-
摘要:
分布式电推进飞机大量采用螺旋桨,存在显著的桨-翼气动耦合效应。通过改变轴向诱导速度分布控制螺旋桨滑流,从而得到螺旋桨弦长和扭转角分布,提出一种考虑滑流效应的高效螺旋桨设计方法,并验证方法的可行性。计算所设计螺旋桨在孤立和分布式构型的巡航和悬停气动特性,并和最小诱导损失方法进行对比。结果表明:巡航升力系数相同时,所设计螺旋桨效率比最小诱导损失法高3.4%~6.6%;不同转速时,单独螺旋桨悬停效率比最小诱导损失法高10.4%~13.5%;分布式构型,设计螺旋桨悬停效率为比最小诱导损失法高13%。设计螺旋桨在巡航和悬停状态都能满足其设计要求,且都保持较高的效率运行。
Abstract:Propellers are widely used in distributed electric propulsion aircraft, where a significant propeller-wing aerodynamic coupling effect exists. By changing the axial induced velocity distribution to control the propeller slipstream, the propeller chord length and torsion angle distributions were obtained. An efficient propeller design method considering the slipstream effect was proposed, and the feasibility of the method was verified. The cruise and hover aerodynamic characteristics of the designed propellers in isolated and distributed configurations were calculated and compared with the minimum induced loss method. The results show that, for the same cruising lift coefficient, the efficiency of the designed propeller is 3.4%–6.6% higher than that of the minimum induced loss method. The hovering efficiency of a single propeller is 10.4%–13.5% higher than that of the minimum induced loss method at different rotational speeds. In the distributed configuration, the designed propeller’s hover efficiency is 13% higher than that of the minimum induced loss method. The designed propeller meets its design requirements in both cruise and hover states, maintaining high-efficiency operation.
-
表 1 不同螺旋桨巡航状态下的性能参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of performance parameters of different propellers in cruise state
螺旋桨类型 拉力T/N 力矩Q/(N·m) 效率η/% CST螺旋桨 796 207 73.13 MIL螺旋桨 841 224 71.67 表 2 分布式构型计算模型参数和计算条件
Table 2. Distributed configuration calculation model parameters and conditions
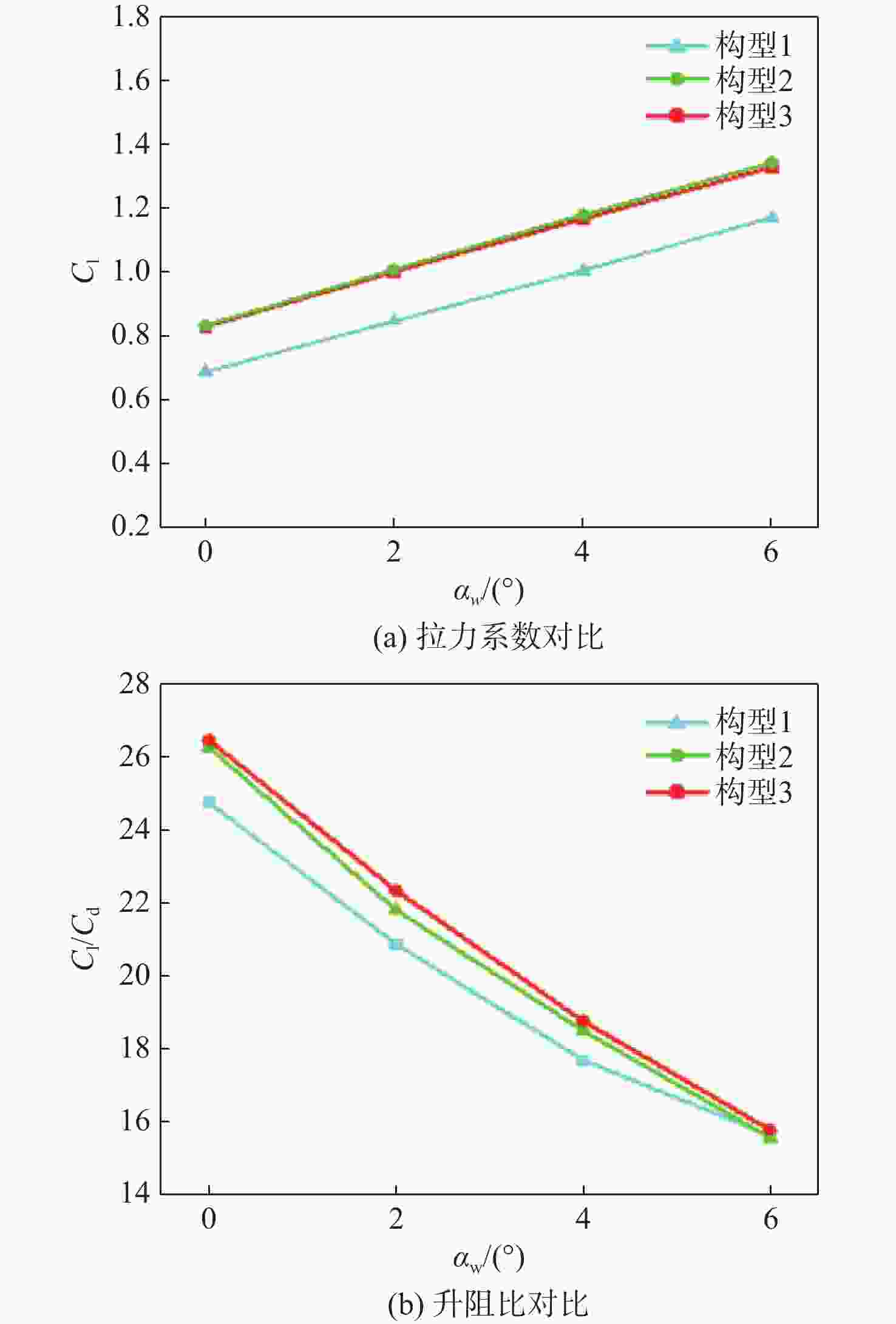
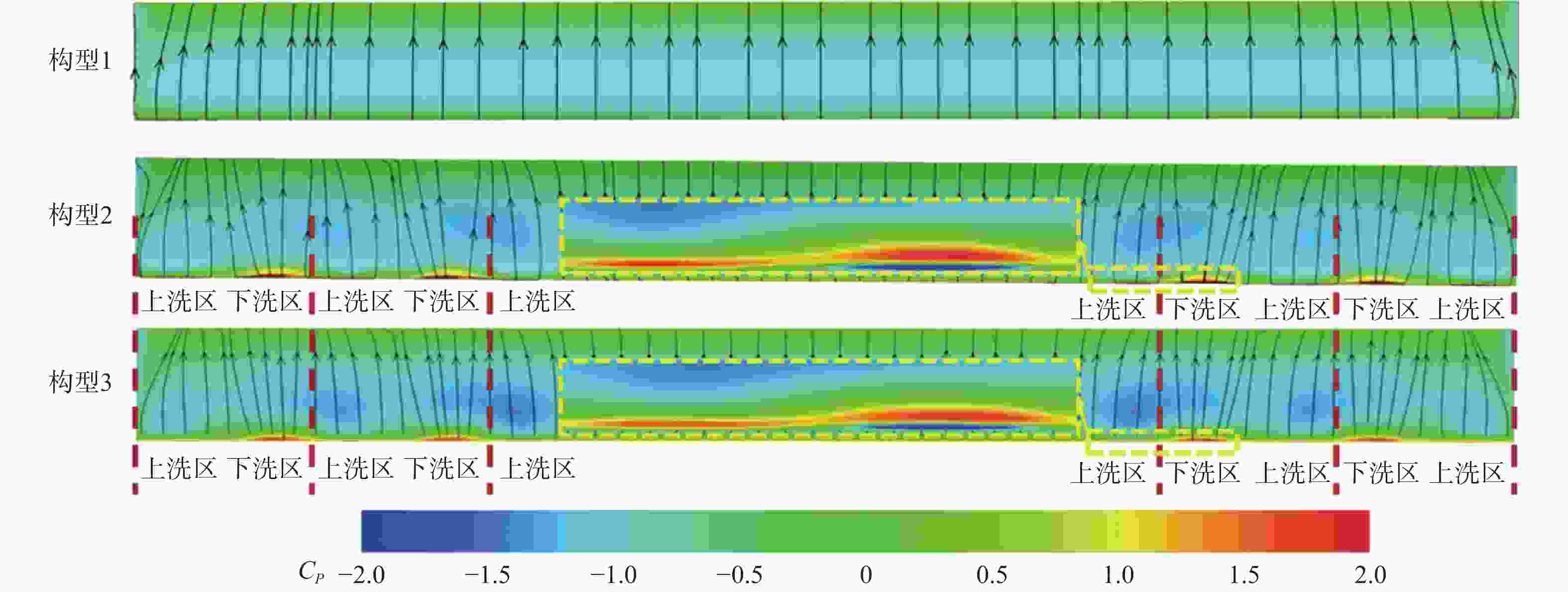
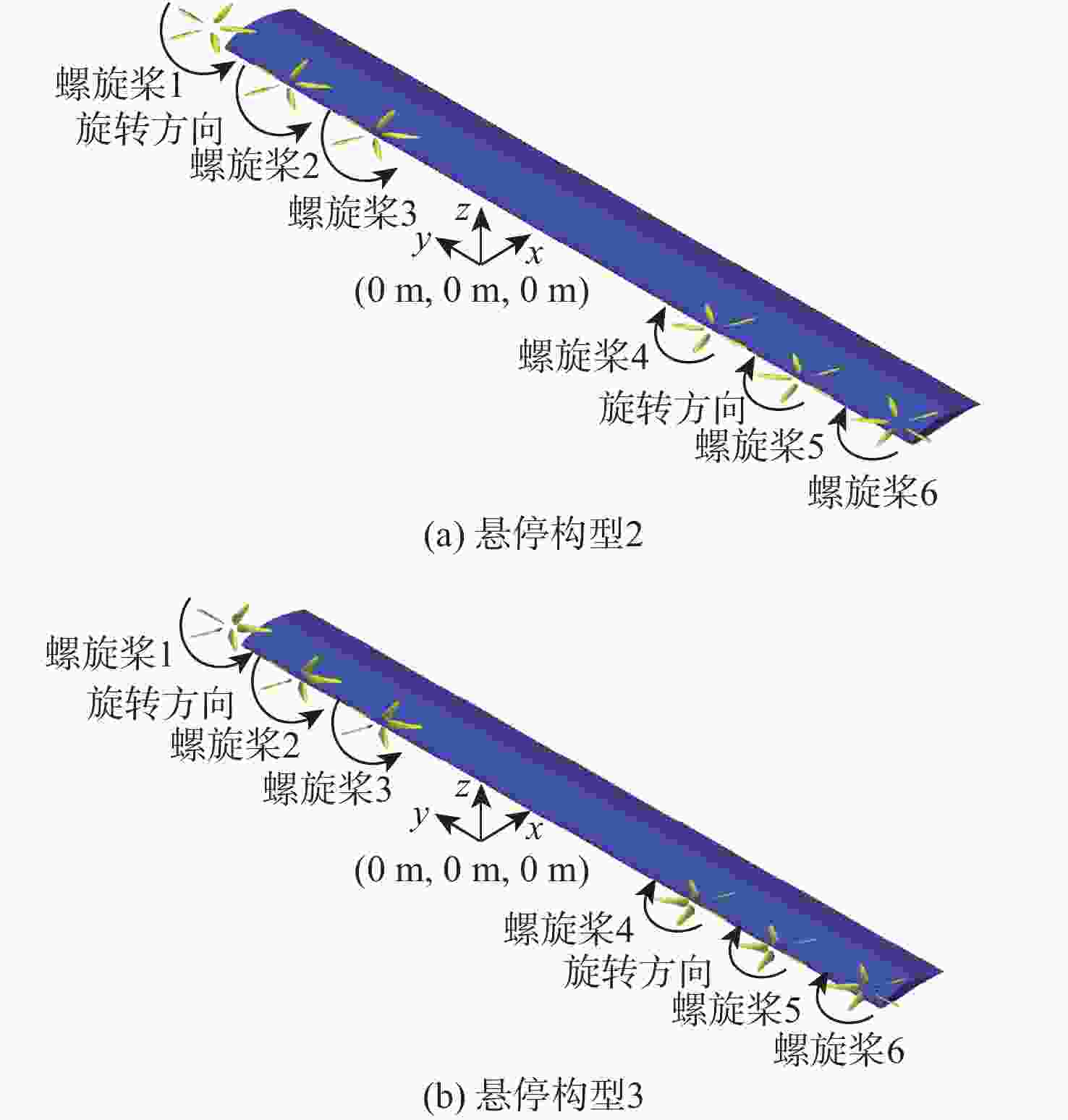
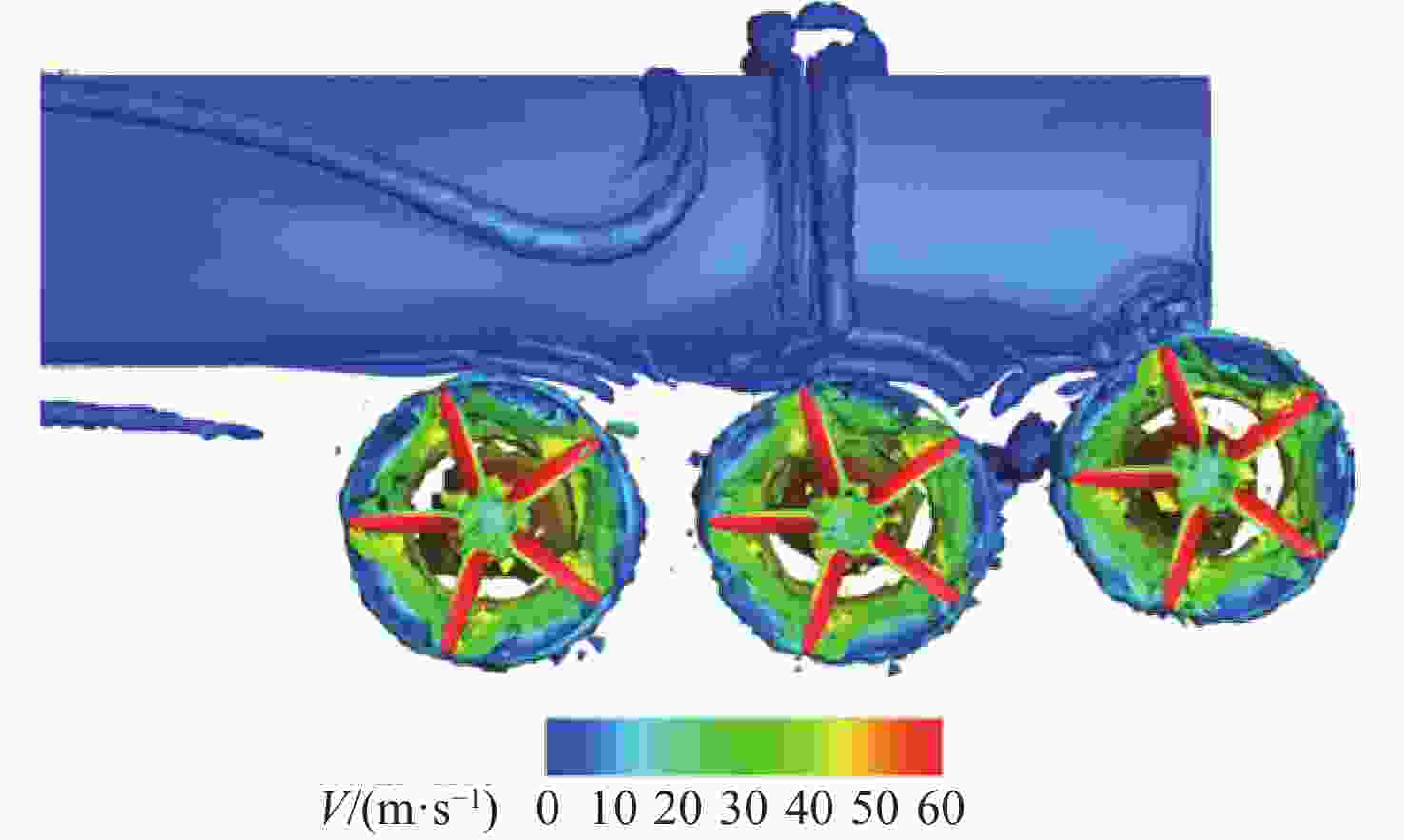
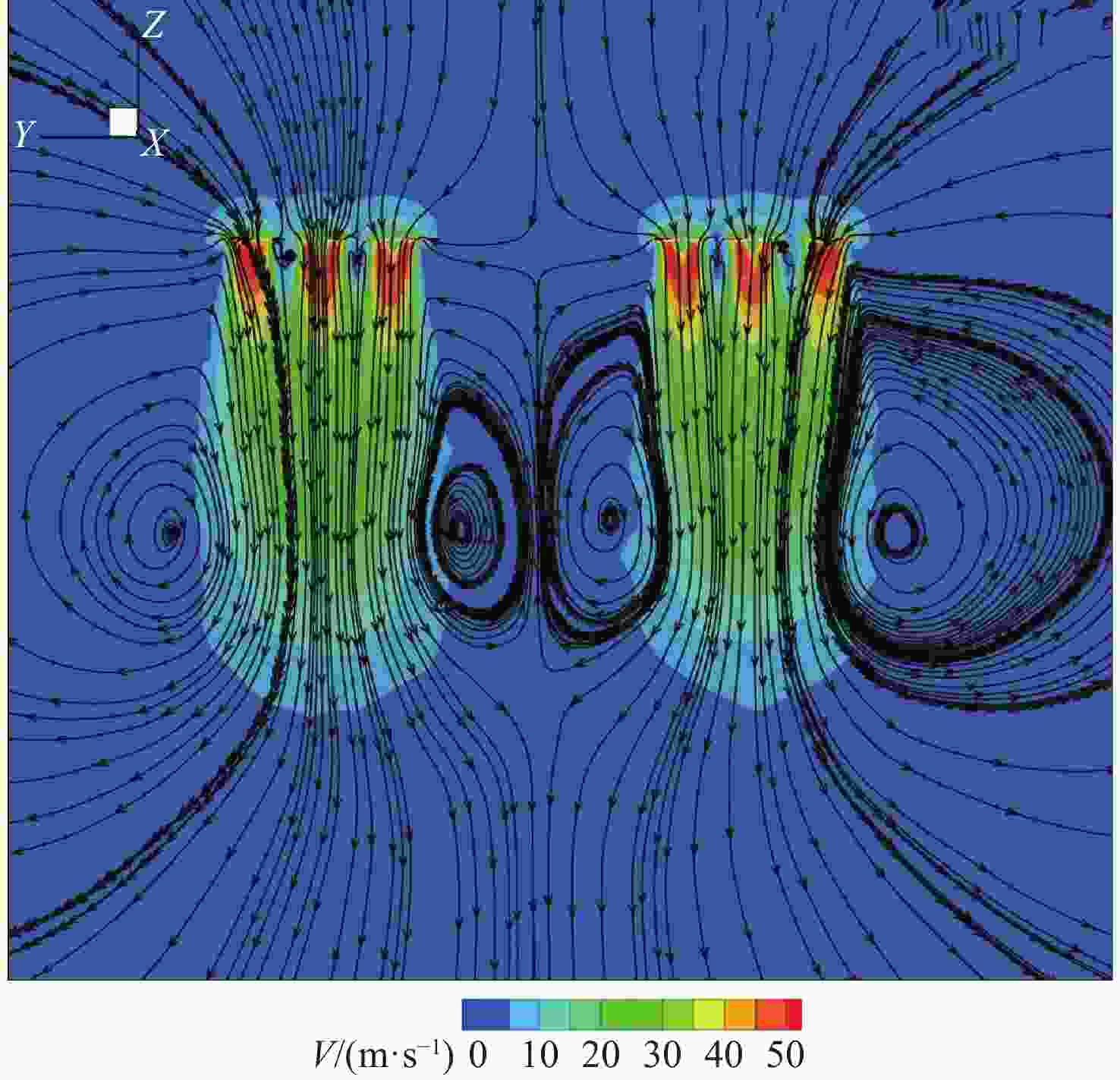
参数 数值 机翼展长/m 10 机翼弦长/m 1 螺旋桨半径R/m 0.48 螺旋桨轮毂半径Rhub/m 0.096 螺旋桨位置坐标 (0, ±5, 0.333)(0, ±3.74, 0.178)(0, ±2.48, 0.178) 巡航速度V0/(m·s−1) 60 巡航高度/m 500 机翼攻角αw/(°) 0、2、4、6 螺旋桨转速/(r·min−1) 3 000 马赫数Ma 0.176 雷诺数Re/106 7 表 3 3种构型升阻特性对比
Table 3. Comparison of lift and drag characteristics of three configurations
攻角
αw/(°)Cl Cd Cl/Cd 构1 构2 构3 构1 构2 构3 构1 构2 构3 0 0.69 0.028 24.80 0.83 0.032 26.33 0.83 0.031 26.53 2 0.85 0.044 20.91 1.01 0.046 21.84 1.00 0.045 22.38 4 1.01 0.057 17.71 1.18 0.064 18.52 1.17 0.062 18.79 6 1.17 0.075 15.63 1.34 0.086 15.57 1.33 0.084 15.79 表 4 螺旋桨悬停状态的气动性能参数
Table 4. Aerodynamic performance parameters of propeller in hover state
转速/(r·min−1) 拉力/N 悬停效率/% CST MIL CST MIL 2 000 242 114 68.48 56.85 2 500 383 180 68.62 58.23 3 000 556 262 68.71 57.18 3 500 765 356 68.68 56.02 4 000 1 010 469 68.64 55.10 表 5 分布式构型悬停状态计算模型参数和计算条件
Table 5. Calculation model parameters and conditions for distributed configuration in hover state
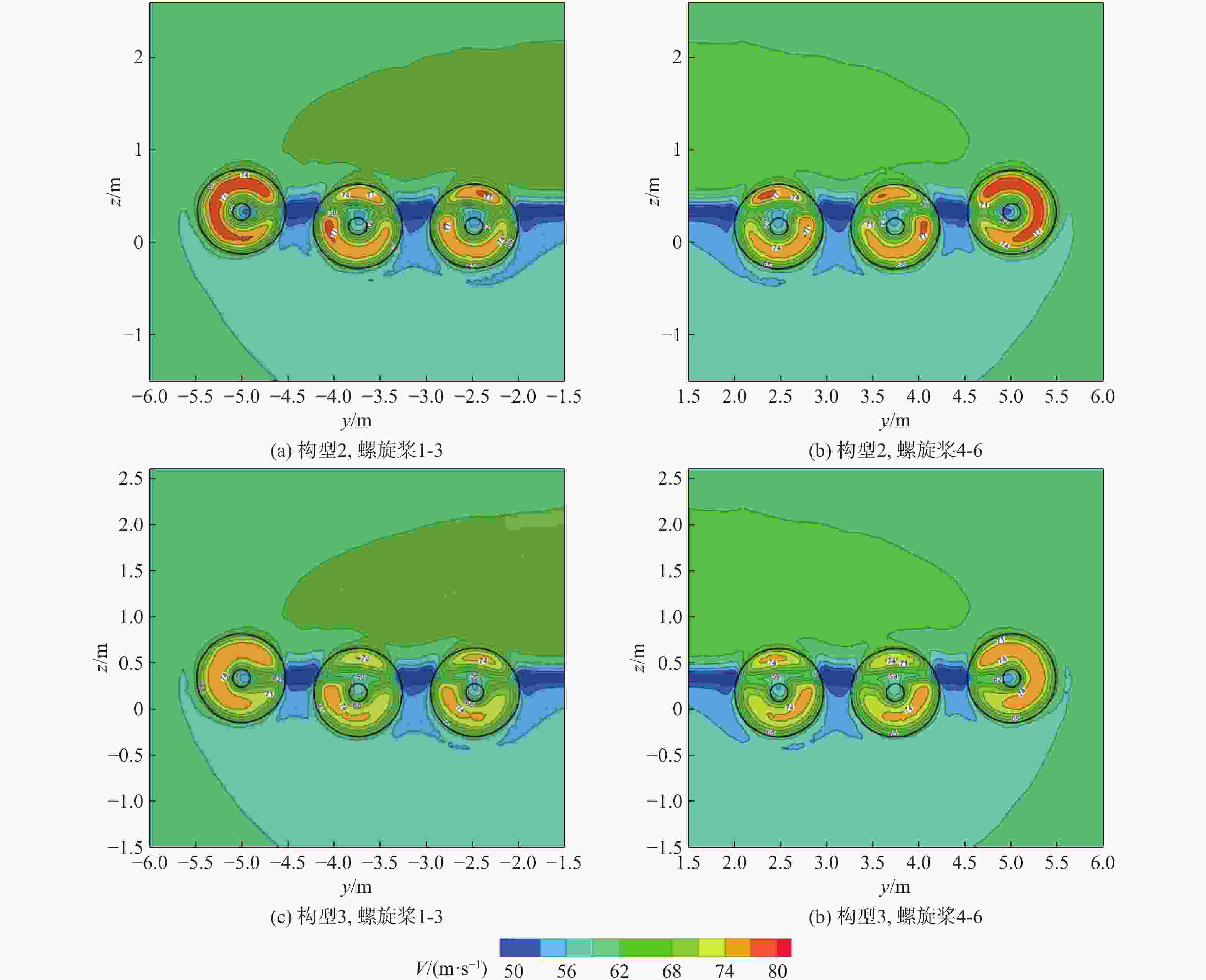
参数 数值 螺旋桨坐标 (−0.045, ±5, 0.696)(−0.2, ±3.74, 0.696)(−0.2, ±2.48, 0.696) 速度V1(m·s−1) 0 转速/(r·min−1) 4 000 雷诺数Re/106 2 表 6 螺旋桨悬停状态的气动性能参数
Table 6. Aerodynamic performance parameters of configuration 4 propeller in hover state
类型 拉力/N 悬停效率/% CST MIL CST MIL Prop1 978 479 61.13 48.35 Prop2 970 472 60.40 47.30 Prop3 978 480 61.10 48.51 Prop4 979 480 61.04 48.51 Prop5 969 466 60.53 46.40 Prop6 976 479 61.10 48.35 -
[1] KIM H D, PERRY A T, ANSELL P J. A review of distributed electric propulsion concepts for air vehicle technology[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA/IEEE Electric Aircraft Technologies Symposium. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 4998. [2] 黄俊. 分布式电推进飞机设计技术综述[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(3): 624037.HUANG J. Survey on design technology of distributed electric propulsion aircraft[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 624037 ( in Chinese). [3] PATTERSON M D, DERLAGA J M, BORER N K. High-lift propeller system configuration selection for NASA's SCEPTOR distributed electric propulsion flight demonstrator[C]//Proceedings of the 16th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2016: 3922. [4] Patterson M D. Conceptual design of high-lift propeller systems for small electric aircraft[D]. Atlanta: Georgia Institute of Technology, 2016. [5] DROANDI G, ZANOTTI A, GIBERTINI G, et al. Experimental investigation of the rotor-wing aerodynamic interaction in a tiltwing aircraft in hover[J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2015, 119(1215): 591-612. doi: 10.1017/S0001924000010708 [6] SHUKLA D, KOMERATH N. Multirotor drone aerodynamic interaction investigation[J]. Drones, 2018, 2(4): 43. doi: 10.3390/drones2040043 [7] STOKKERMANS T C A, USAI D, SINNIGE T, et al. Aerodynamic interaction effects between propellers in typical eVTOL vehicle configurations[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2021, 58(4): 815-833. doi: 10.2514/1.C035814 [8] Young L A, Derby M R. Rotor/wing interactions in hover, NASA/TM-2002-211392[R]. Washington D.C.: NASA, 2002. [9] Veldhuis L L. Review of propeller-wing aerodynamic interference[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Congress of the Aeronautical Sciences. Beijing: ICAS, 2004: 2004-2006. [10] PATTERSON M D, BORER N K, GERMAN B. A simple method for high-lift propeller conceptual design[C]//Proceedings of the 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 2016: 0770. [11] XUE C, ZHOU Z. Propeller-wing coupled aerodynamic design based on desired propeller slipstream[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 97: 105556. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.105556 [12] 范中允, 周洲, 祝小平. 一种可任意给定环量分布的螺旋桨设计方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2019, 32(2): 434-441.FAN Z Y, ZHOU Z, ZHU X P. A design method for propeller with arbitrary circulation distribution[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2019, 32(2): 434-441 (in Chinese). [13] 郭佳豪, 周洲, 范中允. 一种给定拉力分布的螺旋桨设计方法及应用[J]. 航空动力学报, 2020, 35(6): 1238-1246.GUO J H, ZHOU Z, FAN Z Y. A method of propeller design with given thrust distribution and it’s application[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2020, 35(6): 1238-1246 (in Chinese). [14] D’ANGELO S, BERARDI F, MINISCI E. Aerodynamic performances of propellers with parametric considerations on the optimal design[J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2002, 106(1060): 313-320. doi: 10.1017/S0001924000096068 [15] 项松, 王吉, 张利国, 等. 一种高效率螺旋桨设计方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2015, 30(1): 136-141.XIANG S, WANG J, ZHANG L G, et al. A design method for high efficiency propeller[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2015, 30(1): 136-141 (in Chinese). [16] 唐伟, 宋笔锋, 张玉刚, 等. 两个设计点的螺旋桨气动性能[J]. 航空动力学报, 2017, 32(2): 354-363.TANG W, SONG B F, ZHANG Y G, et al. Aerodynamic performance of propeller with two design points[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2017, 32(2): 354-363 (in Chinese). [17] ADKINS C N, LIEBECK R H. Design of optimum propellers[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1994, 10(5): 676-682. doi: 10.2514/3.23779 [18] LARRABEE E E. Practical design of minimum induced loss propellers[J]. SAE Transactions, 1979: 2053-2062. [19] 薛臣, 周洲, 范中允, 等. 螺旋桨/机翼耦合下的目标螺旋桨滑流设计[J]. 航空动力学报, 2021, 36(1): 104-118.XUE C, ZHOU Z, FAN Z Y, et al. Design of target propeller slipstream under propeller-wing interaction[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2021, 36(1): 104-118 (in Chinese). [20] VELDHUIS L L M. Propeller wing aerodynamic interference[D]. Delft: Technische Universiteit Delft, 2005. [21] DANTSKER O D, CACCAMO M, DETERS R W, et al. Performance testing of APC electric fixed-blade UAV propellers[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2022 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2022: 4020. [22] 王适存. 直升机空气动力学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1959.Wang S C, Helicopter aerodynamics[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 1959. -







 下载:
下载: