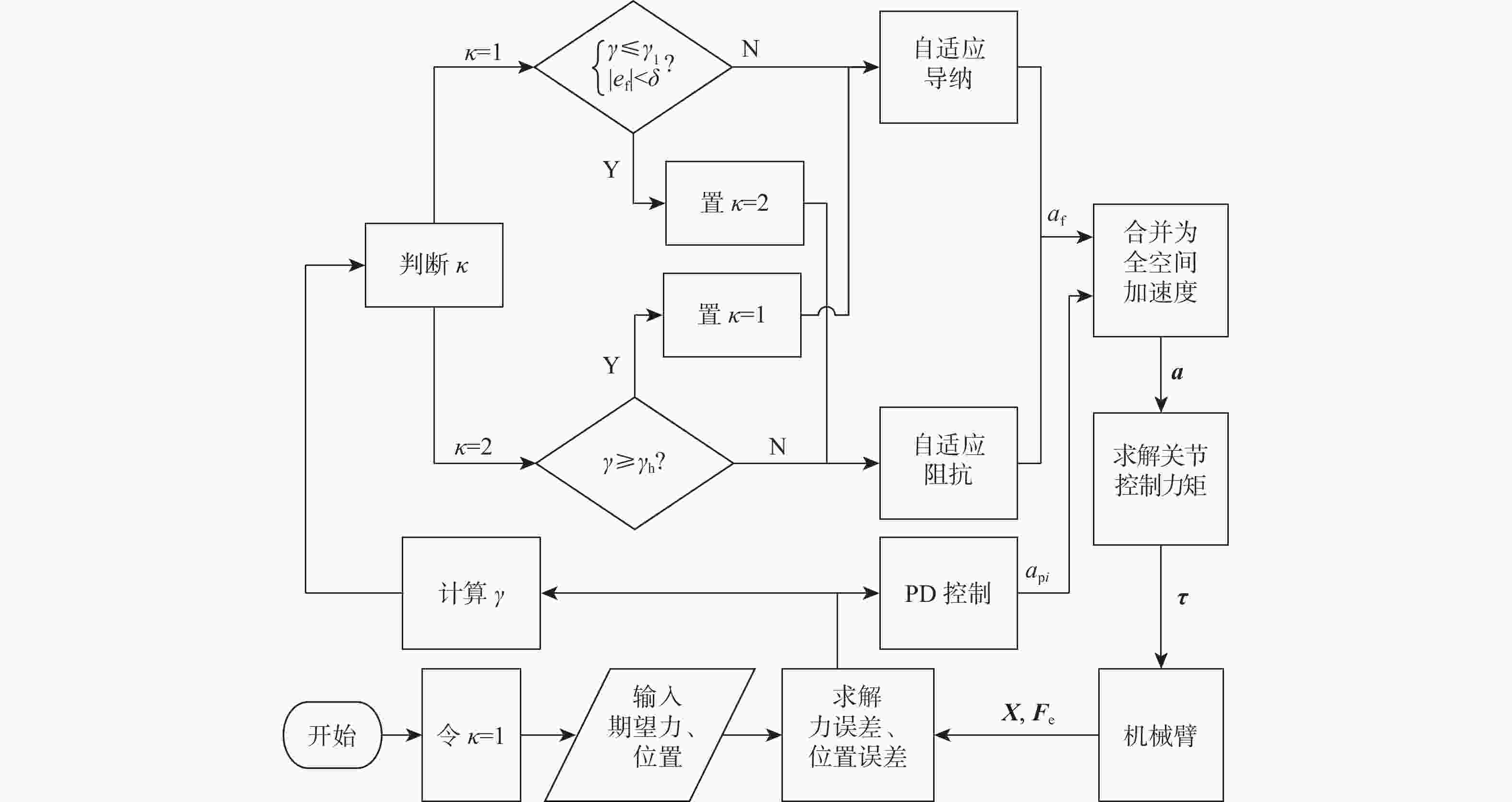
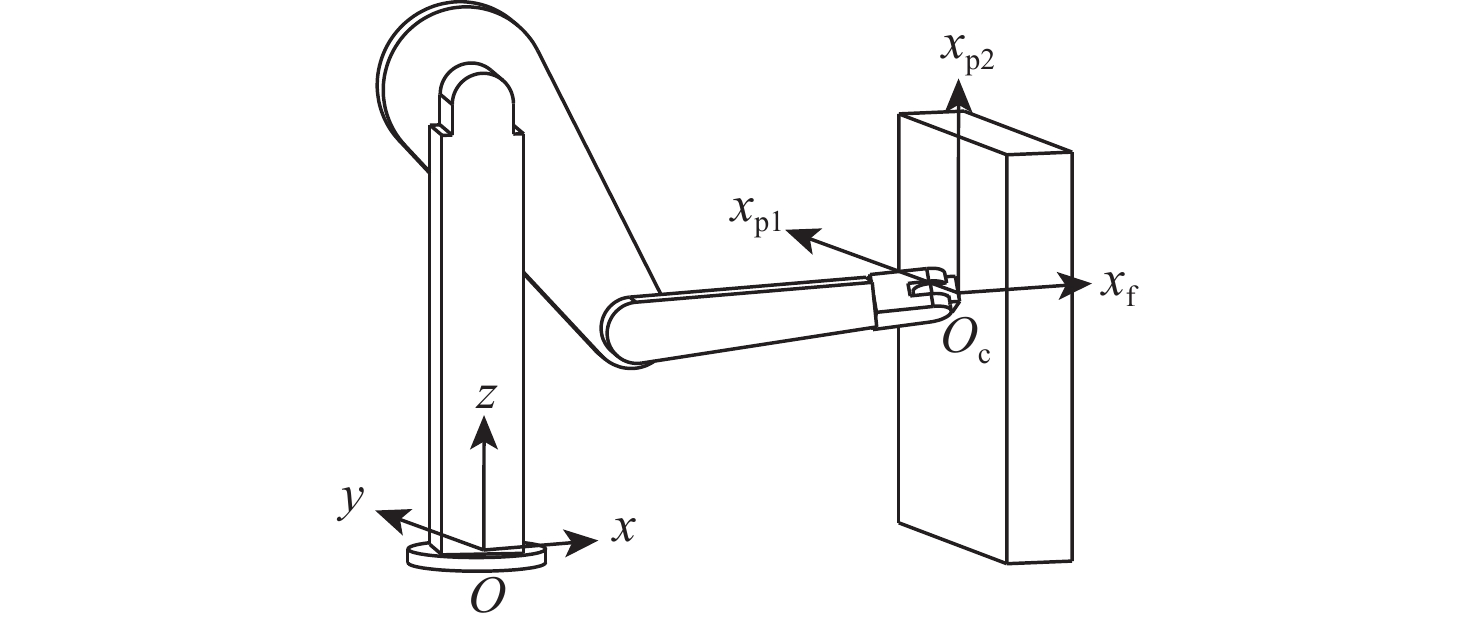
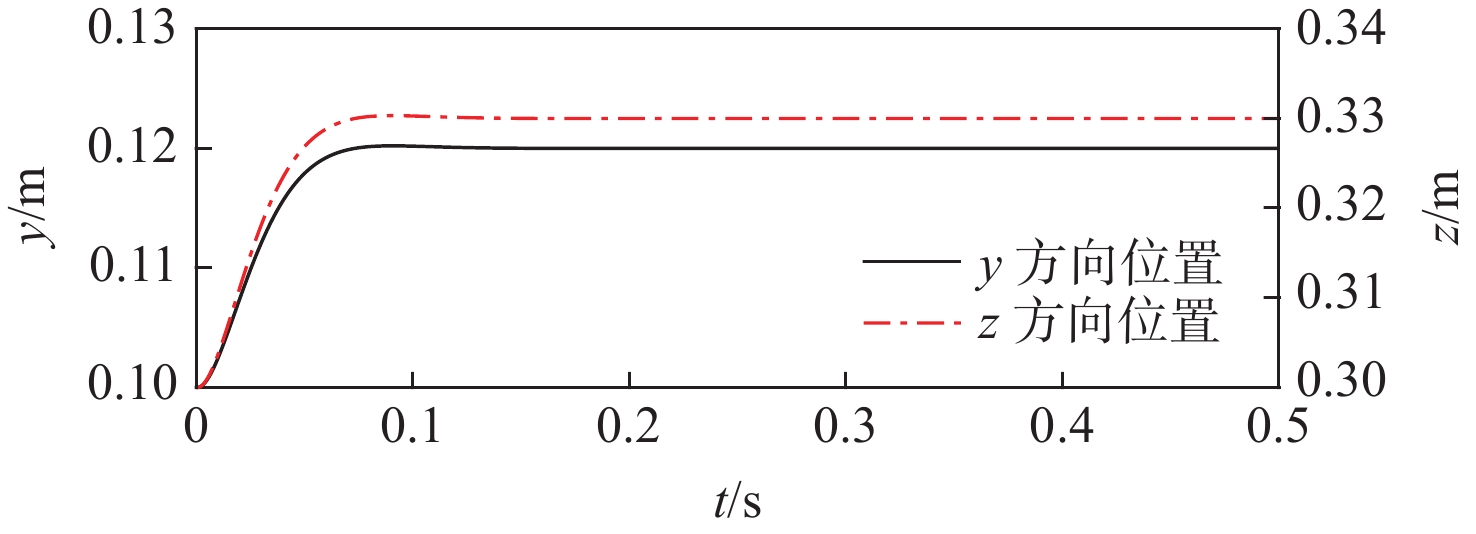
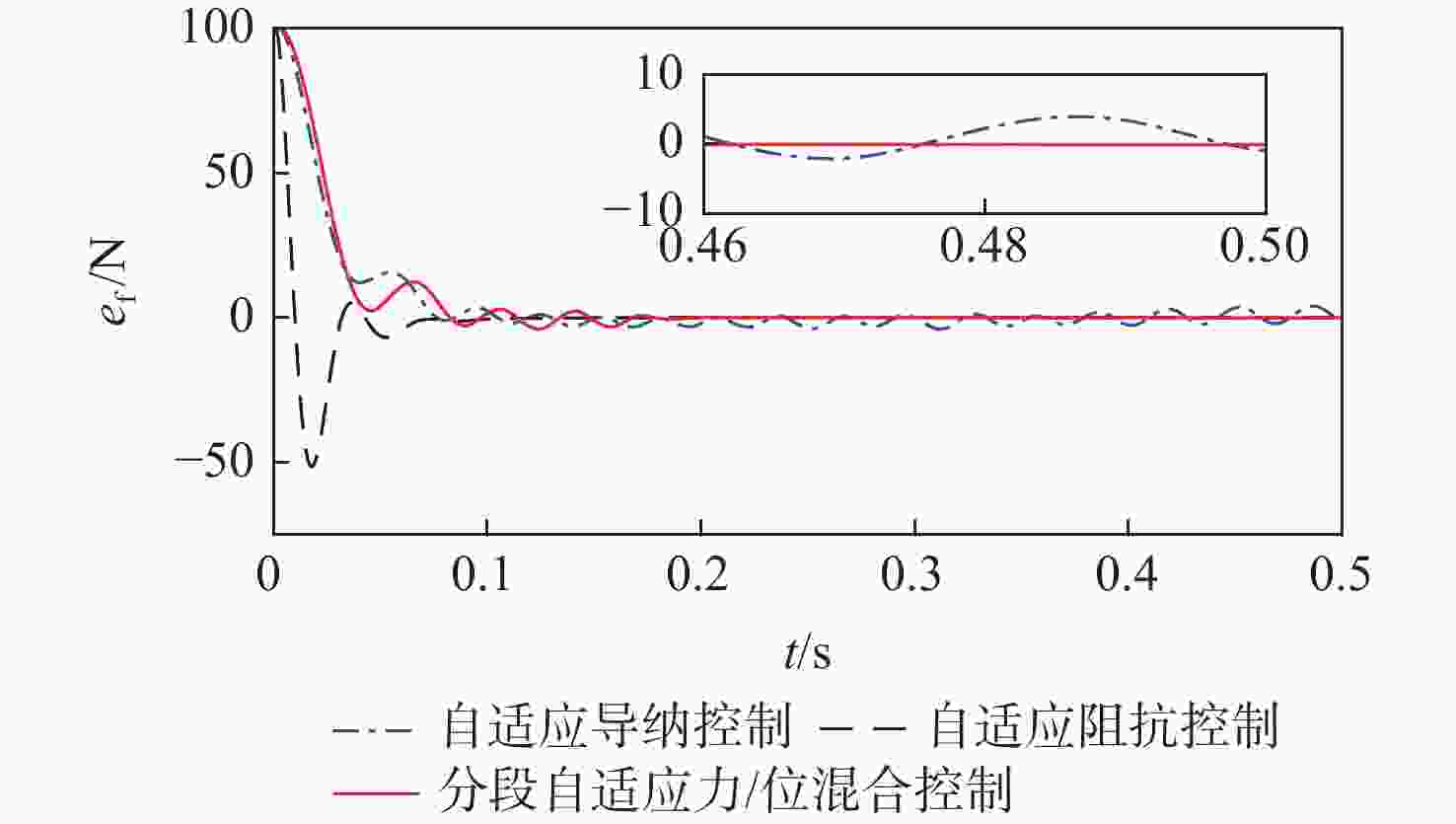
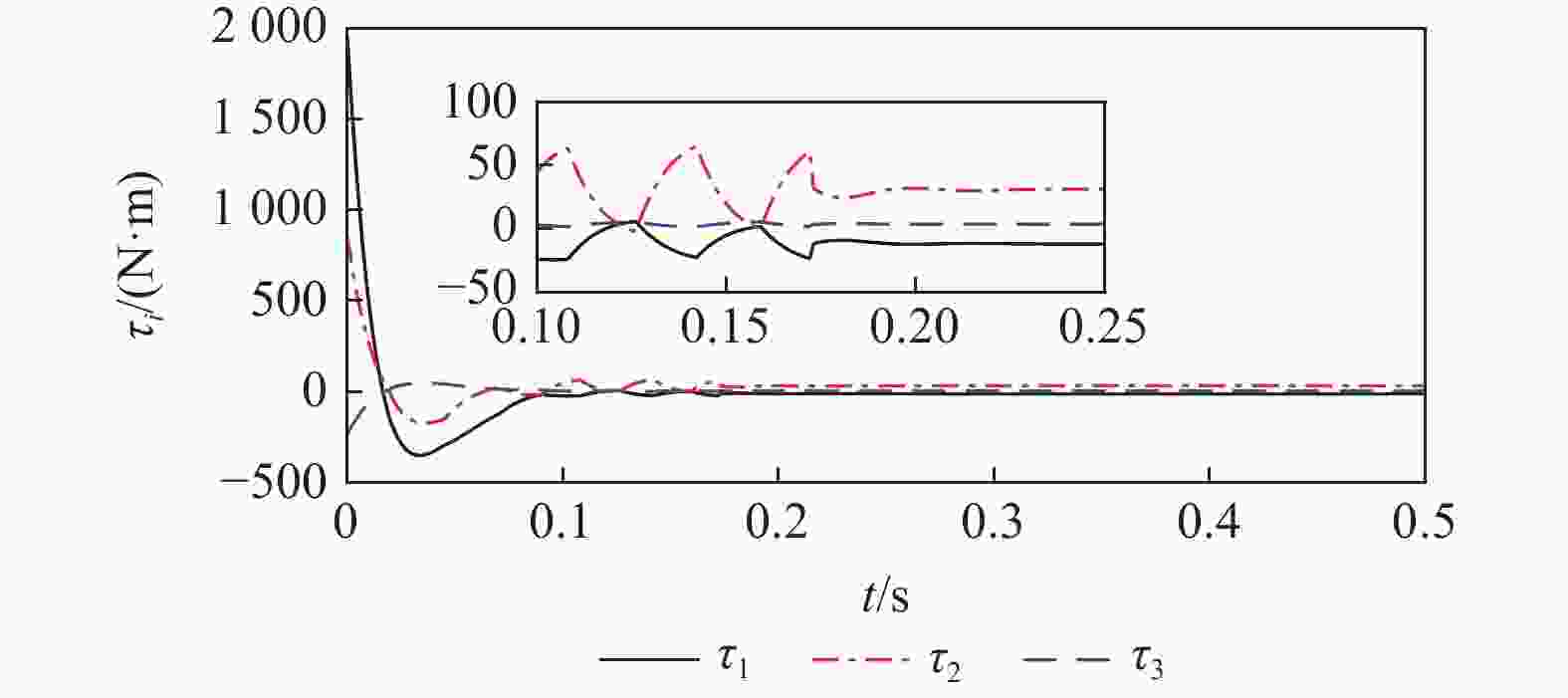
空间操作任务对空间机械臂的柔顺控制品质要求不断提高,采用单一控制方法易造成较大的末端接触力超调或动态偏差。结合自适应阻抗与自适应导纳控制方法的优点,提出一种基于分段自适应的力/位混合控制方法。所提方法按空间实现力、位分控,并基于子空间期望末端加速度叠加的方式,求取关节控制力矩。力空间控制中,采用自适应导纳控制实现初始位置到目标位置的快速过渡,在接近目标位置时,采用自适应阻抗控制实现末端的高精度稳定控制;由于位置空间控制中期望力和接触力均为0,直接采用PD控制即可获得与自适应控制方法相同的效果。仿真结果表明:相较于自适应阻抗或自适应导纳单一控制,采用所提方法时接触力超调量和动态偏差更小,全程控制品质更优。
Abstract:The requirements for the compliant control quality of the space manipulator are continuously improved in space manipulation tasks. Using a single control method is likely to cause large end contact force overshoot or dynamic deviation. This study proposes and implements a force/position hybrid control approach based on staged adaptation, which combines the advantages of adaptive impedance and adaptive admittance control systems. The method realizes separate control of force and position according to space and calculates the joint control torque based on the superposition of expected terminal acceleration in subspace. Because the expected force and the contact force are both 0 in the position space control, the same result as the adaptive control method can be obtained by directly using PD control. Adaptive admittance control is used in the force space control to realize the rapid transition from the initial position to the target position, and adaptive impedance control is used to realize the high-precision and stable control of the end when approaching the target position. The simulation results show that compared with the single use of adaptive impedance or adaptive admittance control, the contact force overshoot and dynamic deviation are smaller when the staged adaptive force/position hybrid control method is adopted, and the whole process control quality is better.
-
Key words:
- manipulators /
- compliance control /
- force control /
- stages /
- adaptive algorithms
-
表 1 机械臂标准DH参数
Table 1. Standard DH parameters of manipulator
连杆号 α/(°) l/mm d/mm 1 90 0 660 2 180 432 149 3 90 0 60.0 4 −90 0 433 5 90 0 0 6 0 0 56.3 注:α为关节扭角;l为连杆长度;d为关节偏移。 表 2 机械臂惯性参数
Table 2. Inertia parameters of manipulator
连杆号 χ/kg px/mm py/mm pz/mm Ixx/(kg·mm2) Iyy/(kg·mm2) Izz/(kg·mm2) Ixy/(kg·mm2) Iyz/(kg·mm2) Izx/(kg·mm2) 1 75.0 0 −323 −0.235 1.08×107 1.77×105 1.07×107 0 0 0 2 50.8 −282 0 1.97 1.78×105 5.39×106 5.51×106 0 −4.51×104 0 3 14.4 0 −0.917 142 4.74×105 4.76×105 1.23×104 0 0 0 4 2.66 0 38.9 0 7.64×103 1.73×103 7.55×103 0 0 0 5 0.484 0 0 14.4 282 294 102 0 0 0 6 0.010 0 0 −8.13 0.938 0.938 0.124 0 0 0 注:χ为连杆质量;px、py、pz为连杆质心在由DH参数建立的连杆坐标系下的位置分量;Ixx、Iyy、Izz、Ixy、Iyz、Izx为连杆在连杆坐标系的二阶惯量。 表 3 3种控制方法下接触力动态响应
Table 3. Dynamic response of contact force by three control methods
控制方法 超调量/% 动态偏差/% 自适应导纳控制 3.94 3.31 自适应阻抗控制 51.5 0.30 分段自适应力/位混合控制 3.92 0.30 -
[1] 王宪伦. 不确定环境下机器人柔顺控制及可视化仿真的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2006.WANG X L. Research on robot compliance control and visual simulation in uncertain environment[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2006(in Chinese). [2] 殷跃红, 朱剑英, 尉忠信. 机器人力控制研究综述[J]. 南京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 1997, 29(2): 220-230.YIN Y H, ZHU J Y, WEI Z X. Force control of robot: An overview[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 1997, 29(2): 220-230(in Chinese). [3] RAIBERT M H, CRAIG J J. Hybrid position/force control of manipulators[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1981, 103(2): 126-133. doi: 10.1115/1.3139652 [4] HOGAN N. Impedance control: An approach to manipulation: Part I—Theory[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1985, 107(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1115/1.3140702 [5] HOGAN N. Impedance control: An approach to manipulation: Part II—Implementation[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1985, 107(1): 8-16. doi: 10.1115/1.3140713 [6] HOGAN N. Impedance control: An approach to manipulation: Part III—Applications[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1985, 107(1): 17-24. doi: 10.1115/1.3140701 [7] 李志雄. 七自由度协作机械臂避障与柔顺控制方法研究及仿真分析[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2021: 8.LI Z X. Research and simulation analysis on obstacle avoidance and compliance control method of 7-DOF cooperative manipulator[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2021: 8(in Chinese). [8] SERAJI H. Adaptive admittance control: An approach to explicit force control in compliant motion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1994: 2705-2712. [9] SERAJI H, COLBAUGH R. Adaptive force-based impedance control[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1993: 1537-1544. [10] JUNG S, HSIA T C, BONITZ R G. Force tracking impedance control for robot manipulators with an unknown environment: Theory, simulation, and experiment[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2001, 20(9): 765-774. doi: 10.1177/02783640122067651 [11] ROVEDA L, VICENTINI F, PEDROCCHI N, et al. Force-tracking impedance control for manipulators mounted on compliant bases[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 760-765. [12] WANG X B, ZHANG Y, LU C. Adaptive impedance control in uncertain environment for uncertain manipulator[C]//Proceedings of the 40th Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 3937-3942. [13] 王邢波, 葛胜. 基于BP神经网络的腱驱动灵巧手的自适应阻抗控制[J]. 信息技术与网络安全, 2019, 38(4): 71-75.WANG X B, GE S. Self-adaptive impedance control of tendon-driven dexterous hands based on BP neural network[J]. Information Technology and Network Security, 2019, 38(4): 71-75(in Chinese). [14] 戚毅凡, 贾英宏, 赵宝山, 等. 基于改进神经网络的空间机械臂阻抗控制方法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2022, 42(2): 82-90.QI Y F, JIA Y H, ZHAO B S, et al. Impedance control of space manipulator based on improved neural network[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2022, 42(2): 82-90(in Chinese). [15] ZHANG X, SUN L T, KUANG Z A, et al. Learning variable impedance control via inverse reinforcement learning for force-related tasks[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(2): 2225-2232. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3061374 [16] 王小冬. 基于力/位控制的机械臂纤维铺放技术研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2019: 25-27.WANG X D. Research on fiber placement technology of manipulator based on force/position control[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2019: 25-27(in Chinese). [17] JUNG S, HSIA T C, BONITZ R G. Force tracking impedance control of robot manipulators under unknown environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2004, 12(3): 474-483. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2004.824320 [18] 彭光宇, 董洪波, 马斌. 两种DH模型的机器人运动学建模对比研究[J]. 机械研究与应用, 2019, 32(6): 62-65.PENG G Y, DONG H B, MA B. Comparative study of robot kinematics modeling based on two DH models[J]. Mechanical Research & Application, 2019, 32(6): 62-65(in Chinese). -






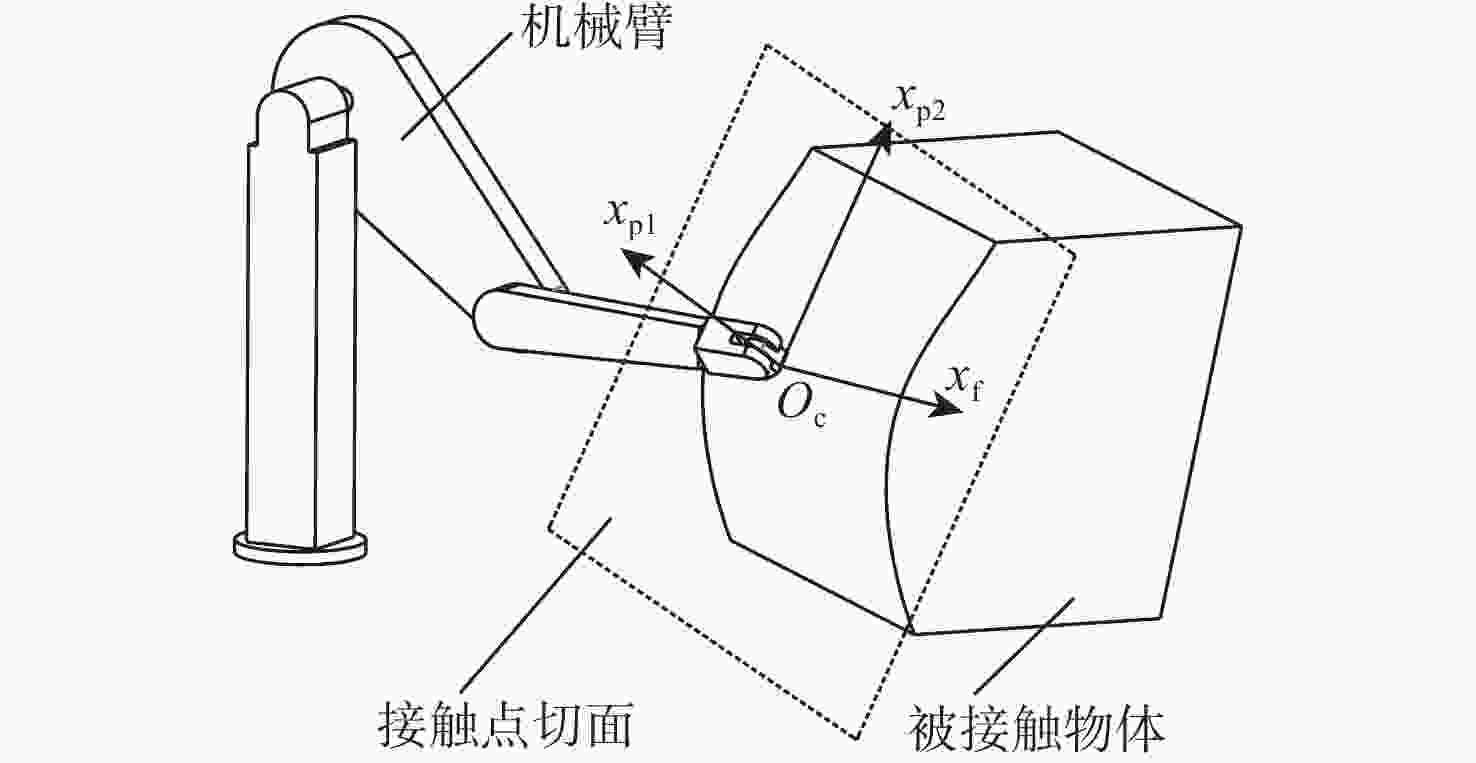
 下载:
下载: