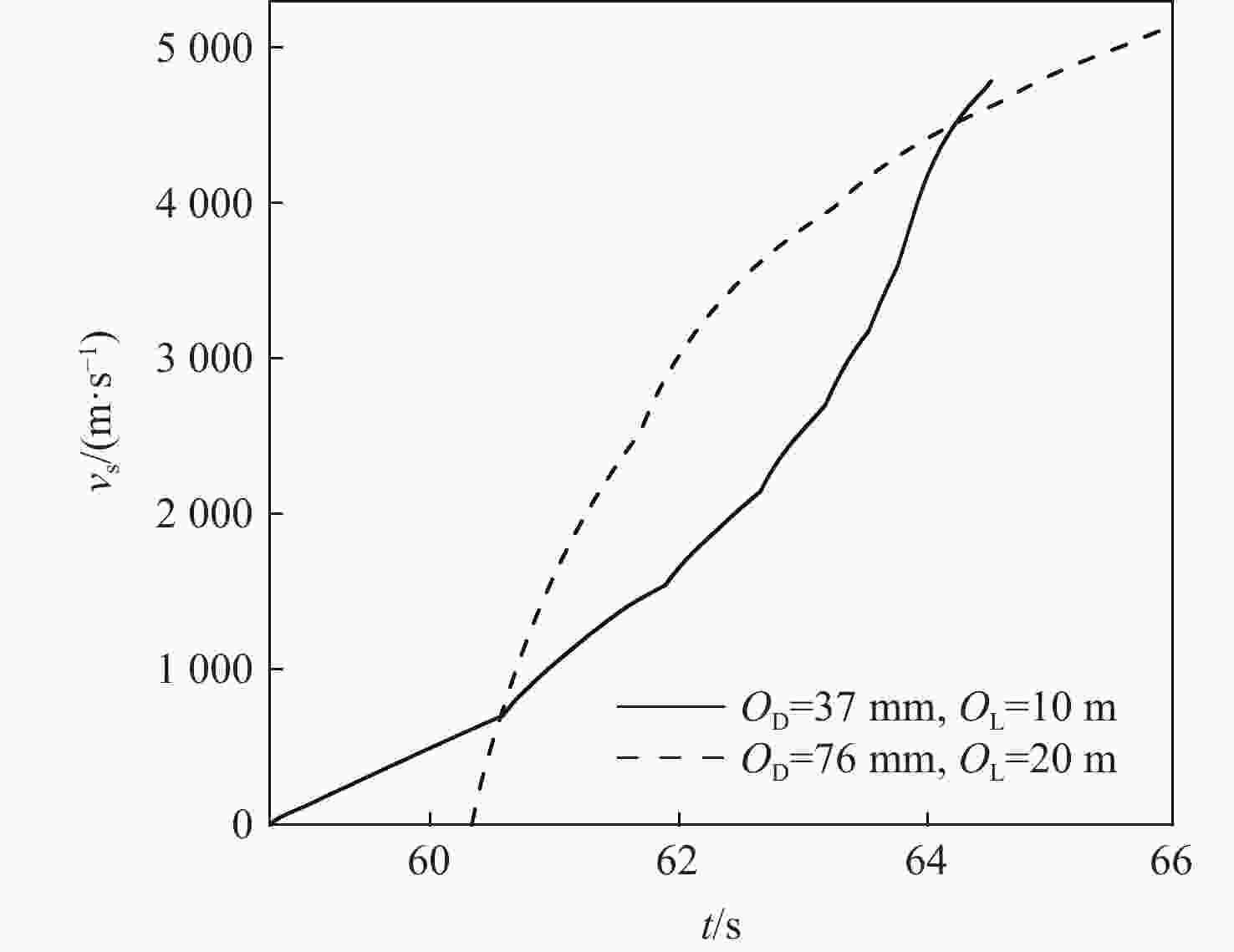
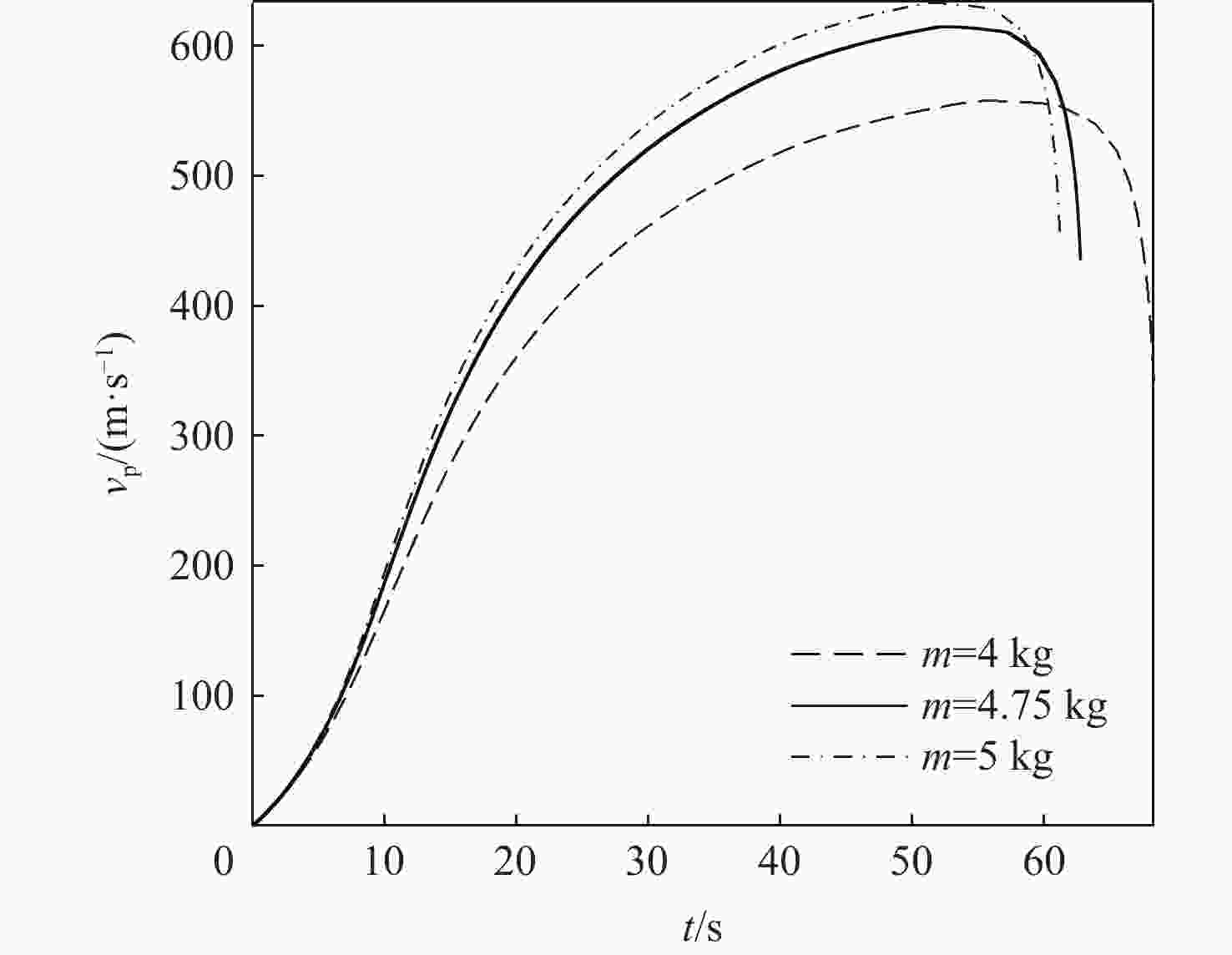
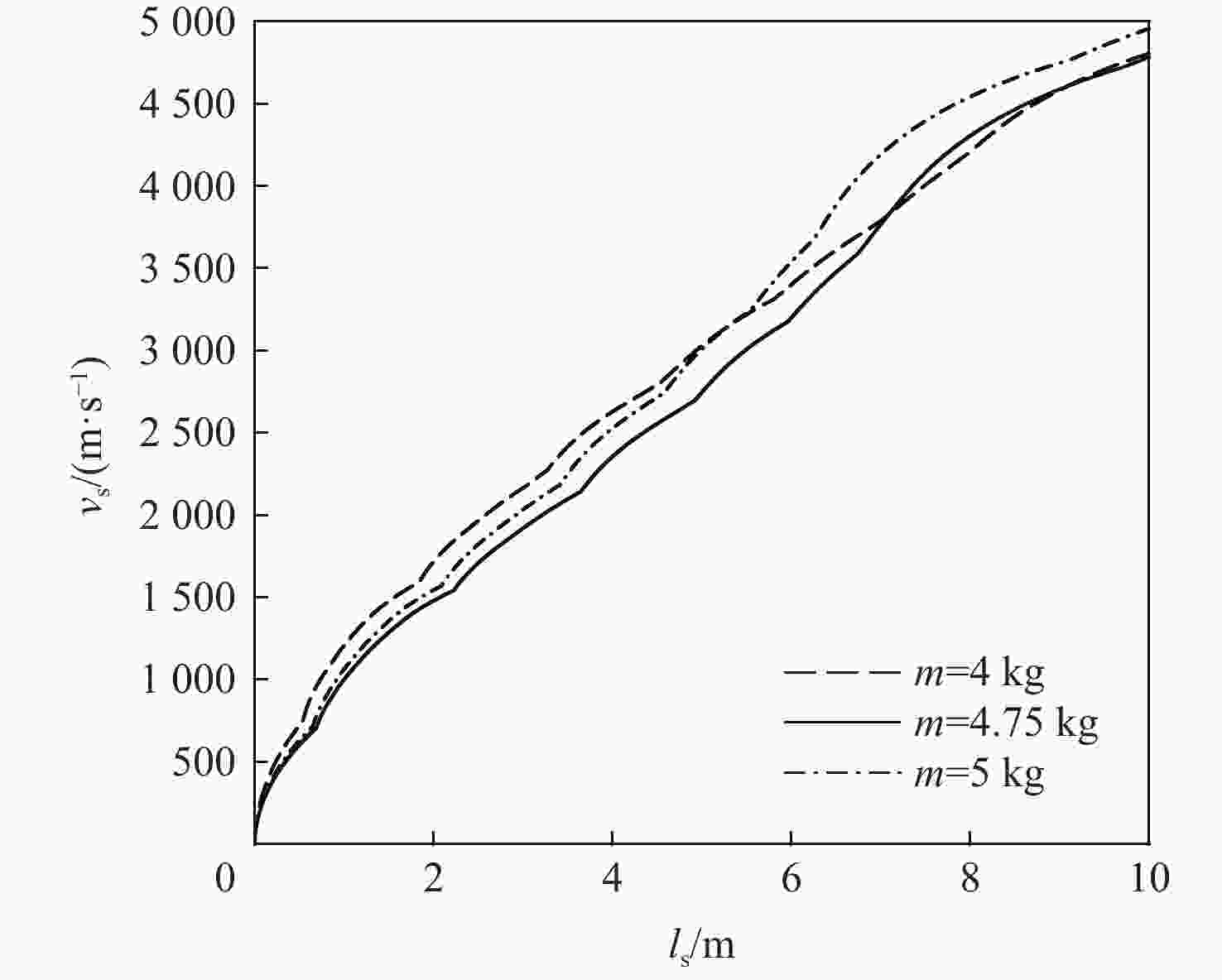
-
摘要:
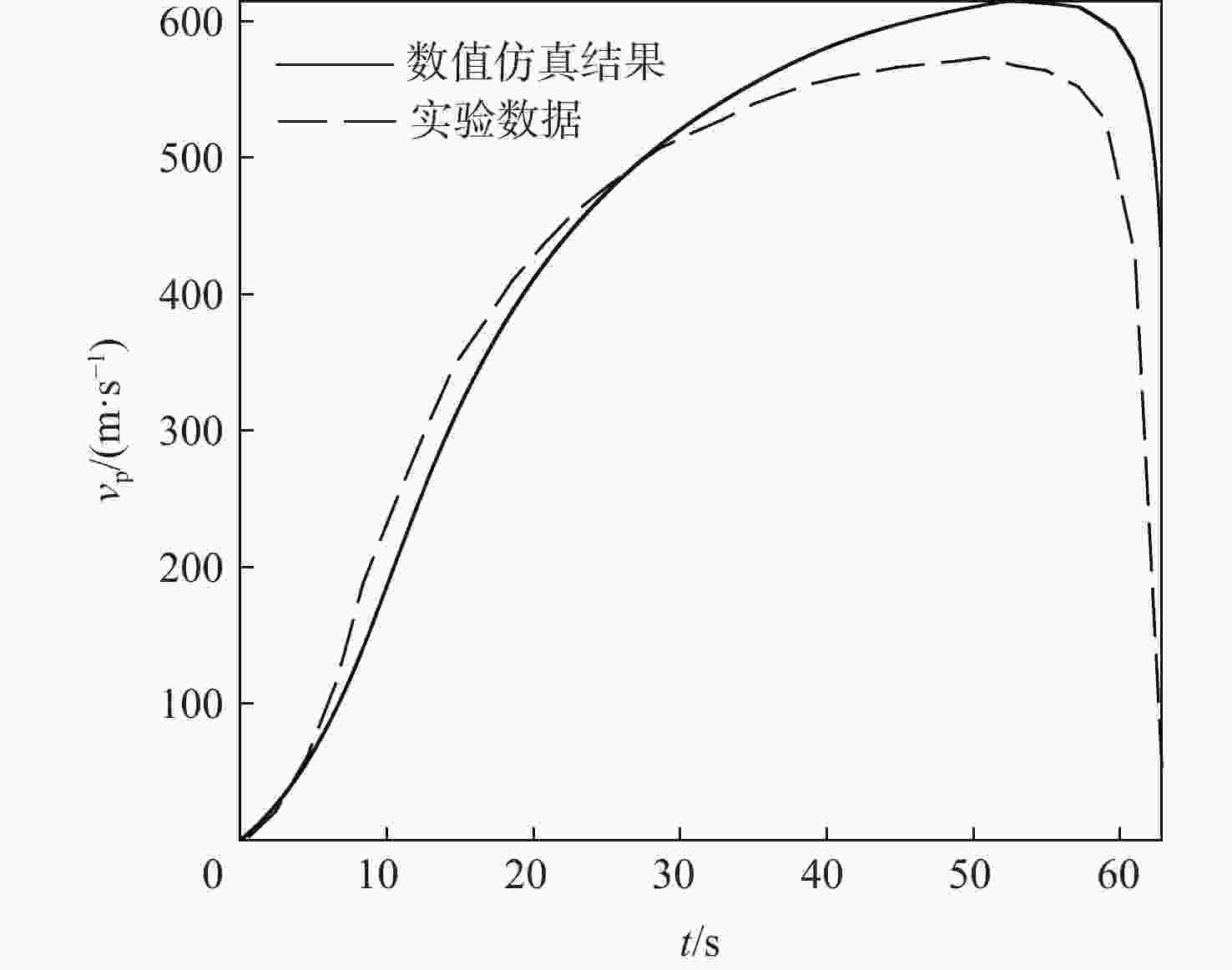
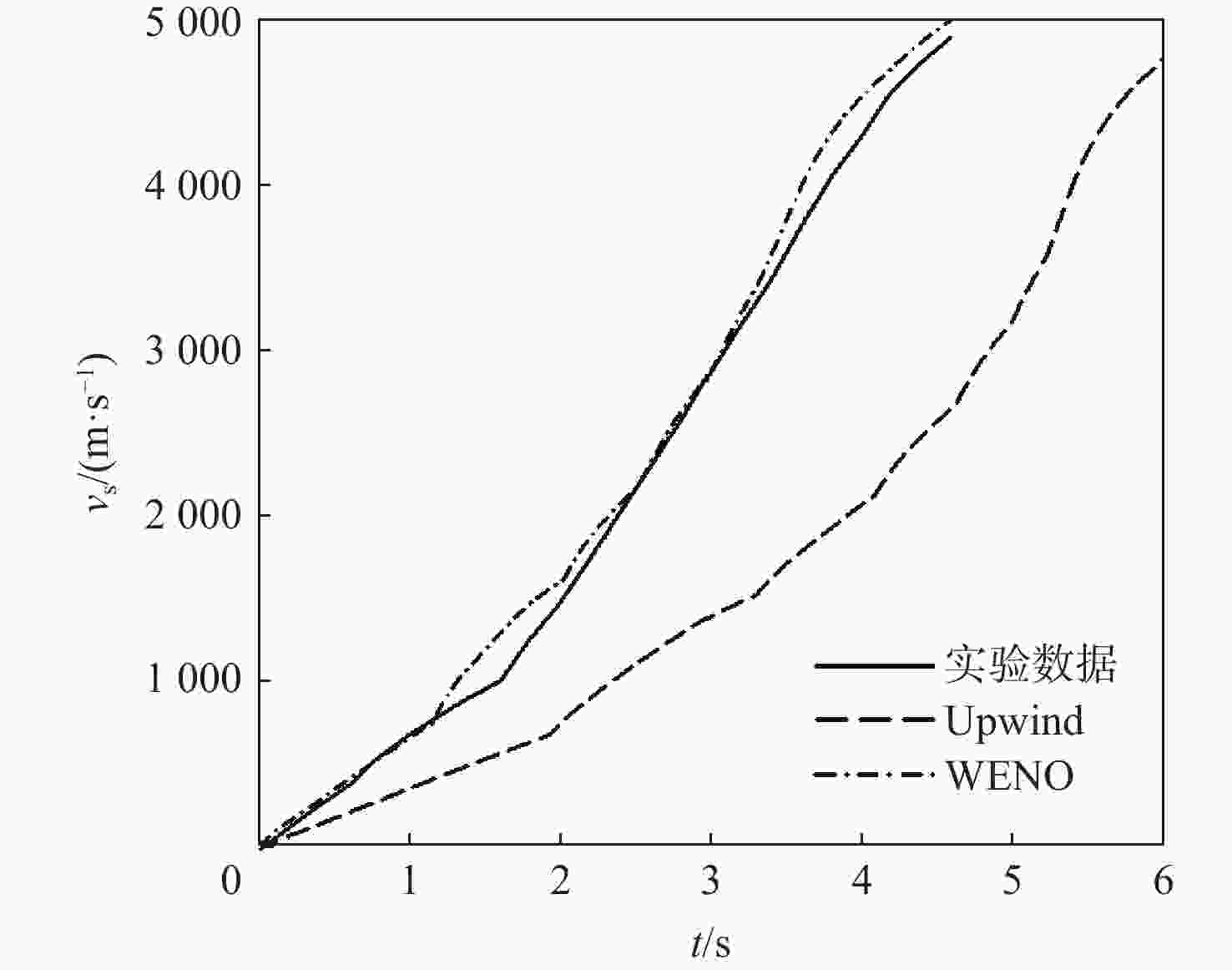
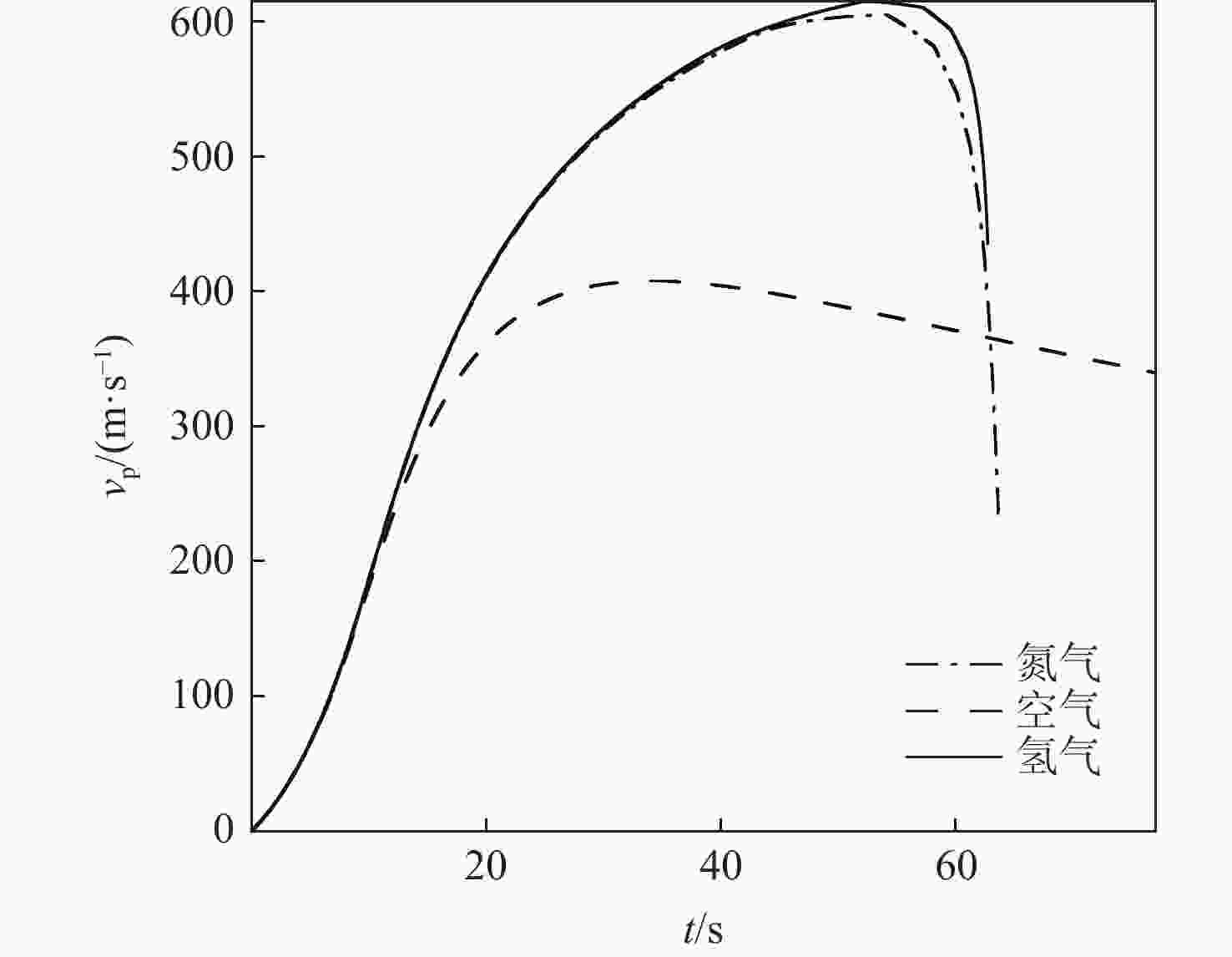
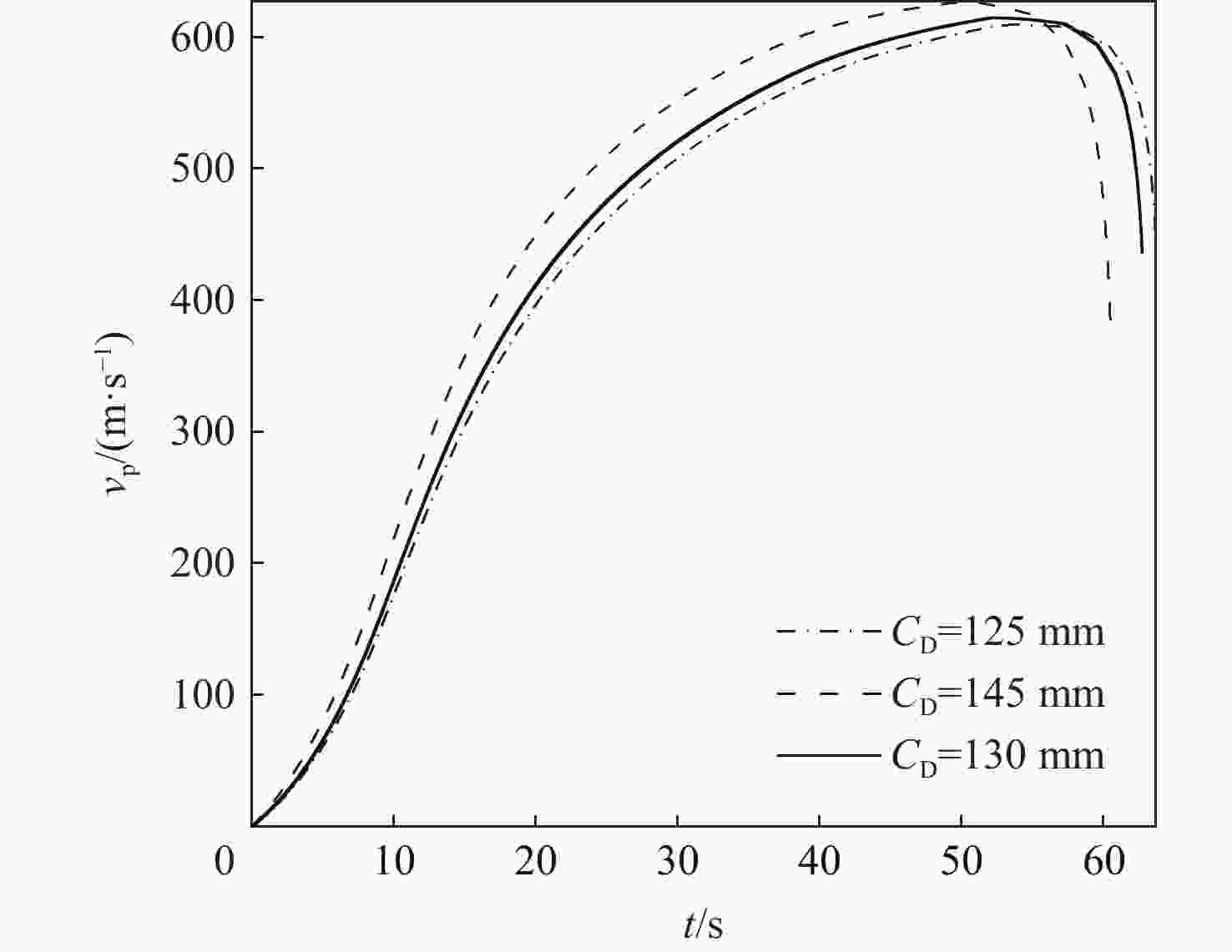
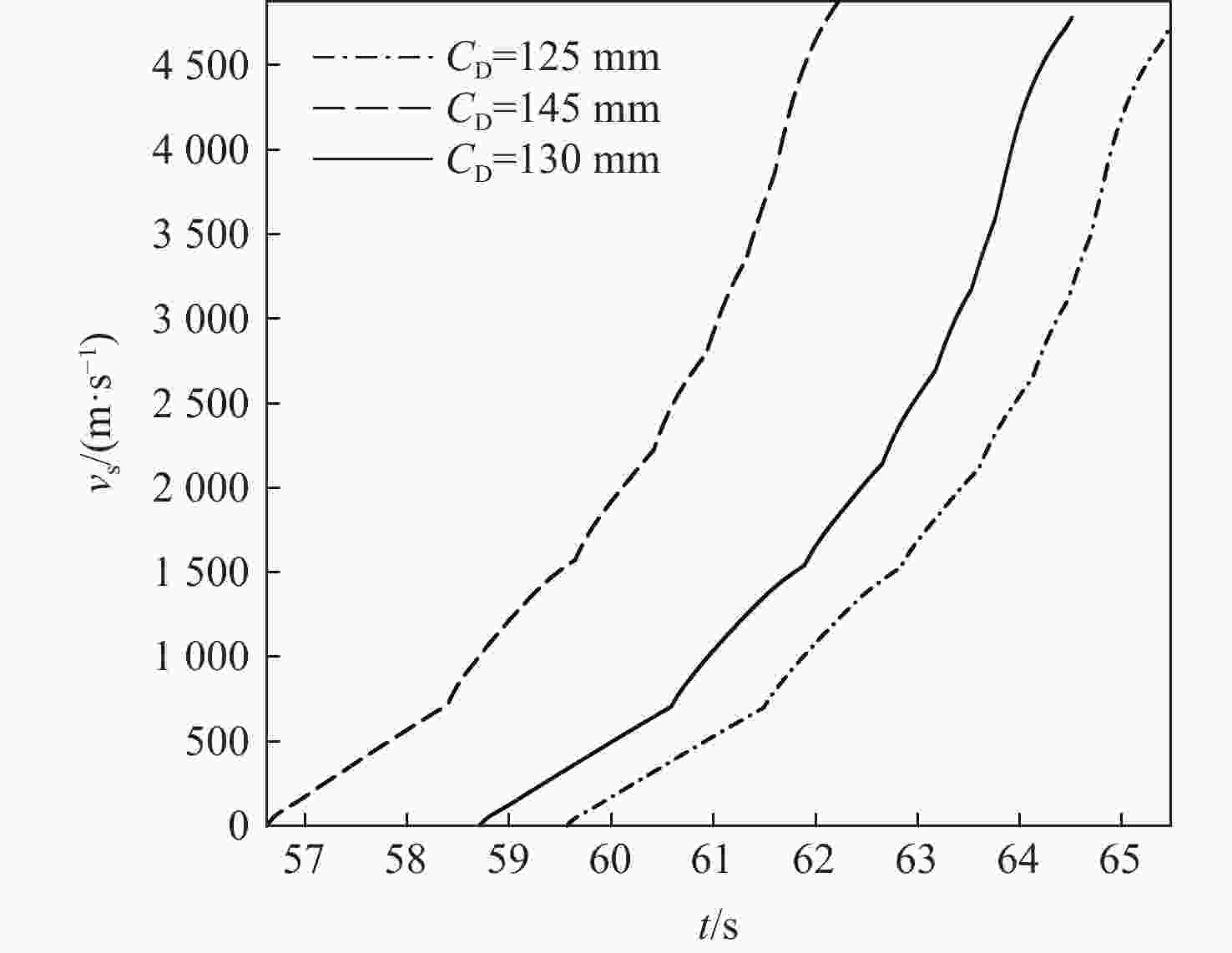
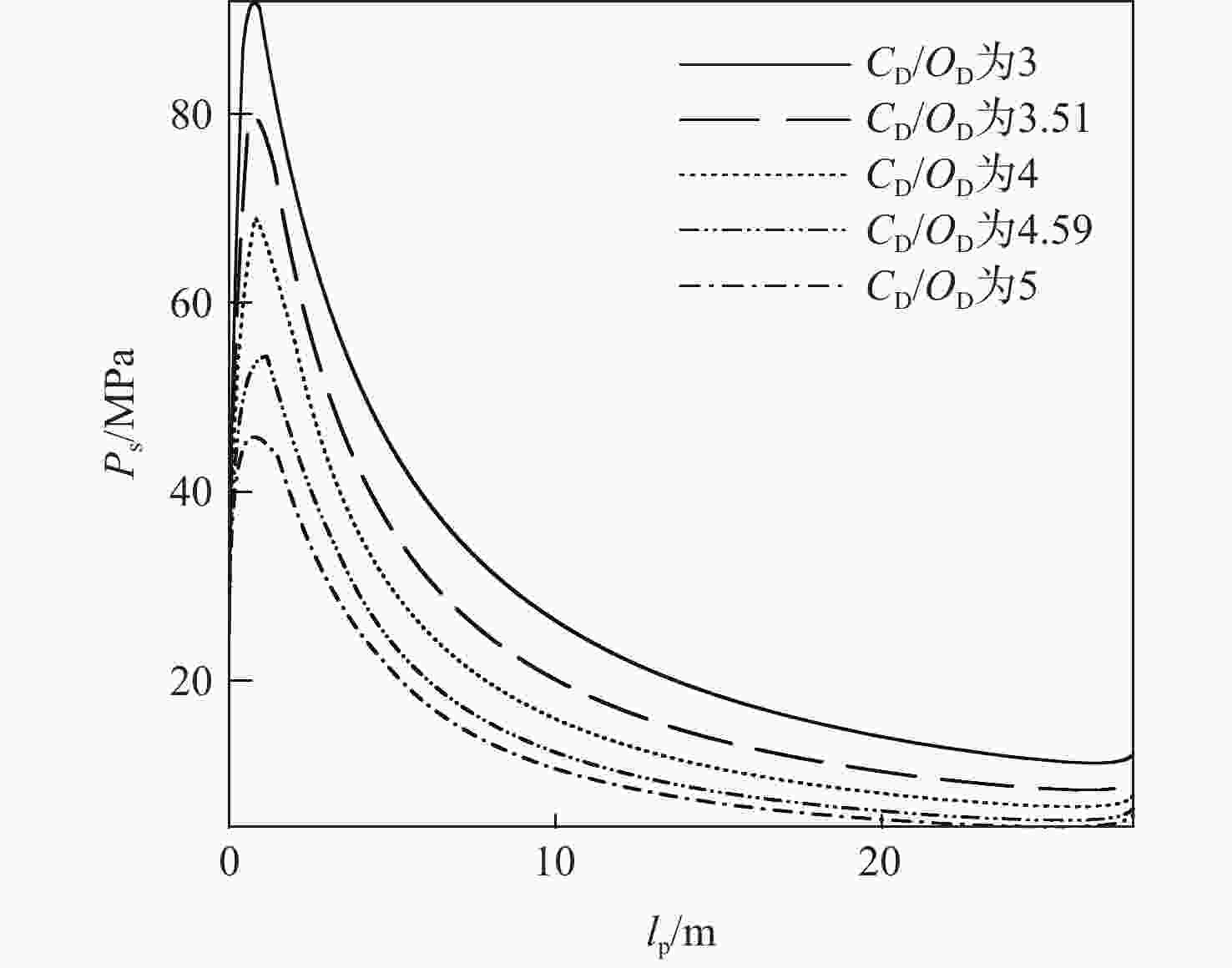
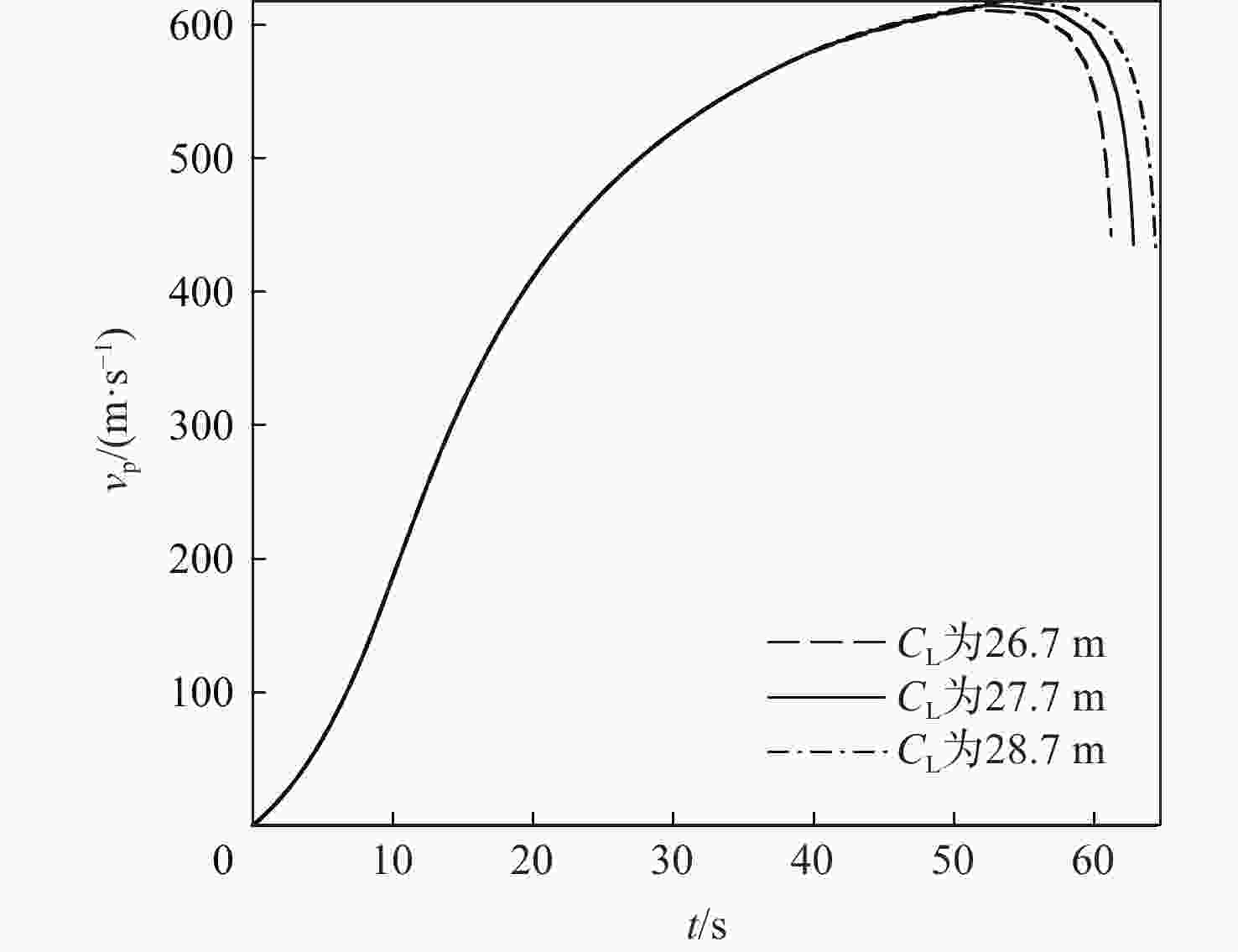
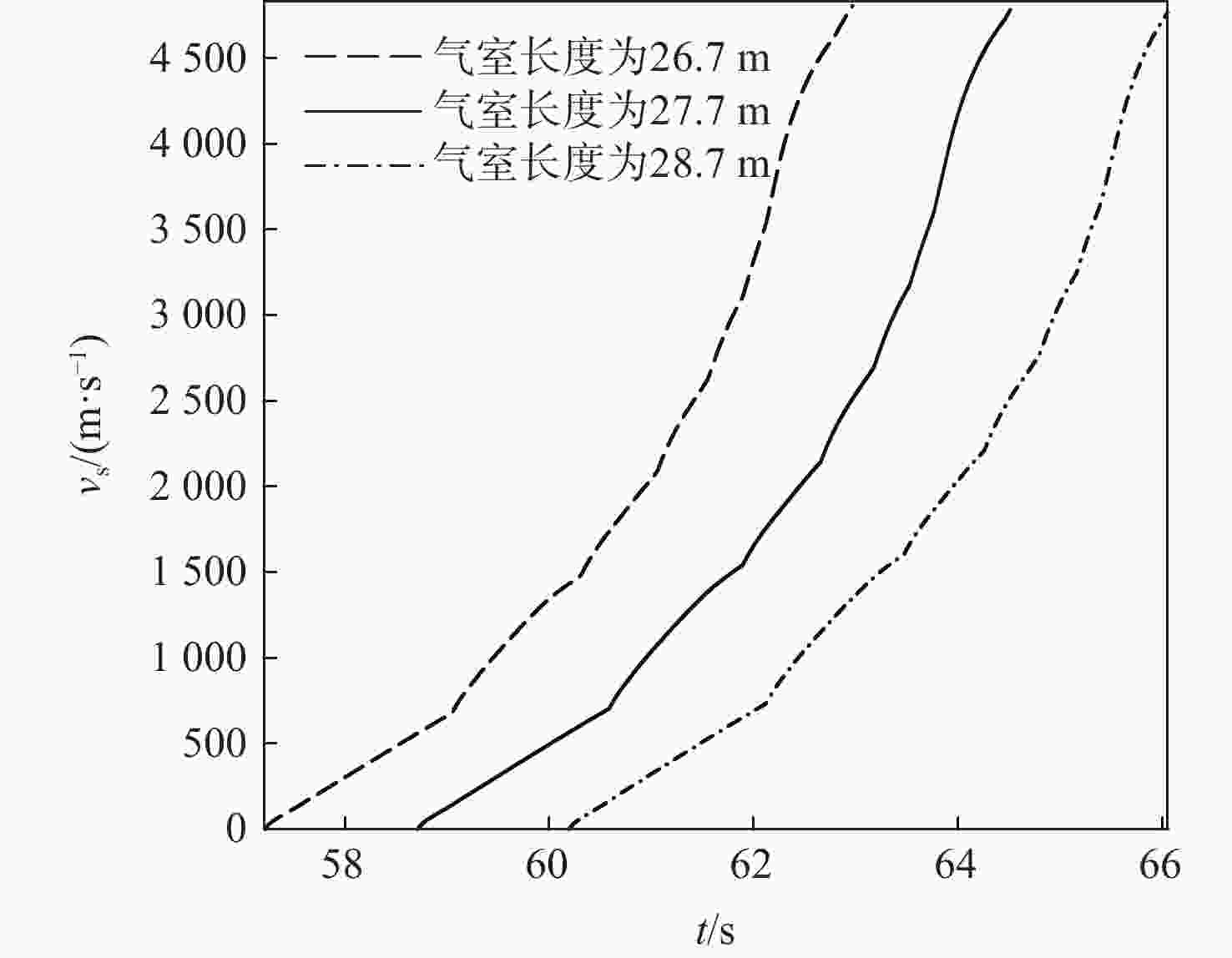
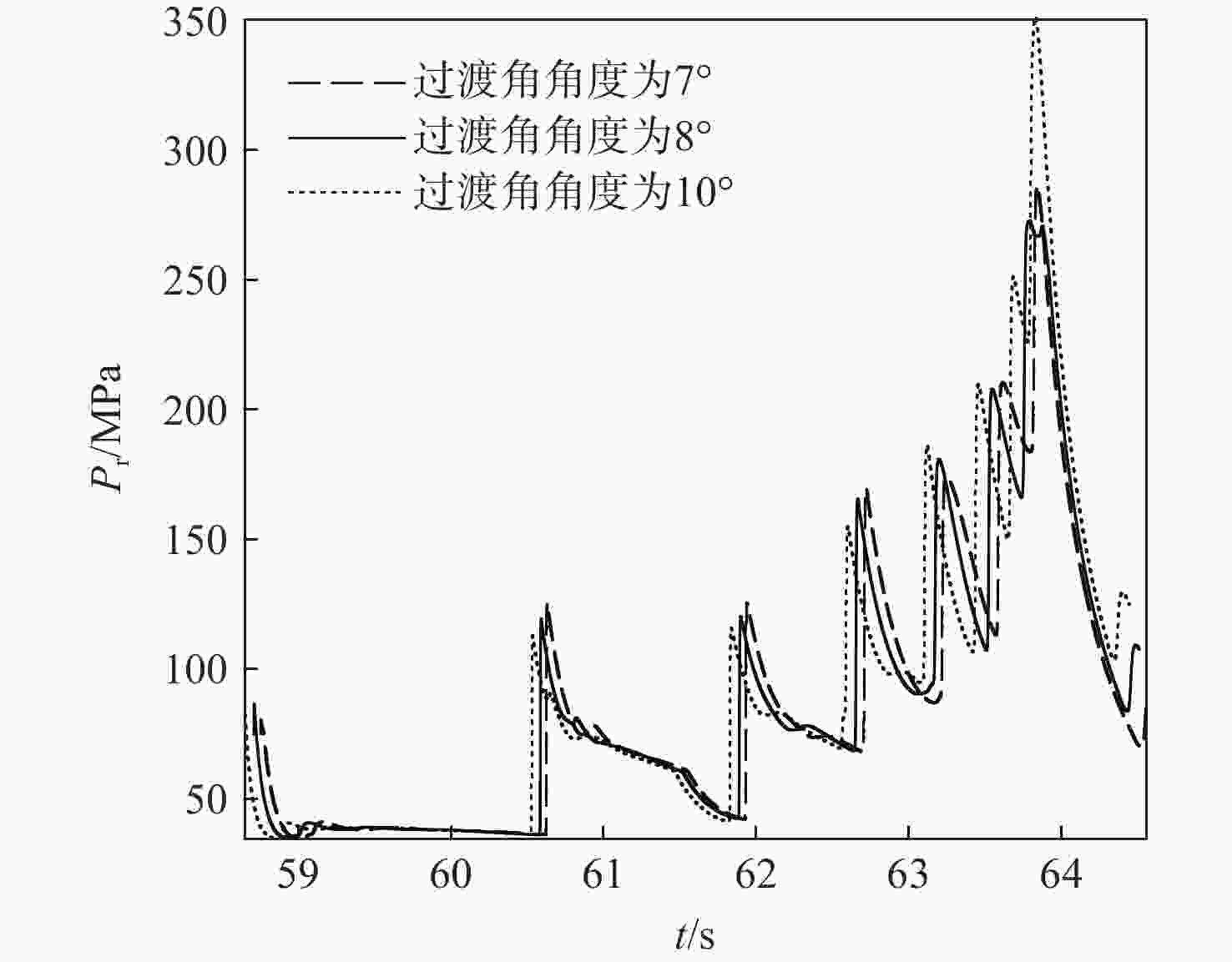
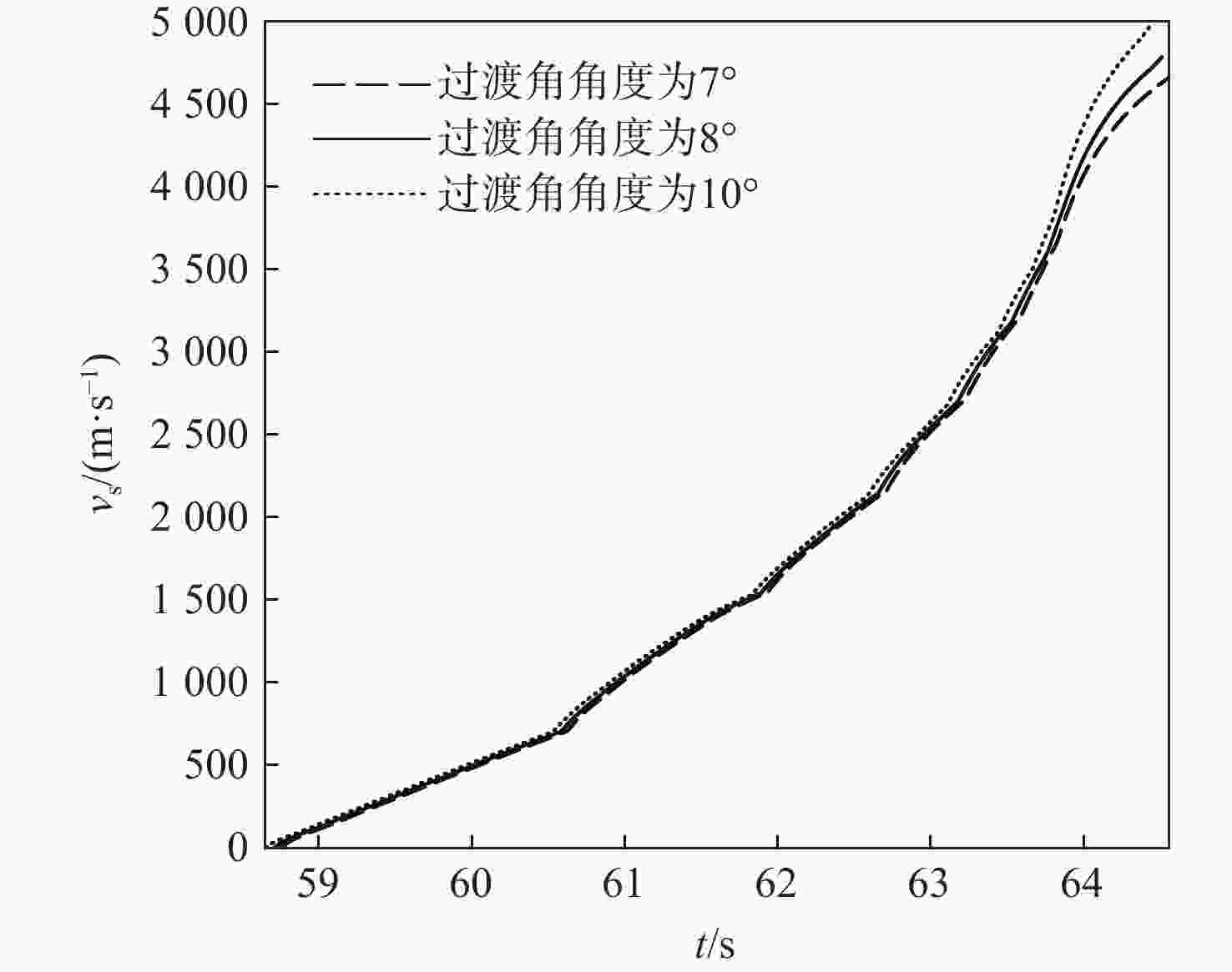
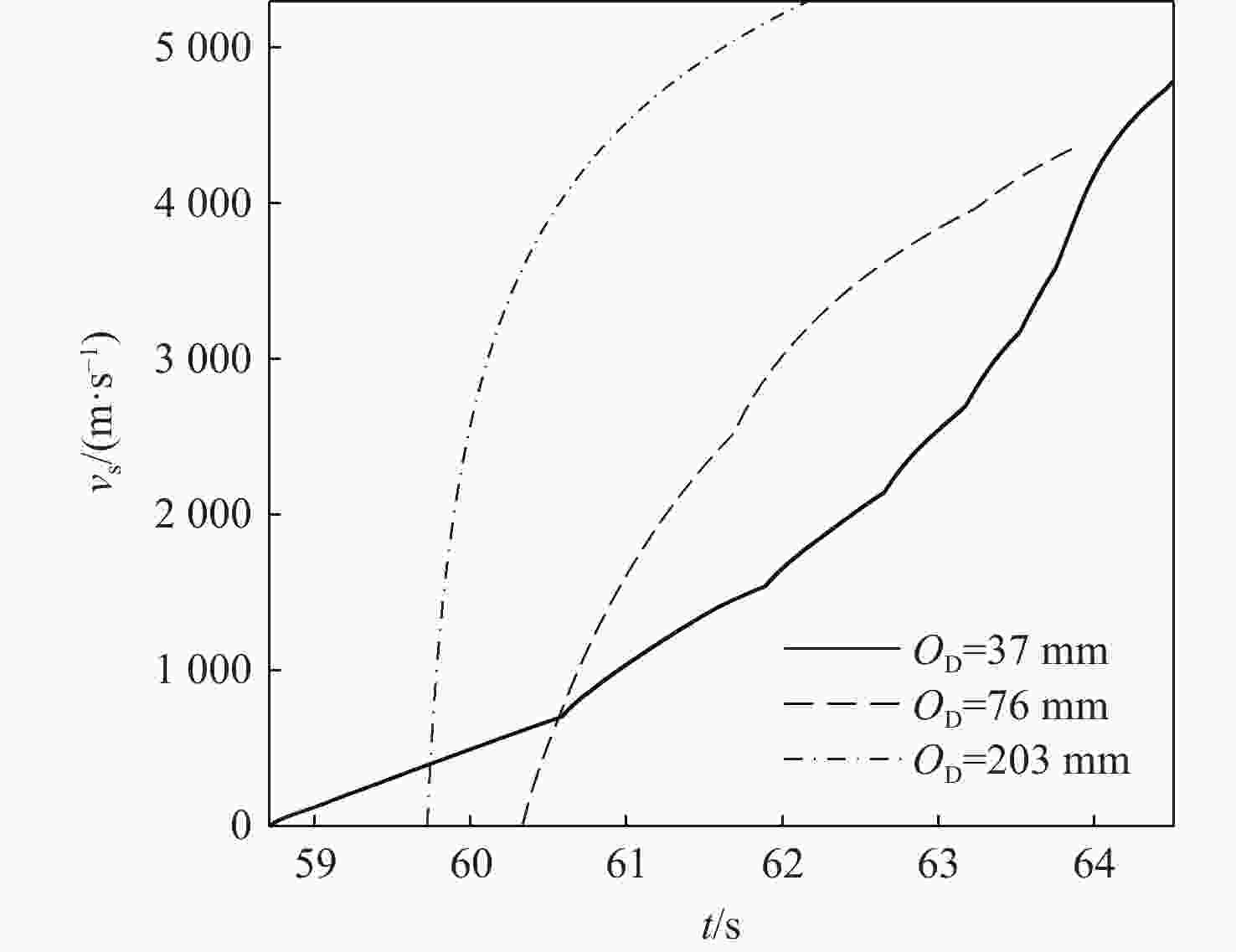
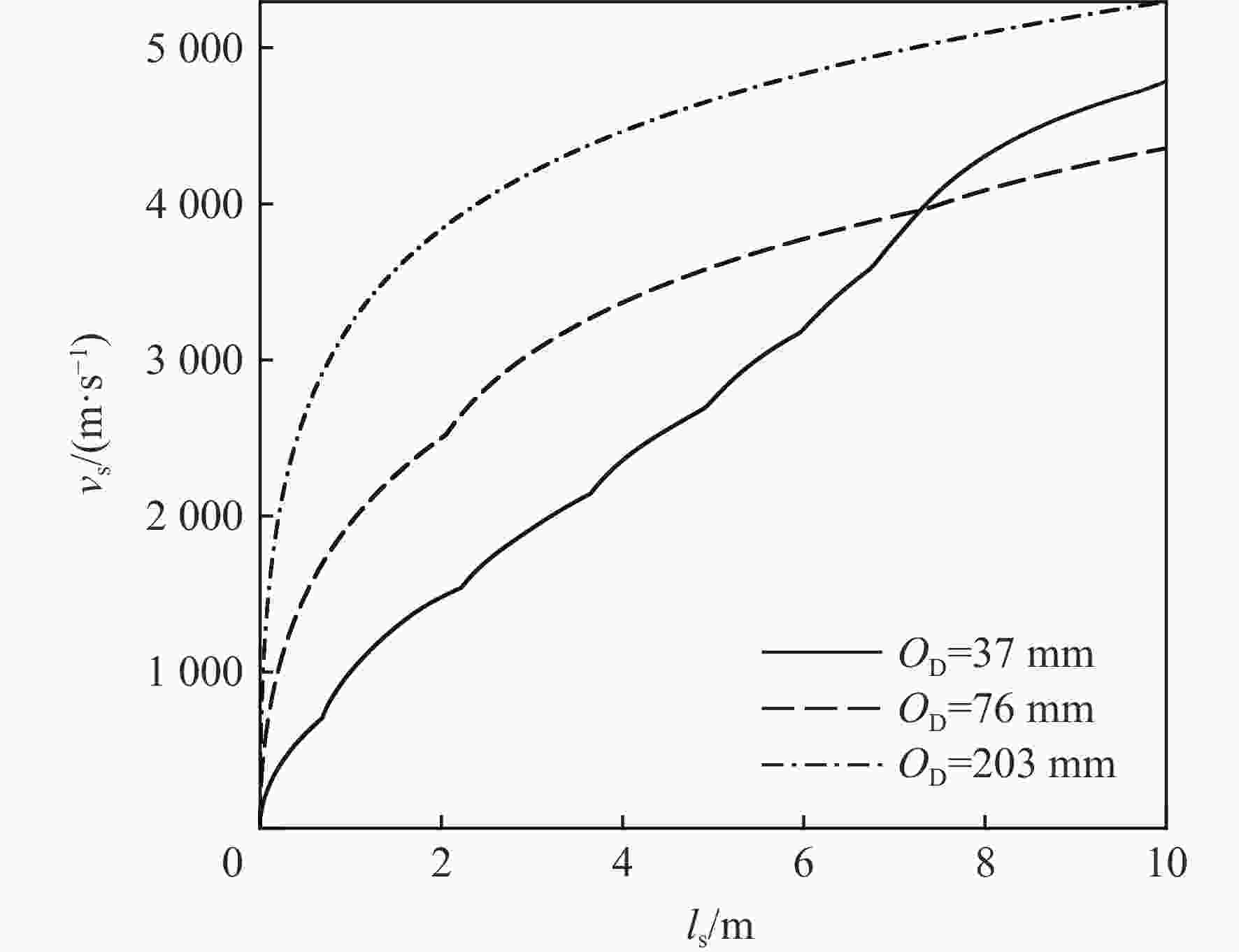
针对超高速发射技术中弹丸速度与能量转换效率的优化问题,采用经典内弹道模型对一维非定常可压缩流动下药室内火药燃烧状态、活塞运动和气室内气体流动状态、弹丸运动进行研究。药室部分通过四阶Runge-Kutta算法求解,气室部分求解Euler方程并采用WENO格式进行高精度激波捕捉。分别对不同初始注气条件、气室尺寸、发射管尺寸、火药质量下的二级轻气炮进行数值模拟,得到相关参数对轻气炮性能影响规律。研究发现:泵管内轻质气体能明显提高轻气炮的性能,气室尺寸、管径及长度对活塞底部压力和速度影响较大,但对弹丸速度影响较小;增加火药质量、发射管尺寸及管径可显著增大弹丸出膛速度;为新型二级轻气炮的设计制造提供重要理论和数据支撑。
Abstract:Focusing on the optimization of projectile velocity and energy conversion efficiency in hypervelocity launch technology, this paper uses the classical interior ballistic model to investigate the combustion in the chamber and the piston motion. The two components create a mathematical model for the interior ballistic launching process of a two-stage light gas cannon by describing the flow characteristics in the light gas chamber and the projectile velocity using a dimensional unstable compressible fluid model. The basic equations in the powder chamber are solved numerically with the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, and the equations in the light gas chamber are solved with the Euler method and the WENO scheme is used to capture the shock wave. The effects of the initial gas injection conditions, light gas chamber size, launch tube size and gunpowder quality on the performance of two-stage light gas guns are studied. It is found that the performance of a light gas gun can be improved obviously by using light gas in the pump tube. The size, diameter and length of the gas chamber have significant influence on the pressure and velocity at the bottom of the piston, while their influence on the velocity of the projectile is small. Increasing the mass of propellant, the size and diameter of the launch tube can significantly increase the velocity of the projectile. This work offers crucial data and theoretical support for the light gas gun's engineering application and experimental investigation.
-
Key words:
- two-stage light gas gun /
- interior ballistics /
- mathematical model /
- WENO scheme /
- numerical simulation
-
-
[1] BERGGREN R E, REYNOLDS R M. The light-gas-gun model launcher[J]. Ballistic Range Technology, 1970: 9-54. [2] CROZIER W D, HUME W. High-velocity, light-gas gun[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1957, 28(8): 892-894. doi: 10.1063/1.1722882 [3] CHARTERS A C, DENARDO B P, ROSSOW V J. Development of a piston-compressor type light-gas gun for the launching of free-flight models at high velocities: NACA-TN-4143[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1957: 93R14291. [4] CHARTERS A C. Development of the high-velocity gas-dynamics Gun[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1987, 5(1-4): 181-203. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(87)90038-8 [5] STEPHENSON W B, KNAPP R E. Performance of a two-stage launcher using hydrogen: AEDC TDR 62-32[R]. Chicago: Arnold Engineering Development Center, 1962: 386079. [6] CURTIS J S. An accelerated reservoir light-gas gun: NASA TN D-1144[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1962. [7] KAMIYA T, UCHIKAWA H, SHIRAKI K. Performance assessment of debris shield with hyper velocity impact testing for the japanese experiment module (JEM) and HII transfer vehicle (HTV)[C]//Proceedings of the 56th International Astronautical Congress of the International Astronautical Federation, the International Academy of Astronautics, and the International Institute of Space Law. Reston: AIAA, 2005. [8] 滕宏辉, 杨鹏飞, 张义宁, 等. 斜爆震发动机的流动与燃烧机理[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2020, 50(9): 129-151.TENG H H, YANG P F, ZHANG Y N, et al. Flow and combustion mechanism of oblique detonation engines[J]. Scientia Sinica (Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica), 2020, 50(9): 129-151(in Chinese). [9] 滕宏辉, 姜宗林. 斜爆轰的多波结构及其稳定性研究进展[J]. 力学进展, 2020, 50(1): 43-50. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-19-011TENG H H, JIANG Z L. Progress in multi-wave structure and stability of oblique detonations[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2020, 50(1): 43-50(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-19-011 [10] 罗凯, 汪球, 李逸翔, 等. 基于高温气体效应的磁流体流动控制研究进展[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(6): 1515-1531. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-067LUO K, WANG Q, LI Y X, et al. Research progress on magnetohydrodynamic flow control under test conditions with high temperature real gas effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(6): 1515-1531(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-067 [11] 韩信, 张子健, 马凯夫, 等. 超燃冲压发动机喷管推力性能理论预测[J]. 气体物理, 2022, 7(1): 1-8.HAN X, ZHANG Z J, MA K F, et al. Theoretical prediction on the nozzle thrust of scramjets[J]. Physics of Gases, 2022, 7(1): 1-8(in Chinese). [12] 沈欢, 张子健, 刘云峰, 等. 超燃冲压发动机推进性能理论分析[J]. 气体物理, 2018, 3(1): 12-19.SHEN H, ZHANG Z J, LIU Y F, et al. Analysis on the propulsion performance of scramjet engine[J]. Physics of Gases, 2018, 3(1): 12-19(in Chinese). [13] 李逸翔, 汪球, 罗凯, 等. 高超声速MHD球头激波脱体距离理论求解[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(9): 2493-2500. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-127LI Y X, WANG Q, LUO K, et al. Theoretical analysis on hypersonic mhd shock stand-off distance of blunt body[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(9): 2493-2500(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-127 [14] 姚轩宇, 王春, 喻江, 等. JF12激波风洞高Mach数超燃冲压发动机实验研究[J]. 气体物理, 2019, 4(5): 25-31.YAO X Y, WANG C, YU J, et al. High-Mach-number scramjet engine tests in JF12 shock tunnel[J]. Physics of Gases, 2019, 4(5): 25-31(in Chinese). [15] 邓放, 韩桂来, 孟宝清, 等. 超声速后台阶流动/射流相互作用的数值模拟[J]. 气体物理, 2018, 3(6): 41-50.DENG F, HAN G L, MENG B Q, et al. Numerical simulation of supersonic flow/jet interaction at the double backward-facing step[J]. Physics of Gases, 2018, 3(6): 41-50(in Chinese). [16] 郗雪辰, 杨鹏飞, 滕宏辉. 一维爆轰波在扰动来流中传播的数值研究[J]. 气体物理, 2022, 7(4): 1-9.XI X C, YANG P F, TENG H H. Numerical study of one-dimensional detonation propagation in perturbed inflow[J]. Physics of Gases, 2022, 7(4): 1-9(in Chinese). [17] 吴锦涛, 吕一品, 董刚, 等. 并行建表化学加速算法研究及其在气相斜爆轰模拟中的应用[J]. 气体物理, 2022, 7(1): 9-21.WU J T, LYU Y P, DONG G, et al. Parallel chemistry acceleration algorithms and application in numerical simulations of gaseous oblique detonation wave[J]. Physics of Gases, 2022, 7(1): 9-21(in Chinese). [18] 陈大年. 二级轻气炮内弹道的数值模拟与性能分析[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1989, 9(1): 37-42. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(1989)01-0037-6CHEN D N. Numerical simulation and performance analysis of the two-stage light gas Gun[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1989, 9(1): 37-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(1989)01-0037-6 [19] 管小荣, 徐诚. 二级轻气炮发射过程数学模型和计算方法[J]. 南京理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(1): 22-26.GUAN X R, XU C. Mathematical model and computing method for launch process of two-stage light-gas Gun[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2007, 31(1): 22-26(in Chinese). [20] 冯福全. 二级轻气炮内弹道仿真研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2008.FENG F Q. Simulation study on interior ballistics of two-stage hydrogen Gun[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2008(in Chinese). [21] 庄宇, 陆欣. 二级轻气炮内弹道过程数学建模及数值仿真[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2016, 37(12): 75-79. doi: 10.11809/scbgxb2016.12.018ZHUANG Y, LU X. Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation for interior ballistics process of two-stage light-gas Gun[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2016, 37(12): 75-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.11809/scbgxb2016.12.018 [22] 刘海明. 二级轻气炮内弹道过程计算机仿真[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2006.LIU H M. Computer simulation of interior ballistic process of two-stage light gas Gun[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2006(in Chinese). [23] 朱斌. 与内弹道耦合的多管发射膛口非定常流场数值模拟[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2006.ZHU B. Numerical simulation of unsteady flow field in muzzle of multi-tube launcher coupled with interior ballistics[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2006(in Chinese). [24] 庄宇. 轻气发射装置内弹道性能数值仿真及优化设计[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2017.ZHUANG Y. Numerical simulation and optimization design of interior ballistic performance of light gas launcher[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [25] 金志朋. 枪炮内弹道学[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2007.JIN Z P. Interior ballistics of guns[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2007(in Chinese). [26] 冯福全. 二级轻气炮内弹道仿真研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2008.FENG F Q. Simulation of the internal ballistics of a two-stage light gas gun[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2008(in Chinese). [27] SHU C W, OSHER S. Efficient implementation of essentially non-oscillatory shock-capturing schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1988, 77(2): 439-471. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(88)90177-5 [28] JIANG G S, SHU C W. Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1996, 126(1): 202-228. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1996.0130 [29] 吴应湘, 郑之初, 林同骥. 轻气炮性能计算[J]. 兵工学报, 1993, 14(4): 79-84.WU Y X, ZHENG Z C, LIN T J. Performance analysis of chambered launchers[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 1993, 14(4): 79-84(in Chinese). [30] 王金贵. 气体炮原理及技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001: 96-106.WANG J G. Principle and technology of gas cannon[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2001: 96-106(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: