-
摘要:
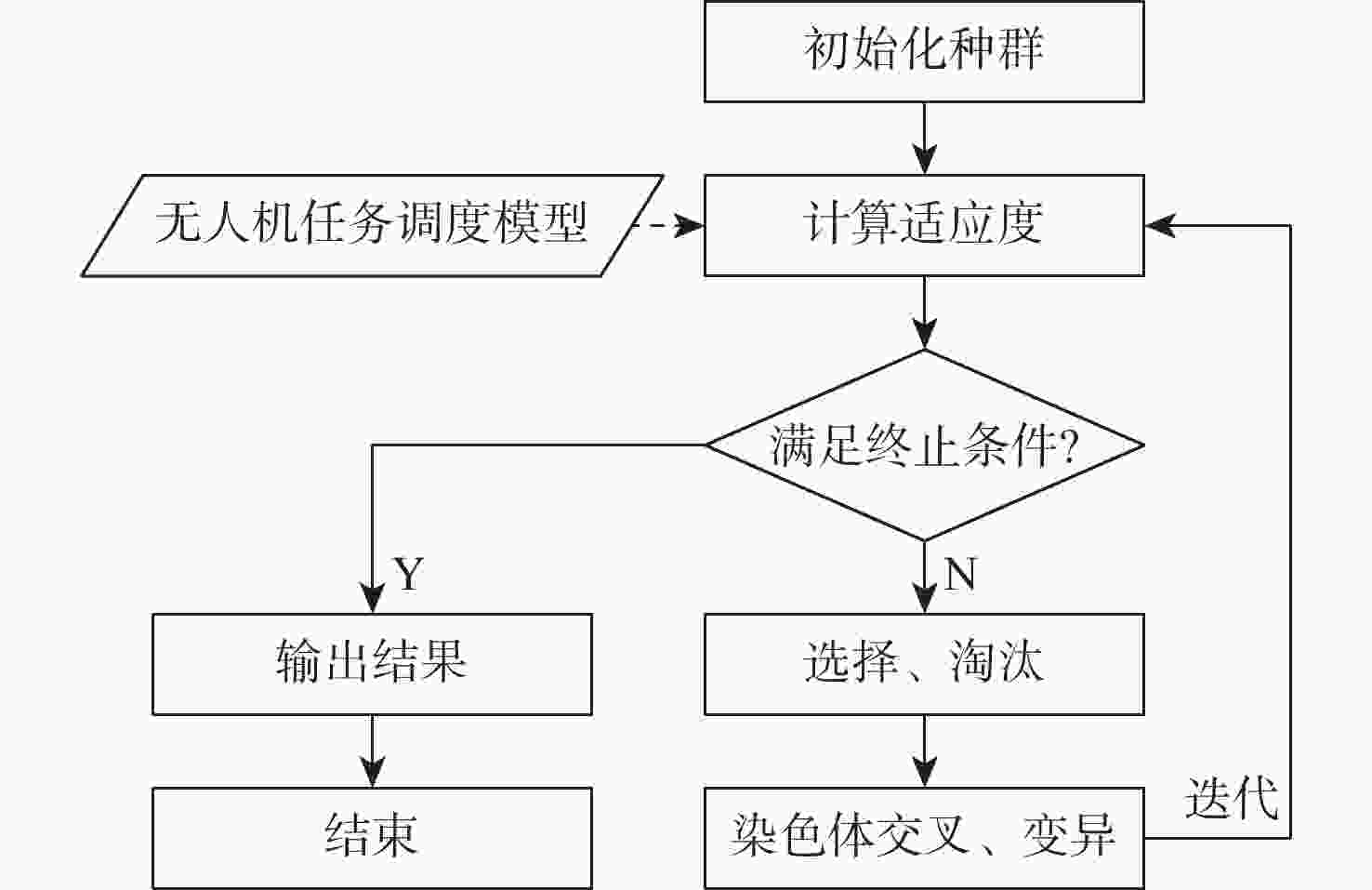
蜂群无人机因其数量多、成本低和统一调度等特点,具有广泛应用前景。统一调度是蜂群无人机研究的热点和难点,现有研究主要针对小规模、短时间场景,未考虑充电任务等复杂场景。面向未来多任务和长时间应用,调度优化需考虑中途充电等因素的影响。提出一种基于统一调度模型和遗传算法改进的蜂群无人机任务调度方法。将无线充电平台资源纳入无人机工作环境中,并对工作场景进行系统建模;使用遗传算法对任务和充电平台资源调配进行优化求解。利用仿真实验进行验证,结果表明:所提方法可以有效适应任务、环境和资源的变化,适用于大规模蜂群无人机多任务场景。
Abstract:The swarm unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), characterized by their large quantity, low cost, and unified scheduling, have broad application prospects. Unified scheduling is a focal point and challenge in swarm UAVs research, aiming to the optimal allocation of tasks and resources. Current scheduling research primarily focuses on small-scale, short-term scenarios without considering complex scenarios such as mid-operation charging. However, for future multi-task and long-term applications, scheduling optimization must account for such factors. An improved mission scheduling method for swarm UAVs based on a unified scheduling model and an improved genetic algorithm was proposed. First, the wireless charging platform resources were incorporated into the UAV working environment, and the working scenario was modeled systematically. Then, the genetic algorithm was used to optimize the mission and charging platform resource allocation. Finally, the proposed method was tested for validation using simulated scenarios. Test results show that the method proposed can better adapt to changes in missions, environment, and resources, showing good performance even for large-scale swarm UAVs.
-
Key words:
- swarm UAV /
- scheduling optimization /
- genetic algorithm /
- scheduling model /
- UAV charging
-
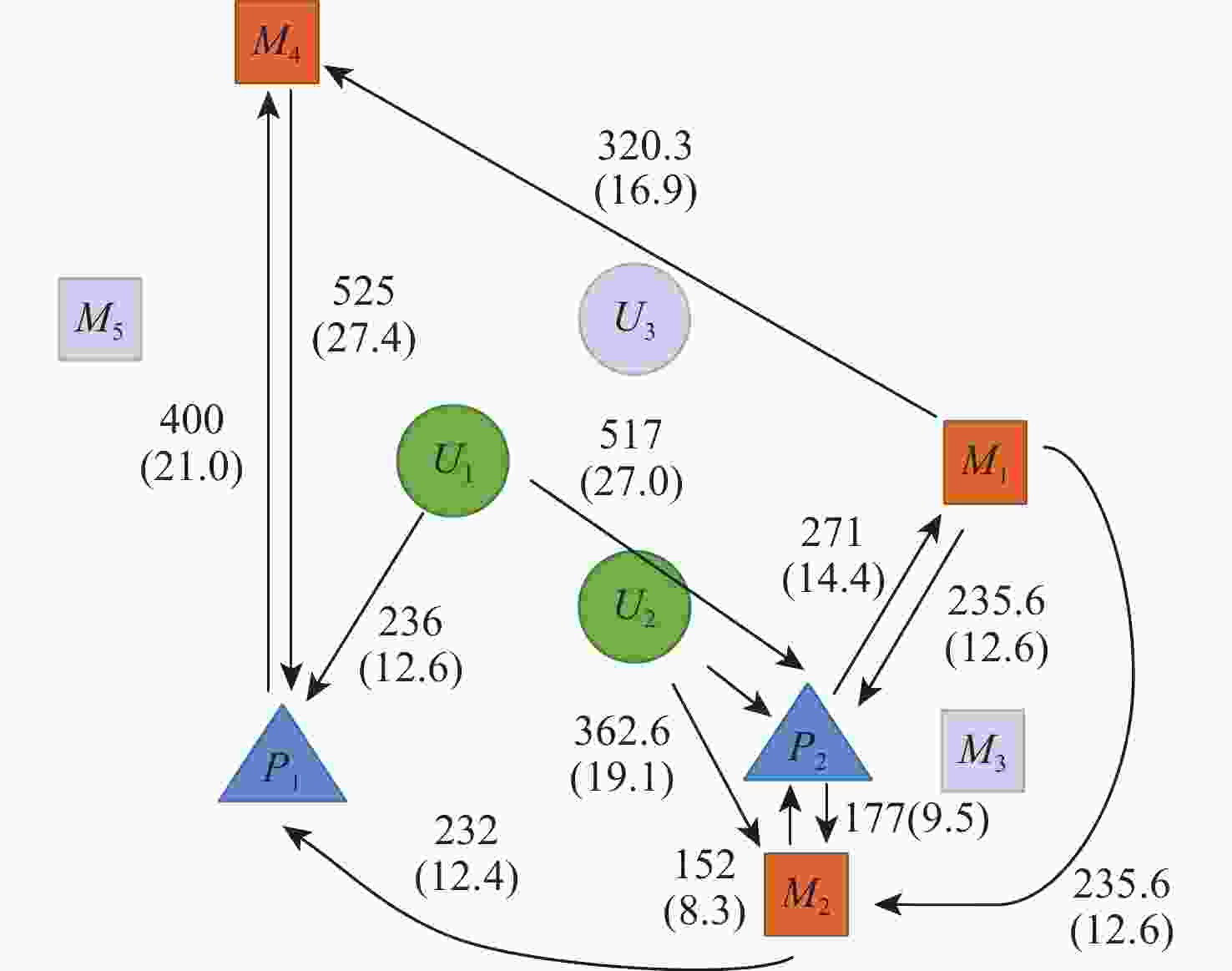
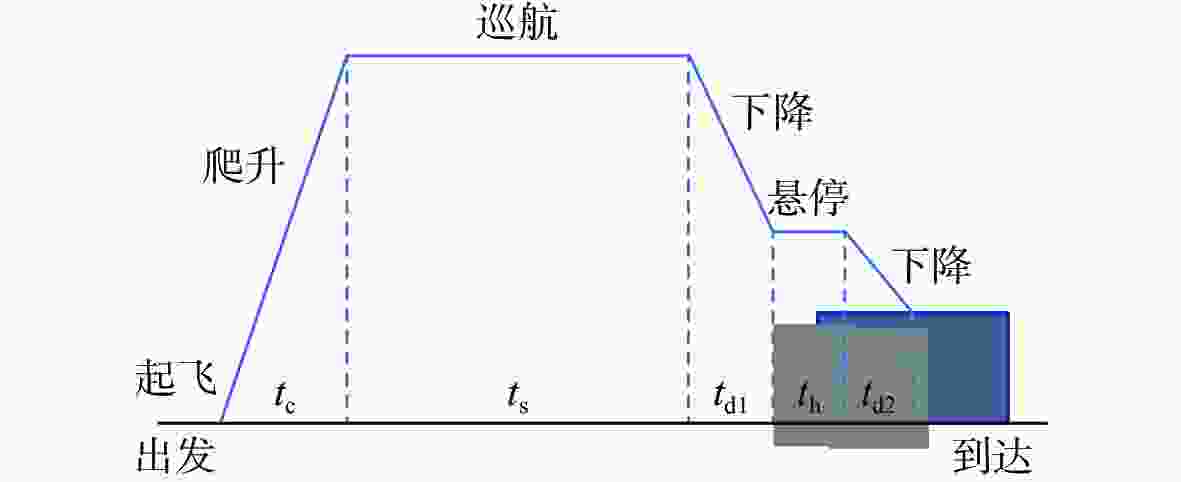
表 1 无人机不同飞行状态下的平均速度及平均功率
Table 1. Average speed and average power consumption of UAV in different flight conditions
状态 平均速度/(m·s−1) 平均功率/W 悬停 160.8 爬升 3 320.0 巡航 14 185.0 下降 3 128.0 表 2 测试样本环境及任务参数
Table 2. Test case environment and mission parameters
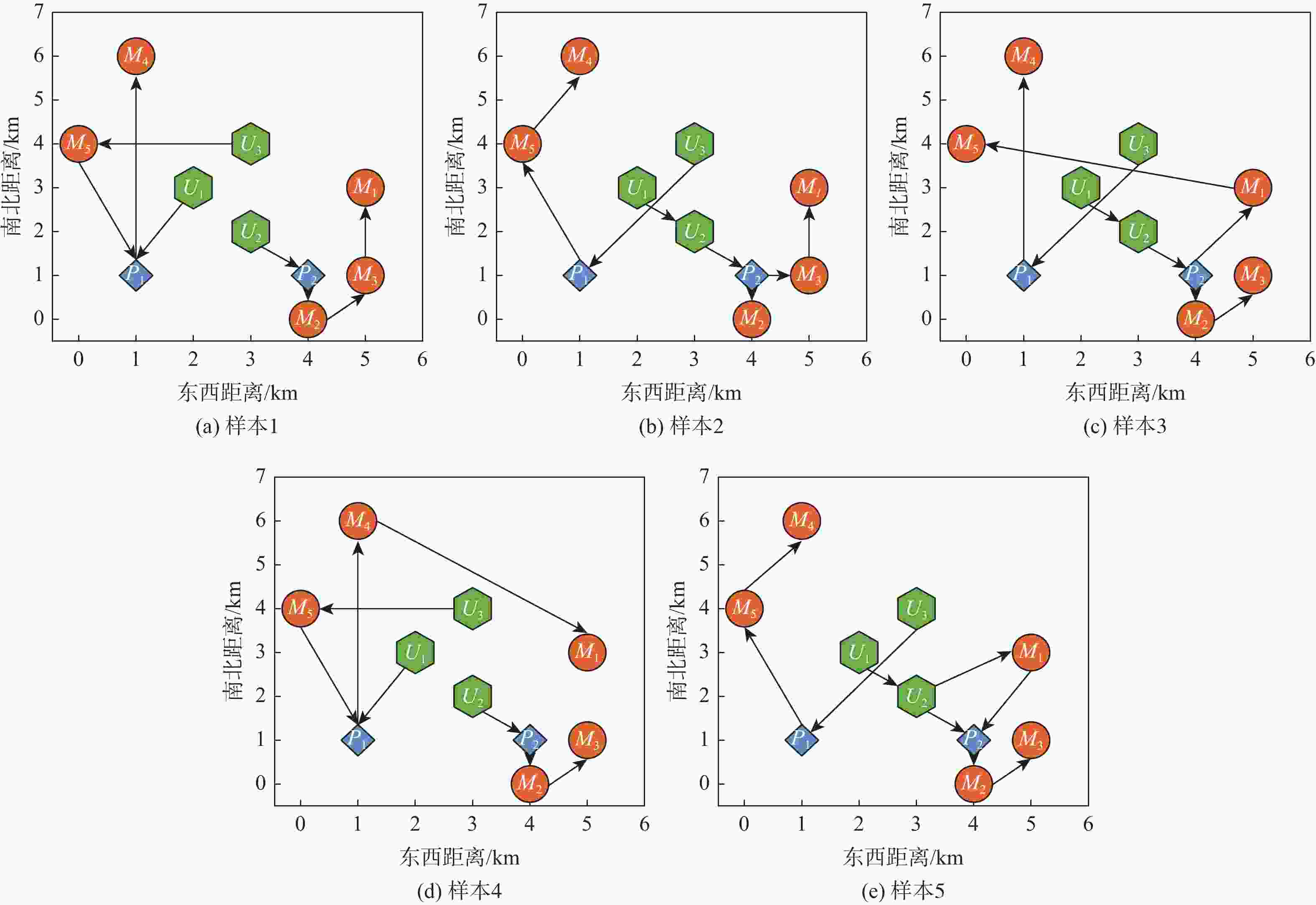
样本 特征 1(基准) 风力:无风
目标点高度:均为0 m
任务截止时间:均为1 h
充电平台功率:120 W
无人机初始电量:U1、U2为30 Wh,
U3为40 Wh2(有风) 风力:东风 8 m/s(约5级风) 3(高度) 目标点高度:M1为30 m;M2为90 m;M4为500 m 4(截止时间) 任务截止时间:
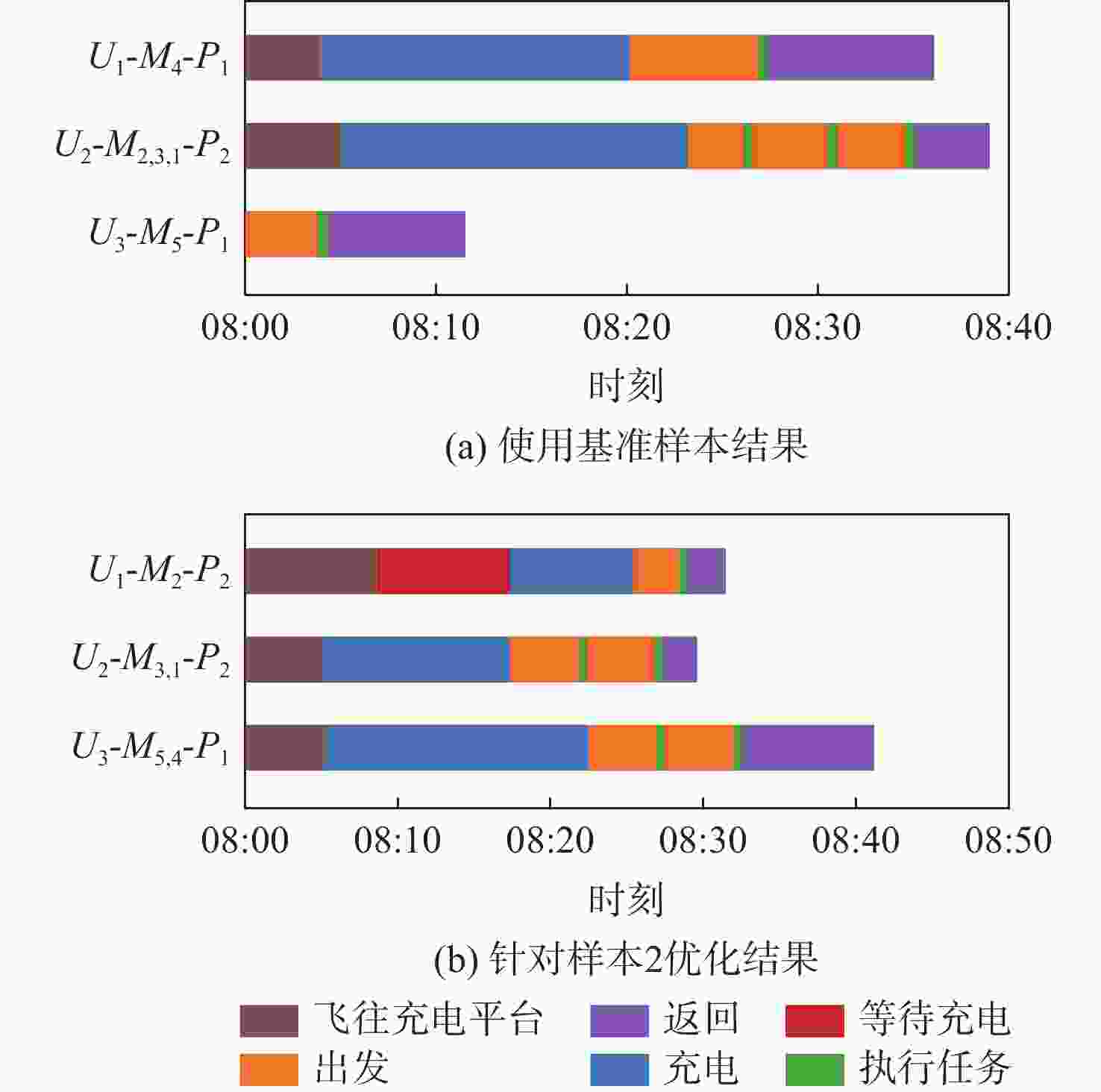
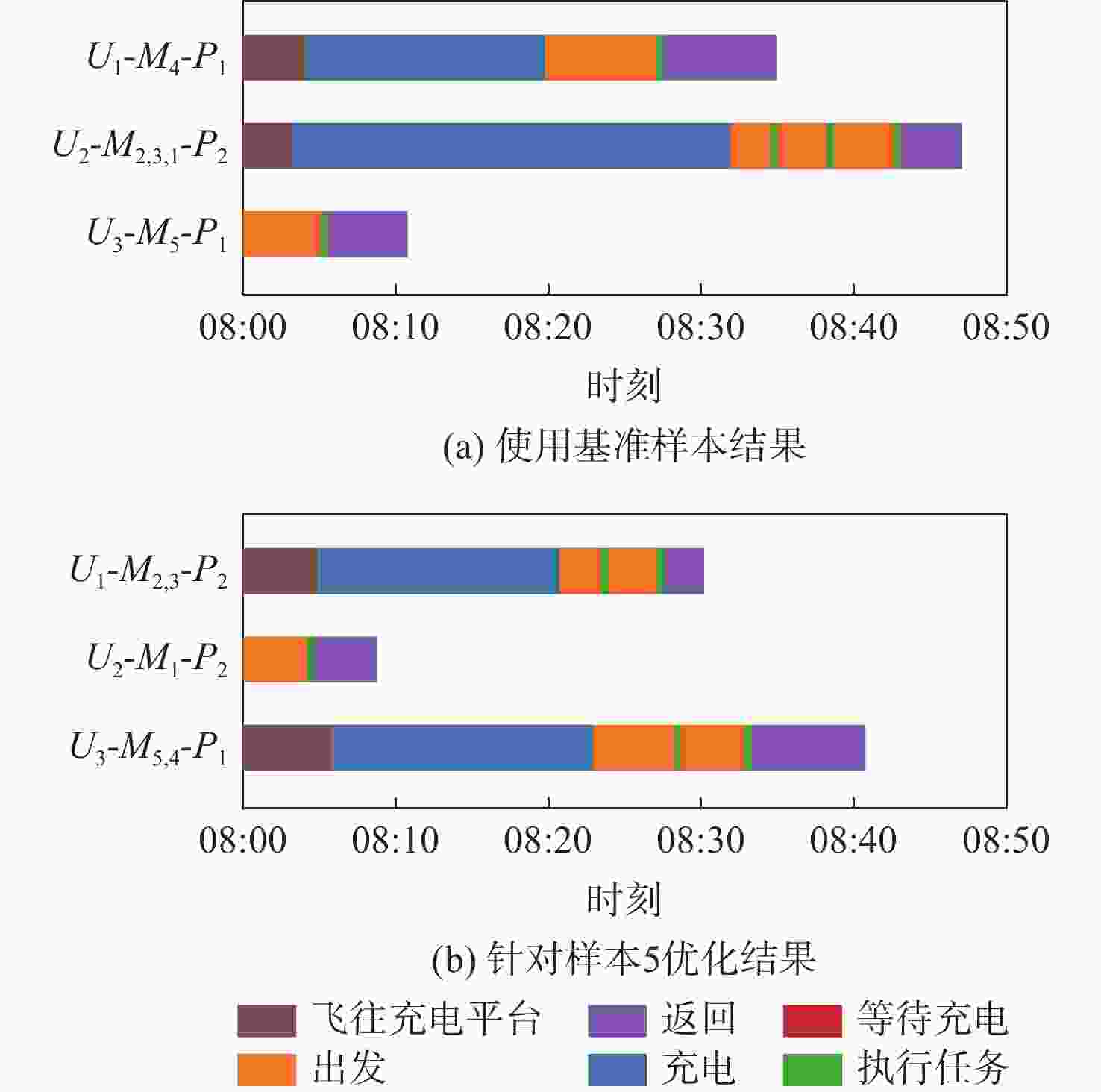
M2为15 min;M3为20 min;M5为10 min5(充电平台) 充电平台功率:P1为120 W;P2为60 W 表 3 基准与针对性优化对比
Table 3. Comparison between benchmark and case-by-case optimization
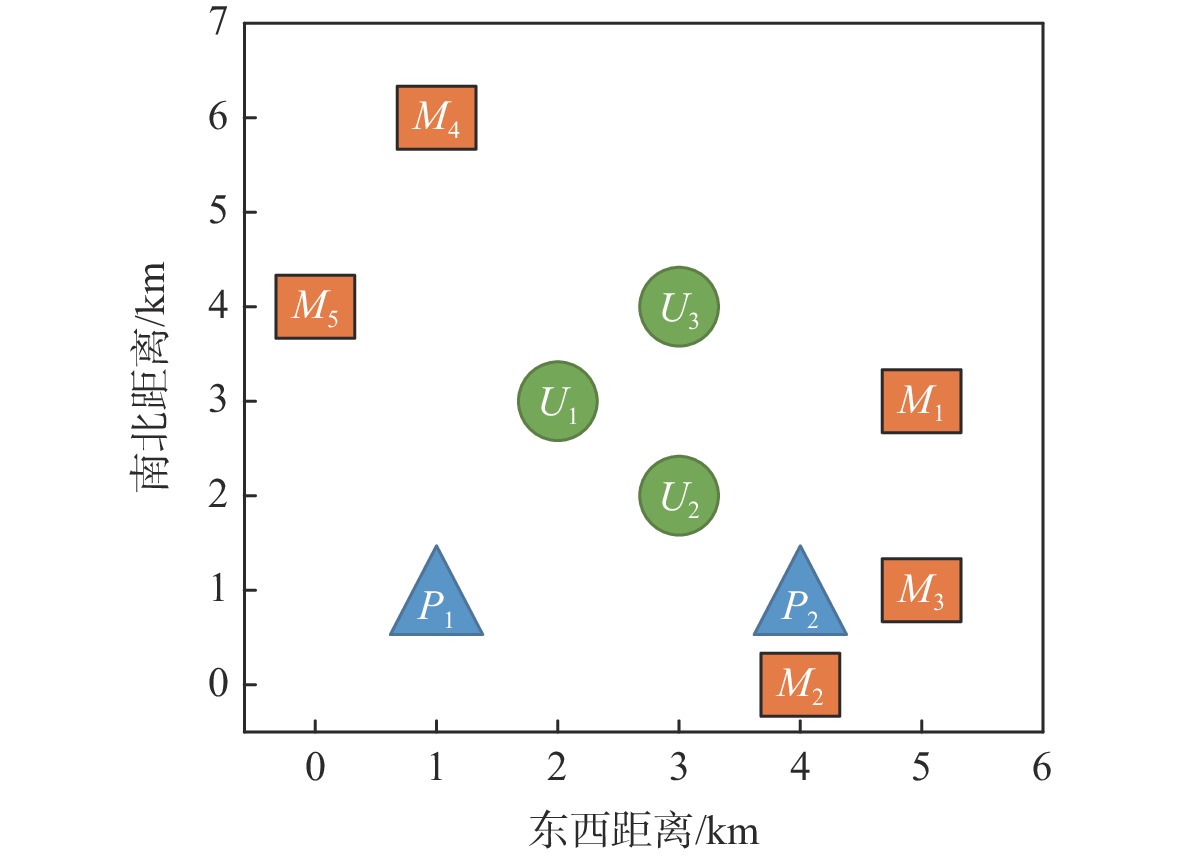
样本 最大用时$ \max \; ({{T_i}})/{{\mathrm{s}}} $ 总能耗$\displaystyle\sum\limits_n {{E_i}} {\text{/J}}$ 总超时$\displaystyle\sum\limits_m {{\tau _i}} /{{\mathrm{s}}} $ 基准 优化 差值 变化幅度/% 基准 优化 差值 变化幅度/% 基准 优化 差值 变化幅度/% 2 2099.4 1943.4 −156.0 −7.4 593073 631580 38507 6.5 3 2459.0 2408.6 −50.4 −2.0 649034 737293 88259 13.6 4 1736.0 2586.9 850.9 49 556448 543233 −13 215 −2.4 565.2 0 −565.2 −100 5 2605.6 2046.7 −558.9 −21 556447 570351 13904 2.5 注:差值负数表示针对性优化减小。 表 4 大规模测试充电平台位置
Table 4. Charging platform location in large-scale tests
样本 平面位置/km 高度/m 充电功率/W 1 (5.000, 2.000) 0 120 2 (7.598, 3.500) 25 120 3 (7.598, 6.500) 0 90 4 (5.000, 8.000) 0 120 5 (2.401, 6.500) 25 80 6 (2.401, 3.500) 0 120 表 5 测试样本任务及无人机数量
Table 5. Number of missions and UAVs in test cases
样本 任务数 无人机数 1 10 10 2 20 16 3 32 24 4 48 32 5 64 48 表 6 不同任务规模样本测试结果
Table 6. Test results for samples with different mission scales
样本 种群规模N 最大迭代数 $\max ({T_i}){\text{ /}}{{\mathrm{s}}}$ $\displaystyle\sum\limits_m {{\tau _i}} {\text{ /}}{{\mathrm{s}}}$ $\min (f)$ 计算用时/s 1 256 100 3130 0 4.5×104 7.2 256 100 3136 0 4.5×104 7.3 256 100 3014 0 4.5×104 7.3 2 512 100 7803 361.9 1.7×105 19.8 512 100 7249 2850 5.4×105 20.5 256 200 6683 2435 4.7×105 19.7 3 512 200 6644 31803 5.0×106 56.4 1024 100 7164 32238 5.1×106 57.3 1024 200 6320 23506 3.7×106 112.3 4 1024 200 9177 89641 1.4×107 149.5 2048 200 11888 145724 2.3×107 303.9 2048 200 11889 145723 2.3×107 304.2 5 2048 200 7057 64259 1.0×107 432.2 2048 200 7976 67623 1.1×107 442.4 2048 400 7334 59060 9.6×106 879.9 表 7 大规模随机样本测试结果
Table 7. Test results of large-scale random samples
样本 (任务数,
无人机数)平均适应度函数
变异系数平均运行
时间/s1 (10,10) 0.07 7.91 2 (20,16) 0.01 19.47 3 (32,24) 0.03 112.75 -
[1] 杨健, 程程, 谢旭, 等. 无人机蜂群对面攻击任务规划能力需求研究[C]//第九届中国指挥控制大会. 北京: 中国指挥与控制学会, 2021: 252-258.YANG J, CHENG C, XIE X, et al. Study on the mission planning requirements in the UAV swarms air to surface attack operations[C]//Proceedings of the 9th China Command and Control Conference. Beijing: Chinese Institute of Command and Control, 2021: 252-258(in Chinese). [2] 焦士俊, 王冰切, 刘剑豪, 等. 国内外无人机蜂群研究现状综述[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2019, 35(1): 61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2019.01.014JIAO S J, WANG B Q, LIU J H, et al. Review of drone swarm research at home and abroad[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2019, 35(1): 61-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2019.01.014 [3] 杜永浩, 邢立宁, 蔡昭权. 无人飞行器集群智能调度技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(2): 222-241.DU Y H, XING L N, CAI Z Q. Survey on intelligent scheduling technologies for unmanned flying craft clusters[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(2): 222-241(in Chinese). [4] CHEN G S, CRUZ J B. Genetic algorithm for task allocation in UAV cooperative control[C]//AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2003: 5582. [5] DI FRANCO C, BUTTAZZO G. Coverage path planning for UAVs photogrammetry with energy and resolution constraints[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2016, 83(3): 445-462. [6] AHMADZADEH A, SAYYAR-ROUDSARI B, HOMAIFAR A. A hybrid projected gradient-evolutionary search algorithm for capacitated multi-source multiuavs scheduling with time windows[M]//BUTENKO S, MURPHEY R, PARDALOS P M. Recent developments in cooperative control and optimization. Berlin: Springer, 2004: 1-21. [7] 赵明, 苏小红, 马培军, 等. 复杂多约束UAVs协同目标分配的一种统一建模方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(12): 2038-2048. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.02038ZHAO M, SU X H, MA P J, et al. A unified modeling method of UAVs cooperative target assignment by complex multi-constraint conditions[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(12): 2038-2048(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.02038 [8] RAMIREZ-ATENCIA C, BELLO-ORGAZ G, R-MORENO M D, et al. A hybrid MOGA-CSP for multi-UAV mission planning[C]//Proceedings of the Companion Publication of the 2015 Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. New York: ACM, 2015: 1205-1208. [9] GAO C, ZHEN Z Y, GONG H J. A self-organized search and attack algorithm for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2016, 54: 229-240. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2016.03.022 [10] WU W N, WANG X G, CUI N G. Fast and coupled solution for cooperative mission planning of multiple heterogeneous unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 79: 131-144. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.05.039 [11] OH G, KIM Y, AHN J, et al. PSO-based optimal task allocation for cooperative timing missions[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2016, 49(17): 314-319. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.09.054 [12] SONG Y Q, SUN X Y, WANG H X, et al. Design of charging coil for unmanned aerial vehicle-enabled wireless power transfer[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Power and Energy Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 268-272. [13] JEONG S, BITO J, TENTZERIS M M. Design of a novel wireless power system using machine learning techniques for drone applications[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-4. [14] 王云哲, 徐国宁, 王生, 等. 蜂群无人机充电排队优化方法[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(10): 323928.WANG Y Z, XU G N, WANG S, et al. Optimization of charging queuing of UAV swarming[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(10): 323928(in Chinese). [15] KIM J, KIM S, JEONG J, et al. CBDN: cloud-based drone navigation for efficient battery charging in drone networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(11): 4174-4191. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2883058 [16] SHIN M, KIM J, LEVORATO M. Auction-based charging scheduling with deep learning framework for multi-drone networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4235-4248. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2903144 [17] 殷人昆. 数据结构: 用面向对象方法与C++语言描述[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2007.YIN R K. Data structure: described by object-oriented method and C++ language[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2007(in Chinese). [18] 张启瑞, 魏瑞轩, 何仁珂, 等. 城市密集不规则障碍空间无人机航路规划[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(10): 1407-1413. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.50351ZHANG Q R, WEI R X, HE R K, et al. Path planning for unmanned aerial vehicle in urban space crowded with irregular obstacles[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(10): 1407-1413(in Chinese). doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.50351 [19] 赵嶷飞, 郑雨欣. 城市物流无人机飞行任务剖面构建与优化[J]. 飞行力学, 2021, 39(3): 54-59.ZHAO Y F, ZHENG Y X. Construction and optimization of flight mission profile of urban logistics UAV[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2021, 39(3): 54-59(in Chinese). [20] SHI D J, DAI X H, ZHANG X W, et al. A practical performance evaluation method for electric multicopters[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(3): 1337-1348. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2675913 [21] DIETRICH T, KRUG S, ZIMMERMANN A. An empirical study on generic multicopter energy consumption profiles[C]//Proceedings of the Annual IEEE International Systems Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [22] KADDANI S, VANDERPOOTEN D, VANPEPERSTRAETE J M, et al. Weighted sum model with partial preference information: application to multi-objective optimization[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 260(2): 665-679. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2017.01.003 [23] YU Y, TANG J, HUANG J Y, et al. Multi-objective optimization for UAV-assisted wireless powered IoT networks based on extended DDPG algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(9): 6361-6374. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3089476 [24] GIAGKIOZIS I, FLEMING P J. Methods for multi-objective optimization: an analysis[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 293: 338-350. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.071 [25] KATOCH S, CHAUHAN S S, KUMAR V. A review on genetic algorithm: past, present, and future[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(5): 8091-8126. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-10139-6 -






 下载:
下载: