Dynamically changeable human-robot collaborative assembly based on limb motion prediction
-
摘要:
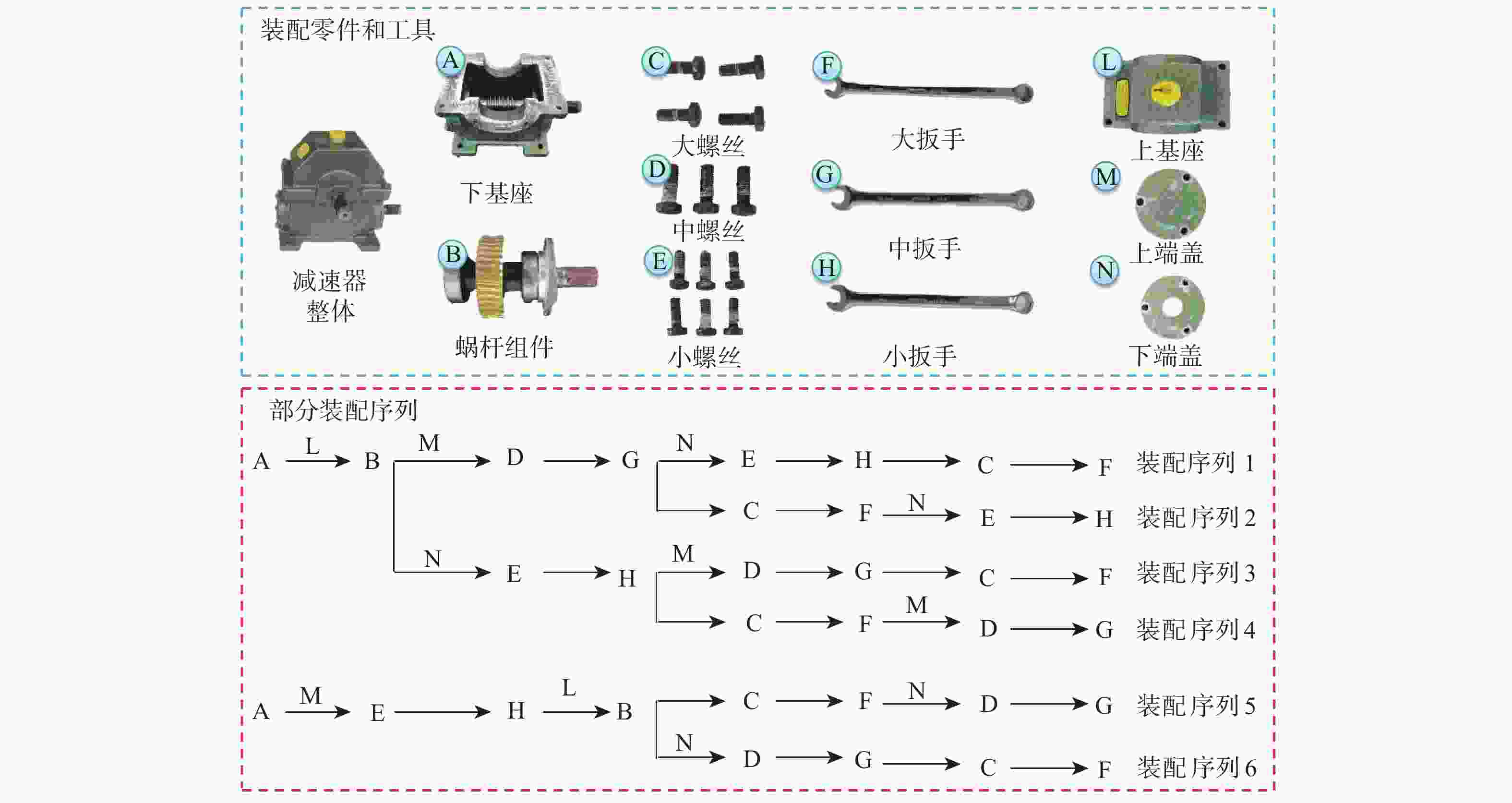
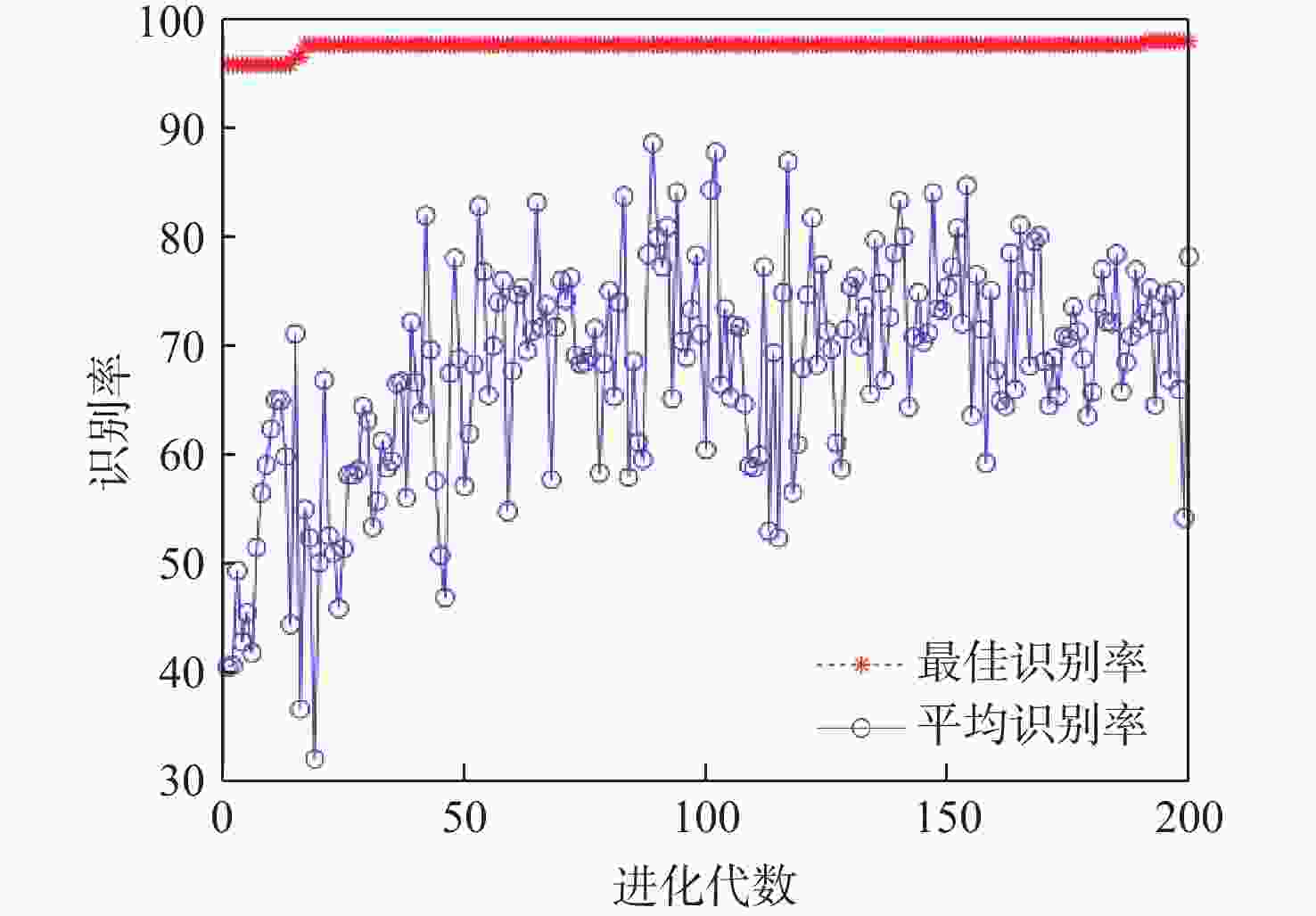
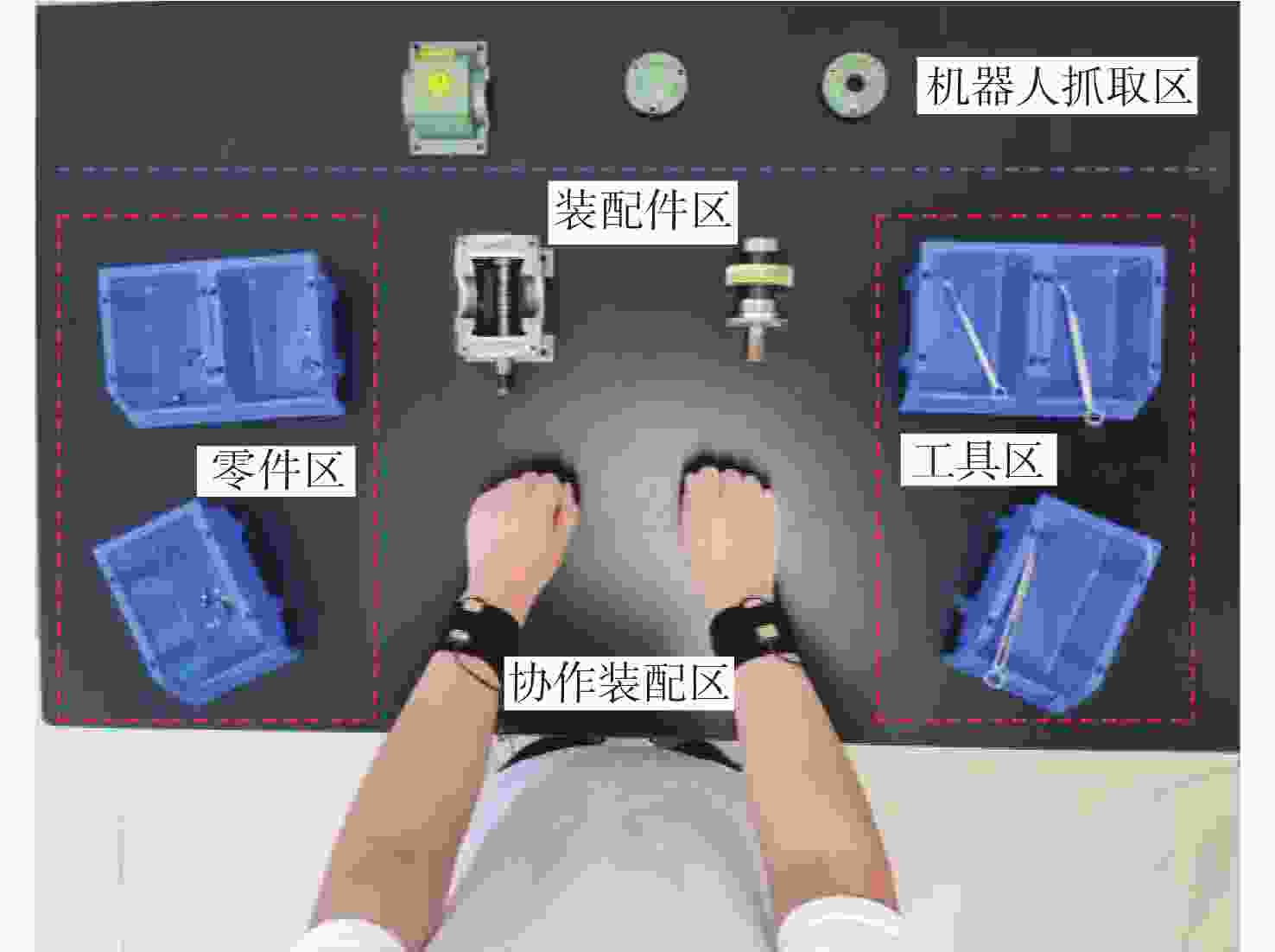
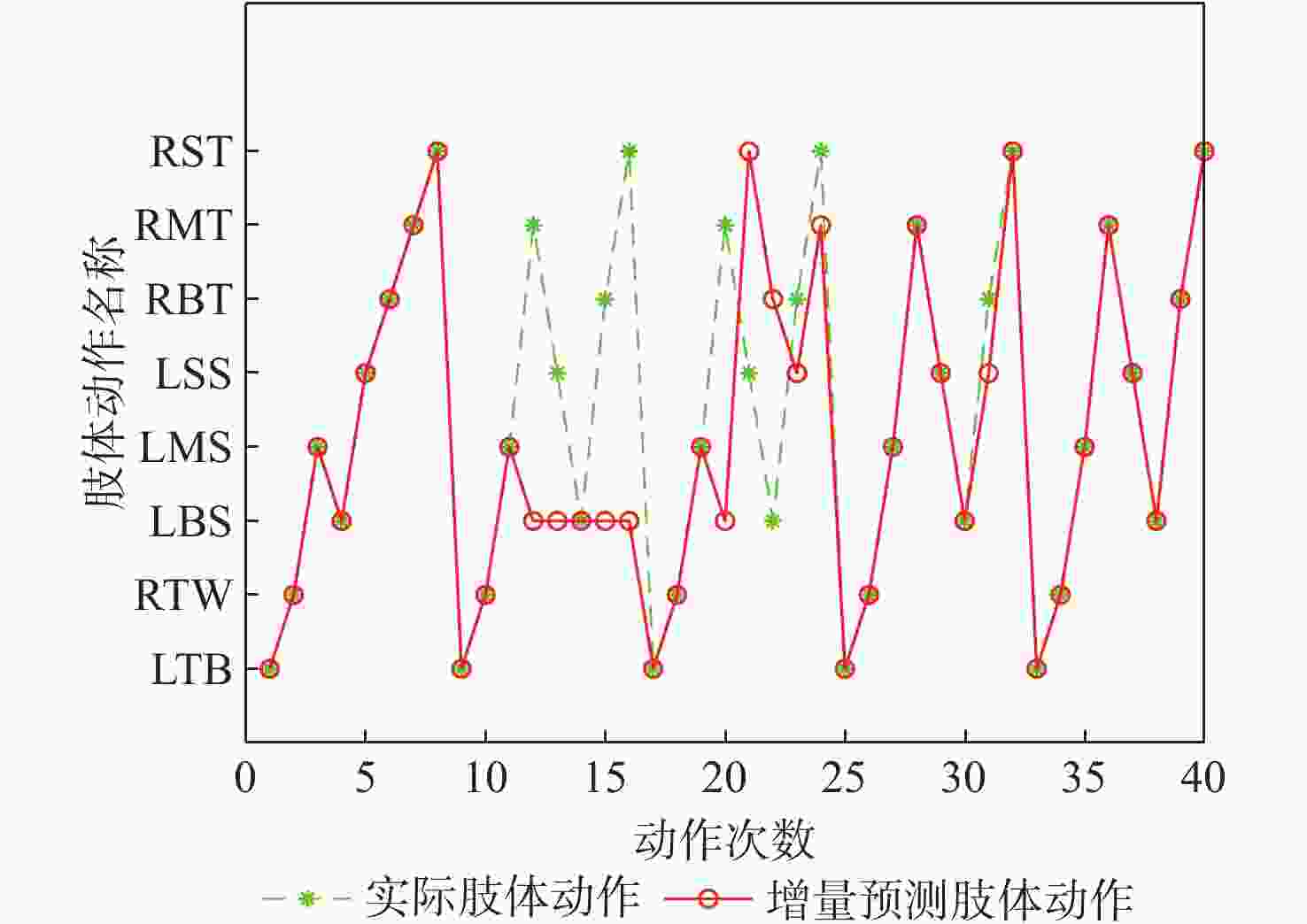
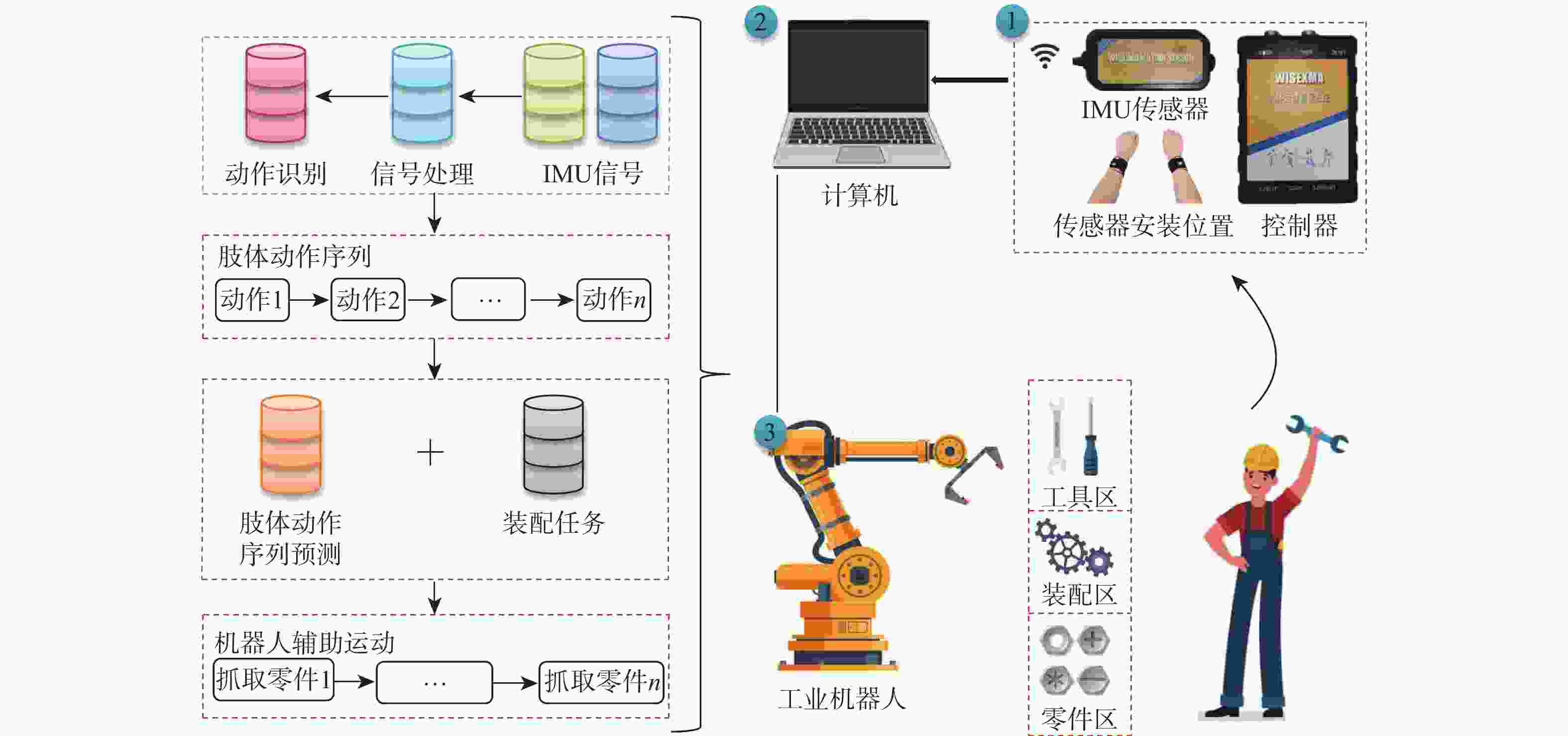
在复杂的装配领域中,单纯依靠机器人很难完成,进行人机协作装配才能确保装配过程顺利进行,但人机协作过程中,机器人缺乏根据人的不同操作作出响应的能力。针对产品组装过程中存在多种不同的组装方案和顺序的情况,提出一种通过识别和预测操作者肢体动作,使机器人根据操作者不同的选择做出对应配合的装配动作,实现动态可变的人机协作装配方案。利用惯性测量单元(IMU)采集操作者的肢体动作信息,提取惯性测量单元信号特征,为提高识别准确率,提出一种同时利用时域和时频域特征的粒子群优化(PSO)支持向量机(SVM)算法,用于肢体动作识别;同时,提出一种参数可变的隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)实时预测肢体动作序列,在监督训练和零训练状态下,推断出操作者的未来意图,实现装配序列的动态可变性。实验结果表明:在减速器人机协作装配实验中,所提方案肢体动作平均识别率达到96.7%,并且能够有效预测操作者肢体动作,实现装配顺序可变的动态人机协作装配,显著提升了装配系统的适应性,降低了人机协作装配的复杂度。
Abstract:Human-robot collaborative assembly is necessary to ensure that the assembly process goes successfully in some complex assembly areas where it is challenging to rely entirely on robots to complete the assembly. However, in the process of human-robot collaboration, the robot cannot respond to different human operations. We propose a dynamic variable human-robot collaborative assembly scheme to address the challenges in complex assembly domains. The scheme achieves dynamic variability in the assembly process by recognizing and predicting the operator’s limb movements, and the robot responds accordingly. We use an inertial measurement unit (IMU) to collect motion information and propose a particle swarm optimization (PSO) support vector machine (SVM) algorithm for accurate limb motion detection. In addition, we introduce a parameter-variable hidden Markov model (HMM) to predict action sequences in real-time. This allows the robot to infer the operator’s future intentions. The decelerator human-robot collaborative assembly experiment showed that the suggested approach obtained an average limb motion recognition rate of 96.7%. It was also able to effectively predict operator actions, enabling dynamic human-robot collaborative assembly with adjustable assembly sequences. This significantly enhanced the adaptability of the assembly system and reduced the complexity of human-robot collaborative assembly.
-
表 1 特征提取
Table 1. Feature extraction
特征 公式 均值 $ \overline x = \dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {{x_i}} $ 峰值 $ {x_{\mathrm{p}}} = \max \left\{ {\left| {{x_1}} \right|,\left| {{x_2}} \right|, \cdots ,\left| {{x_N}} \right|} \right\} $ 标准差 $ {\sigma _x} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {{{\left( {{x_i} - \overline x } \right)}^2}} } $ 均方根 $ {x_{{\mathrm{rms}}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {x_i^2} } $ 峰值因子 $ C = \dfrac{{{x_{\mathrm{p}}}}}{{{x_{{\mathrm{rms}}}}}} $ 波形因子 $ W = \dfrac{{{x_{{\mathrm{rms}}}}}}{{\dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {\left| {{x_i}} \right|} }} $ 小波包能量 $ {E_{j,k}} = {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{l = 1}^m {\left| {d_l^{j,k}} \right|} ^2} $ 表 2 初始状态矩阵参数
Table 2. Initial state matrix parameter
状态 数值 LTB 1 RTW 0 LBS 0 LMS 0 LSS 0 RBT 0 RMT 0 RST 0 表 3 状态转移矩阵参数
Table 3. State transition matrix parameter
状态 数值 AS1 AS2 AS3 AS4 AS5 AS6 AS7 AS8 AS1 0 $ \dfrac{31}{40} $ 0 0 $ \dfrac{9}{40} $ 0 0 0 AS2 0 0 $ \dfrac{21}{80} $ $ \dfrac{41}{80} $ $ \dfrac{9}{40} $ 0 0 0 AS3 0 0 0 $ \dfrac{11}{40} $ $ \dfrac{7}{20} $ $ \dfrac{3}{16} $ $ \dfrac{1}{10} $ $ \dfrac{7}{80} $ AS4 0 0 $ \dfrac{9}{20} $ 0 $ \dfrac{3}{20} $ $ \dfrac{1}{10} $ $ \dfrac{9}{40} $ $ \dfrac{9}{40} $ AS5 0 $ \dfrac{3}{20} $ $ \dfrac{7}{40} $ $ \dfrac{3}{20} $ 0 $ \dfrac{19}{80} $ $ \dfrac{1}{20} $ $ \dfrac{19}{80} $ AS6 0 0 0 $ \dfrac{2}{55} $ $ \dfrac{1}{55} $ 0 $ \dfrac{34}{55} $ $ \dfrac{18}{55} $ AS7 0 0 $ \dfrac{5}{58} $ 0 $ \dfrac{3}{58} $ $ \dfrac{10}{29} $ 0 $ \dfrac{15}{29} $ AS8 0 $ \dfrac{6}{47} $ $ \dfrac{4}{47} $ $ \dfrac{3}{47} $ 0 $ \dfrac{18}{47} $ $ \dfrac{16}{47} $ 0 表 4 发射矩阵参数
Table 4. Transmit matrix parameter
状态 数值 LTB RTW LBS LMS LSS RBT RMT RST AS1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 AS2 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 AS3 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 AS4 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 AS5 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 AS6 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 AS7 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 AS8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 -
[1] ZHOU J, LI P G, ZHOU Y H, et al. Toward new-generation intelligent manufacturing[J]. Engineering, 2018, 4(1): 11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2018.01.002 [2] 黄海丰, 刘培森, 李擎, 等. 协作机器人智能控制与人机交互研究综述[J]. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(4): 780-791. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.4.bjkjdxxb202204028HUANG H F, LIU P S, LI Q, et al. Review: intelligent control and human-robot interaction for collaborative robots[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(4): 780-791(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.4.bjkjdxxb202204028 [3] WANG P, LIU H Y, WANG L H, et al. Deep learning-based human motion recognition for predictive context-aware human-robot collaboration[J]. CIRP Annals, 2018, 67(1): 17-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2018.04.066 [4] 常玉青. 人机协作中基于多Kinect的人体行为识别研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018: 5-7.CHANG Y Q. Research on human behavior recognition based on multi-Kinect in human-computer cooperation[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018: 5-7(in Chinese). [5] LU G L, ZHOU Y Q, LI X Y, et al. Efficient action recognition via local position offset of 3D skeletal body joints[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2016, 75(6): 3479-3494. doi: 10.1007/s11042-015-2448-1 [6] SHI M, YANG C Y, ZHANG D L. A novel human-machine collaboration model of an ankle joint rehabilitation robot driven by EEG signals[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021(1): 5564235. [7] ÇOBAN M, GELEN G. Realization of human-robot collaboration in hybrid assembly systems by using wearable technology[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Control Engineering & Information Technology. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-6. [8] SYED A S, SHERHAN Z, SHEHRAM M, et al. Using wearable sensors for human activity recognition in logistics: a comparison of different feature sets and machine learning algorithms[J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2020, 11(9): 644-649. [9] WANG W T, LI R, DIEKEL Z M, et al. Controlling object hand-over in human-robot collaboration via natural wearable sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Human Machine Systems, 2019, 49(1): 59-71. doi: 10.1109/THMS.2018.2883176 [10] 陈友东, 刘嘉蕾, 胡澜晓. 人机协作中人的动作终点预测[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2019, 45(1): 35-43.CHEN Y D, LIU J L, HU L X. Human motion end point prediction in human-robot collaboration[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(1): 35-43(in Chinese). [11] LIU Z T, LIU Q, XU W J, et al. Deep learning-based human motion prediction considering context awareness for human-robot collaboration in manufacturing[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2019, 83: 272-278. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2019.04.080 [12] KWON W Y, SUH I H. Planning of proactive behaviors for human-robot cooperative tasks under uncertainty[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2014, 72: 81-95. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2014.08.021 [13] HAWKINS K P, VO N, BANSAL S, et al. Probabilistic human action prediction and wait-sensitive planning for responsive human-robot collaboration[C]//Proceedings of the 13th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 499-506. [14] LIU H Y, WANG L H. Human motion prediction for human-robot collaboration[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2017, 44: 287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2017.04.009 [15] CRAMER M, CRAMER J, KELLENS K, et al. Towards robust intention estimation based on object affordance enabling natural human-robot collaboration in assembly tasks[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2018, 78: 255-260. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2018.09.069 [16] ZANCHETTIN A M, CASALINO A, PIRODDI L, et al. Prediction of human activity patterns for human-robot collaborative assembly tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 15(7): 3934-3942. [17] 祁亨年. 支持向量机及其应用研究综述[J]. 计算机工程, 2004, 30(10): 6-9.QI H N. Support vector machines and application research overview[J]. Computer Engineering, 2004, 30(10): 6-9(in Chinese). [18] CHANG C C, LIN C J. LIBSVM[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2011, 2(3): 1-27. [19] YE M Y, YAN X A, JIA M P. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on VMD-MPE and PSO-SVM[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23(6): 762. doi: 10.3390/e23060762 [20] TONG L N, SONG Q J, GE Y J, et al. HMM-based human fall detection and prediction method using tri-axial accelerometer[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2013, 13(5): 1849-1856. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2013.2245231 -






 下载:
下载: