-
摘要:
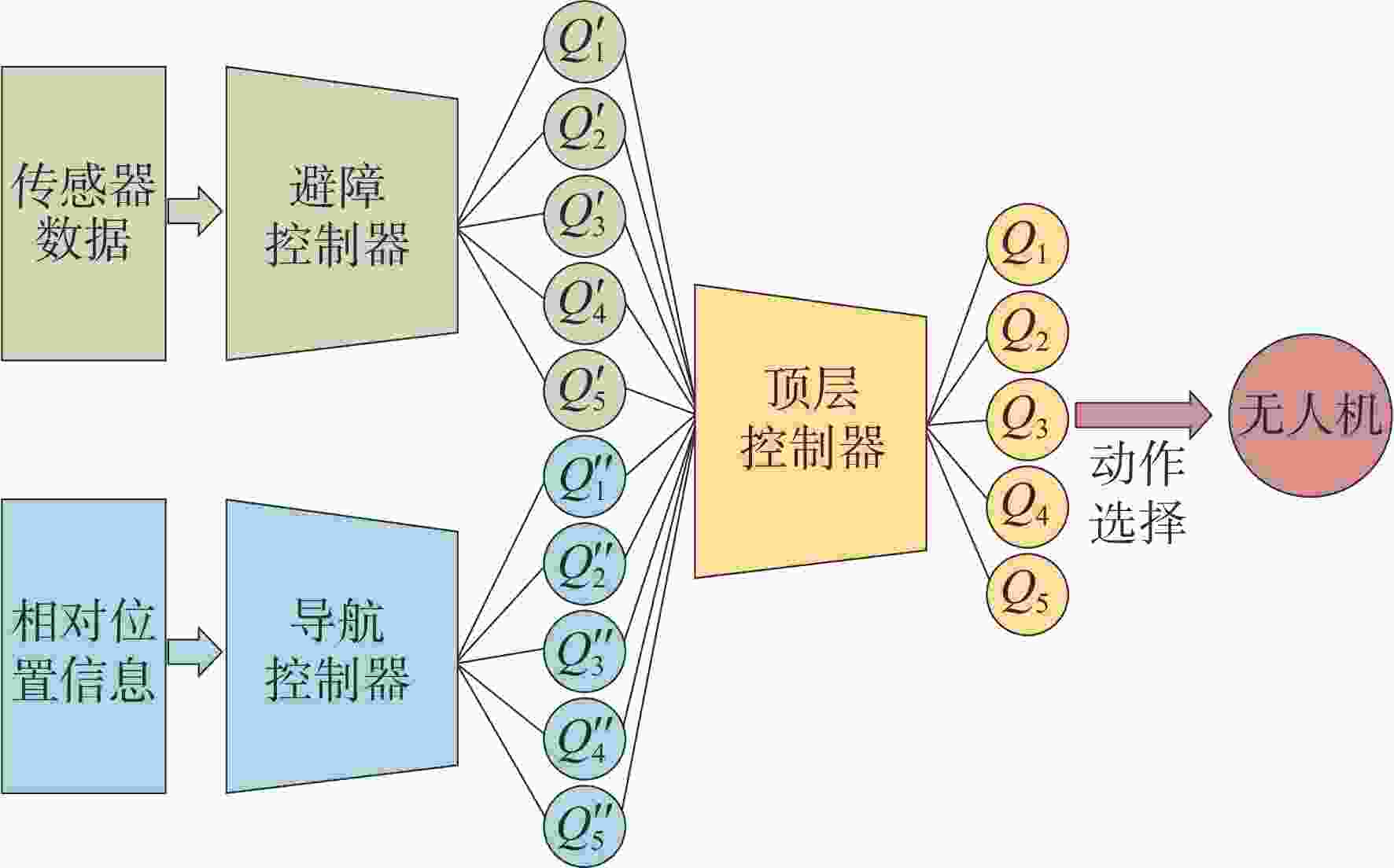
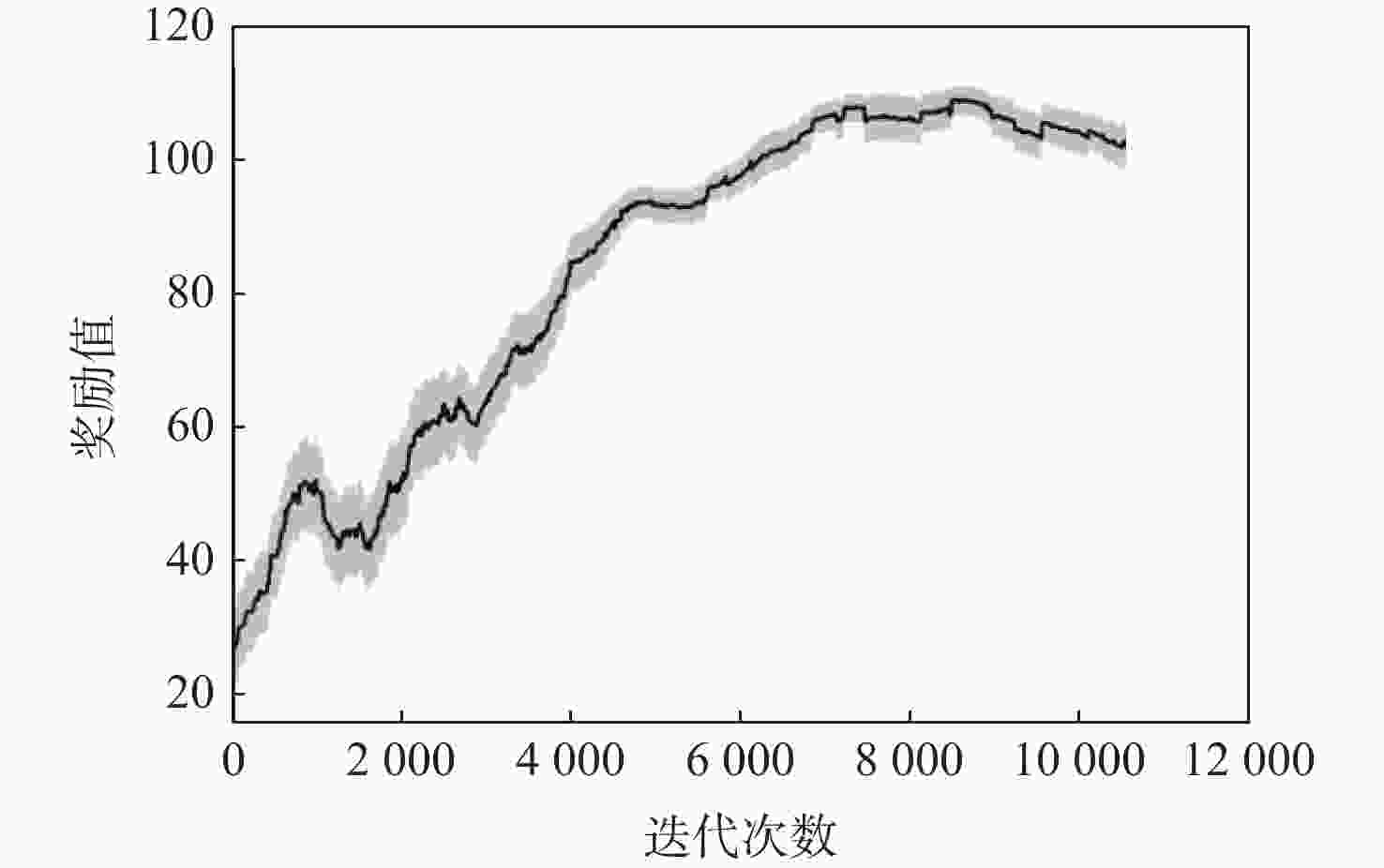
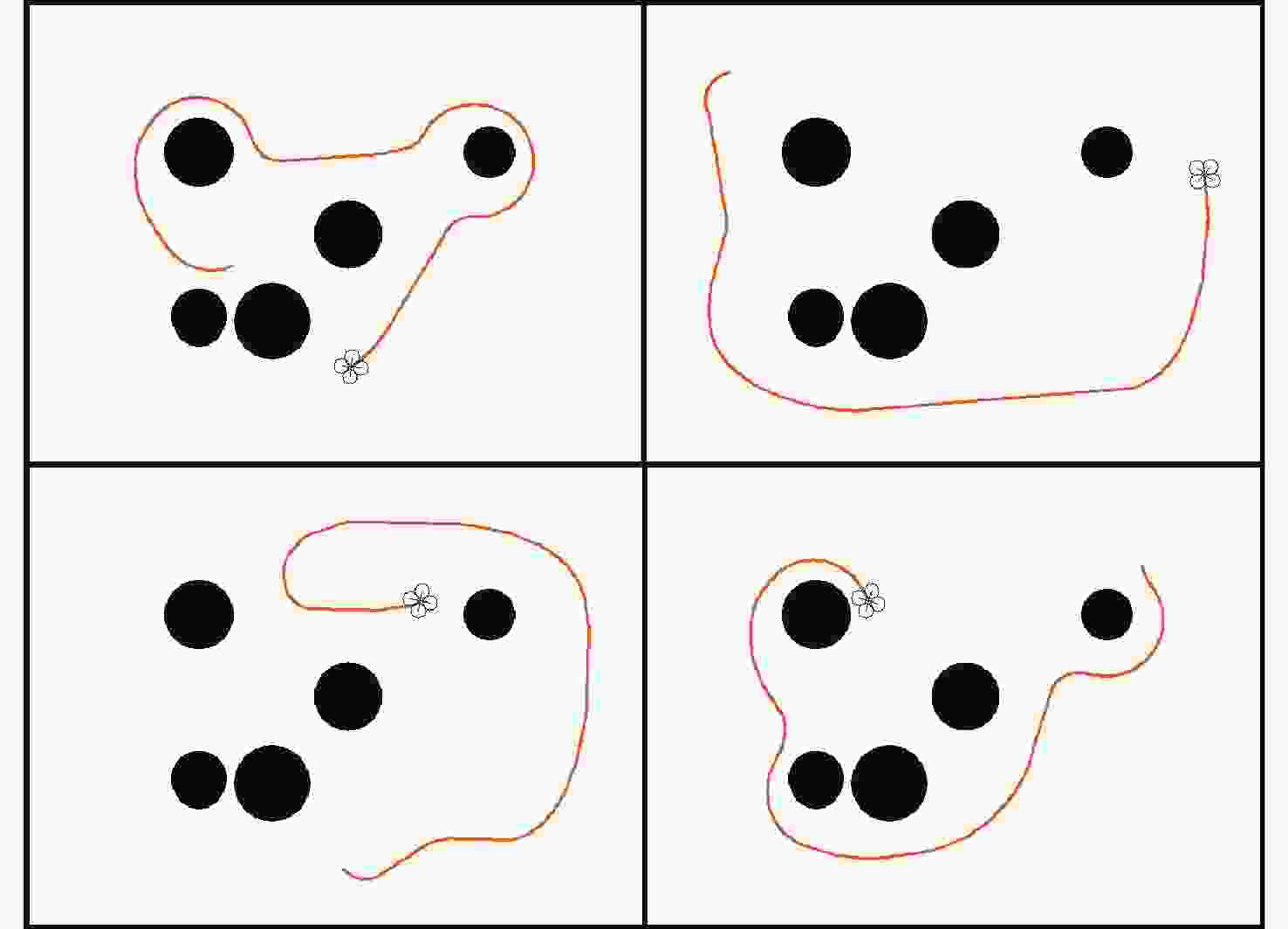
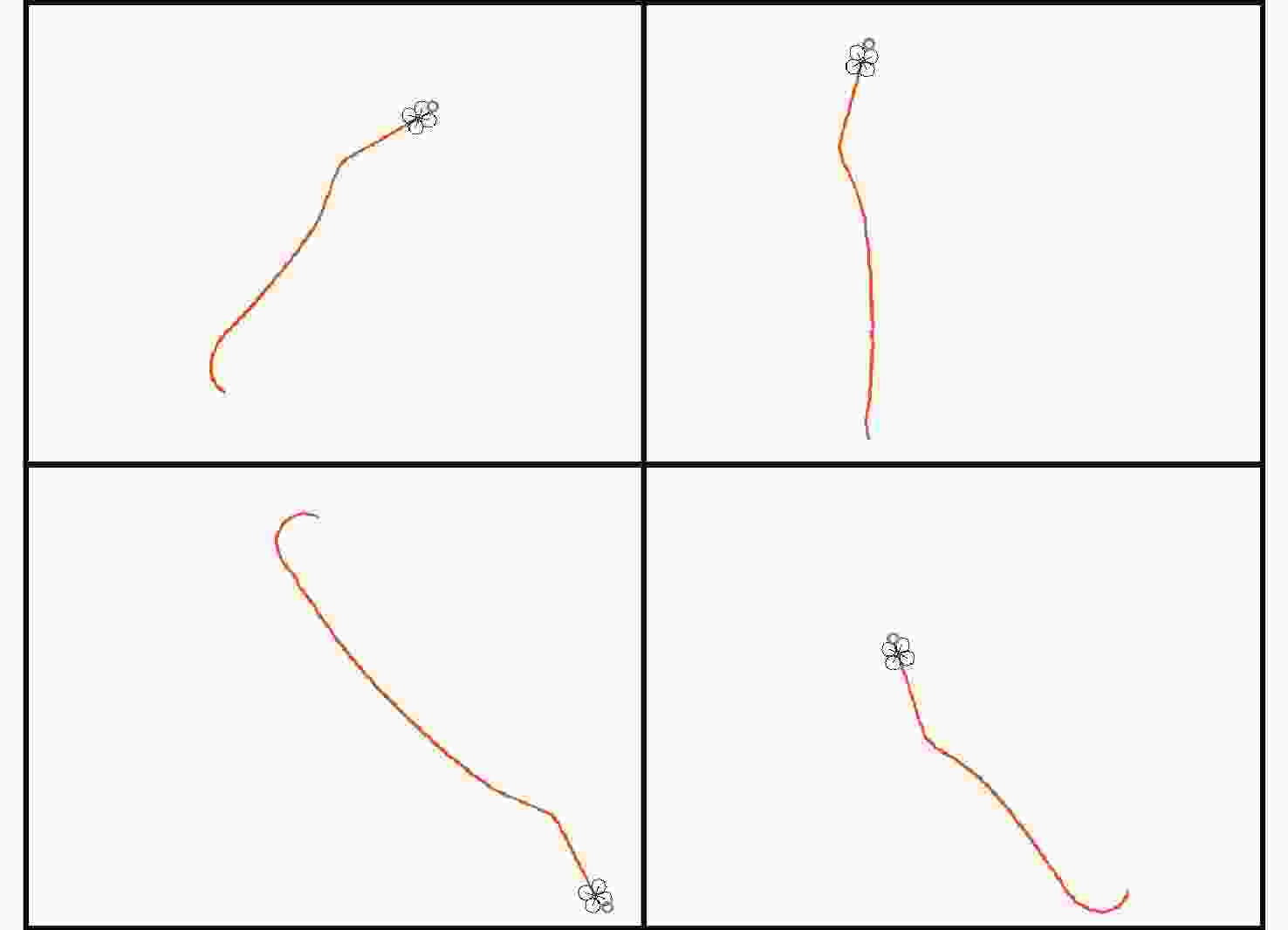
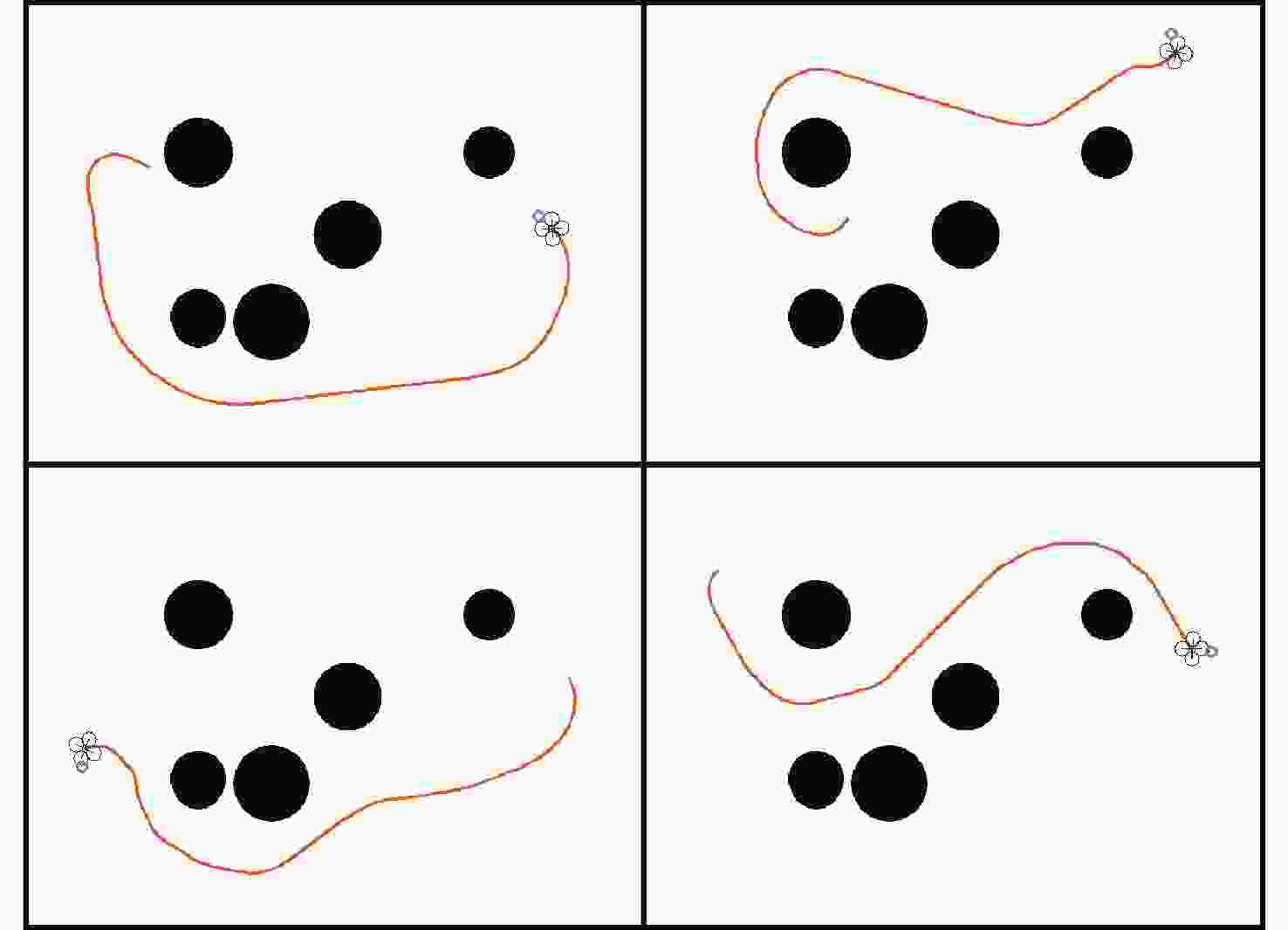
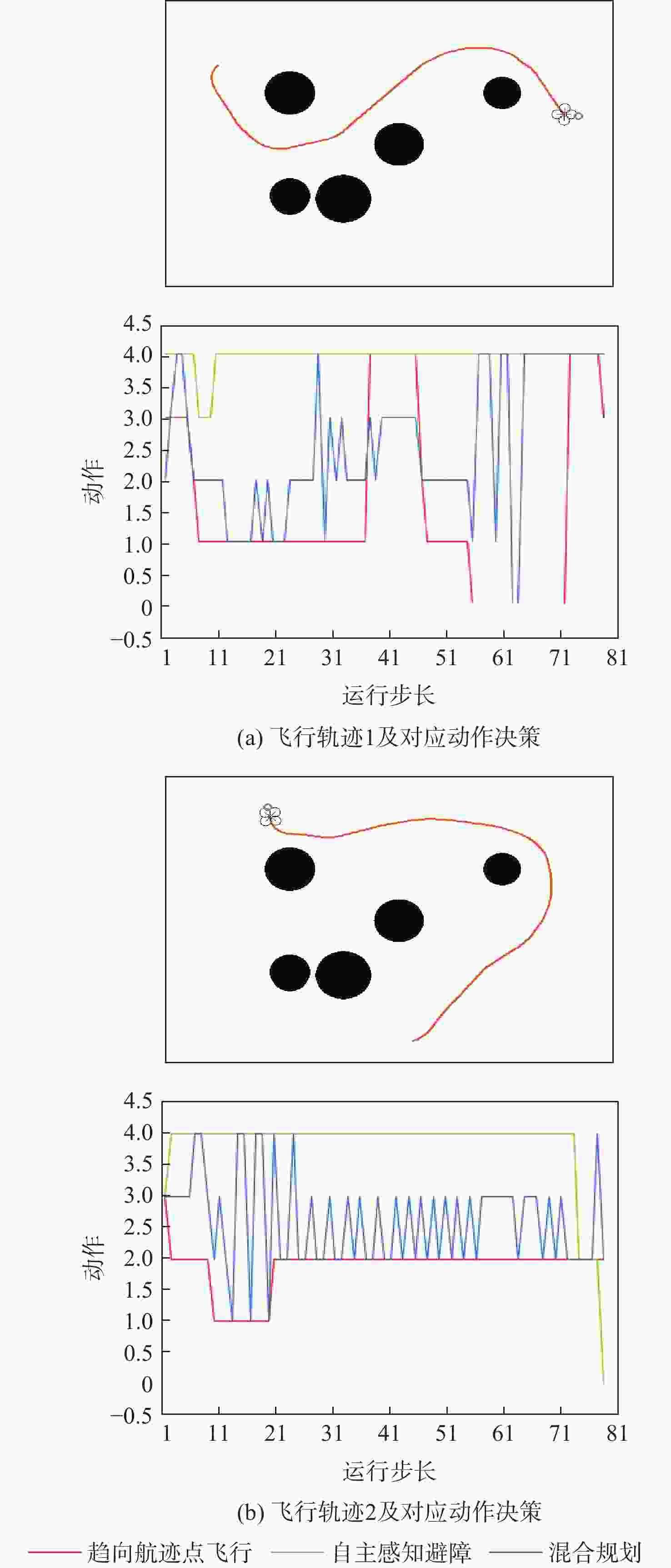
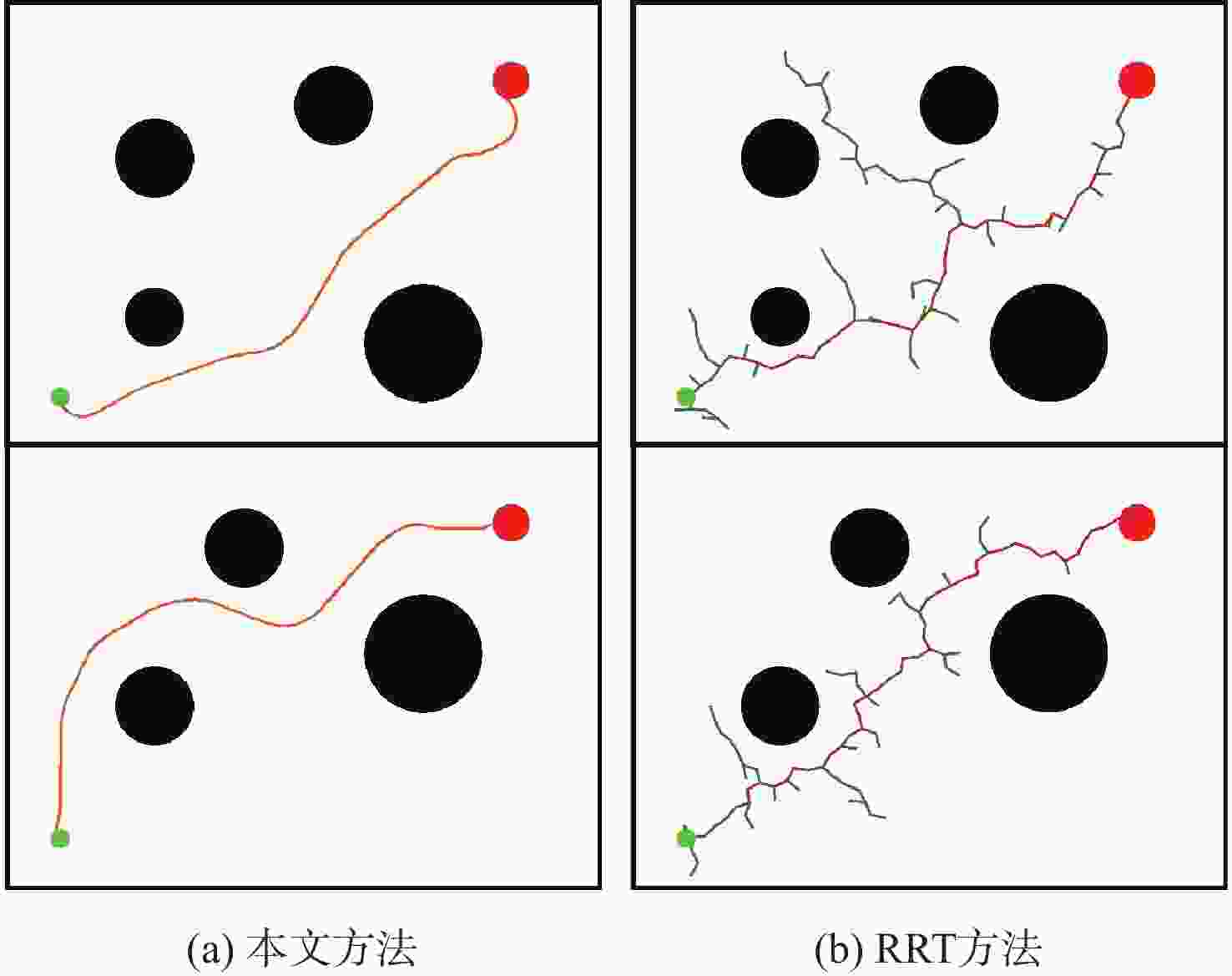
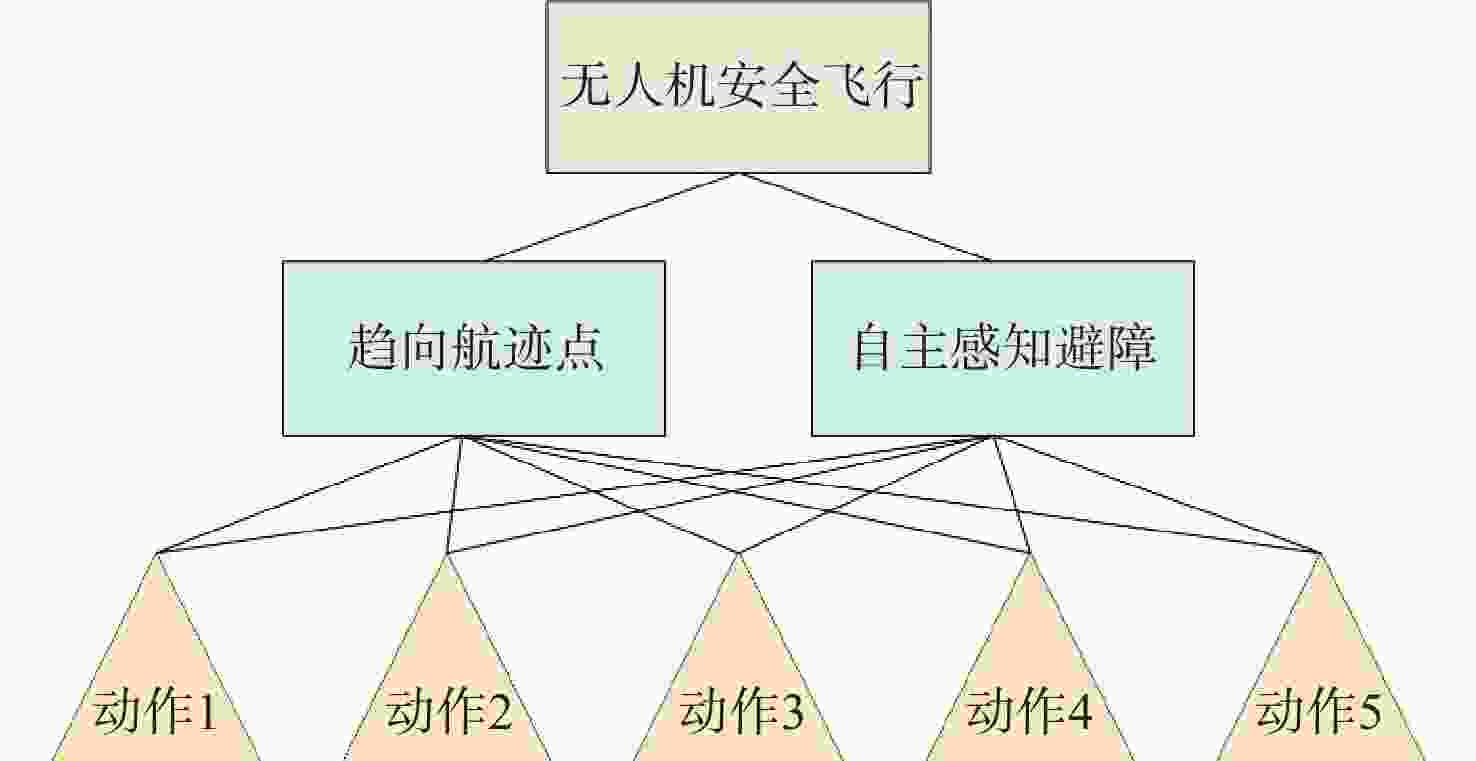
无人机应用中需要在非净空环境中实现自主安全飞行,其中障碍物存在部分已知、部分未知的特点,需在基于已知障碍物进行全局路径规划的同时,开展针对未知障碍物的自主避障。为实现障碍物半已知环境下的安全飞行,提出基于分层深度强化学习的混合路径规划方法。该方法将自主感知避障和趋向全局路径规划航迹点飞行2个无人机自主飞行中需要执行的子任务,利用分层模型有机结合,实现功能的有效复合。分层深度强化学习模型中,避障和导航2个子任务模型可分别单独训练,并通过2个训练后的模型对系统状态进行抽象,在此基础上训练顶层模型,实现对2个任务输出的有效调度。试验表明:所提分层深度强化学习方法可在趋向全局路径规划航迹点飞行和自主感知避障的子任务控制器基础上,实现功能扩展,完成更为复杂的任务,可在降低模型训练难度的同时,保持模型任务执行能力。
Abstract:In the application of UAV, it is necessary to realize autonomous and safe flight in a non-clearance environment. For both known and unknown obstacles, it is necessary to carry out autonomous obstacle avoidance for unknown obstacles while making global path planning based on known obstacles. To achieve safe flight in the semi-known obstacle environment, a hybrid path planning method based on hierarchical deep reinforcement learning is proposed, which naturally combines autonomous perception, obstacle avoidance, and global path planning, two sub-tasks that UAV must perform in autonomous flight, to achieve an efficient combination of functions. In the hierarchical deep reinforcement learning model, the obstacle avoidance and navigation sub-task models can be trained separately, and the system state can be abstracted through the two trained models. On this basis, the top-level model can be trained to achieve effective scheduling of the two sub-task outputs. The obstacle avoidance and navigation sub-task models can be trained independently in the hierarchical deep reinforcement learning model, and the system state can be abstracted through the two trained models. It can reduce the difficulty of model training while maintaining the ability to execute the model task.
-
Key words:
- UAV /
- path planning /
- autonomous obstacle avoidance /
- deep reinforcement learning /
- hierarchical model
-
表 1 无人机动作空间定义
Table 1. The definition of the UAV action space
动作编号 线速度/(m·s−1) 航向控制量/(°) 1 (10,0,0) 0 2 (10,0,0) +5 3 (10,0,0) −5 4 (10,0,0) +10 5 (10,0,0) −10 表 2 避障控制器网络模型主要参数
Table 2. The main parameters of obstacle avoidance controller network model
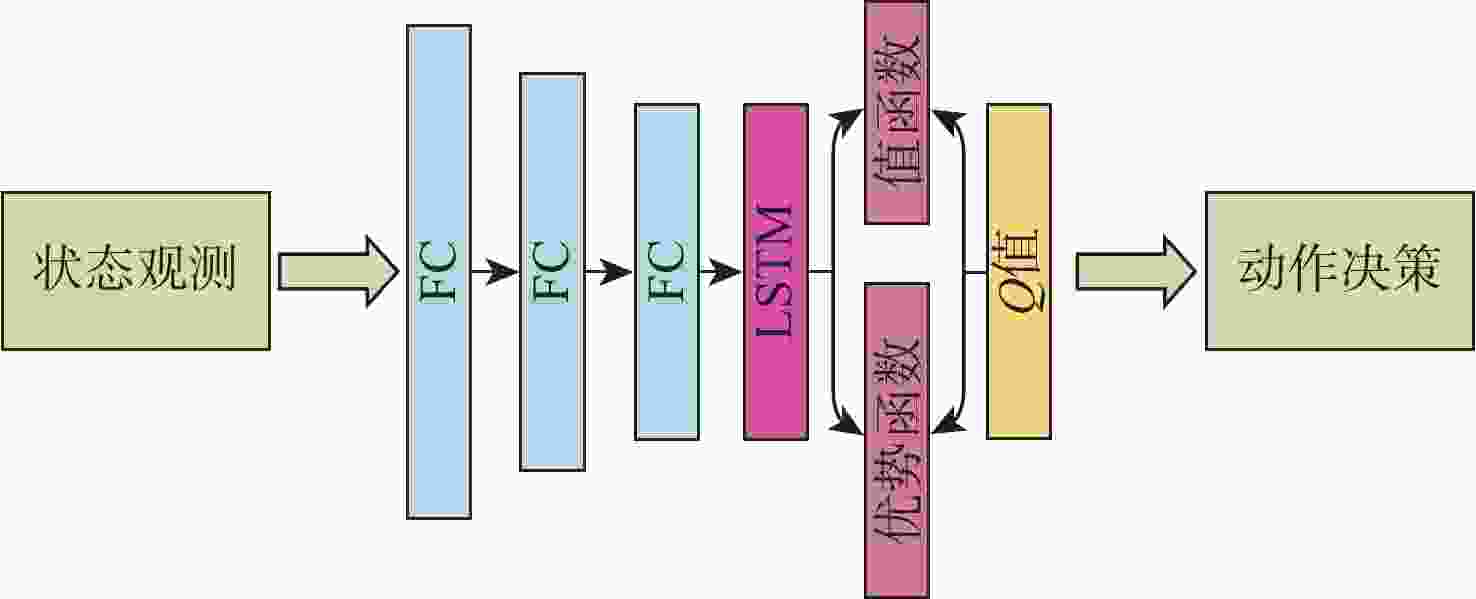
层号 类别 输入尺度 输出尺度 激活函数 1 FC 32 128 ReLU 2 FC 128 128 ReLU 3 FC 128 128 ReLU 4 LSTM 128 128 5(A(s,a)) FC 128 5 ReLU 5(V(s)) FC 128 1 ReLU 表 3 导航控制器网络模型主要参数
Table 3. The main parameters of navigation controller network model
层号 类别 输入尺度 输出尺度 激活函数 1 FC 2 32 ReLU 2 FC 32 32 ReLU 3 FC 32 32 ReLU 4 LSTM 32 32 5(A(s,a)) FC 32 5 ReLU 5(V(s)) FC 32 1 ReLU 表 4 顶层控制器网络模型主要参数
Table 4. The main parameters of top controller network model
层号 类别 输入尺度 输出尺度 激活函数 1 FC 10 128 ReLU 2 FC 128 128 ReLU 3 FC 128 128 ReLU 4 LSTM 128 128 5(A(s,a)) FC 128 5 ReLU 5(V(s)) FC 128 1 ReLU 表 5 控制器训练参数
Table 5. The parameters of controller training
场景 地图尺度/(m×m) 障碍物数量 训练批量 折扣因子 学习率 输入数据维度 动作时间间隔/s 网络更新频率/步 优化器 优化器参数 场景1 640×480 4 64 0.99 1×10−4 32 0.5 400 Adam [0.9,0.999,0] 场景2 640×480 0 64 0.99 1×10−4 2 0.5 400 Adam [0.9,0.999,0] 场景3 640×480 4 32 0.99 1×10−4 34 0.5 400 Adam [0.9,0.999,0] -
[1] 支琛博, 张爱军, 杜新阳, 等. 改进A*算法的移动机器人全局路径规划研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(2): 486-491. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.02.090ZHI C B, ZHANG A J, DU X Y, et al. Research on global path planning of mobile robot based on improved A* algorithm[J]. Computer Simulation, 2023, 40(2): 486-491(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.02.090 [2] 栾添添, 王皓, 孙明晓, 等. 基于动态变采样区域RRT的无人车路径规划[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(6): 1721-1729.LUAN T T, WANG H, SUN M X, et al. Path planning of unmanned vehicle based on dynamic variable sampling area RRT[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(6): 1721-1729(in Chinese). [3] 李樾, 韩维, 陈清阳, 等. 基于快速扩展随机树算法的多无人机编队重构方法研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2019, 37(3): 601-611. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20193730601LI Y, HAN W, CHEN Q Y, et al. Research on formation reconfiguration of UAVs based on RRT algorithm[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2019, 37(3): 601-611(in Chinese). doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20193730601 [4] HARIK E H, KORSAETH A. Combining hector SLAM and artificial potential field for autonomous navigation inside a greenhouse[J]. Robotics, 2018, 7(2): 22. doi: 10.3390/robotics7020022 [5] RHODES C, LIU C J, CHEN W H. Autonomous source term estimation in unknown environments: from a dual control concept to UAV deployment[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 2274-2281. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3143890 [6] YU X Q, WANG P, ZHANG Z X. Learning-based end-to-end path planning for lunar rovers with safety constraints[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(3): 796. doi: 10.3390/s21030796 [7] WU K Y, ESFAHANI M A, YUAN S H, et al. TDPP-Net: achieving three-dimensional path planning via a deep neural network architecture[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 357: 151-162. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.05.001 [8] 黄昱洲, 王立松, 秦小麟. 一种基于深度强化学习的无人小车双层路径规划方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2023, 50(1): 194-204.HUANG Y Z, WANG L S, QIN X L. Bi-level path planning method for unmanned vehicle based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Computer Science, 2023, 50(1): 194-204(in Chinese). [9] 封硕, 舒红, 谢步庆. 基于改进深度强化学习的三维环境路径规划[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(1): 250-255.FENG S, SHU H, XIE B Q. 3D environment path planning based on improved deep reinforcement learning[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2021, 38(1): 250-255(in Chinese). [10] GUPTA S, TOLANI V, DAVIDSON J, et al. Cognitive mapping and planning for visual navigation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(5): 1311-1330. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01236-7 [11] XIE L H, WANG S, MARKHAM A, et al. Towards monocular vision based obstacle avoidance through deep reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. (2017-06-29) [2023-08-20]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09829. [12] SINGLA A, PADAKANDLA S, BHATNAGAR S. Memory-based deep reinforcement learning for obstacle avoidance in UAV with limited environment knowledge[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 22(1): 107-118. [13] ZHU Y K, MOTTAGHI R, KOLVE E, et al. Target-driven visual navigation in indoor scenes using deep reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3357-3364. [14] WEN S H, ZHAO Y F, YUAN X, et al. Path planning for active SLAM based on deep reinforcement learning under unknown environments[J]. Intelligent Service Robotics, 2020, 13(2): 263-272. doi: 10.1007/s11370-019-00310-w [15] HAUSKNECHT M, STONE P. Deep recurrent Q-learning for partially observable MDPS[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Learning Representations. New York: ACM, 2015: 29-37. [16] WANG Z Y, SCHAUL T, HESSEL M, et al. Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2016, 48: 1995-2003. [17] VAN H H, GUEZ A, SILVER D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: AAAI Press, 2016, 30(1): 2094-2100. -






 下载:
下载: