-
摘要:
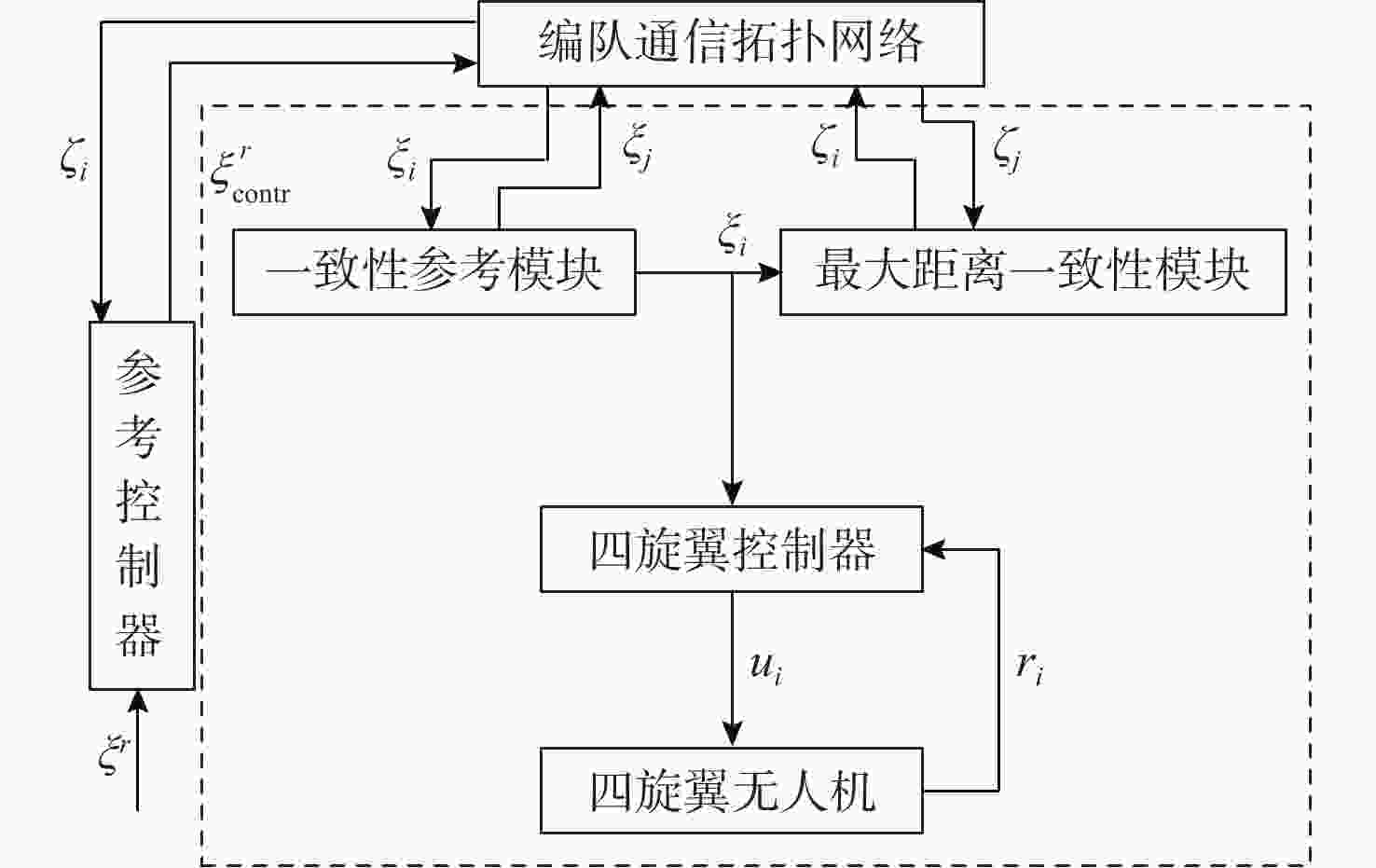
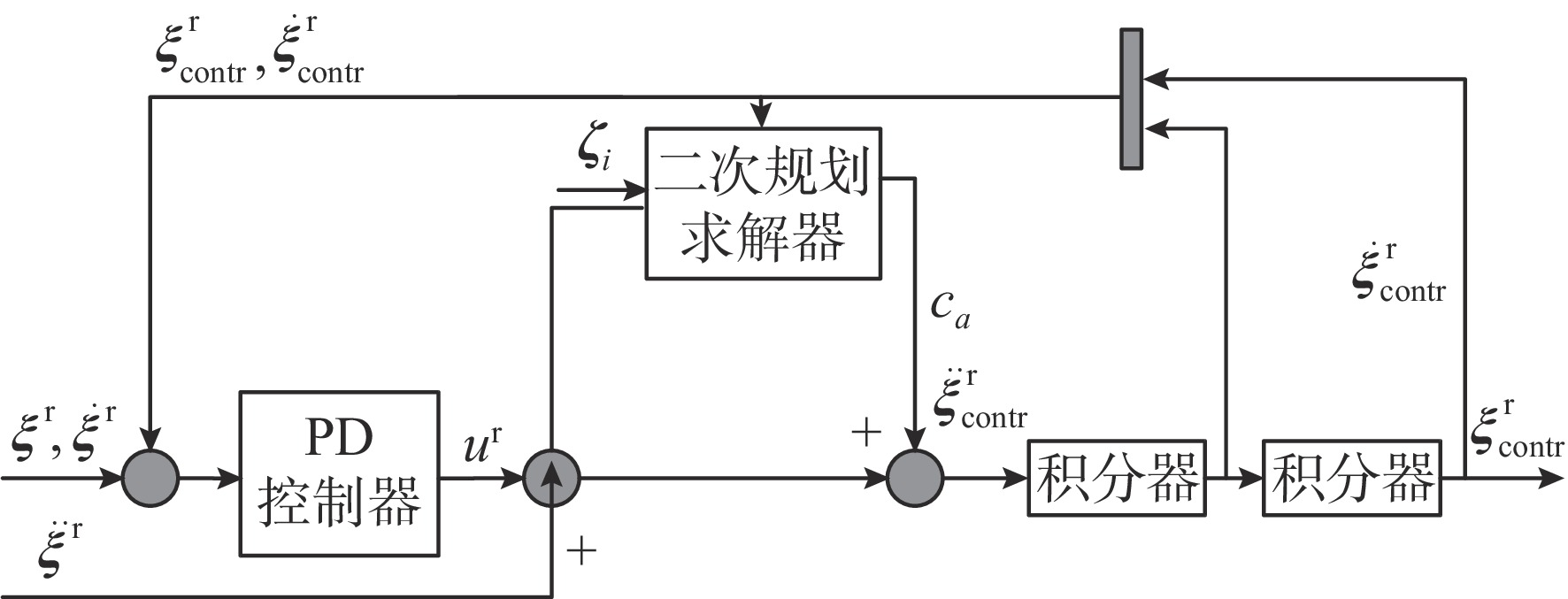
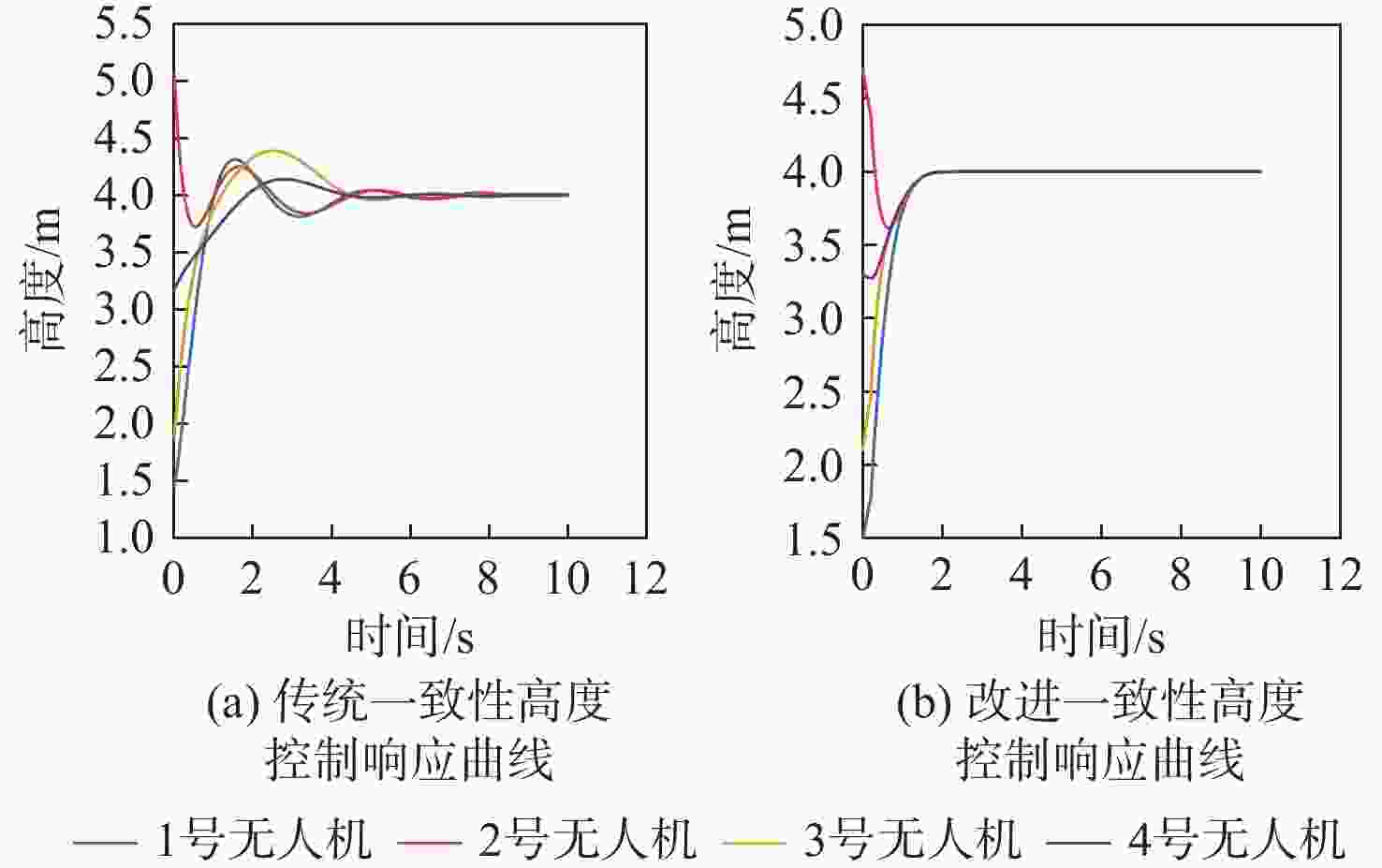
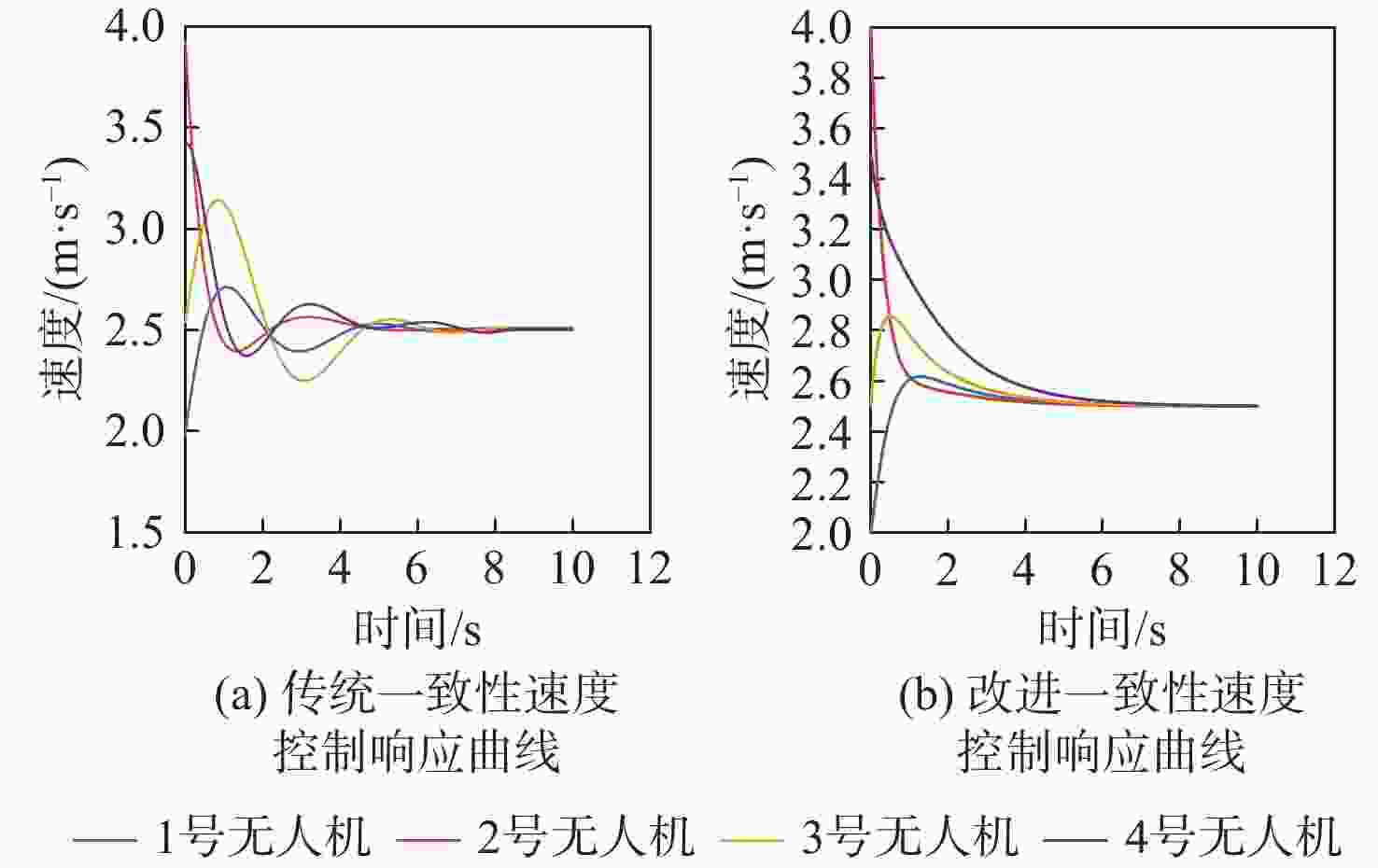
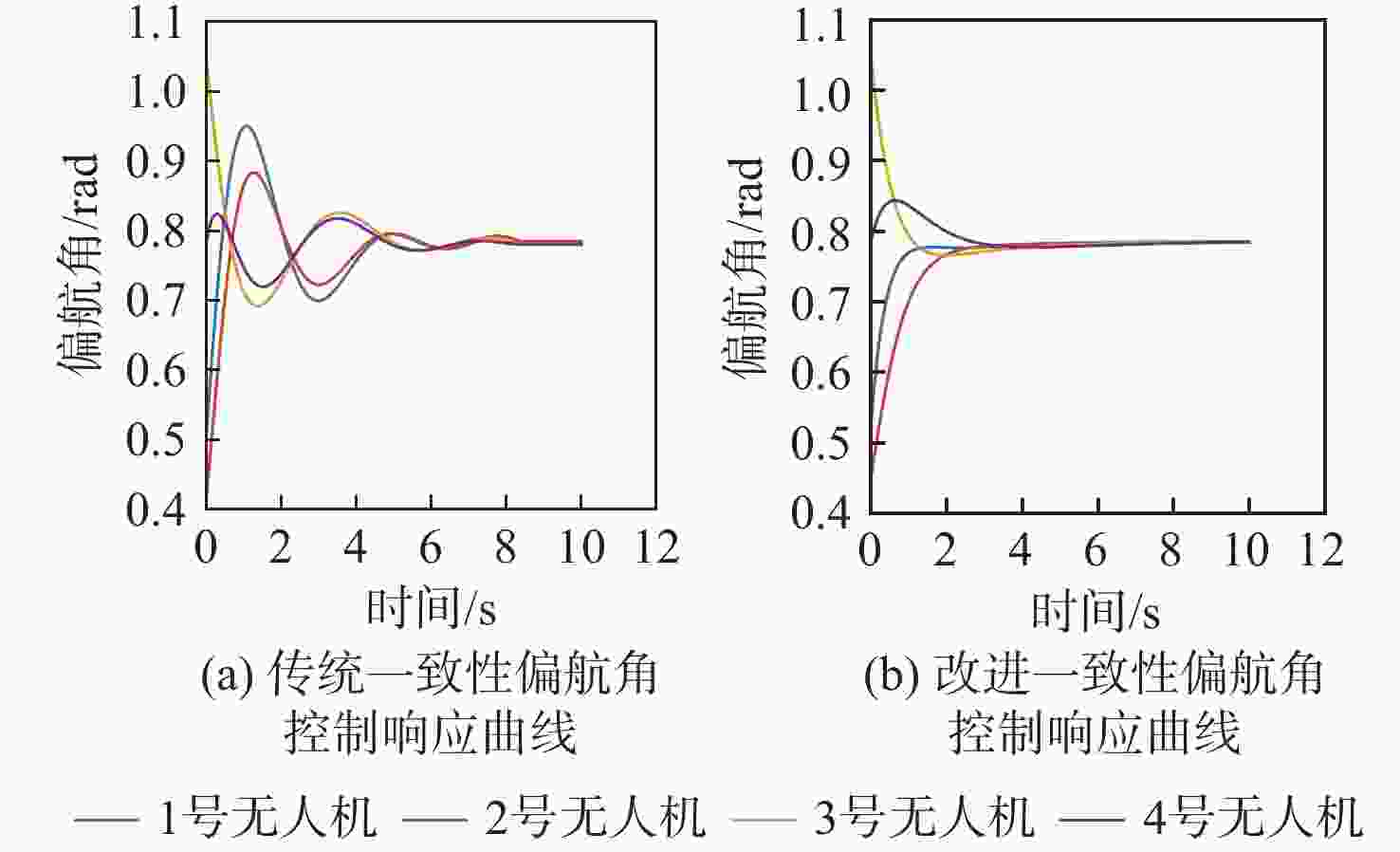
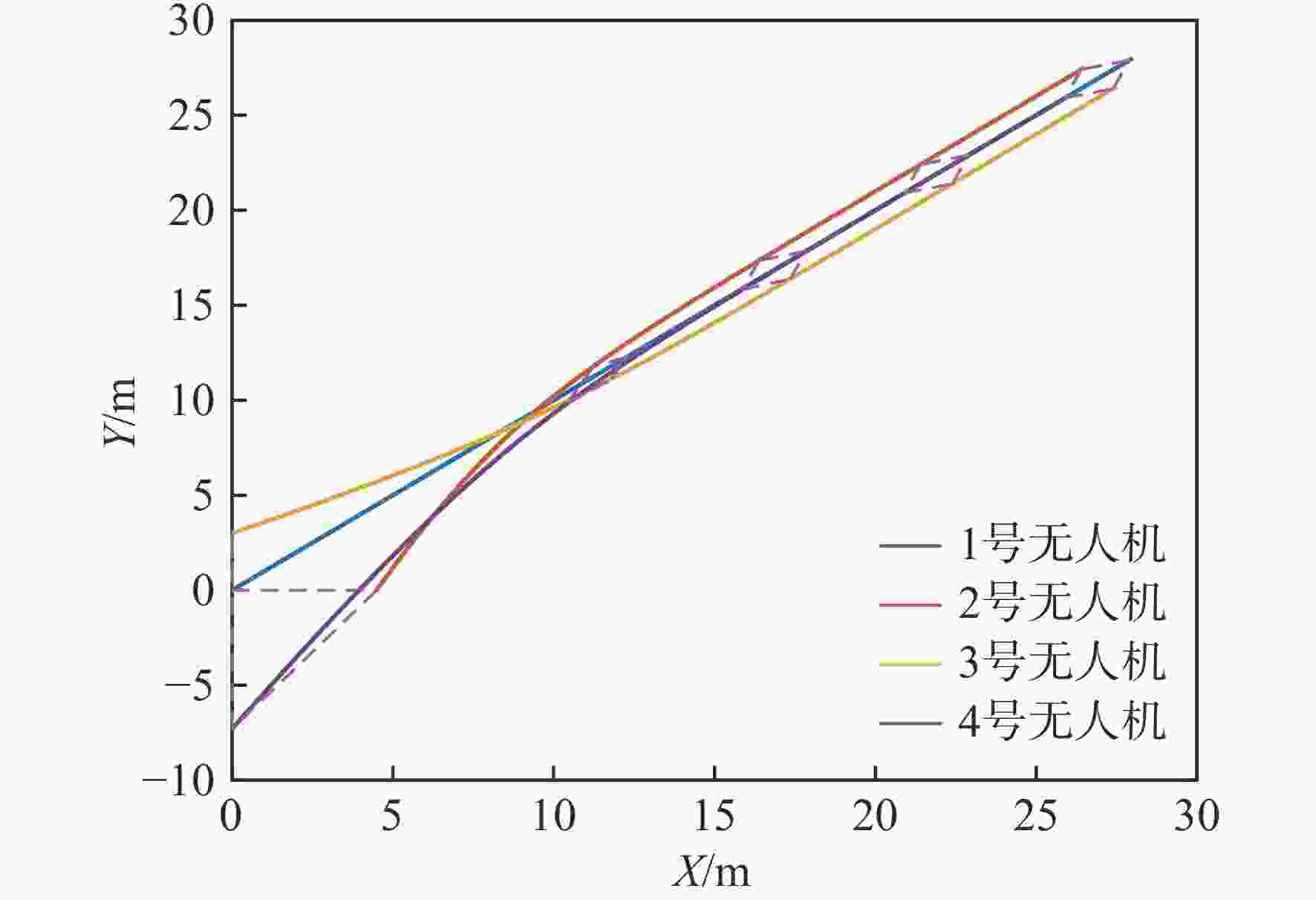
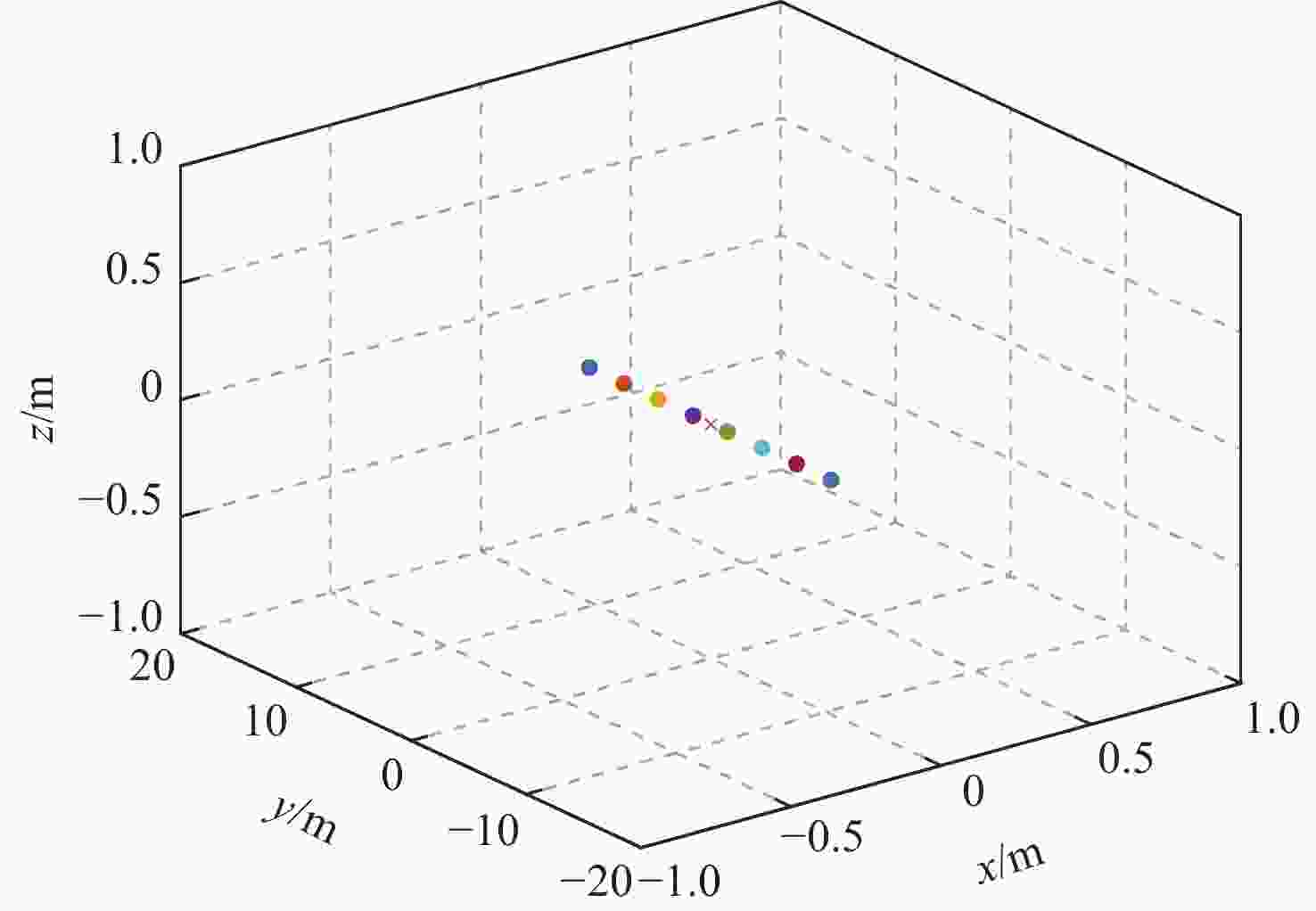
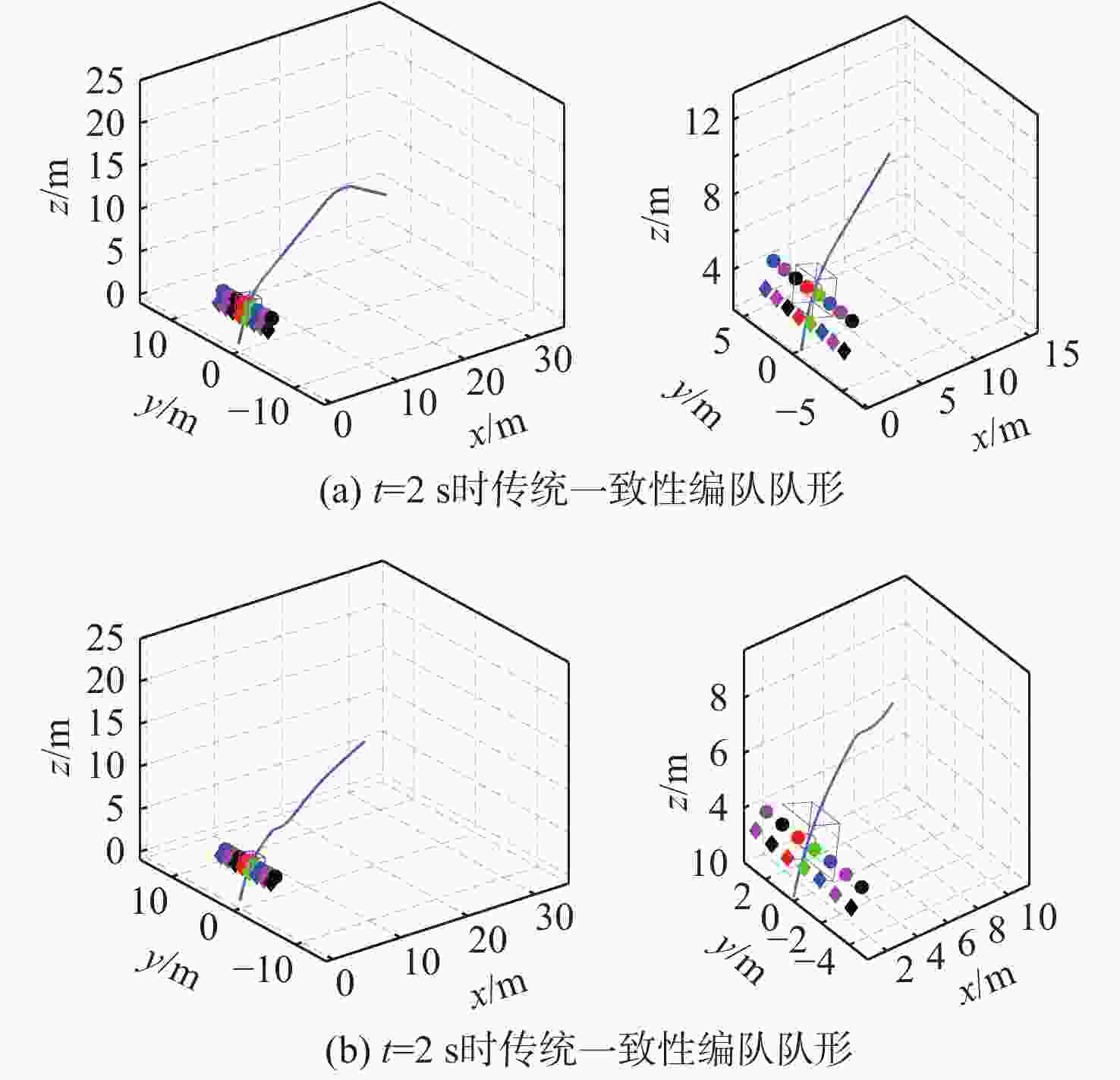
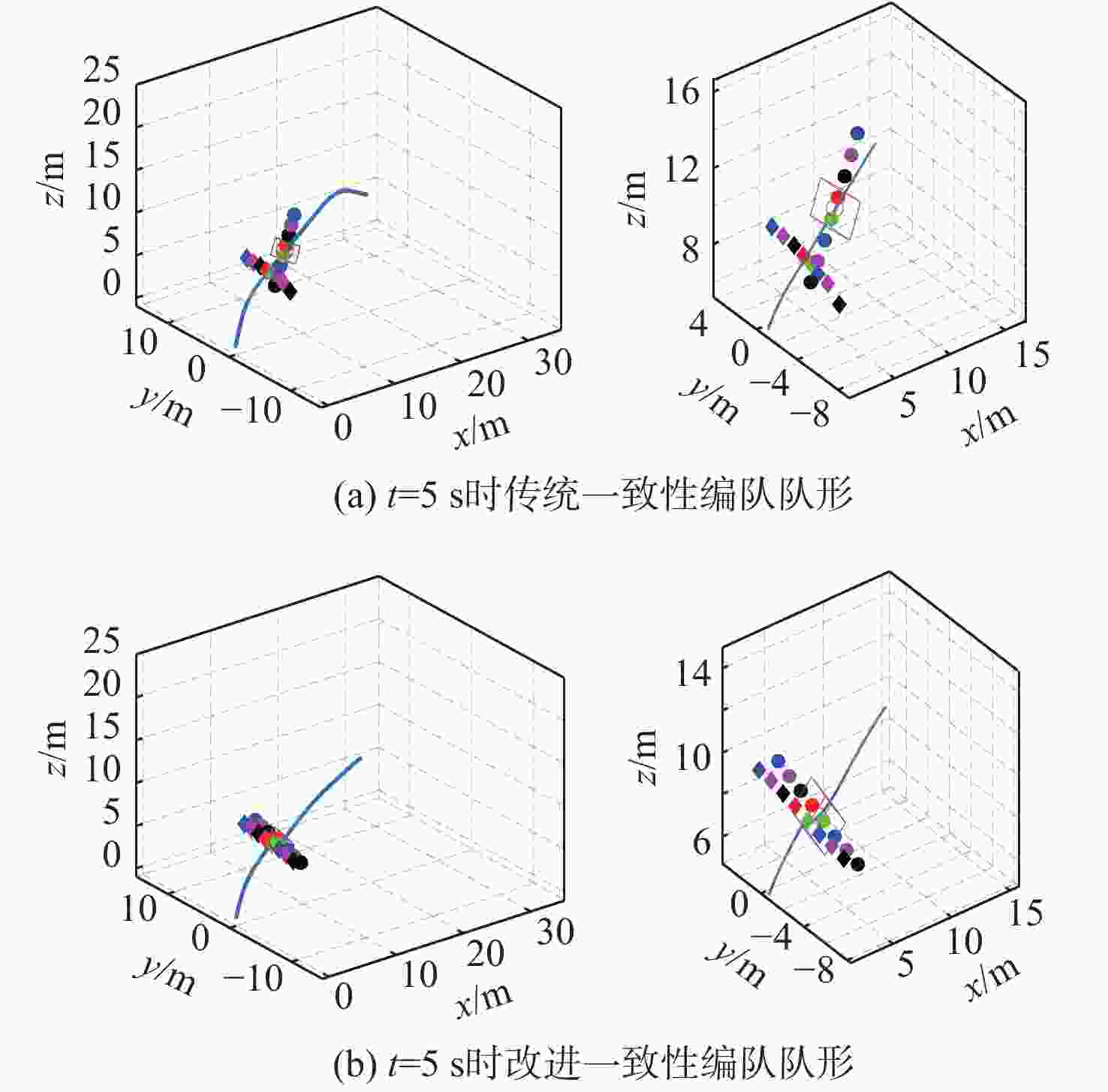
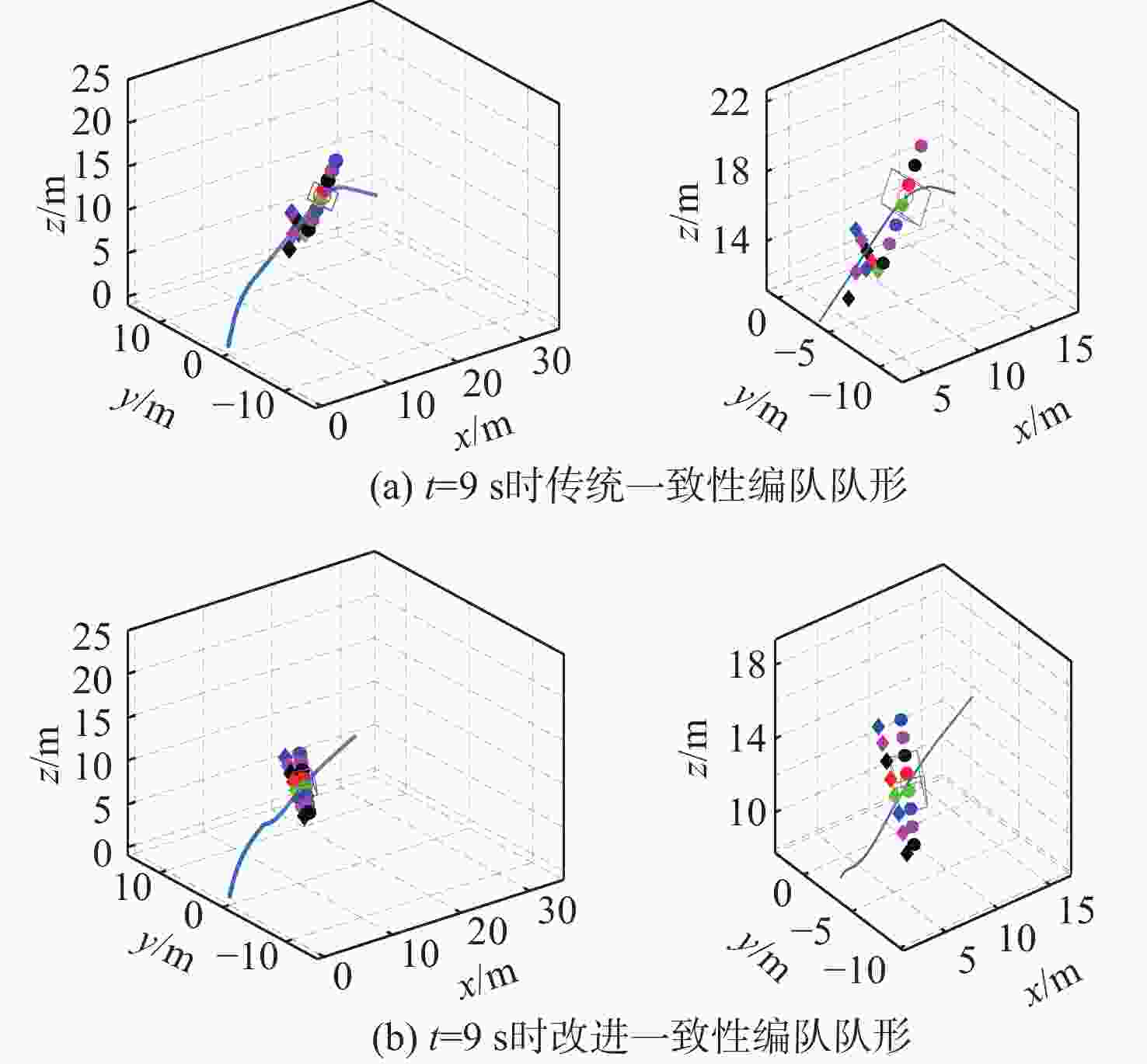
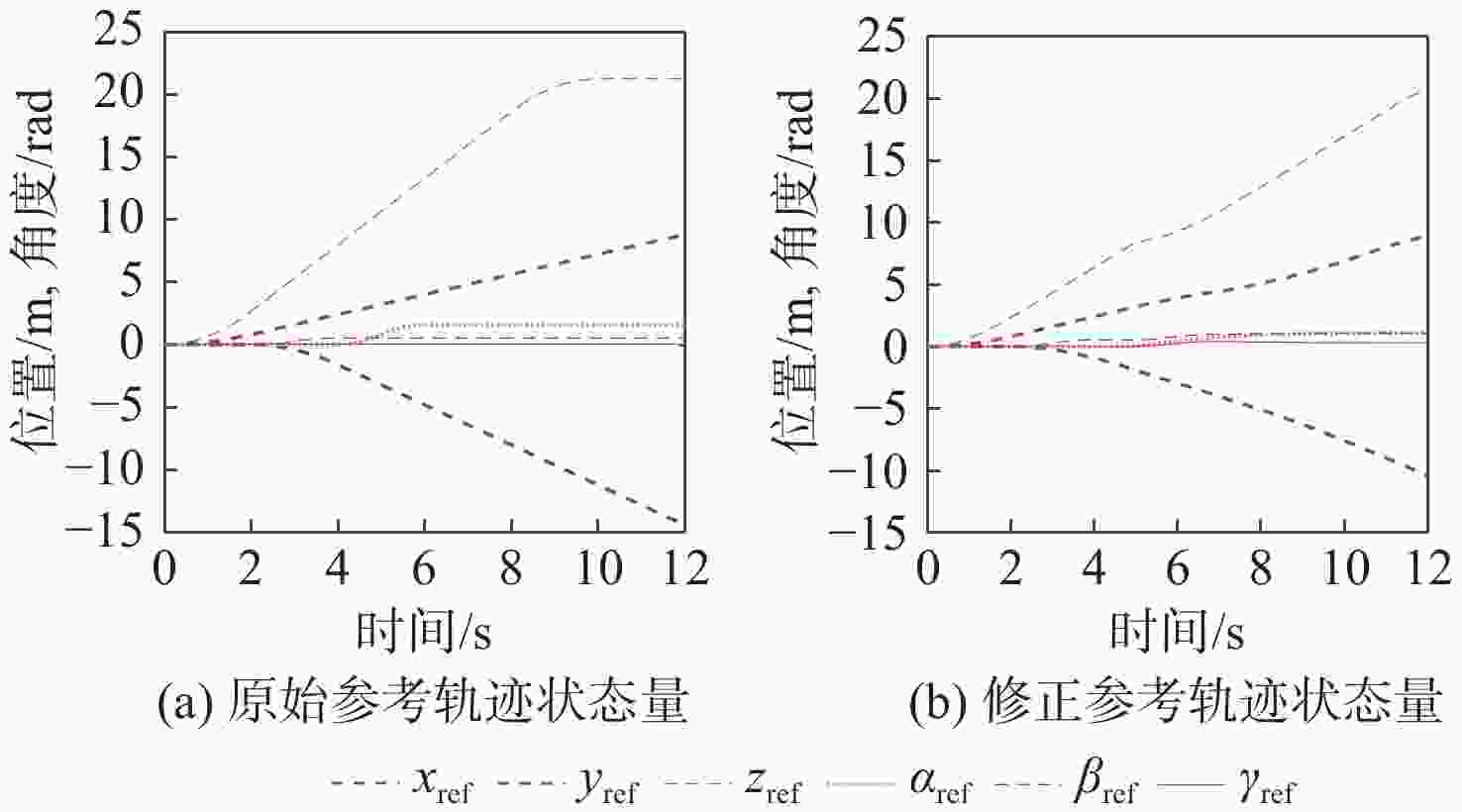
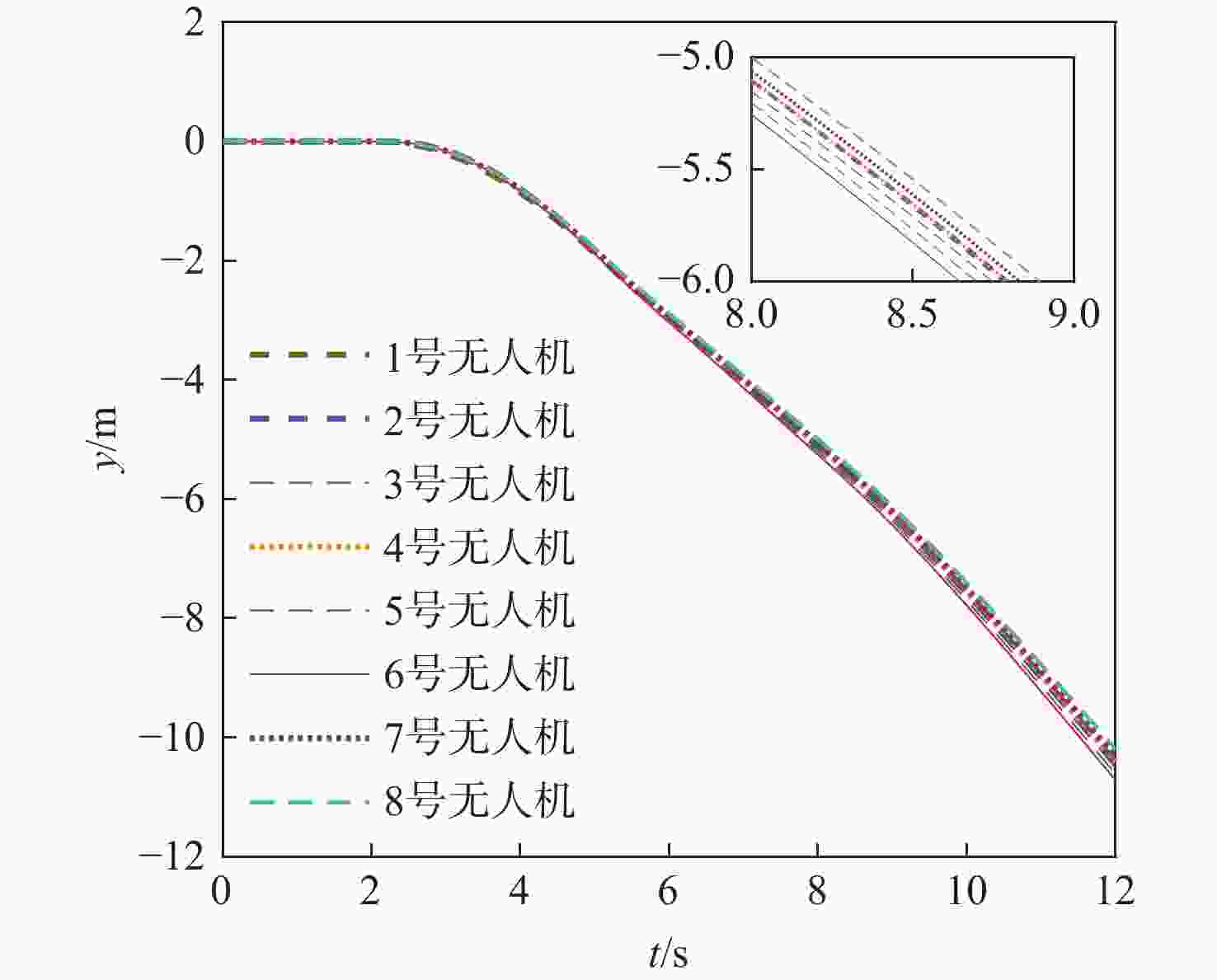
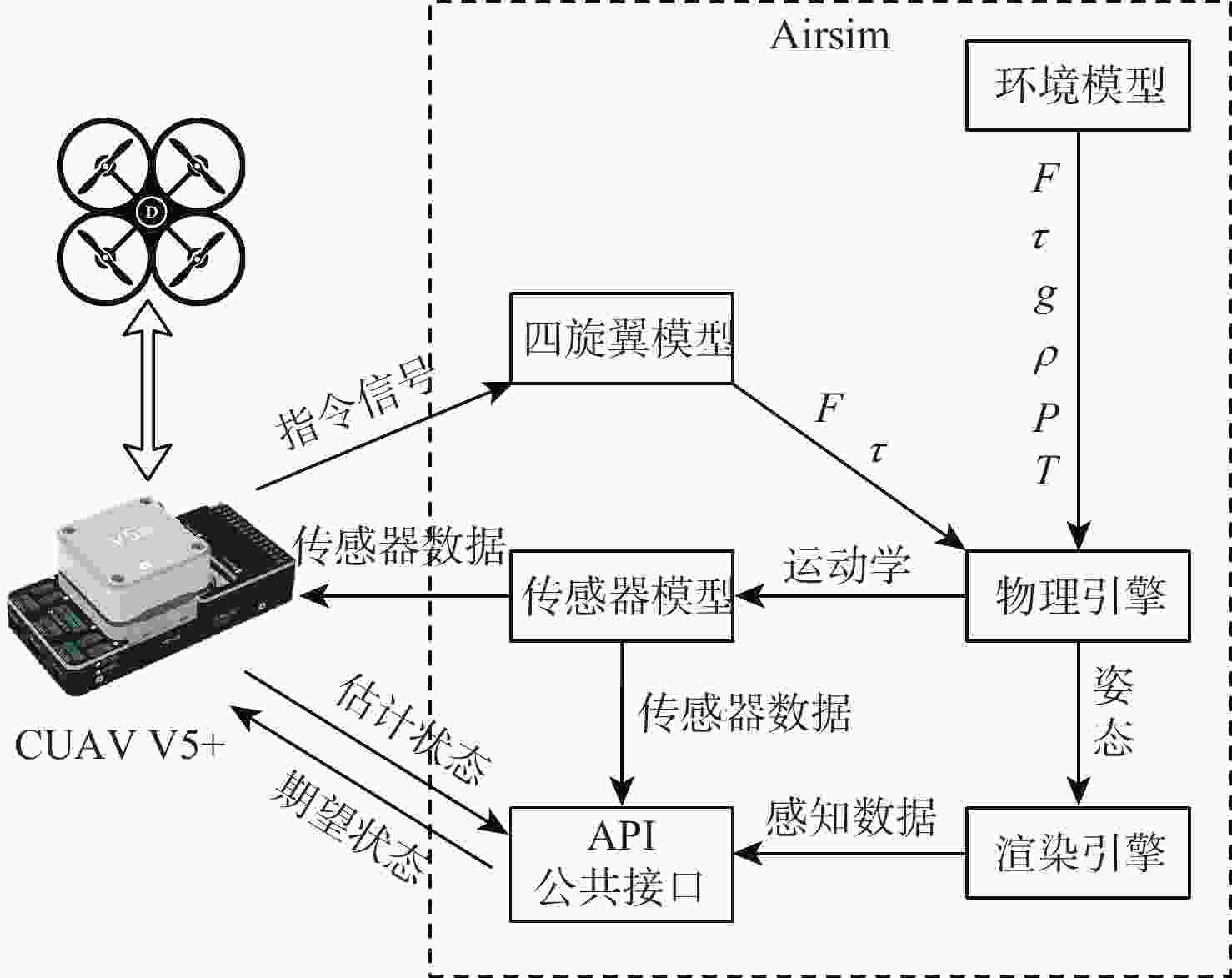
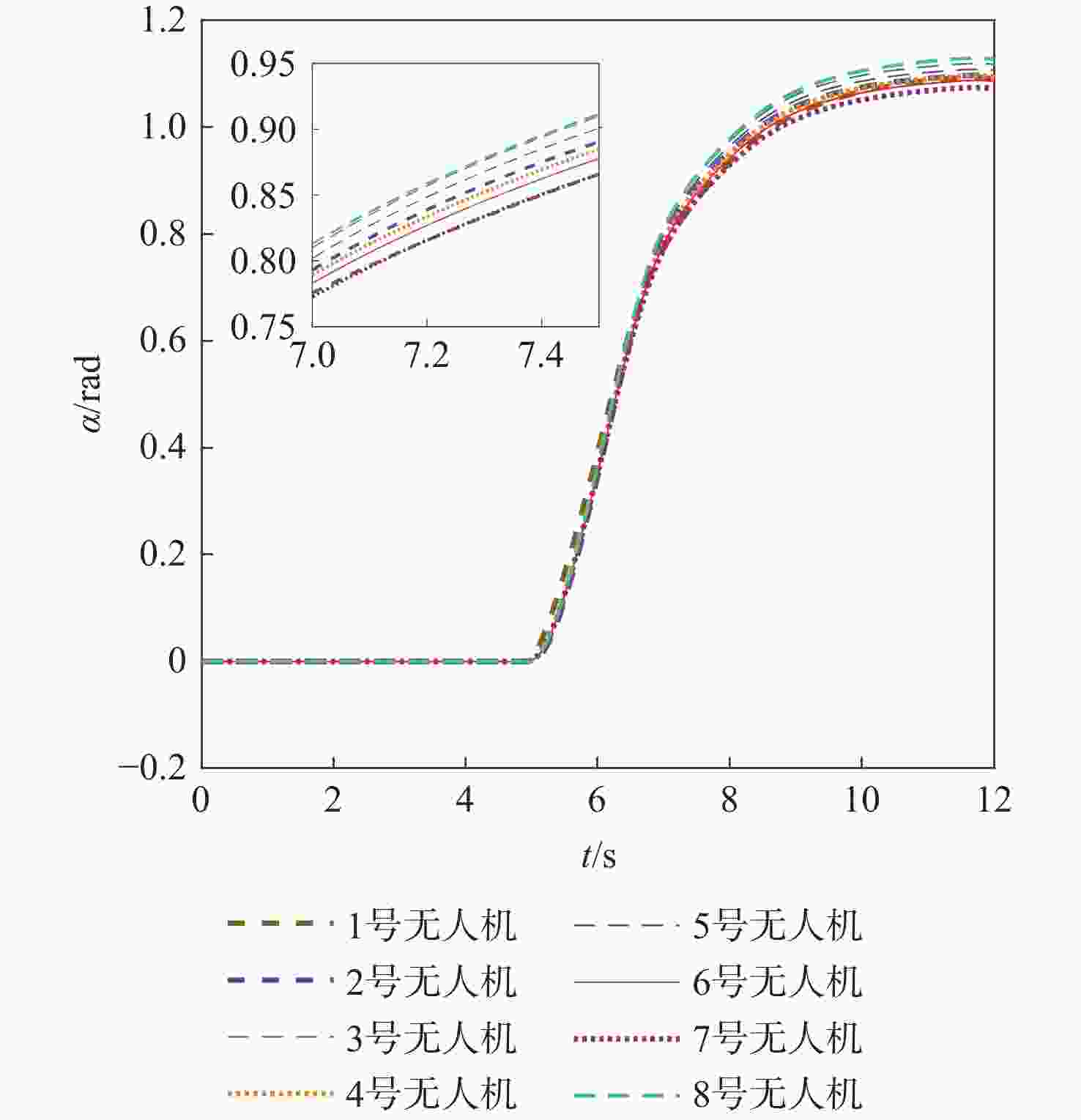
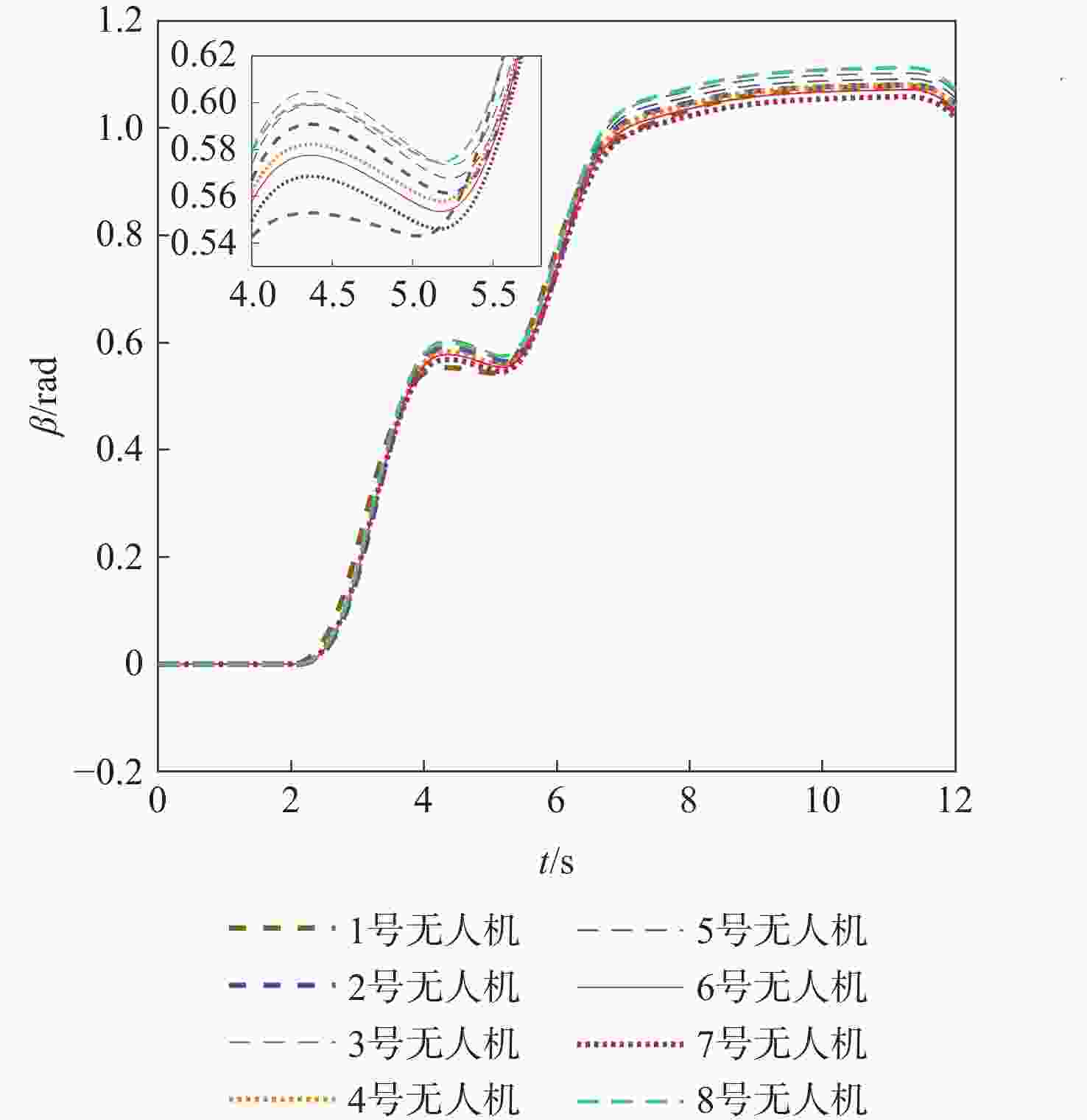
针对传统一致性算法中存在的大增益收敛振荡以及当编队队形受到平动转动同时施加的问题进行了深入研究。在传统一致性编队算法基础上引入虚拟长机,定义新的范数来扩展原有的一致性算法,以解决线性一致性算法中大增益收敛振荡的问题。针对传统一致性编队过程中平动转动的施加导致队形无法保持的问题,引入最大距离作为参考控制器的反馈,修正参考输入轨迹,以确保编队队形的同时,实现平动转动过程中的良好跟踪队形。结合开源飞控Ardupilot和开源仿真平台Airsim进行了联合半物理仿真,进一步验证了改进算法的可行性。研究结果表明:所提算法在解决传统一致性协议中存在的问题方面具有显著的改进,并在实际应用中具有较好的可行性。
Abstract:This paper conducted in-depth research on the problems of large-gain convergence oscillation and the simultaneous application of translational and rotational motions in traditional consistency algorithms. First, based on the traditional consistent formation algorithm, a virtual leader was introduced, and a new norm was defined to extend the original algorithm, aiming to solve the issue of convergence oscillation caused by large gains in linear consistency algorithms. Second, to address the issue of formation loss during translational and rotational movements, the maximum inter-agent distance was introduced as feedback to the reference controller. This allowed for modification of the reference input trajectory and ensured stable formation tracking during motion. Finally, a joint semi-physical simulation was conducted using the open-source flight control system Ardupilot and the simulation platform AirSim to verify the feasibility of the improved algorithm. The results indicate that the proposed algorithm significantly improves the limitations of traditional consistency protocols and demonstrates good feasibility in practical applications.
-
Key words:
- consistency algorithm /
- UAV formation /
- distributed formation /
- formation keeping /
- AirSim simulation
-
-
[1] 胡春鹤, 陈宗基. 基于Helly定理的多智能体最短时间一致性[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2015, 41(9): 1701-1707.HU C H, CHEN Z J. Helly-theorem-based time-optimal consensus for multi-agent systems[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(9): 1701-1707(in Chinese). [2] REN W. Consensus strategies for cooperative control of vehicle formations[J]. IET Control Theory& Applications, 2007, 1(2): 505-512. [3] 姚辉, 席建祥, 王成, 等. 二阶多智能体系统自抗扰编队跟踪与避撞控制[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2020, 46(5): 960-977.YAO H, XI J X, WANG C, et al. Active disturbance rejection based formation tracking and collision avoidance control for second-order multi-agent system[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(5): 960-977(in Chinese). [4] KUSHLEYEV A, MELLINGER D, POWERS C, et al. Towards a swarm of agile micro quadrotors[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2013, 35(4): 287-300. doi: 10.1007/s10514-013-9349-9 [5] 周文惠, 齐瑞云, 姜斌. 面向突发故障的分布式多无人机任务重规划方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(05): 1373-1385.ZHOU W H, QI R Y, JIANG B. A mission replanning method of distributed multiple unmanned aerial vehicles for pop-up faults[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(05): 1373-1385(in Chinese). [6] REN W, SORENSEN N. Distributed coordination architecture for multi-robot formation control[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(4): 324-333. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2007.08.005 [7] KURIKI Y, NAMERIKAWA T. Formation control with collision avoidance for a multi-UAV system using decentralized MPC and consensus-based control[J]. SICE Journal of Control, Measurement, and System Integration, 2015, 8(4): 285-294. doi: 10.9746/jcmsi.8.285 [8] YUAN W, CHEN Q Y, HOU Z X, et al. Multi-UAVs formation flight control based on leader-follower pattern[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1276-1281. [9] 李正平, 鲜斌. 基于虚拟结构法的分布式多无人机鲁棒编队控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(11): 2423-2431.LI Z P, XIAN B. Robust distributed formation control of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles based on virtual structure[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(11): 2423-2431(in Chinese). [10] 邱华鑫, 段海滨, 范彦铭. 基于鸽群行为机制的多无人机自主编队[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(10): 1298-1304. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.50314QIU H X, DUAN H B, FAN Y M. Multiple unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous formation based on the behavior mechanism in pigeon flocks[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(10): 1298-1304(in Chinese). doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.50314 [11] CHALLA V R, RATNOO A. Analysis of UAV kinematic constraints for rigid formation flying[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2016: 2105. [12] CROWTHER W J. Rule-based guidance for flight vehicle flocking[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2004, 218(2): 111-124. doi: 10.1243/0954410041322005 [13] 任伟, 兰德尔. W. 比尔德. 多航行体协同控制中的分布式一致性: 理论与应用[M]. 吴晓锋, 译. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2014: 5-7.REN W, BEARD R W. Distributed consensus in multi-vehicle cooperative control [M]. WU X F, translated. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014: 5-7(in Chinese). [14] REN W. Consensus based formation control strategies for multi-vehicle systems[J]. Proceedings of the American Control Conference, 2006: 4237-4242. [15] 苟进展, 梁天骄, 陶呈纲, 等. 基于一致性理论的无人机编队控制与集结方法[J]. 北京麻豆精品秘 国产传媒学报, 2024, 50(5): 1646-1654.GOU J Z, LIANG T J, TAO C G, et al. A Method of UAV Formation control and assembly based on consistency theory[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(5): 1646-1654(in Chinese). [16] 刘志江, 宋友, 李国宾, 等. 一致性算法和领航跟随法结合的多机编队控制[J]. 航天控制, 2022, 40(6): 46-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2022.06.007LIU Z J, SONG Y, LI G B, et al. A Multi-aircraft formation control based on consistency algorithm and pilot following method[J]. Aerospace Control, 2022, 40(6): 46-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2022.06.007 [17] BOYD S, GHOSH A, PRABHAKAR B, et al. Analysis and optimization of randomized gossip algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the 2004 43rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 5310-5315. [18] DOUGLAS B W. Introduction to graph theory[M]. 2ed. Hoboken: Prentice Hall, 2000. -







 下载:
下载: