-
摘要:
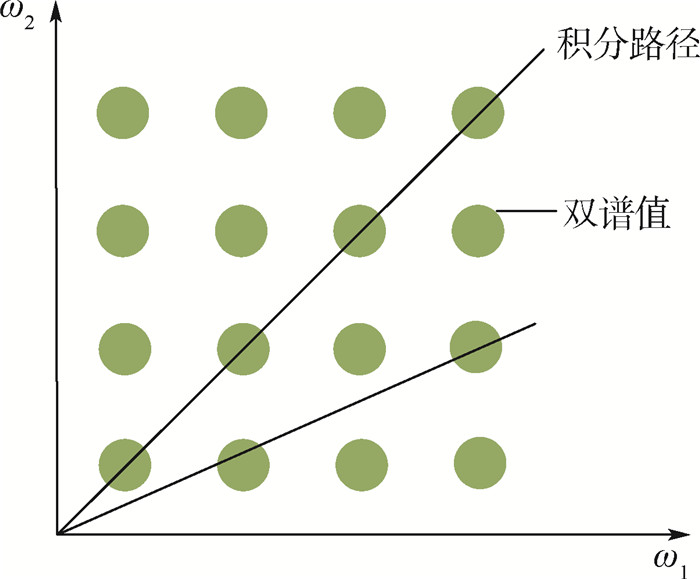
目标的回波信号是无线电引信获得目标信息的最重要方式,为了太赫兹频段的引信前端未来能够投入高原战场,适应高原不同的地貌环境,利用双谱对高原在灌木地形下不同高度的太赫兹波回波特性进行了分析。为减少分类时间,对双谱数据进行积分,得到实采信号双谱切片的特征,进而利用最邻近算法对此进行分类。利用经验模态分解(EMD)提取原始数据内在模态函数的特征,再次分类并与前一组分类结果进行对比。通过一系列数据的分类,结果表明:利用一维的积分双谱信息可以有效提取出距离地面分别为2 m、3 m、4 m、5 m时的特征并进行分类,经验模态分解也可以有效提高分类的成功率,成功率最高可达90%以上。
Abstract:The echo signal of the target is the most important way for radio fuze to obtain target information. This research employs bispectral analysis to examine the echo properties of terahertz wave at different heights of plateau in shrub terrain in order that the front-end of terahertz band fuze can be implemented into the plateau battle field in the future and adapt to the different landform environments of the plateau. In order to reduce the classification time, the bispectral data is integrated to obtain the bispectral slice features of the actual signal, and then the
k -nearest neighbor algorithm is used for classification. Empirical mode decomposition (EMD) is used to extract the intrinsic mode function features of the original data, and the classification results are compared with the previous group. Through a series of data classification, the results show that using one-dimensional integrated bispectral information can effectively extract the features of 2 m, 3 m, 4 m, 5 m from the ground and classify them, empirical mode decomposition can also effectively improve the success rate of classification, the success rate can reach more than 90%.-
Key words:
- terahertz /
- echo signal /
- bispectrum analysis /
- plateau /
- classification /
- Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT)
-
表 1 分类结果汇总
Table 1. Summary of classification results
分类方法 准确率/% 平均/% θ=20° θ=45° θ=65° θ=85° RIB 61.7 61.7 69.2 66.7 64.8 AIB 89.2 91.7 80.0 82.5 85.8 CIB 84.2 80.8 80.0 80.0 81.3 SIB 81.7 64.2 60.0 53.3 64.8 平均/% 79.2 74.6 72.3 70.6 74.2 表 2 优化双谱分类结果
Table 2. Optimization of bispectral classification results
分类方法 准确率/% 平均/% θ=20° θ=45° θ=65° θ=85° RIB 68.3 65.8 75.0 70.8 69.9 AIB 90.8 92.5 81.7 84.2 87.3 CIB 86.7 84.2 83.3 82.5 84.1 SIB 83.3 69.2 66.7 61.7 70.2 平均/% 82.2 77.9 76.6 74.7 77.8 -
[1] 王玉文, 董志伟. 太赫兹波沿倾斜路径在云层中的衰减[J]. 微波学报, 2016, 32(S2): 421-425.WANG Y W, DONG Z W. Cloud attenuation for terahertz wave along slant path[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2016, 32(S2): 421-425(in Chinese). [2] 邓琥, 尚丽平, 张泽林, 等. 不同行程下水蒸汽太赫兹传输特性[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(3): 979-984.DENG H, SHANG L P, ZHANG Z L, et al. Transmission cha-racteristics of water vapor based on different transmission distance[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(3): 979-984(in Chinese). [3] 王海彬, 黄峥, 文瑞虎. 太赫兹技术在引信中应用的探讨[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2016, 38(6): 1-6.WANG H B, HUANG Z, WEN R H. Discussion on terahertz techniques application in radar fuze[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2016, 38(6): 1-6(in Chinese). [4] 段锐, 张海, 陈祝明, 等. 垂直入射区雷达地面散射系数测量与特性研究[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2012, 41(3): 373-377.DUAN R, ZHANG H, CHEN Z M, et al. Radar terrain scattering return measurement and characteristics research in vertical incidence region[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012, 41(3): 373-377(in Chinese). [5] CALLA O P N, HARIT K C, VYAS R, et al. Comparison of measured scattering coefficient of dry soil at X-band with the scattering coefficient estimated using the dielectric constant[C]//2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 3135-3137. [6] JUNG G, OPPIZZI F, RAVENNI A, et al. The integrated angular bispectrum[J]. Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, 2020, 2020: 35. [7] 于凤楠. 双谱分析方法在水下目标特征提取中的应用[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2010: 13-16.YU F N. Bispectrum analysis method applied to extraction of features of underwater target[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2010: 13-16(in Chinese). [8] 韩国川, 张金艺, 李科, 等. 矩形积分双谱和半监督鉴别分析下的通信辐射源识别[J]. 上海大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 25(5): 722-732.HAN G C, ZHANG J Y, LI K, et al. Communication emitter identification under square integral bispectra and semi-supervised discriminant analysis[J]. Journal of Shanghai University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 25(5): 722-732(in Chinese). [9] 陈涛, 姚文杨, 林金秋, 等. 雷达辐射源个体特征的提取与识别[J]. 应用科学学报, 2013, 31(4): 368-374.CHEN T, YAO W Y, LIN J Q, et al. Extraction and identification of radar emitter individual characteristics[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2013, 31(4): 368-374(in Chinese). [10] 李昌志, 田杰, 张扬帆, 等. 基于亮点模型的典型水下目标回波信号仿真[J]. 应用声学, 2010, 29(3): 196-201.LI C Z, TIAN J, ZHANG Y F, et al. Simulation of echoes from underwater target based on highlight model[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2010, 29(3): 196-201(in Chinese). [11] 杜英举. 脑电双谱分析与特征分类识别[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2014: 35-40.DU Y J. The analysis and classification of EEG bispectrum slice[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2014: 35-40(in Chinese). [12] WU W T, LI D N, DU J Y, et al. An intelligent diagnosis method of brain MRI tumor segmentation using deep convolutional neural network and SVM algorithm[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2020, 2020: 6789306. [13] ZHAO J L, FANG Y, CHU G M, et al. Identification of leaf-scale wheat powdery mildew (blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici) combining hyperspectral imaging and an SVM classifier[J]. Plants(Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 9(8): 936. [14] GUÉRIN J, THIERY S, NYIRI E, et al. Combining pretrained CNN feature extractors to enhance clustering of complex natural images[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 423: 551-571. [15] GUO Y M, ZHOU Y F, ZHANG Z S. Fault diagnosis of multi-channel data by the CNN with the multilinear principal component analysis[J]. Measurement, 2021, 171: 108513. [16] 白杨, 姚桂林. 一种基于KNN后处理的鲁棒性抠图方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2020, 37(9): 170-175.BAI Y, YAO G L. A robust matting method based on KNN post processing[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2020, 37(9): 170-175(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: